L26 Cellular Differentiation, Stem Cells & Modern Medicine
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for key terms related to cellular differentiation, stem cells, and modern medicine techniques discussed in CELS191 Lecture 26.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Totipotent cells
An embryo begins as a naive number of these. They are very flexible, but not specialised. Able to give rise to all cell types via division, including trophectaderm.
Pluripotent cells
Can develop into any of the 200 or so cell types in the body given the right conditions. Example is embryonic stem cells. Very specialised, not flexible. Eg ESC and IPSC
A cells fate
Progressivly limited until it becomes terminally differentiated, and can only give rise to the same type of cell, exception is stem cells and germ cells (eggs and sperm)
Differentiation
The process by which cells become specialized in structure and function.
Stem Cell
An undifferentiated cell that can divide without limit and differentiate into specialized cells. Important for tissues that need constant renewing eg blood and skin.
Embryonic Stem Cell (ESC)
Pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass (ICM) of a mammalian blastocyst embryos. Cells derived from ESCs are genetically identical to embryo donor.
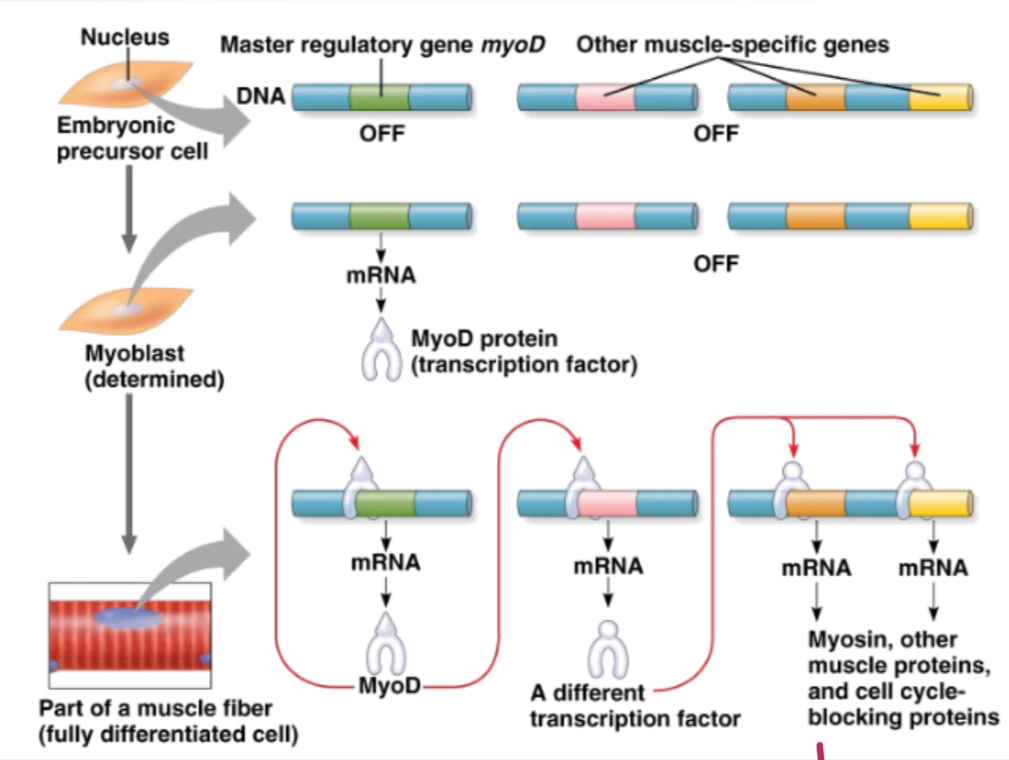
Steps to differentiation.
At first stage cell could become any type of differentiated cell. The fate of the cell is determined after certain control genes coding for transcription factors are activated. Finally the cells is terminally differentiated playing a functional role in the organism.
Adult (Tissue) Stem Cell
Undifferentiated multipotent stem cells that can divide without limit to give rise to stem cells and cells which go on to differentiate into one or more (but not all) types of functional tissue cells.
Multipotent cells
Less flexible than pluripotent, can develope into a subset of the 200 cell types. g adult tissue stem cells and umbilical chord stem cells.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)
Pluripotent stem cells generated by reprogramming adult somatic cells to behave like embryonic stem cells. Can be made from anyone, are genetically identical to source skin cells.
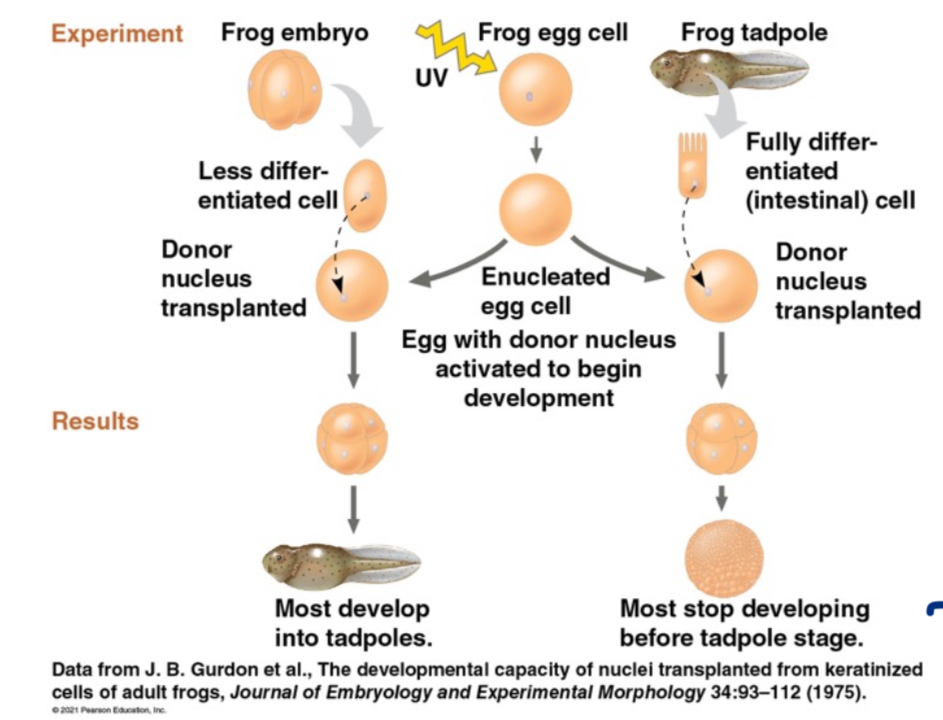
Genomic Equivalence
The principle that differentiated cells contain all the DNA required to build an entire new organism.
Umbilical chord stem cells
Stem cells from blood isolated from umbilical chord of new born babies are frozen (banked). Stem cells are multipotent (immature blood stem cells) and earlier on in developement therefore less restricted than adult blood stem cells. Can be used to treat leukemia and other blood diseases.
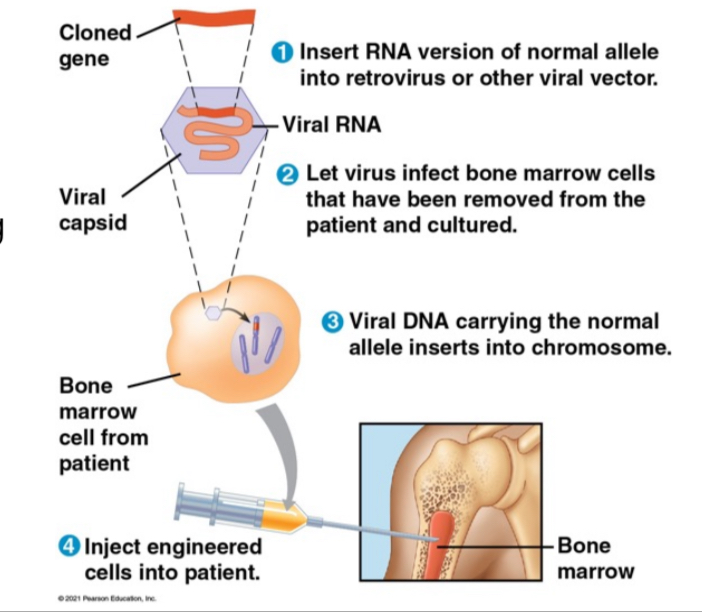
Intergrative gene Therapy
A technique to correct single gene disorders by altering the genetic code of an individual's cells, often by inserting a normal allele into the affected tissue via virus or CRISPR.
Regenerative Medicine
Pluripotent cells can be made from skin or blood cells from patient (genetically identical) or matched donors, or embryos. And then encouraged to differentiate into specific cell types eg neurons or retinal cells. Then transplanted into patient. Repair or replace damaged organs or tissues.
Haematopoietic Stem Cells
Blood stem cells found in bone marrow used for transplants to renew blood and immune cells.
Order of flexibility of stem cells
Totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent.