MLS 332 Unit 2
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Function of Erythrocytes
transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs
Lifespan of an Erythrocyte
~120 days
Dimensions/Shape of an Erythrocyte
-biconcave disc
-7-8 mcM in diameter
-MCV= 80-100 fL
RBC Concentration Age Characteristic
highest at birth then gradually decreases
RBC Concentration Gender Characteristic
higher in males than females
RBC Concentration Location Characteristic
higher in high altitudes
Functions of RBC Membrane
-Special erythropoiesis receptors
-Regulates RBC metabolism
-Takes in vital components
-Release metabolic waste
-Balances exchange of ions
-Provides antigenic expression
-Responsible for strength & deformability
Erythrocyte Membrane Composition
~52% protein
~40% lipid
~8% carbohydrate
Erythrocyte Membrane Lipids
-Phospholipids
-Cholesterol
-Glycolipids
Erythrocyte Inner Membrane Phospholipids
PS, PI, PE
Erythrocyte Outer Membrane Phospholipids
PC, SM
Erythrocyte Membrane Integral Proteins
Glycophorins and transport proteins
Glycophorins
-integral proteins
-A,B,C
-Zeta potential
-RBC antigens
-Anchors skeletal proteins
Zeta Potential
degree of negative charge on the surface of a red blood cell
Transport proteins
-type of internal protein
- >100 types
-Band 3
Band 3
-intergral transport protein
-responsible for the chloride/bicarbonate exchange
-major binding site
-anchors skeletal proteins
Peripheral Proteins
-on the cytoplasmic side of membrane
-structural proteins
Horizontal Structural Proteins
support lipid bilayer
Vertical Structural Proteins
attach protein skeleton
Spectrin
-peripheral proteins
-α and β heterodimers
-interacts horizontally to the cell membrane
-responsible for spring-like deformability of RBC
Ankyrin
-Binds spectrin to Band 3
-Strengthened by band 4.2
Erythrocyte Deformability
-biconcave shape
-internal viscosity
-viscoelastic membrane
Which of the following RBC membrane component is responsible for spring-like deformability of the RBC and interacts horizontally to the cell membrane?
a. glycophorin c
b. spectrin
c. ankyrin
d. band 3
b. spectrin
Erythrocyte Metabolism
energy-dependent metabolic process are required to maintain cation pumps, hgb iron in the reduced state, and membrane integrity/deformability
Glycolytic Pathway Function
-provides RBC with ATP by breaking down glucose
-metabolizes ~90-95% of RBC glucose
Glycolytic Pathway Mechanism
-glucose is broken down lactate or pyruvate
-net gain of 2 ATP per 1 glucose
Hexose Monophosphate (HMP) Shunt Function
-provides NADPH and reduced glutathione (GSH)
-maintain hemoglobin in the reduced (functional) state
-safeguards vital cellular enzymes from oxidation
Raport-Leubering Shunt Function
-controls the amount of 2,3-BPG produced which in turn affects the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin
-regulates oxygen delivery to the tissues
Raport-Leubering Shunt Mechanism
Sacrifices the production of one of the 2 ATP molecules produced by glycolysis to make 2,3 BPG
Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway Function
-protects hemoglobin form oxidation by using NADH (from the glycolytic pathway) and methemoglobin reductase
-maintains methemoglobin levels at ~2% as opposed to 20-40% in its absence
Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway Mechanism
methemoglobin reductase and NADH reduce methemoglobin back to hemoglobin
Which erythrocyte metabolic pathway is responsible for controlling 2,3 BPG production and therefore controlling oxygen affinity within the cell?
a. glycolysis
b. hexose monophosphate shunt
c. rapaport-leubering shunt
d. methemoglobin reductase pathway
c. rapaport-leubering shunt
Erythrocyte Production Regulation
regulated by EPO
Erythropoeietin (EPO)
-thermostable, renal, glycoprotein hormone
-80-90% produced in kidneys
-<15% produced in the liver
-stimulates erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis Release
release of EPO increases rate of bone marrow cell production/rate of release and releasee in response to tissue hypoxia
EPO Action
-EPO binds to EPO-R which initiates JAK/STAT pathway and CFU-E
EPO Cellular Effects
-prevents apoptosis
-increases erythropoiesis 5 to 10 fold
RBC Senescence
-decline in cellular enzymes, ATP production, and redox capabilities
-oxidative damage, inability to maintain osmotic equilibrium via cation pumps
-accumulation of IgG on RBC surface
-exposure of PS (inner phospholipid) on outer leaflet
Extravascular RBC Destruction
-located in spleen, bone marrow, and liver
-90% of all RBC destruction
Intravascular RBC Destruction
occurs in the bloodstream
Hemoglobin
highly specialized intracellular tetrameric protein
Hemoglobin Critical Values
<6.6 g/dL
Hemoglobin Subunits
2 alpha and 2 beta global chains and one heme molecule
Hemoglobin Structure
tetrameric molecule with 4 globin chains and one heme molecule held together by salt bonds, hydrophobic contacts, and hydrogen bonds
Heme
tetrapyrrole ring with ferrous iron in center
Ferrous Iron
Fe++
Ferric Iron
Fe+++
Each heme molecule binds with ______
1 oxygen molecule
Globin Chain
-amino acid chain responsible for function & physical properties of hgb
-changes hemoglobin stability and oxygen affinity if altered
-2 identical alpha and 2 identical beta chains
Ontogeny of Hemoglobin
type of hemoglobin is determined by the globin chains it is made up of
Adult Hemoglobins
Hgb A, Hgb A2, Hgb F
HbA Globin Chains
2 alpha ; 2 beta chains
HbA Reference Interval
> 95%
HbA2 Globin Chains
2 alpha ; 2 delta chains
HbA2 Reference Interval
1.5-3.7%
HbF Globin Chains
2 alpha ; 2 gamma chains
HbF Reference Interval
< 2%
Glycosylated Hemoglobin
-Hgb A1c
-3.5% normal
-7.5% diabetes
Which of the following hemoglobin types makes up >95% of hemoglobin in an adult?
a. HgbA
b. HgbA2
c. HgbA1C
d. Hgb F
a. HgbA
What is the globin chain structure of the main type of hemoglobin in adults?
a. 2 alpha ; 2 beta chains
b. 2 alpha ; 2 gamma chains
c. 2 alpha ; 2 delta chains
d. 2 alpha ; 2 epsilon chains
a. 2 alpha ; 2 beta chains
Oxygen Affinity
the ease at which hgb binds and releases oxygen
Oxyhemoglobin
-relaxed (R) structure
-HIGH O2 affinity
-hgb WITH bound oxygen
Deoxyhemoglobin
-tense (T) structure
-LOW O2 affinity
-hgb WITHOUT oxygen
Partial Pressure of O2 (PO2)
-measured in mmHg
-rate at which gases diffuses across membrane
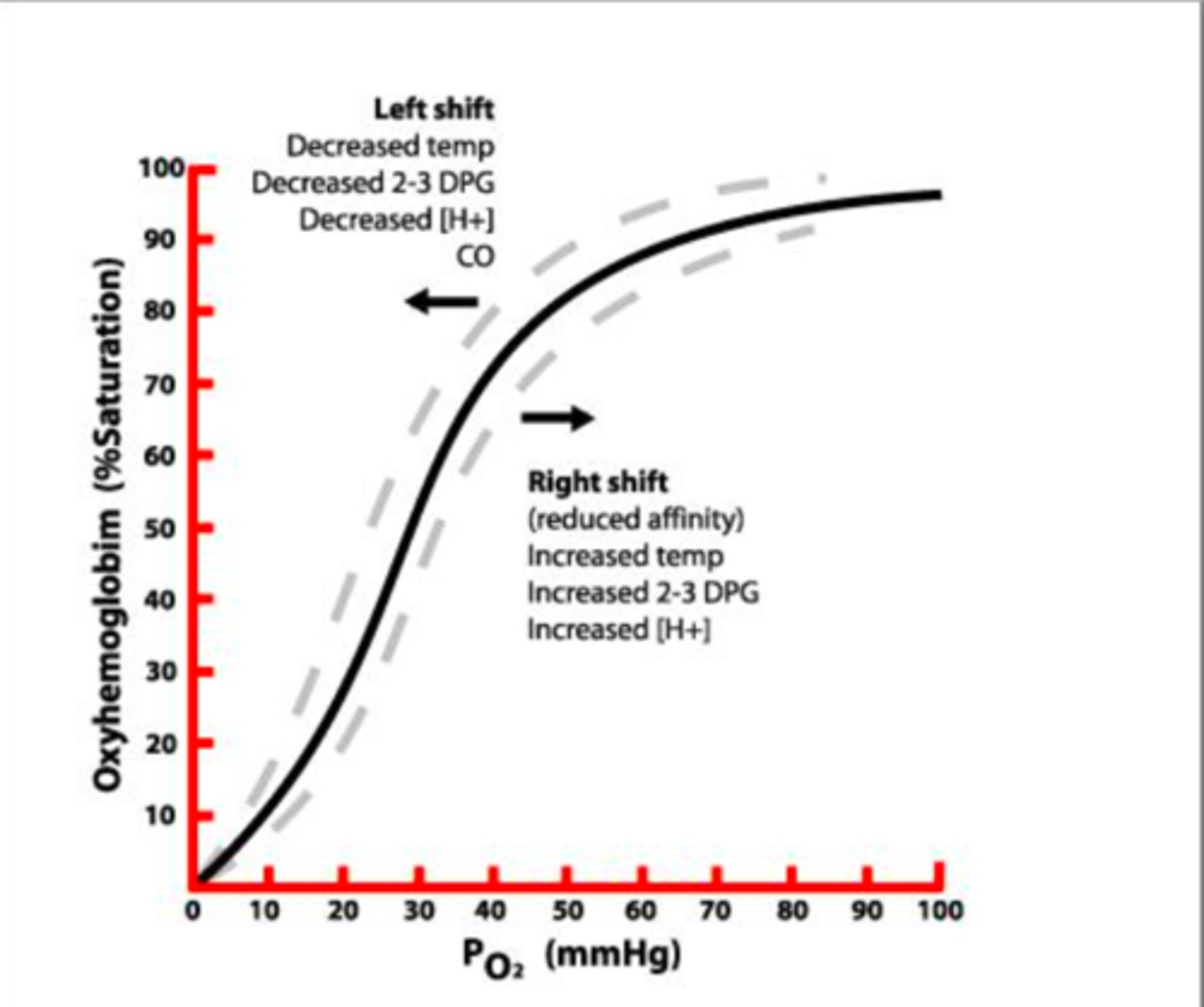
Oxygen Dissociated Curve (ODC)
graph that explains the quantity of hemoglobin that will be saturated with oxygen at different partial pressures of oxygen
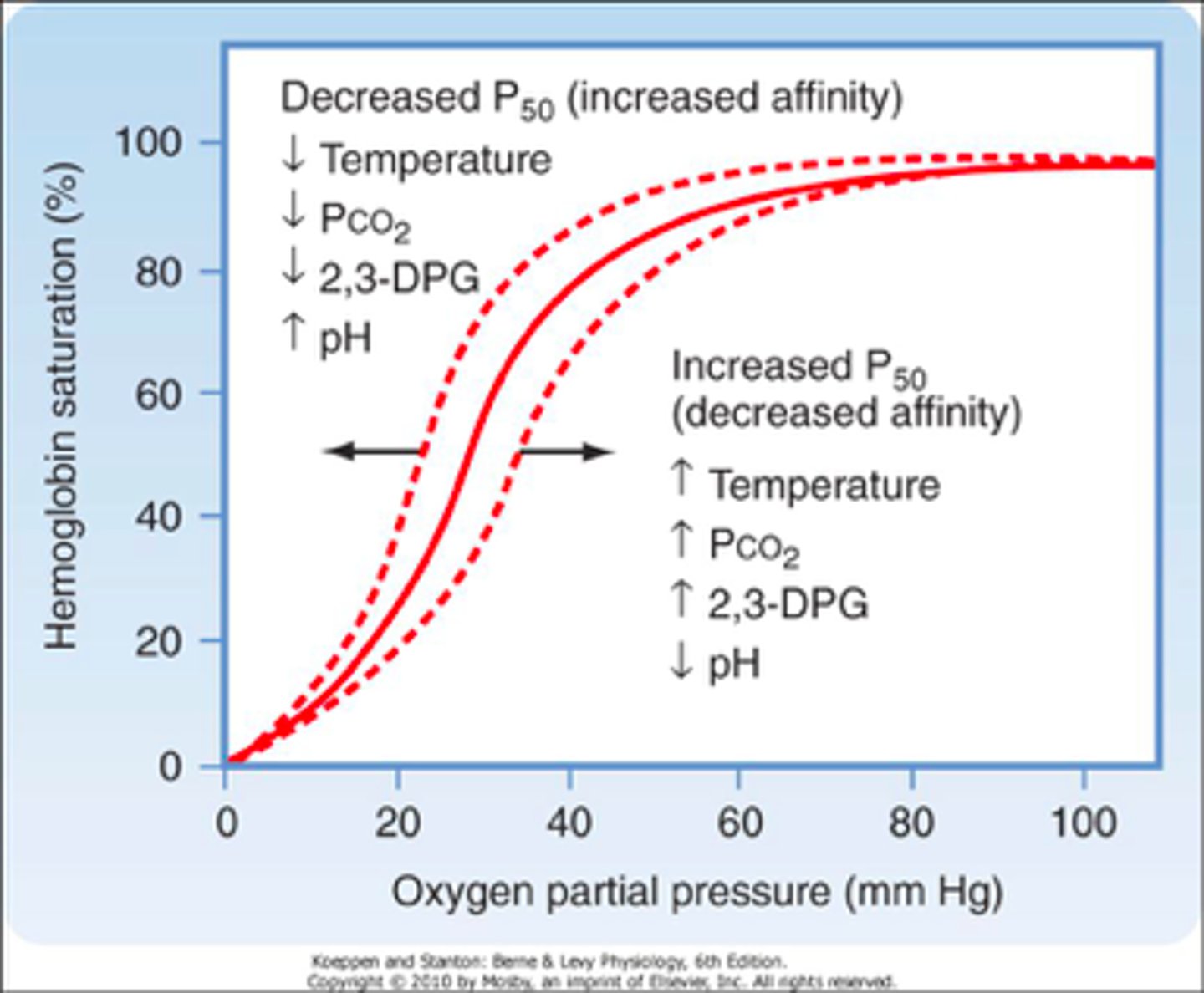
Hgb saturation and PO2 have a ____ relationship, meaning there is progressive binding of O2 to hgb.
sigmoidal
ODC Left Shift
-decreased H+
-decreased CO2
-decreased temp
-decreased 2,3-BPG
HIGHER AFFINITY = O2 BINDS EASIER
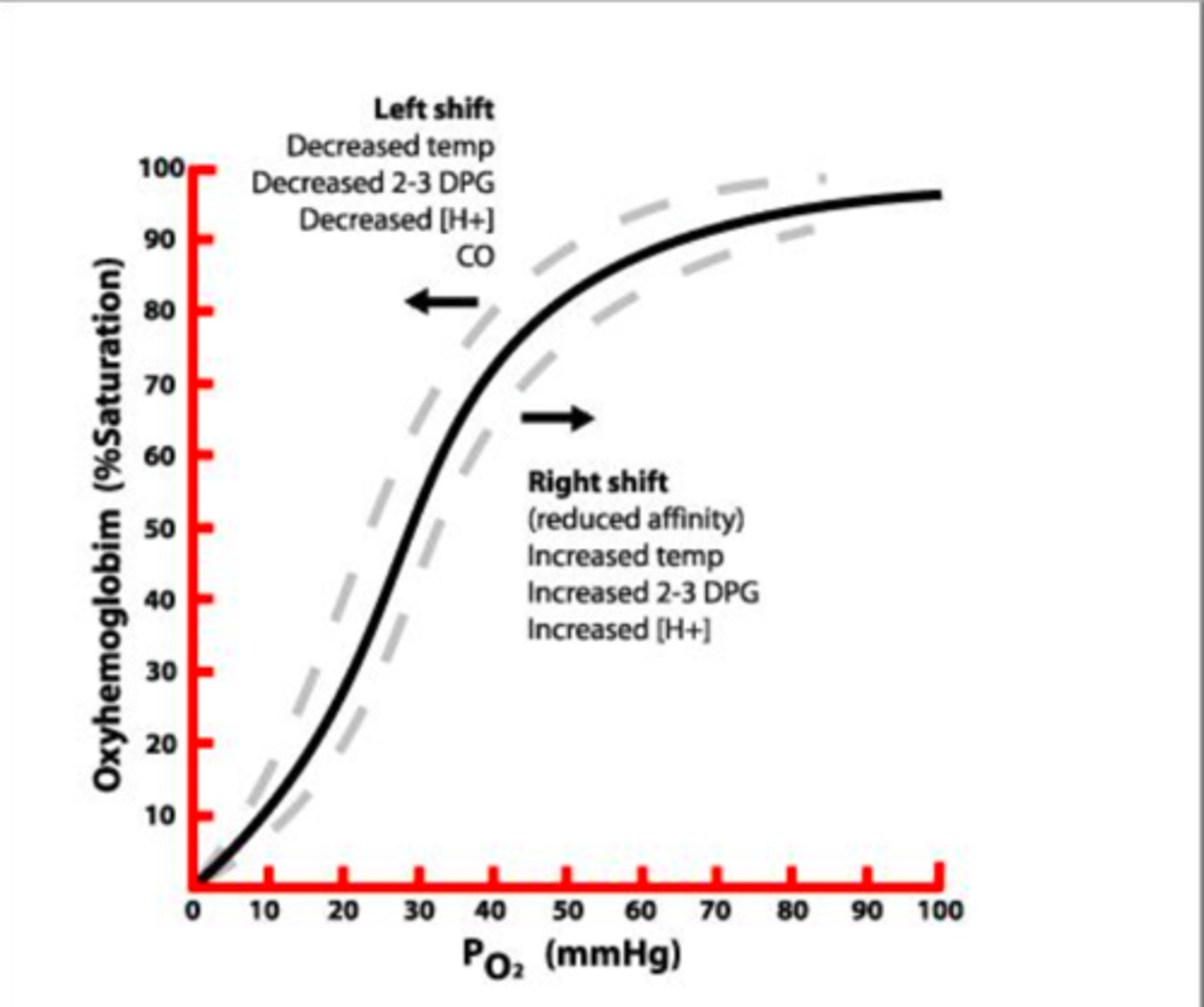
ODC Right Shift
-increased H+
-increased CO2
-increased temp
-increased 2,3-BPG
LOWER AFFINITY = O2 RELEASES EASIER
Allosteric Property of Hemoglobin
-structure and function are affected by other molecules
Hemoglobin and 2,3-BPG
2,3-BPG produced by Rapaport-Leubering Shunt causes a decrease of O2 affinity which encourages release of O2 to tissues
What property of oxygen is responsible for the rate at which it diffuses across cellular membranes?
a. pH
b. partial pressure
c. allosteric properties
d. affinity
b. partial pressure
Which of the following would shift the oxygen dissociation curve to the right (increases release of oxygen to the tissues/decreases oxygen affinity)?
a. decreased H+
b. decreased CO2
c. decreased temperature
d. increased 2,3-BPG
d. increased 2,3-BPG
Extravascular Hemolysis
-90% of hgb destruction
-located in spleen, liver, bone marrow
-done by macrophages
-detected by increased urine/fecal urobillinogen and/or unconjugated bilirubin in plasma
Intravascular Hemolysis
-10% of hgb destruction
-occurs in blood vessels
Intravascular Hemolysis Laboratory Detection
-Hemoglobinuria
-Hemosiderinuria
-Hemoglobinemia
-Methem
oglobinemia
-Decreased haptoglobin/hemopexin
-Increased unconjugated bilirubin
-Increased LDH (lactate dehydrogenase)
Haptoglobin
binds free hgb in blood
Methemoglobin
-ferric iron (Fe3+)
-produced by loss of reducing enzymes, globin chain mutations, toxic substances
-cyanosis
-dark brown blood
-non-functional hgb
Sulfhemoglobin
-sulfur + hemoglobin
-environmental exposure
-greenish blood
-non-functional hgb
Carboxyhemoglobin
-carbon monoxide and hgb
-200x affinity for carbon monoxide compared to oxygen
-cherry-red blood
-non-functional hgb
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
-correlates to the SIZE of RBCs
-calculated by (hematocrit/RBC count)x10
-about 80-100 fL
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
-about 28-34 pg
-calculated by (hemoglobin/RBC count)x10
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
-correlates to HEMOGLOBINATION
-about 32-36 g/dL
-calculated by (hemoglobin/hematocrit)x100
RDW-CV
RBC distribution width
>15 = anisocytosis
<15 = no anisocytosis
Poikilocytes
Change in RBC SHAPE
Anisocytosis
change in RBC SIZE
RBC Size Assessment
compare to small lymphocyte nucleus and MCV
RBC Hemoglobination Assessment
-assess diameter of central pallor and MCHC
Poikliocytosis Terms
1-3 = few
4-6 = moderate
> 6 = many
Anisocytosis Terms
slight
moderate
marked
Would a macrocyte (a larger than normal RBC) be considered a poikilocyte?
a. yes
b. no
b. no
What word best described a RBC whose central pallor is greater than 1/3 the diameter?
a. normochromic
b. hypochromic
c. spherocytic
b. hypochromic
Which of the following poikilocytes is the result of increased surfac area-to-volume ratio?
a. acanthocyte
b. codocyte
c. echinocyte
d. spherocyte
b. codocyte
A drepanocyte (sickle cell) can be seen in iron deficiency anemia.
a. true
b. false
b. false
What is the name of the RBC change in which increased plasma proteins cause the red blood cells to "stick together" in a stack of coins formation?
a. agglutination
b. rouleaux
c. Babesia
d. clumping
b. rouleaux
Rheostat
used to adjust light preference
Condensor
up for stained and down for unstained
Par focal
when one lens is in focus, the other lenses will also have the same focal length and can be rotated into position without further major adjustment.
Par objective
when switching from one objective to the next, the image that was in the center of the field should remain in the center of the field
Azure (Methylene Blue)
purplish basic dye that binds acidic groups like DNA and RNA
EosinY
reddish acidic dye that binds basic components like hemoglobin