Human physiology lesson test 1 matieral
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
what is four types of specialized cells of our organs
Cardiac muscle, Skeletal muscle, nerve tissue, adipose tissue
Amphipathic
having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
What is the fluid mosaic model
describes the plsama membrane as a flexible double bilayer of phospholipids with proteins and other strucutres
What can pass through the plasma membrane
Molecules and ions, other molecules can as well but they have to get guided in through a channel, protein, or endocytosis
Exocytosis
The vesicle will fuse with the plasma membrane to throw out whatever was contained inside
What is receptor mediated endocytosis
when a specific modlcules bind to a receptor at the surface of the cell and triggers the formation of a vesicle which contains that specific molecule
how does the golfi apparatus affect exocytosis
Molecules and proteins that are destined to be exported are packaged in the golgi apparatus,
Regulated Exocytosis
This process happens in very select cells but the vesicles will not fuse with the membrane until they recieve the apprioperite signal
What does the extracellular enviorment have?
It is everything that is outside of the cell, it contains interstital fluid which is part of the ECM and also contains fibroblasts
What makes up connective tissue?
The extra cellular matrix (which contains the interstital fluid), and fibroblasts.
What are hte 4 factors of rate of diffusion thorugh a membrane
the magnitude of the concentration difference across the membrane
the permmeability of the solution
the temperature of the solution
the surface area of the membrane
What can cross the plasma membrane thorugh simple diffusion?
Small non polar molecules such as O2 and CO2
what is carrier mediated transport
it is a active or passive transport across the membrane which uses
How do ions pass thorugh the semi permiable membrane?
They pass through ion channels which can be gated, they will open upon a stimulis which will tell them to let ions of a certain kind in
What is osmotic pressure?
the minimum pressure applied to a solution to stop osmosis
What is the diffrence between molality and molariaty?
Molality is the molal concentration which is the ammount of solute in a specific ammount of mass of solution. While molarity is the molar concentration of solute per unit volume of solution
What is osmolality?
the total molality of a soltion in osm/kg or osm/L
What is the osmolality of normal saline?
0.3 Osm which means that normal saline is isotonic to plasma
What is the regulation of blood osmolality?
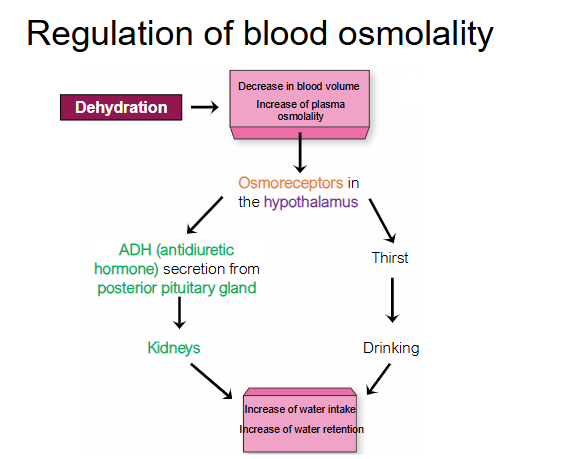
What is the second law of thermodynamics
things go from orderd to disordered unless energy is added
What kind of pump is the sodium/pottasium pump?
it is an active transport carrier, it transports 3 Na+ for every 2 K+, it brings it into the cytoplasm against the concentration gradient
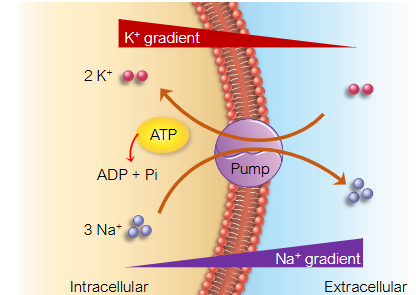
Why is the inside of the cell negative?
it contains a lot of negativly charged anions, such as DNA and other negative moleucles, this attracts cations such as pottasium.
What is the electrochemical gradient
it is the diffrence between the membrane potential and the equilbirum potential of an ion
What factors contriubte to the electrochemical gradient?
the cocentration gradient
the voltage gradient (electrical attraction)
Equilbrium potential of the cell membrane
pottasium is found in higher ammounts in the cell due to the anions however there reaches a point where the forces inside the cell counteract due to cation ions and anions, which is Ek= -90mV which is hte equilbrium potential for pottasium
what is resting membrane potential?
the membrane potential of a cell when it isnt producing any impulses
What are the factors of the resting membrane potential
the concentration gradient of each ion
the specific permeability of each ion
What is the resting membrane potential of neurons?
-70mV, while when neurons are producing a impulse the potential changes to +30mV
what are the three types of cell signaling
Paracrine signaling
Synaptic signaling
Endocrine signaling
What is Paracrine signaling?
This is signlaing that happns within the cells that are apart of an organ and they communite by using the gap junctions to talk to the adjecent cells
What is synaptic signaling?
It is the process of a neuron(s) and their target cell, the neuron will release neurotransmitters to the target cell
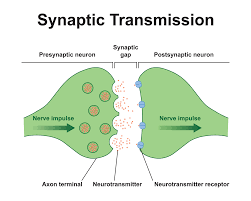
What is endocrine signaling?
This is a hormone signal released by endocrine glands, the hormones bind to certain cells.
What are second messangers?
Second messangers are the molecules that relay the signal given to them form the outside back into the inside
How are second messangers produced?
They are produced indirectly when the regulatory molecule binds to its receptor
What are G-Proteins?
G-proteins are the molecules which take the signal from the receptor to the enzyme which produces the second messanger
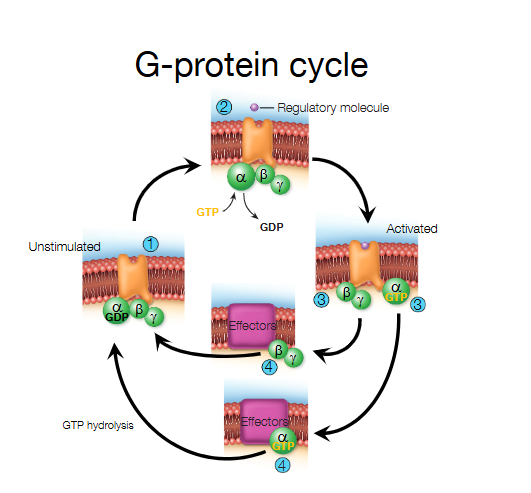
What is this?
G-Protein Cycle, when the GCPs is activated only alpha or beta and gamma are released, not both at once!
What is an excitable cell?
It is a cell that is able to change their membrane potential with stimulius
What is hyperpolarization? what is depolarization? What is repolarization
Hyperpolarization is when negative charges enter the cell
depolarization is when postive charges enter the cell
Repolarization is when the cell returns to its resting membrane potential
What does it mean for a neuron to be exictatory? Inhibitory?
For a neuron to be excitatory means that it is getting depolorzied while a neuron being inhibitory is being hyperpolarizied
what is a sodium ion channel?
it is a channel for the sodium ion to go in and out of and is closed when the cell is RMP
the ion channel can be blocked by diffrent molecules, and we call them sodium channel blockers, example: Tetradotoxin
What happens when depolarization dosnt reach a certain threashold?
the depolorization dissipates and decays back to the RPM
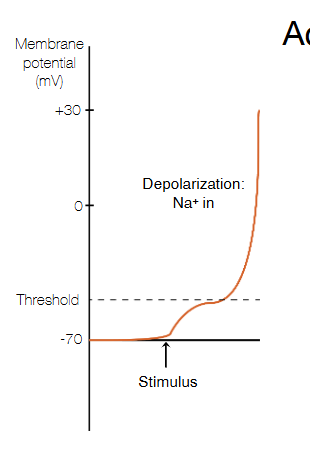
what is this?
voltage gated Na+ channel opening up and sodium ions rushing into the cell
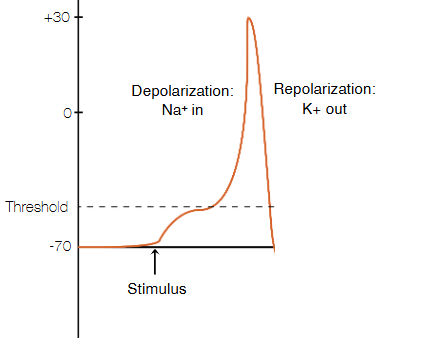
What is this?
This represent the souum channel closed and the pottasum channel then open which allows the pottasium to rush out of the cell
What type of feedback loop happens when the sodium channel opens?
postive feed back loop
What type of feedback loop happens when the pottasium channel opens?
negative feed back loop
What is the all or none law?
it means that if the threashold is not reach no action potential is produced but if it does an action potential is produced
the length of time that the Na + and K +
channels remains open is independent or dependent of the depolarization stimulut?
it is independent