AP Human Geography Unit 5 Key Terms (Agricultural and Rural Land Use Patterns & Processes)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Agriculture
the purposeful planting of crops/raising of livestock.

Climate
the pattern of temperature and precipitation in an area over a 6 year period.

Weather
the day to day atmospheric conditions in a place.

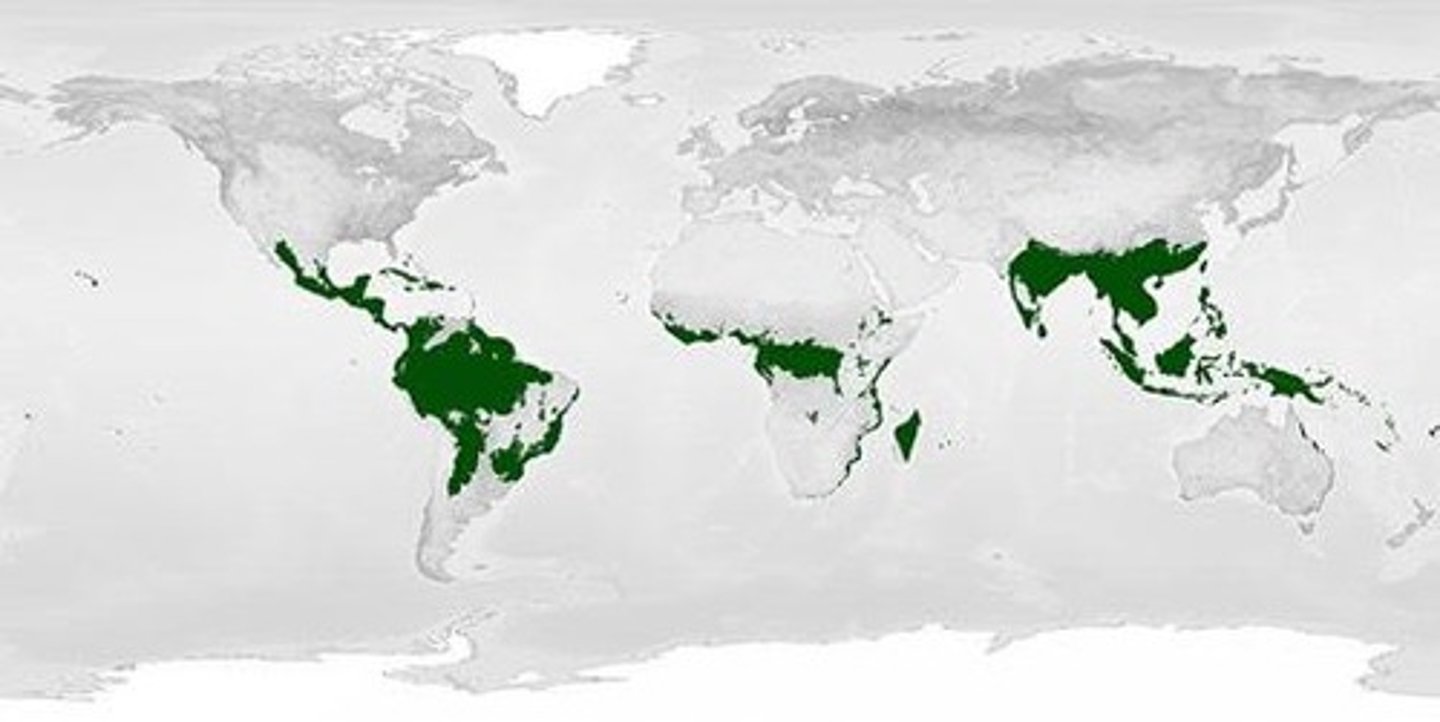
Tropical climate zones
areas near the equator that are hot all year and get lots of rain.
eg: rainforests, jungles
Dry climate zones
get very little rainfall; crops struggle to grow. very hot in summer, very cold in winter.
eg: sahara desert

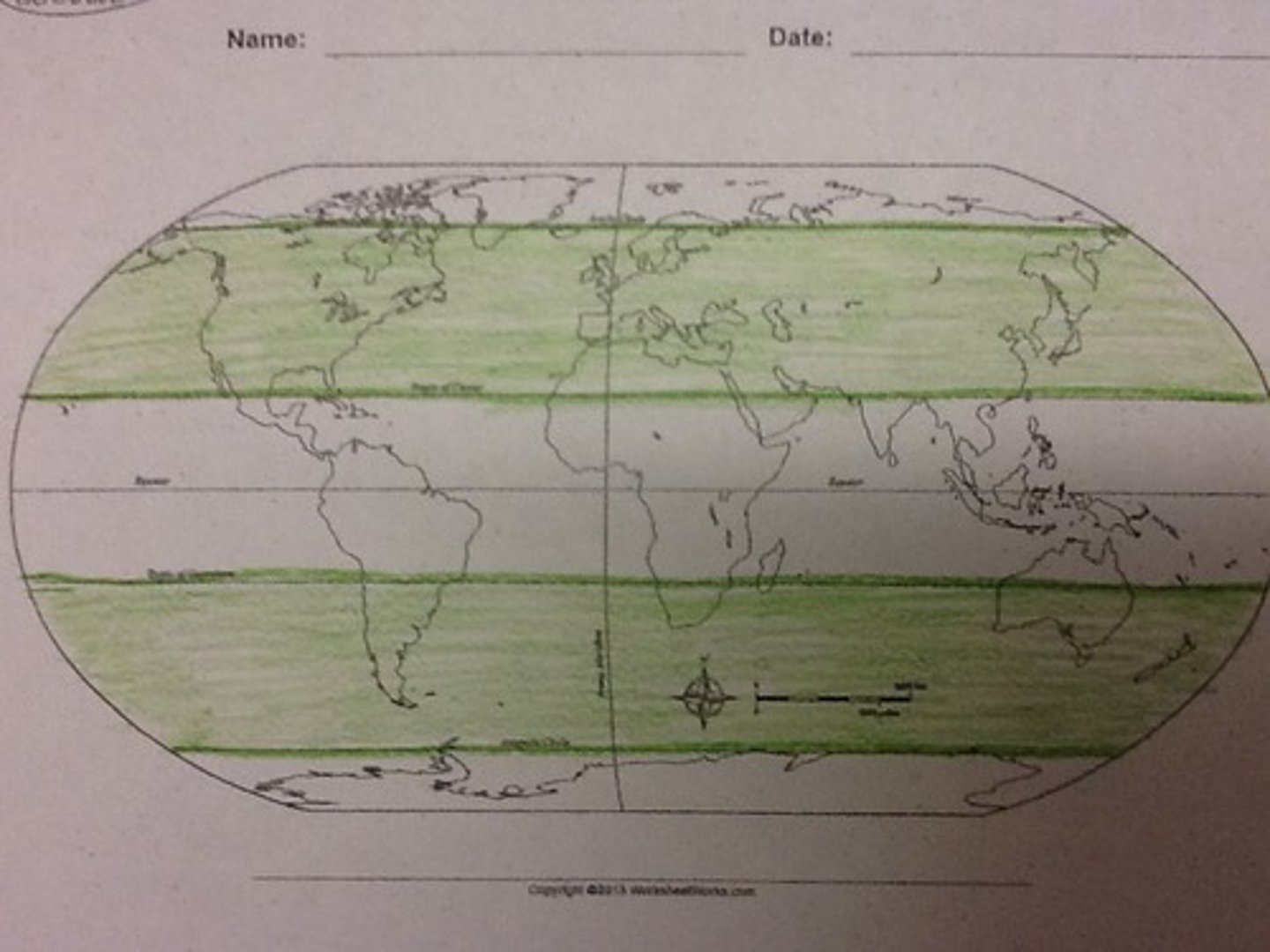
Moderate/mediterranean climate zones
areas with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
eg: south california, mediterranean countries.
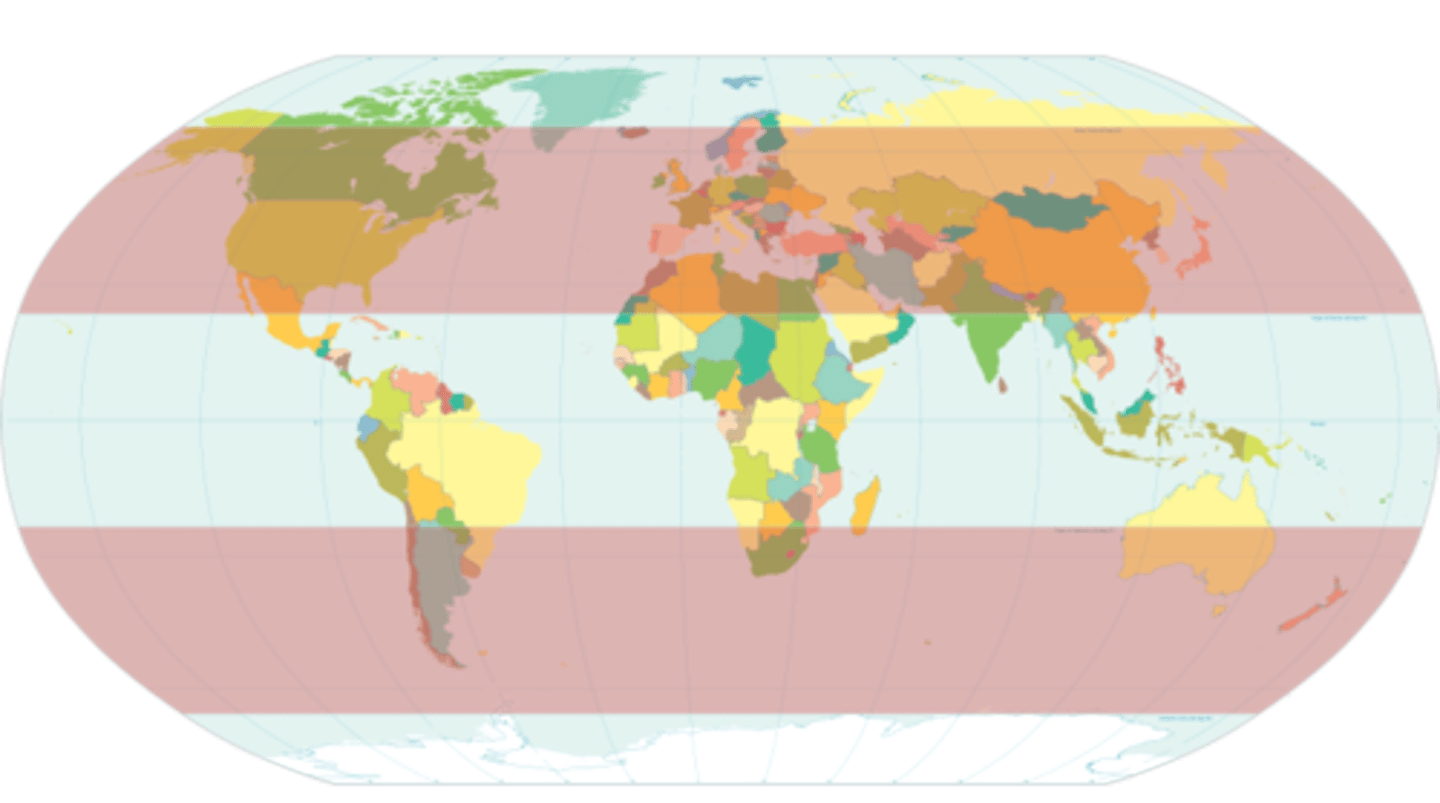
Continental climate zones
areas with hot summers and cold winters, usually far from oceans.
eg: midwest usa, eastern europe.
Environmental possibilism
the idea that the environment limits what people can do, but we're smart enough to choose how to live and change it using technology.
Intensive agriculture
lots of effort is put into making a piece of land as profitable/productive as possible.

Feed lots
places where animals are packed together and fattened up fast using grain-based feed (not grass).

Dairying
specific branch of agriculture focused on the production of milk and milk based products like cheese and yogurt.

Extensive agriculture
minimal effort is put into a piece of land because its natural features already make it productive.

Settlement patterns
how people organize themselves on land.
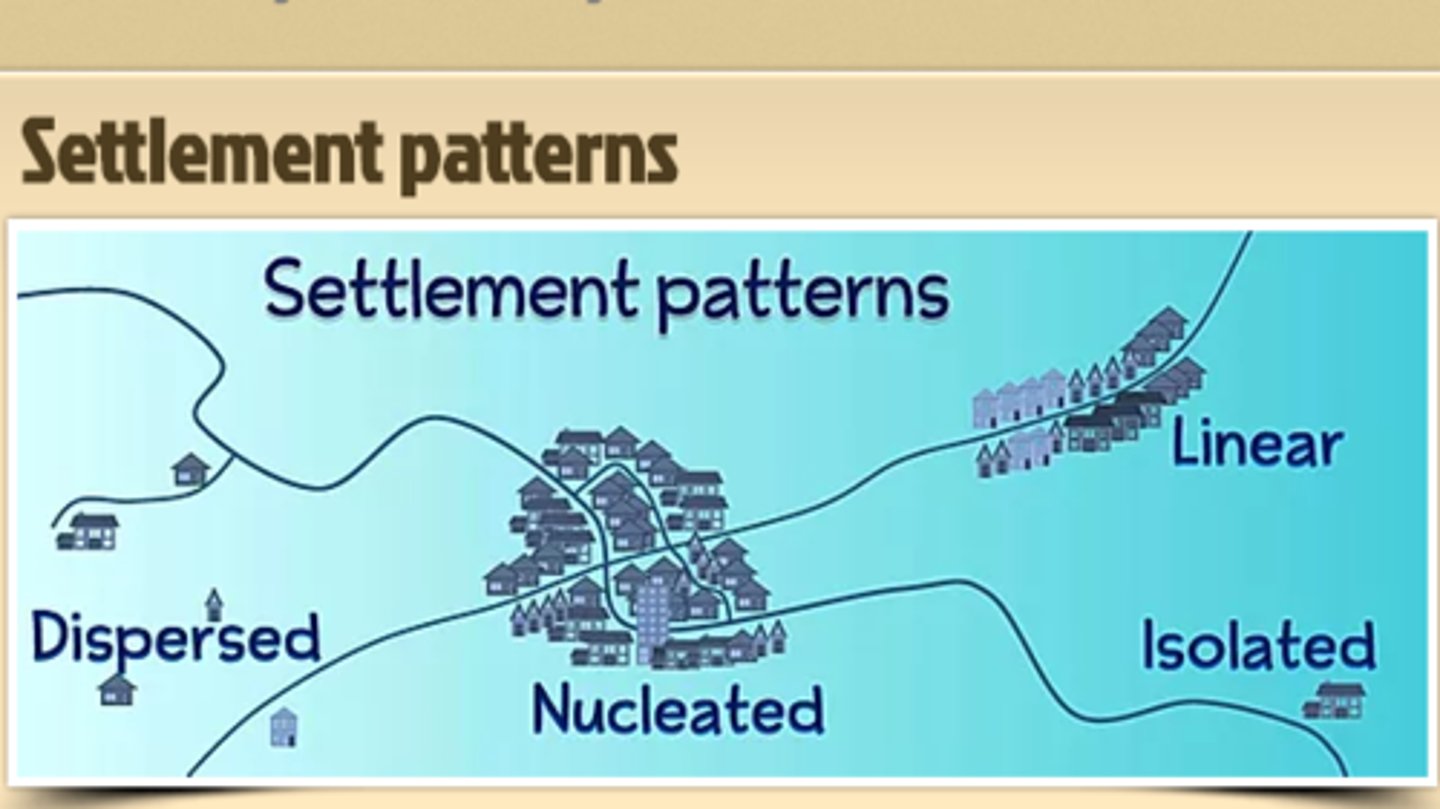
Farm village
clustered rural settlement inhabited by people who are engaged in farming.

Survey methods
the methods used by surveyors to lay out property lines.
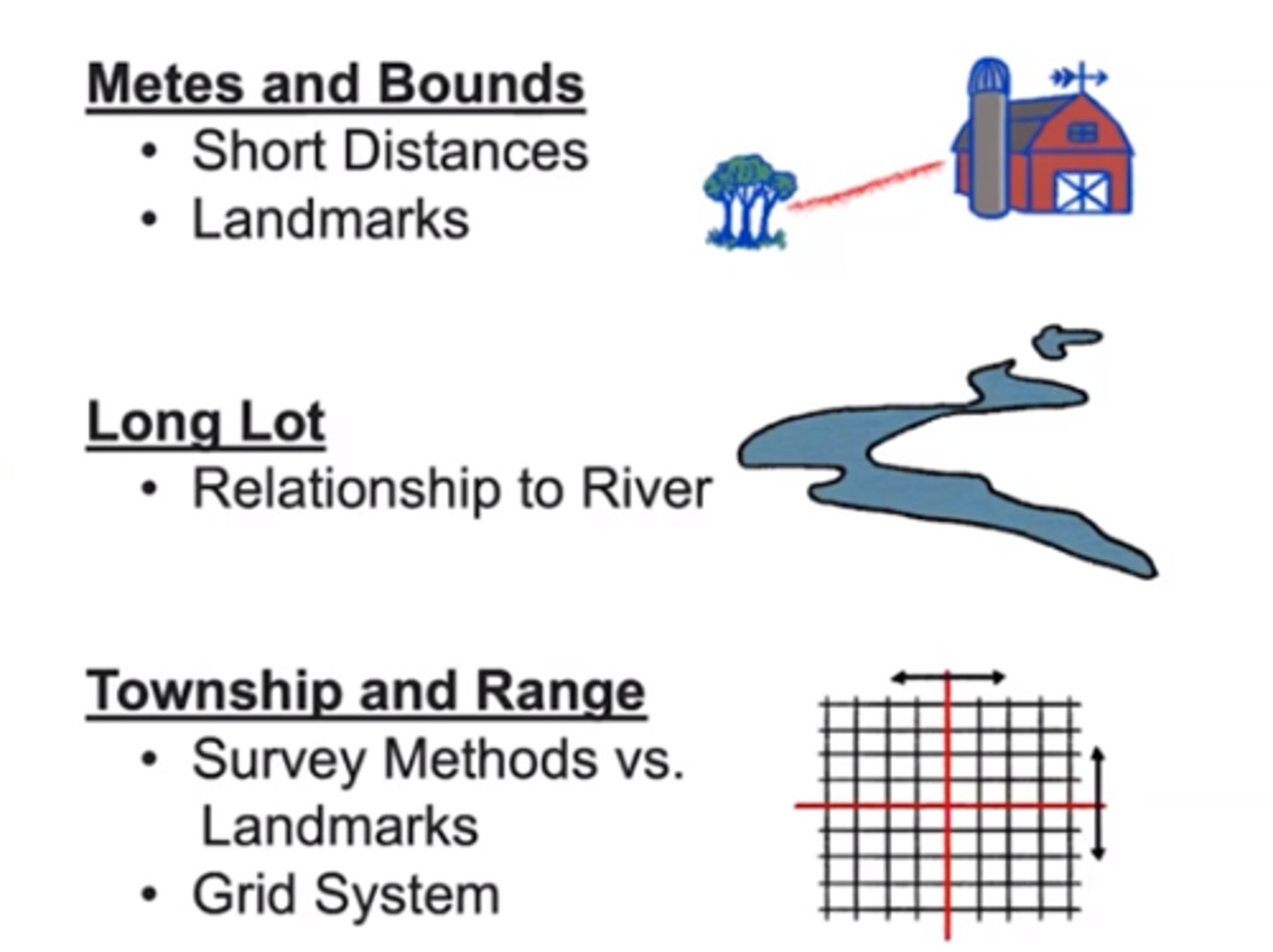
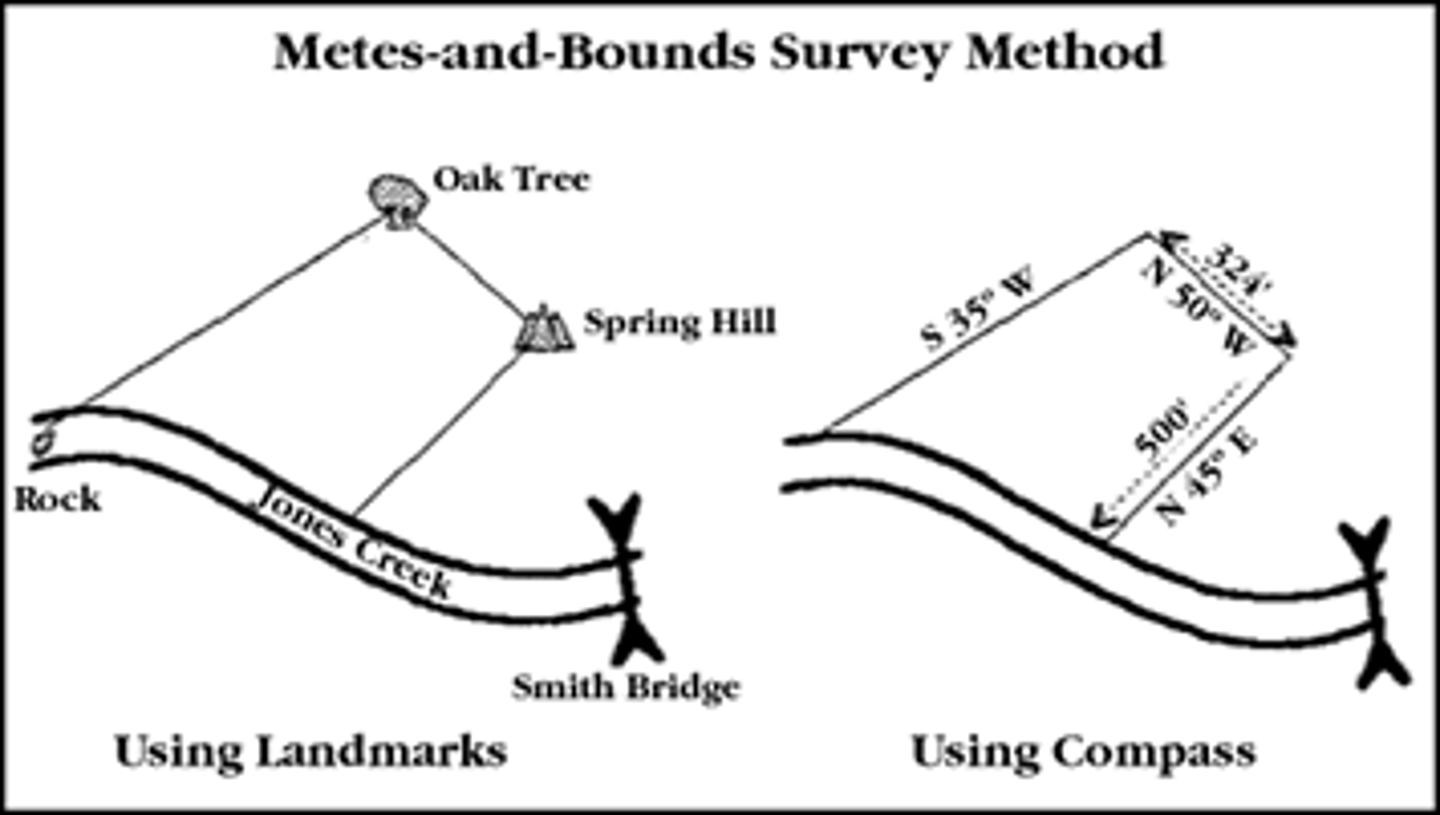
Metes and bounds
land measured using natural landmarks and distances.
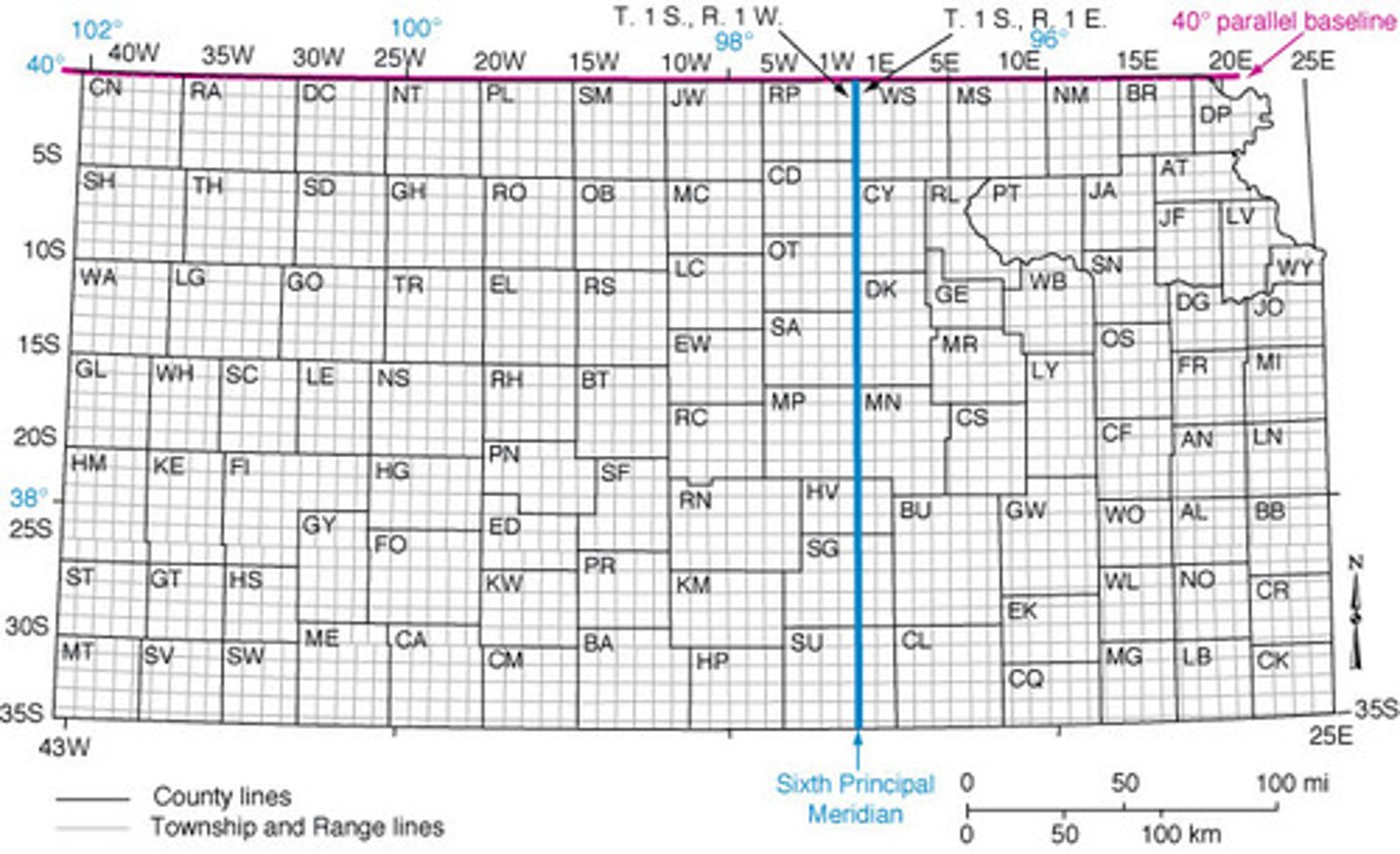
Township and range
land divided into neat square grids using lines of latitude and longitude.
Domestication
humans controlling animals and plants for food, work, or other uses.

Animal husbandry
taking care of farm animals.

Hunting and gathering
a subsistence strategy in which people rely on gathering wild plants and hunting wild animals for food, rather than practicing agriculture or animal domestication.

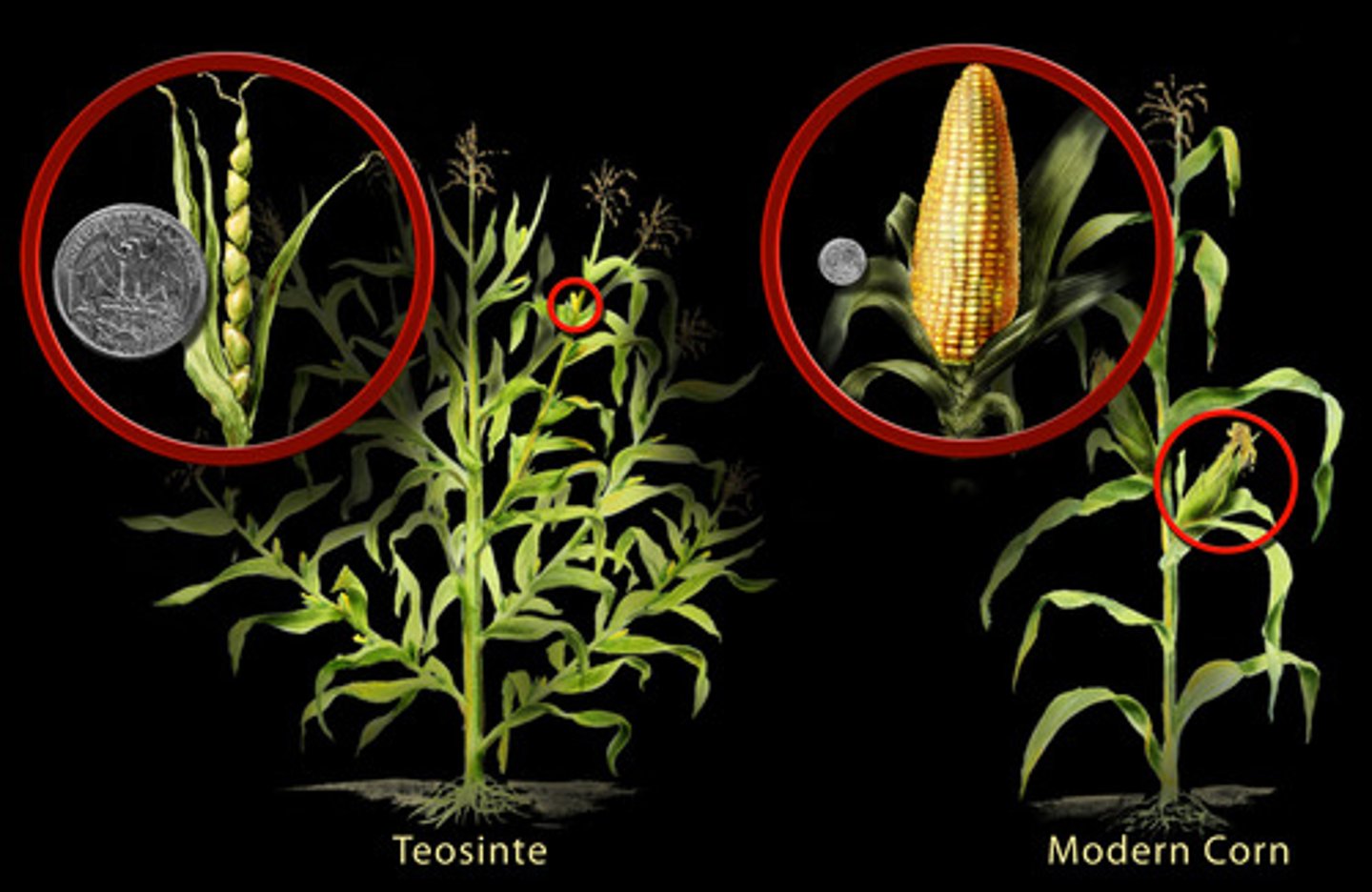
Teosinte
a large wild grass that, before domestication, had small ears of corn less than one inch long.
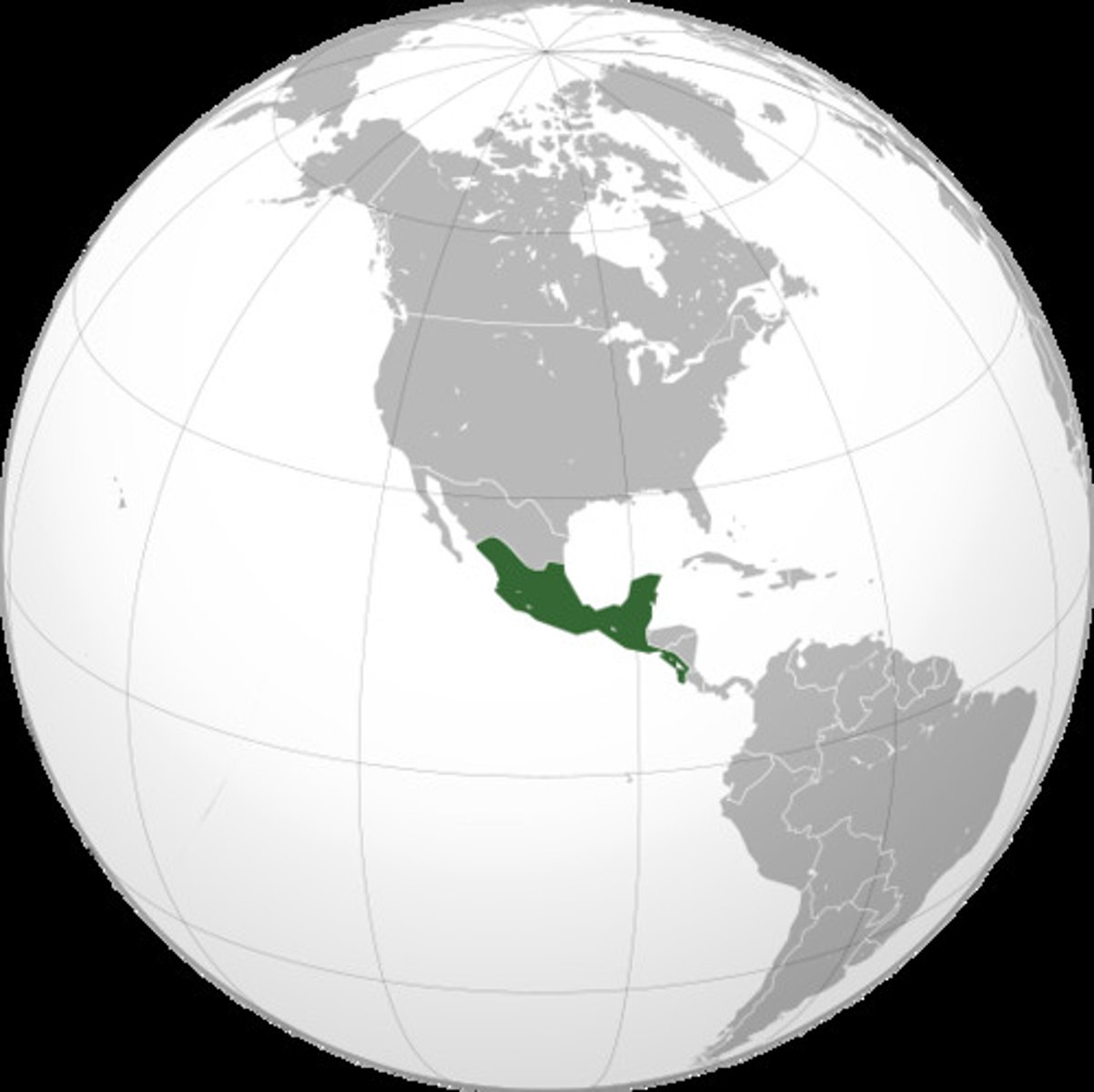
Mesoamerica
the ancient civilizations of mexico and central america.
Hearth
origin center
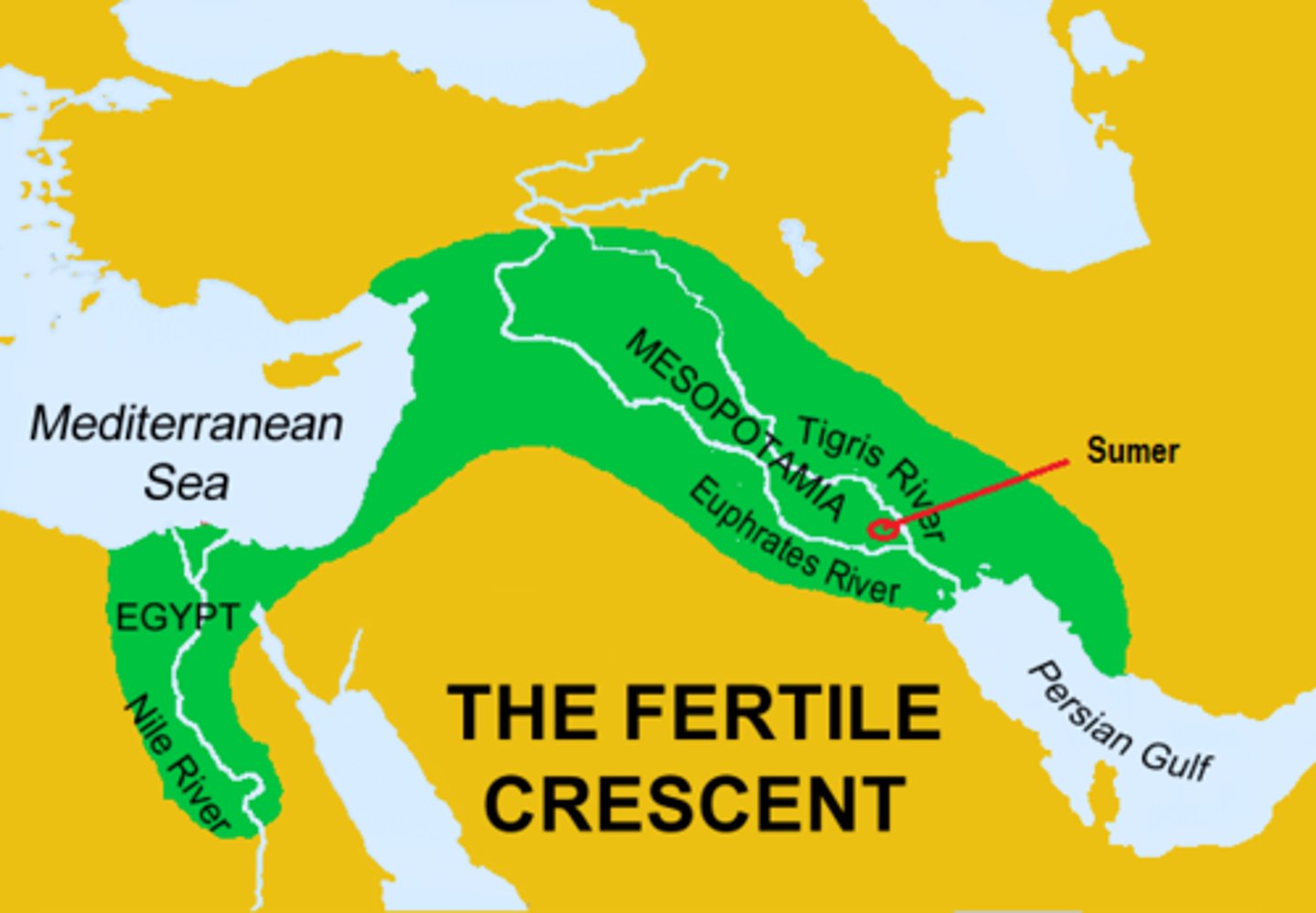
Fertile crescent
a geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East believed to be the very first region where settled farming emerged.
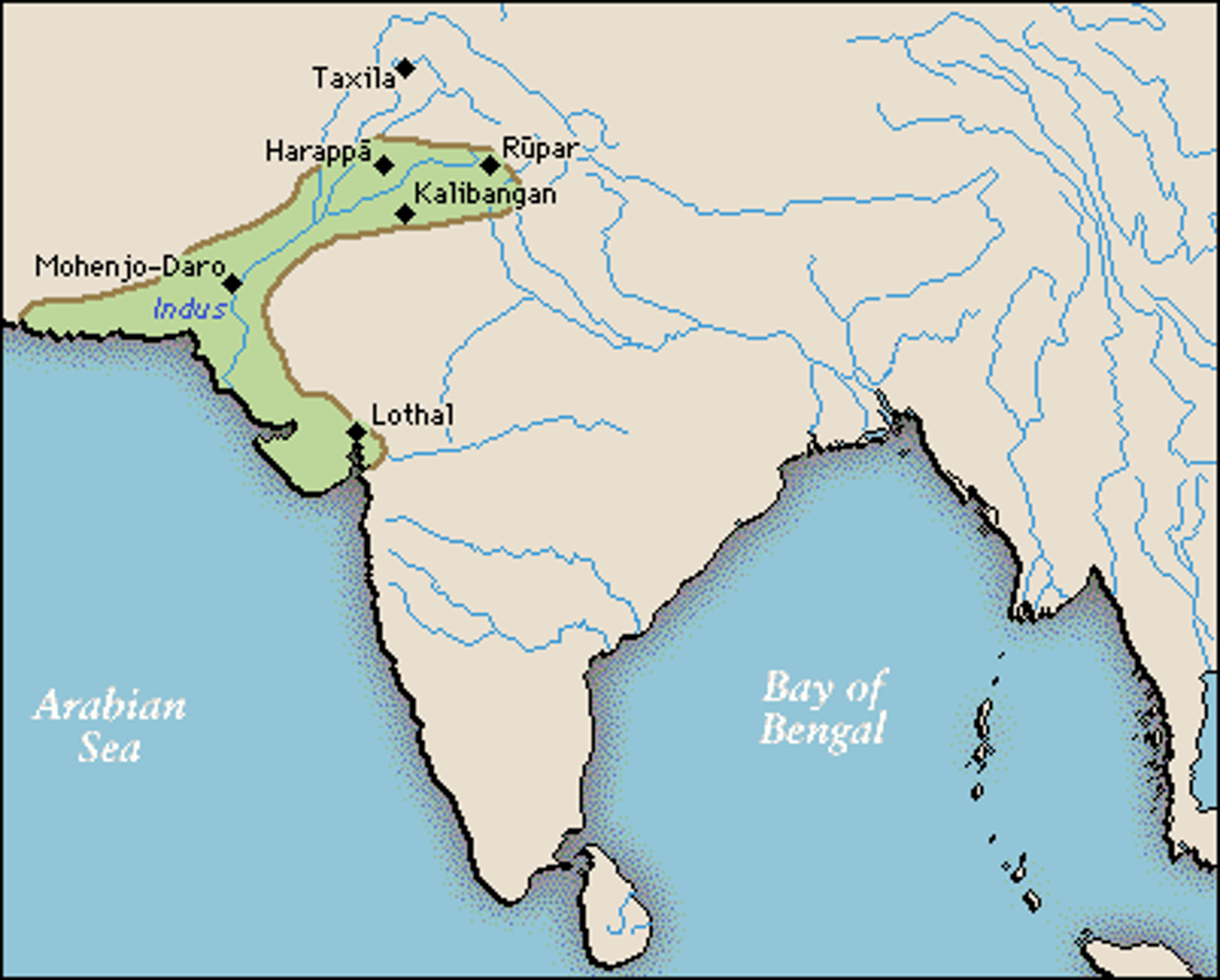
Indus river valley
another hearth of plant and animal domestication which signaled the historical transition from humans being a nomadic species to a special species.
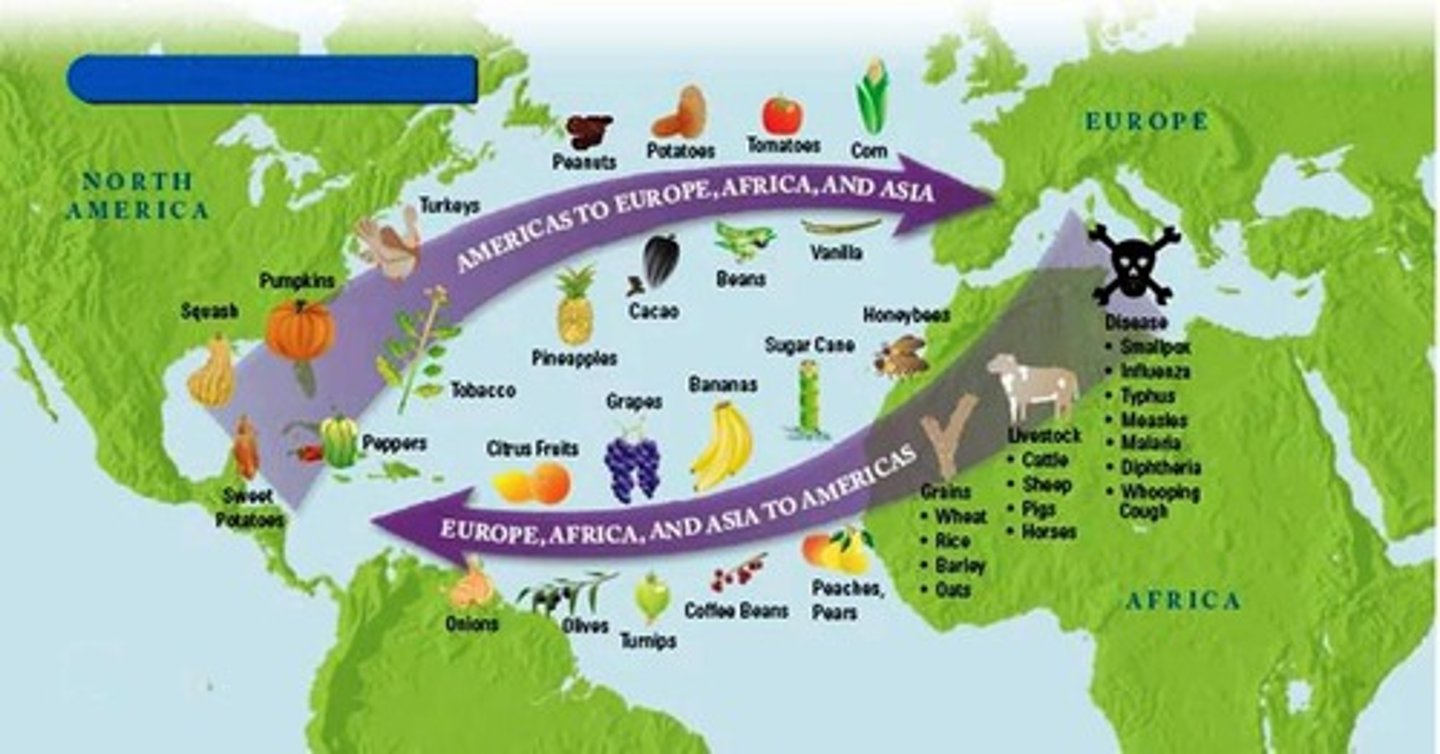
Columbian exchange
the widespread transfer of plants, animals, people, diseases, and cultural practices between the americas, europe, africa, and asia following the voyages of christopher colombus and other explorers.
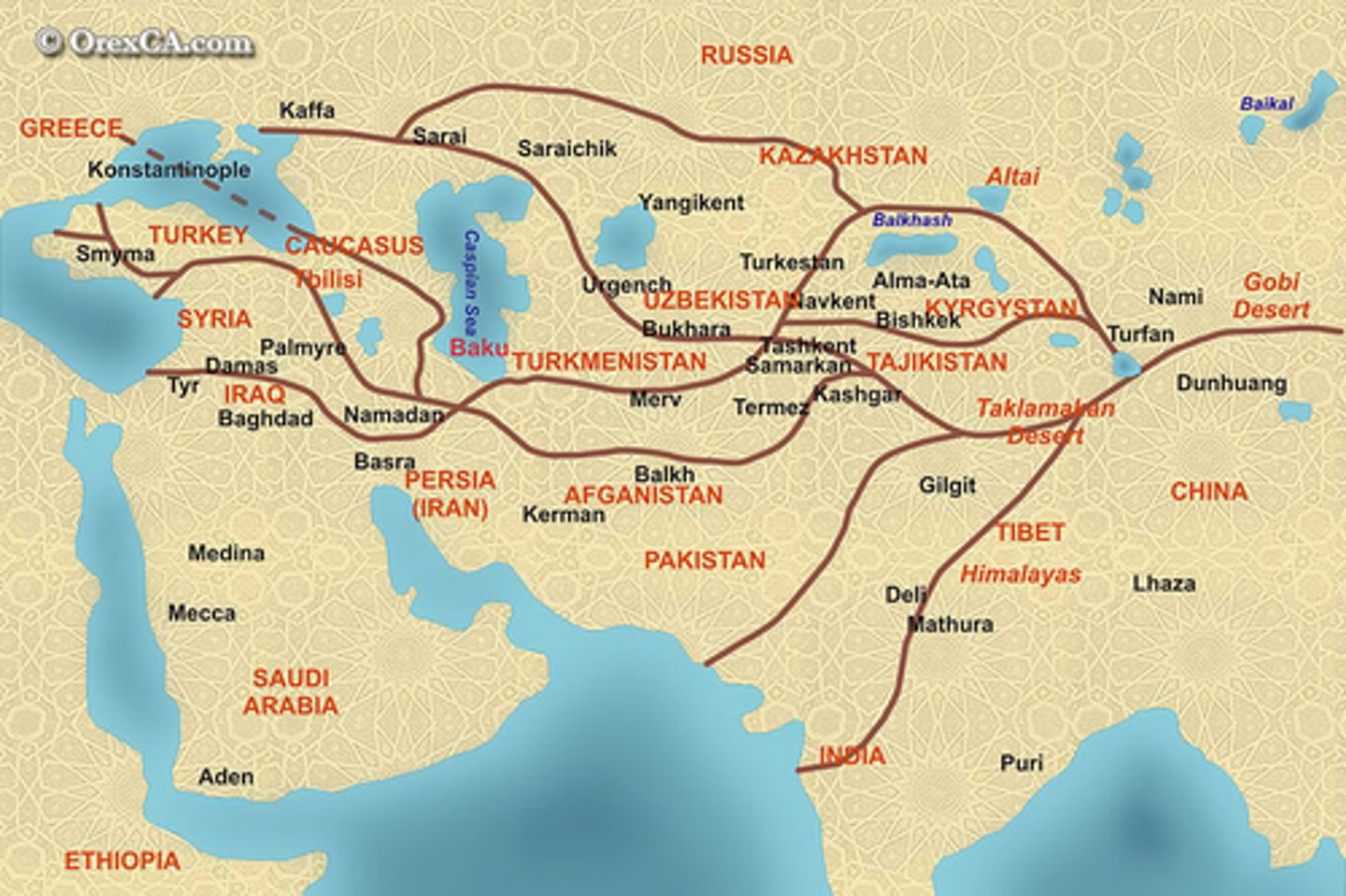
Silk road
an ancient network of trade routes that connected east asia with the middle east, europe, and parts of africa.
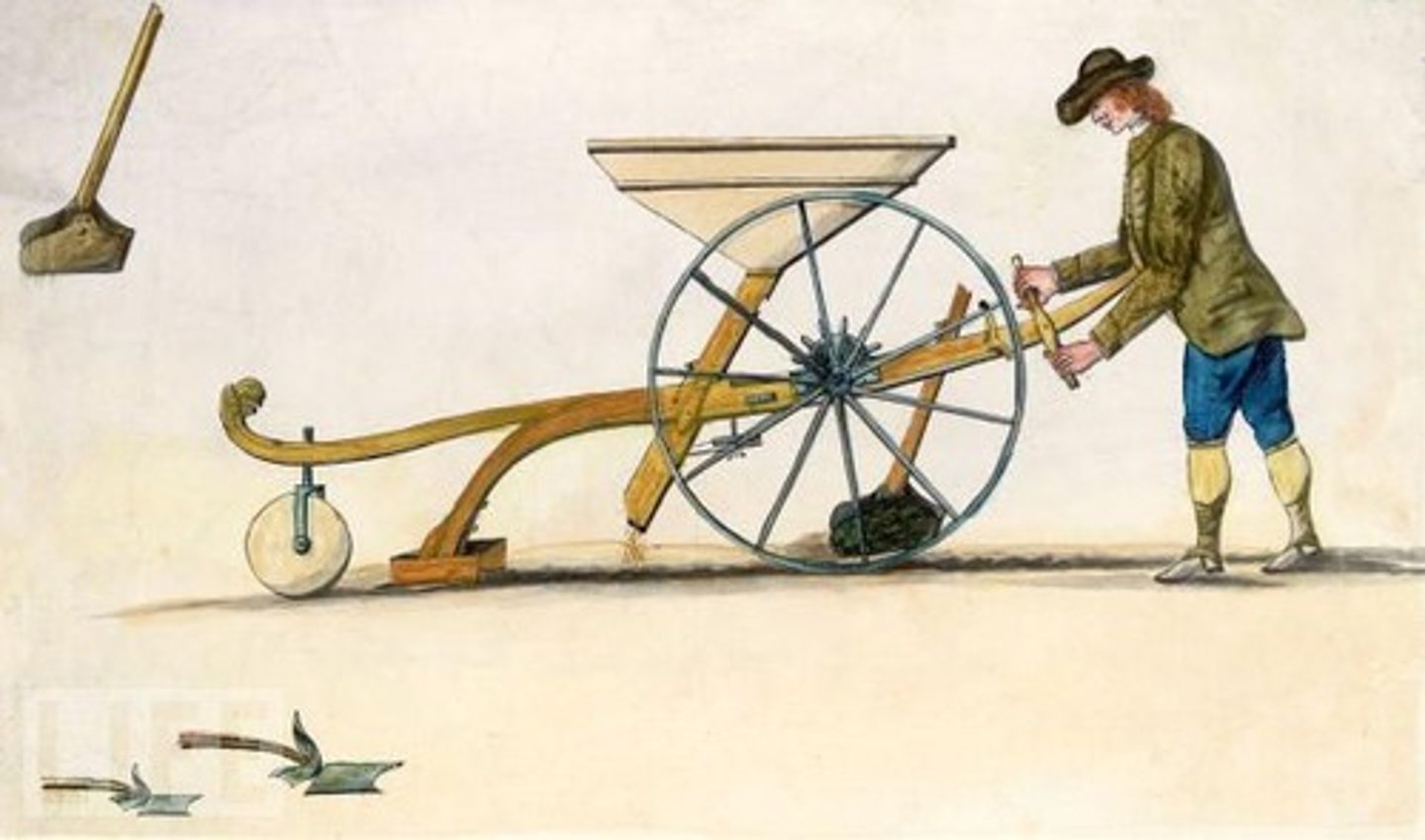
Mechanization
the transition from human labor to machine power on farms or in factories.

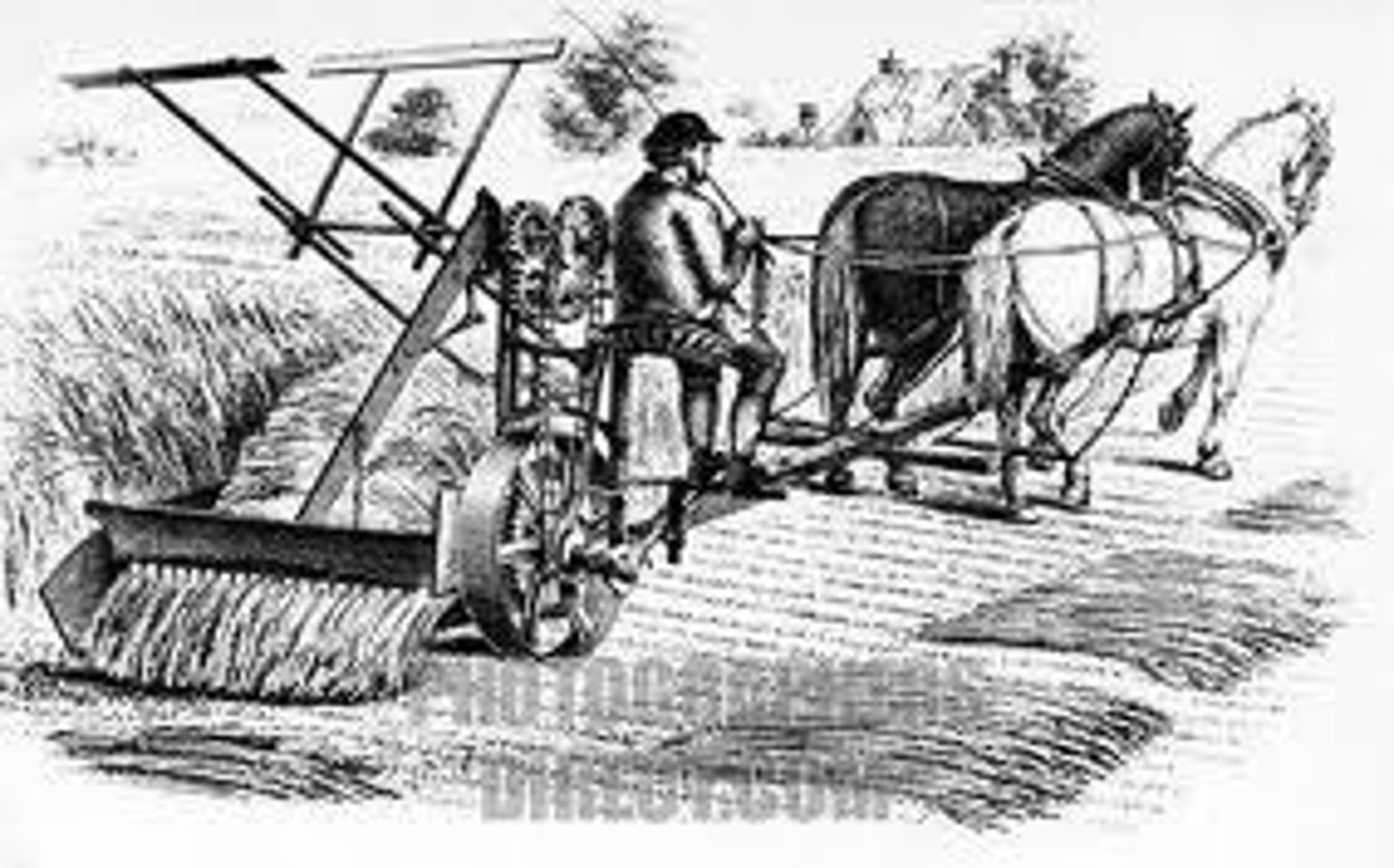
Mechanical reaper
machine that was pulled by horses and cuit and bundled grain automatically.

Seed drill
farming tool that plants seeds in straight rows for better growth and higher crop yields.
Agrichemicals
chemical compounds made from petroleum and natural gas used in agriculture.

Synthetic fertilizers
fertilizer packed with high concentrations of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
Pesticides
chemicals applied to growing plants to keep pests away.

Biotechnology
a form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.

Green revolution
agricultural revolution that increased production through improved seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation; focused on modern farming methods.
Subsistence farming
small scale; done to feed farmer's family.

Commercial farming
large scale; for profit.

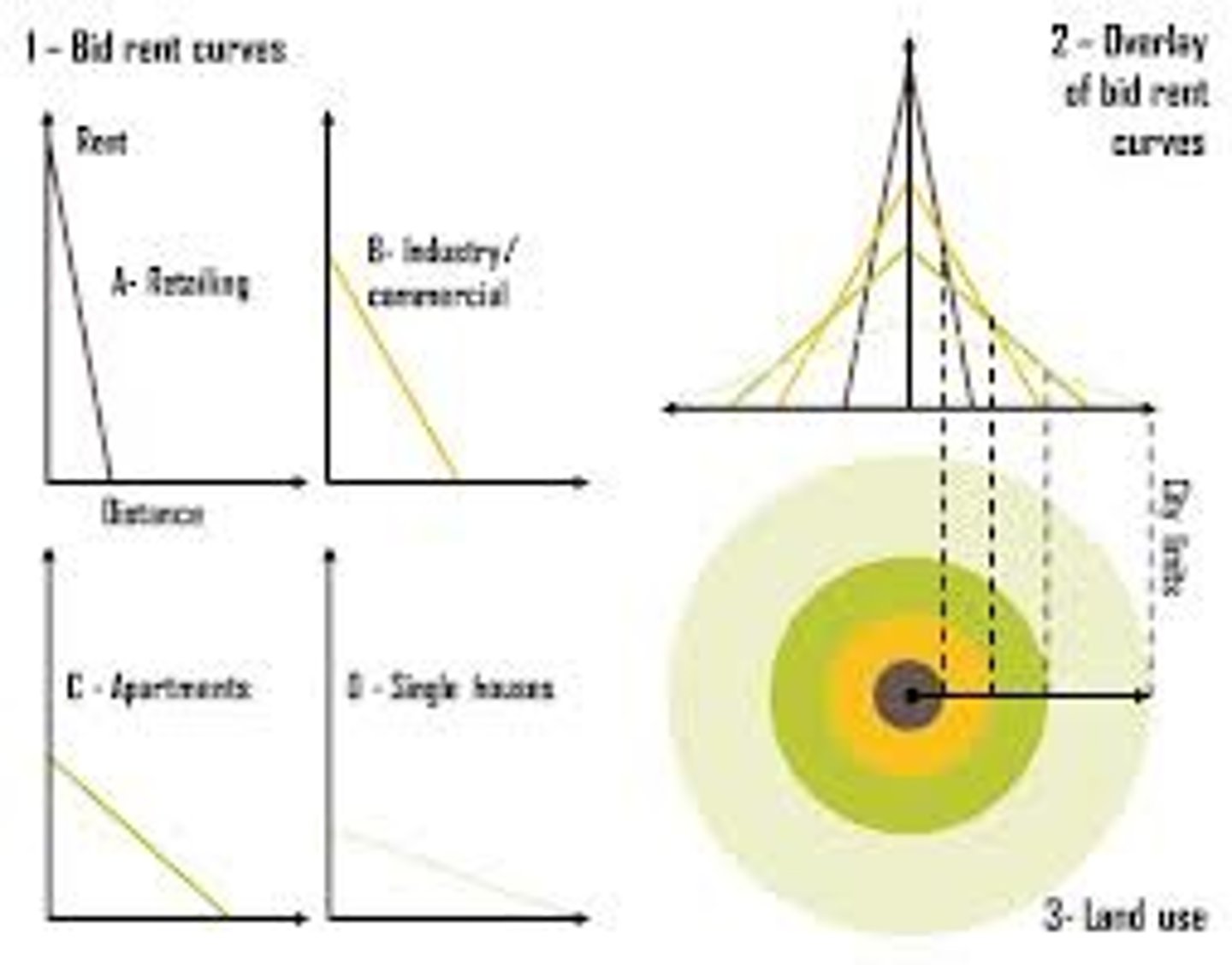
Bid-rent theory
the idea that land closer to a city is more expensive because people will pay more to be near it.
Monocropping
growing only one type of crop on the same land year after year.
Plantation
a large farm in tropical regions that grows one main cash crop like sugar or coffee, often for export.
Mixed crop/livestock agriculture
farm that grows crops and raises animals together using crops to feed animals and animals to fertilize crops.

Market farming
small scale farming that grows fruits and vegetables to sell locally.

Nomadic farming
moving animals from place to place to find fresh pasture.

Livestock ranching/pastoralism
raising animals on large land mainly for meat, wool, or other products.

Transhumance
type of pastoralism where herders and their livestock move seasonally between two fixed places.
Commodity chain
the steps a product goes through from production to consumption.
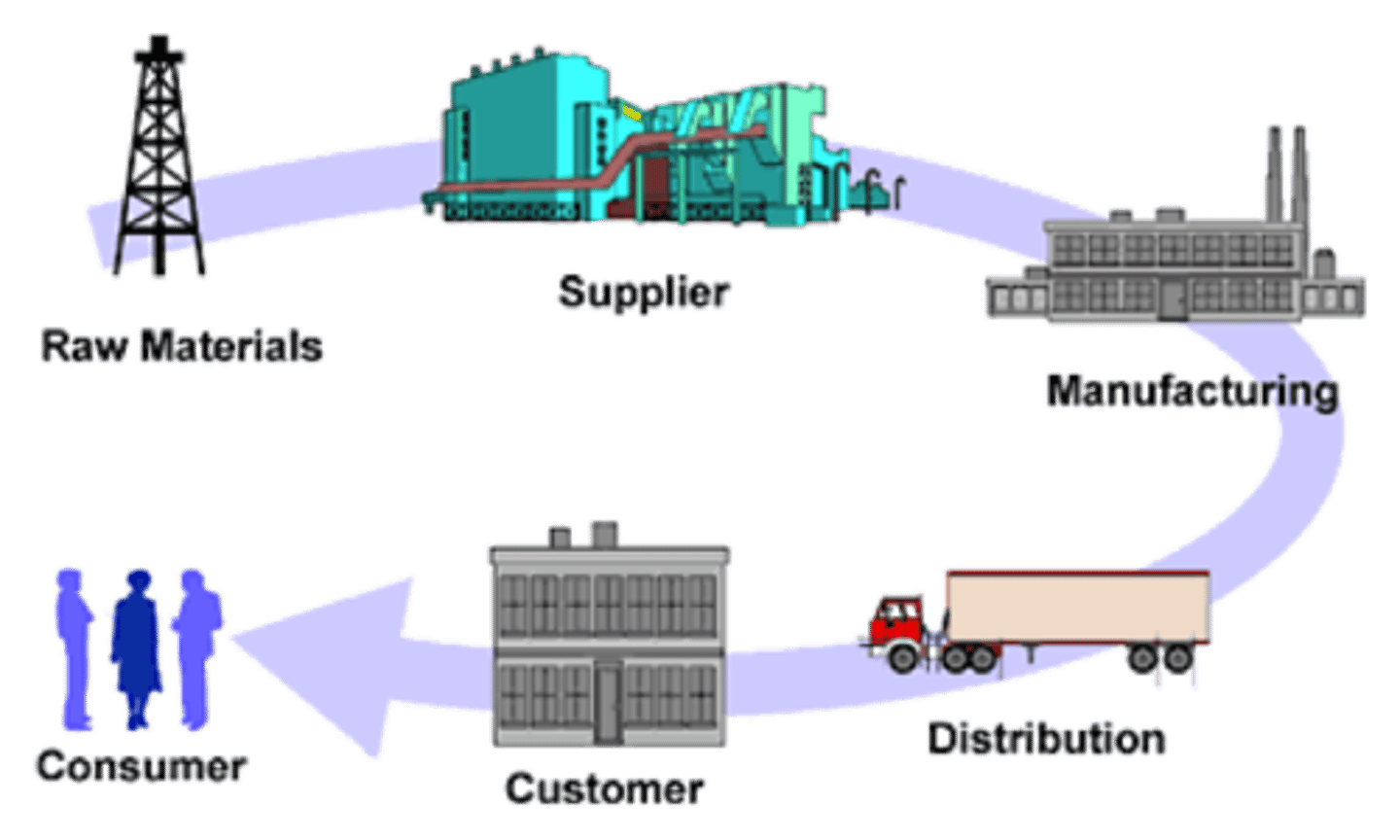
Agribusiness
large scale farming and related businesses that produce, process, and sell food.

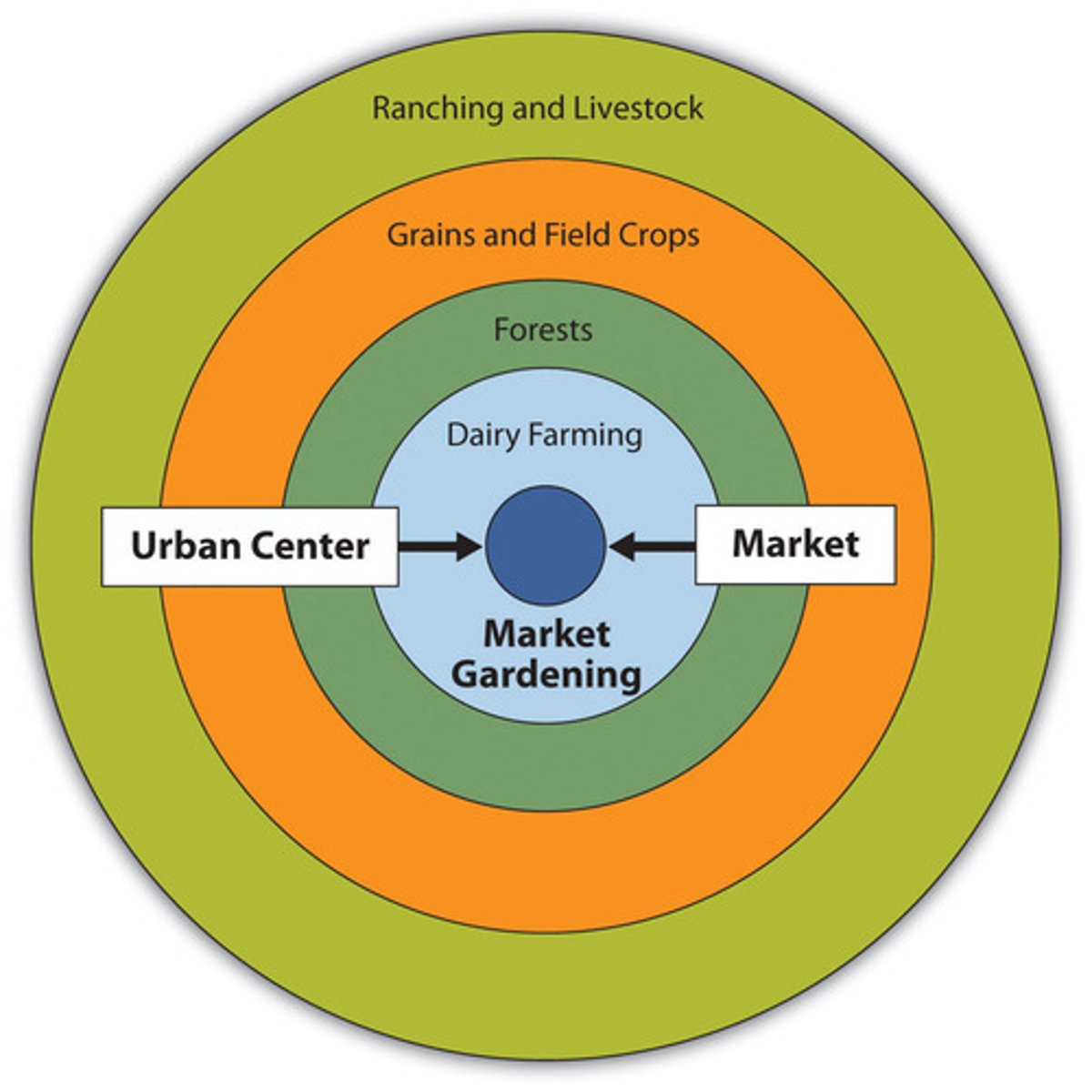
Von Thunen Model
shows how farmers choose crops based on distance from a city, with more valuable crops closer.
Globalization
how the world today is becoming increasingly connected.
Interdependent
when 2 things are dependent on one another.

Commodity dependence
when a country mostly makes money by selling a few raw products instead of many things.
Genetically modified organisms
a living organism that's created through genetic engineering.
Aquaculture/mariculture
the harvesting of organisms that live under water under very controlled conditions.

Urban farming
growing fruits and vegetables on small plots or shared community gardens within the confines of a city.
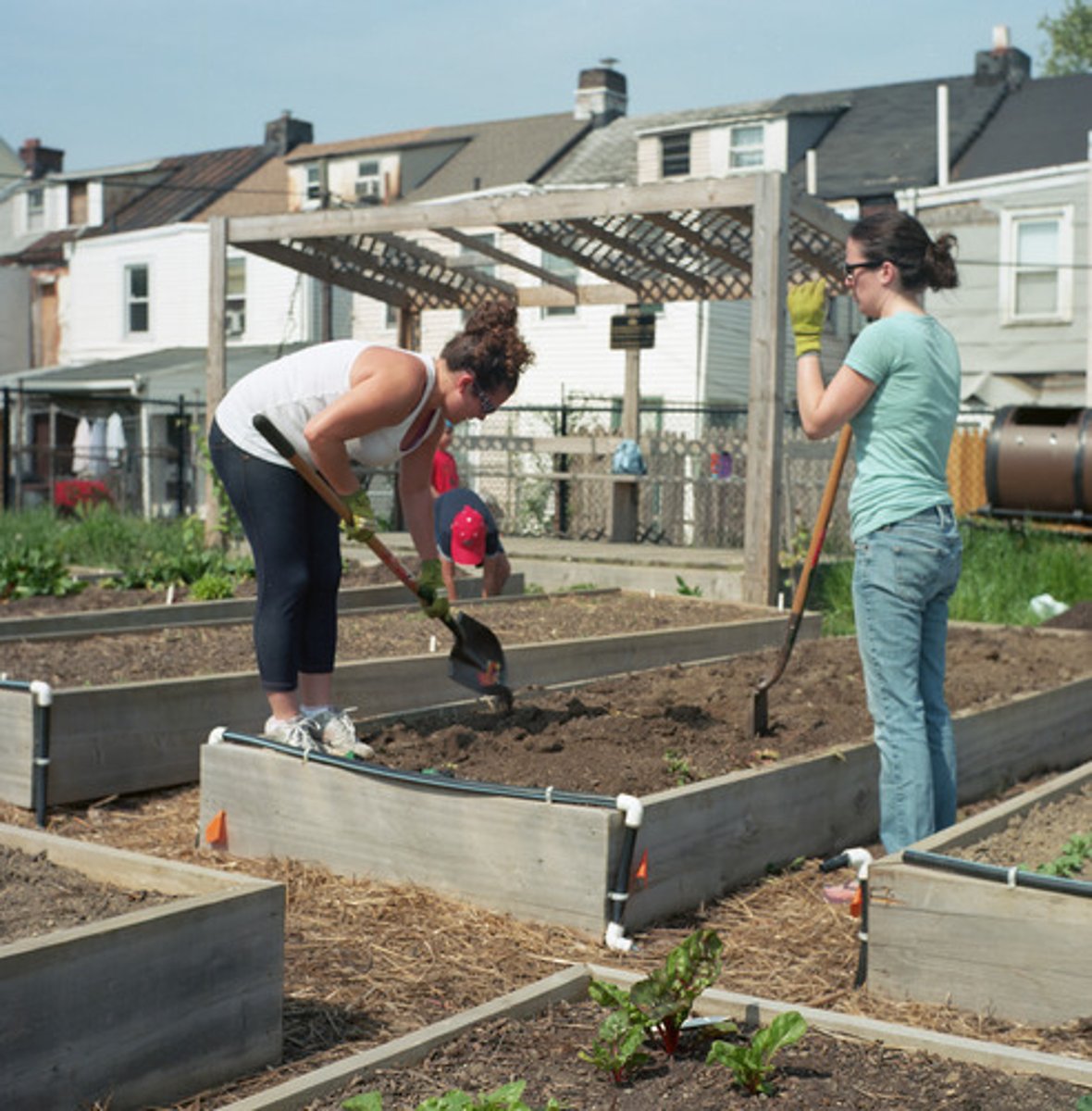

Community supported agriculture
direct relationship between a farmer and the local community through a subscription programme. citizens order food directly from the farmer.

Farmers markets
where farmers sell fresh food directly to consumers.

Organic farming
growing food without synthetic chemicals or pesticides.
Slow food movement
people's resistance to the fast food industry's mass production of unhealthy genetically modified food.
Fair trade certificate
a label showing farmers got fair pay and safe working conditions.

Locavore
a person who eats mostly food grown locally.
Food deserts
area where people have little access to fresh, healthy food.
Food insecurity
not having enough food.
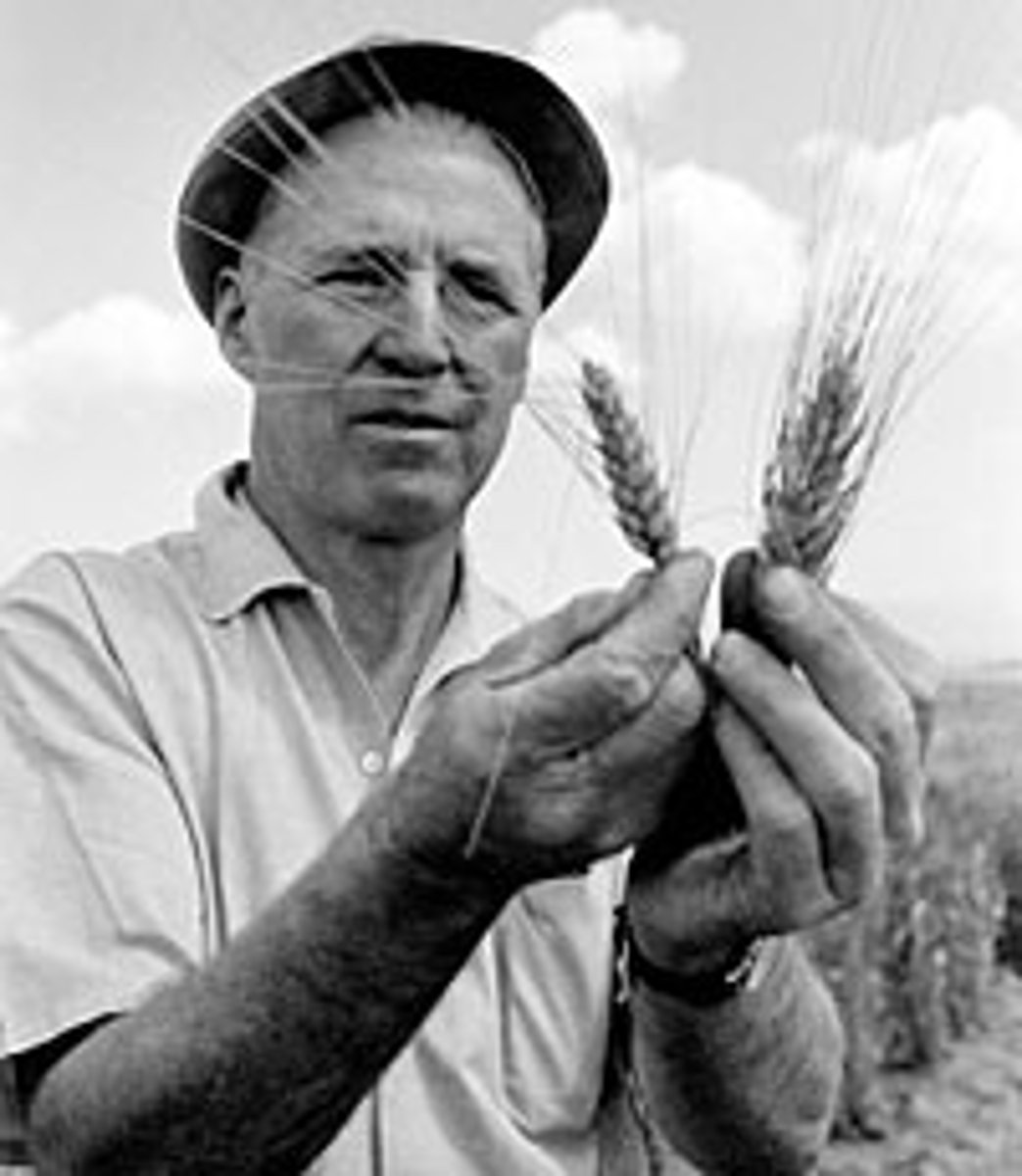
Norman Borlaug
scientist known as "the father of the green revolution" for creating high yield crops.

Desertification
when fertile land becomes desert as a result of human activities and climatic changes.
Shifting cultivation/slash and burn/swidden
farming method where land is cleared by cutting and burning plants, farmed for a few years, then left to regrow.
Governmeny subsidies
financial incentive or payment given by the government to support a specific industry, company, or individual.
Vertical integration
one company controls multiple steps of producing and selling a product.
Horizontal integration
one company buys or merges with other companies that do the same thing.