Strengthening Exercises: Resistance Exercise Types
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Goals of Strengthening Exercises
increase muscular strength
increase endurance
increase power
increase agility
Types of Strength Exercises
Static: Isometric
Dynamic: Isotonic, Isokinetic
Open kinetic chain and Close kinetic chain
Isometric Exercises
safe rehab starting point→ pt controls amount of tension in muscle
gentle contractions w/in p! free limits
Recommended 2-3× 8-10rep/set→ hold 6-10 sec/rep, 30-60 sec rest b/t sets
Isometric: Setting Exercise
almost any muscles
just contracting
avoid or minimize muscle atrophy
often used right after surgery
ex. quad set
Isometric: Static Exercise
Push against wall, no motion
Isometric: multiangle exercise
increase strength through full ROM
contract and move up to hold, go higher, contract, hold

Cautions for Isometric Exercises
make sure pt is breathing
avoid valsalva maneuver→ holding breath increases BP and increases risk of CV damage
count time out loud to make them breath
Isotonic Exercises
during repair stage of healing
better to improve strength→ use when you regain some strength + ROM
Concentric and eccentric
can use equipment or body weight to add resistance
Concentric vs. Eccentric
Con: shortening
Ecc: lengthening
eccentric can produce greater force than concentric
speed ratio= Ecc:Con 2:1
Isotonic Exercises and Rehab
subacute (repair) phase
concentric first, and then eccentric
caution: no overtraining!
Isokinetic Exercises
machine provides constant velocity→ you can’t push harder to go faster
use in late (remodel) phase of rehab to increase functional activity
Benefit of Isokinetic machine
maximal resistance is provided throughout the ROM bc the resistance moves only at the constant speed, regardless of force applied to it.
Improves beginning and end strength bc working through entire ROM with same resistance throughout
Overload principle
increase strength with progressive resistance exercise (PRE)
How?
increase resistance/weight
increase # of reps/sets
increase time to complete exercise
Cautions with Overload principle
Too passive:
no increase strength
no increase functional activity
bored w/ rehab and quit
Too agressive:
increase p!
increase swelling
increase tissue damage
Strengthening principle: SAID
Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demands
you get what you train for
know goals
optimal functional outcomes→ design exercise according to goals
Strengthening principle: SNAP
Specific Exercises
No Pain
Attainable Goals
Progressive Overload
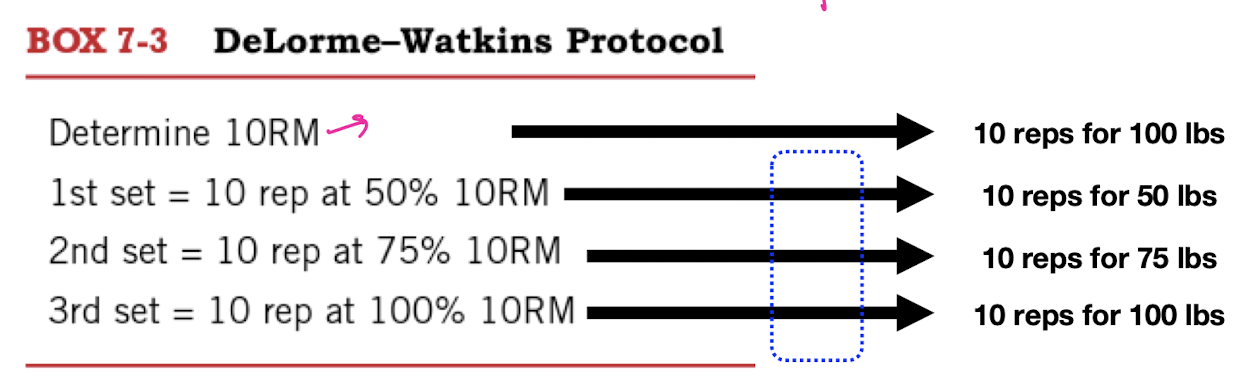
DeLorme Watkins Protocol
3 sets x 10 reps at _% of 10 RM (50, 75, 100)
2 min rest b/t sets to prevent muscle fatigue
might be more beneficial if want to improve more strength
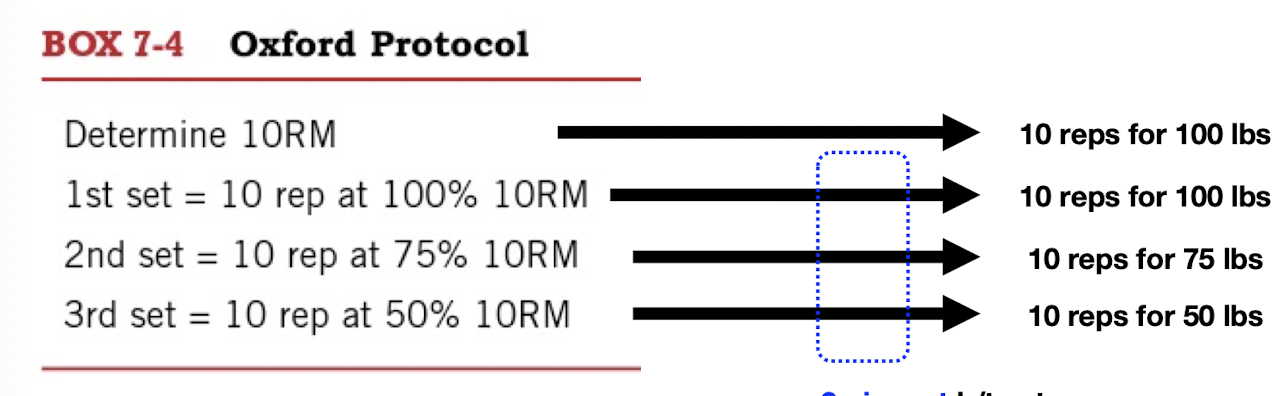
Oxford Protocol
opposite of DeLorme
3 sets x 10 reps at __% of 10 RM (100, 75, 50)
2 min rest b/t sets
may prevent fatigue
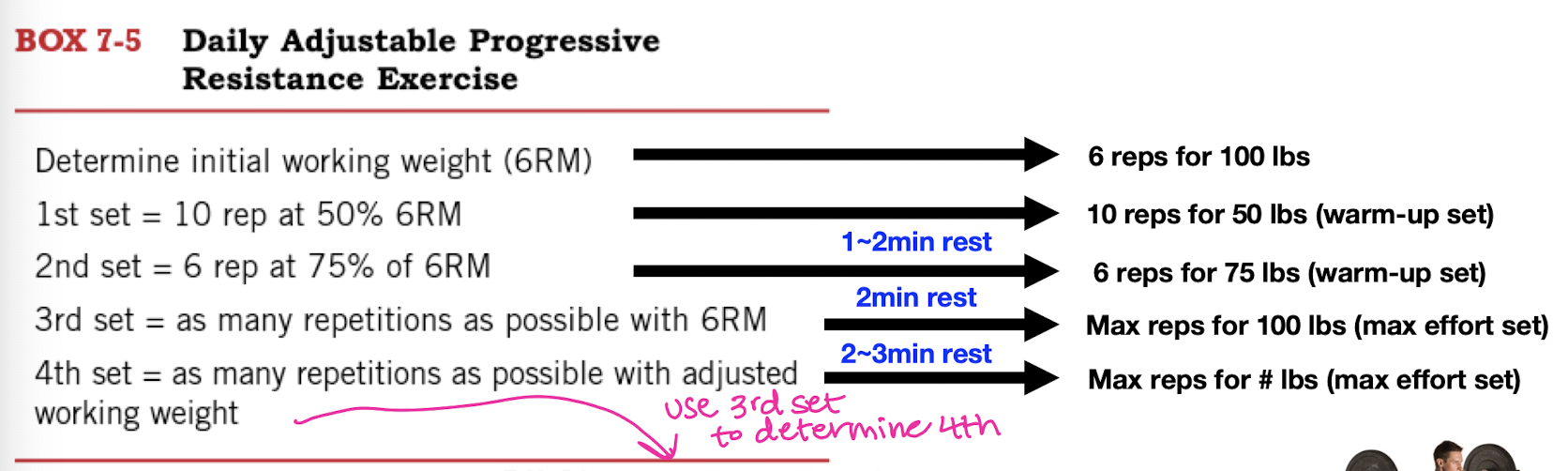
DAPRE (Daily Adjustable Progressive Resistance Exercise)
4 sets x various reps at _% of 6 RM
best with free weight or machine
DAPRE adjusted working weight table

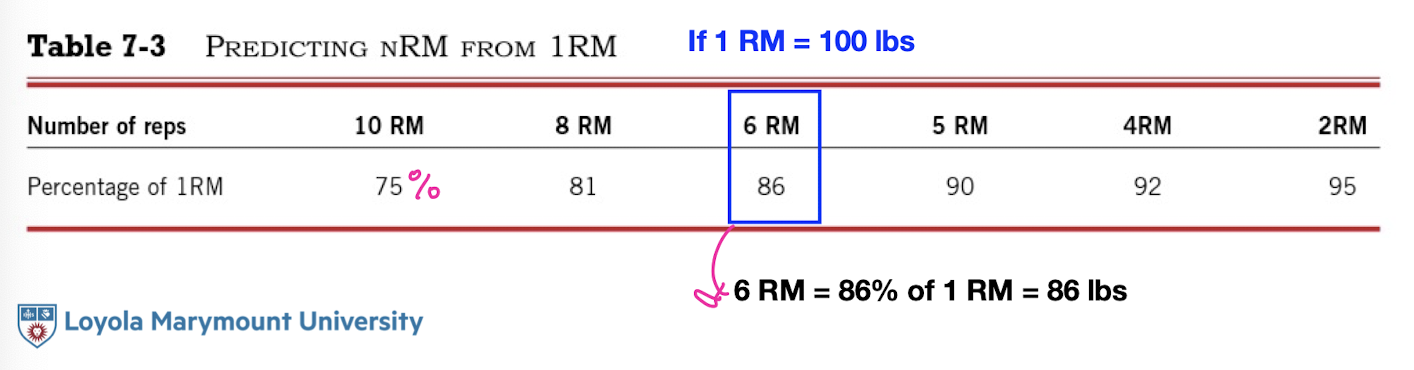
Calculation of 1 RM

Predicting nRM from 1RM
Strength vs Endurance RM and reps
Strength: 90% 1 RM, 3-9 reps
Endurance: 70% 1 RM, 15-20> reps
Strength and Endurance: 70-90% RM, 6-12 reps
* at least 66% 1 RM for strength gain
Precautions to strengthening
overtraining
CV concerns
Fatigue
muscle substitution
muscle weakness
muscle soreness
osteoporosis
Contraindications of strengthening
acute inflammation
severe muscle or jt p!
severe cv disease