States of Matter
5.0(3)Studied by 77 people
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:46 AM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
Solid
Has a fixed shape and volume
Cannot be compressed
Tends to have high densities and do not flow
Cannot be compressed
Tends to have high densities and do not flow
2
New cards
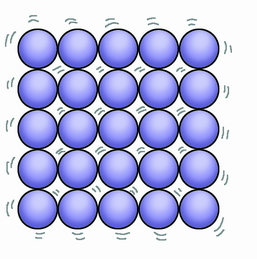
Solid particle arrangement
Close together held by strong forces of attraction
Regular lattice arrangement
Vibrate around a fixed point
Regular lattice arrangement
Vibrate around a fixed point
3
New cards
Liquid
Has a fixed volume
Takes the shape of the bottom of the container
Difficult to compress
Flows easily
Tends to have lower densities than solids
Takes the shape of the bottom of the container
Difficult to compress
Flows easily
Tends to have lower densities than solids
4
New cards
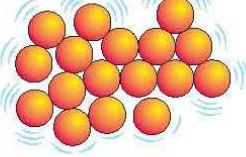
Liquid particle arrangement
Close together (very little separation)
Disordered (random arrangement)
Moves randomly, "sliding" over each other
Disordered (random arrangement)
Moves randomly, "sliding" over each other
5
New cards
Gas
Takes the shape and volume of the container
Can be compressed
Flows easily
Has the lowest densities
Can be compressed
Flows easily
Has the lowest densities
6
New cards
Gas particle arrangement
Far apart
Arranged randomly
Move randomly and rapidly
Arranged randomly
Move randomly and rapidly

7
New cards
Solid to Liquid
Melting
8
New cards
Liquid to Solid
Freezing
9
New cards
Liquid to Gas
Evaporation
10
New cards
Gas to Liquid
Condensation
11
New cards
Solid to Gas
Sublimation
12
New cards
Gas to Solid
Deposition
13
New cards
Boiling
Occurs when the liquid is heated so that the particles are moving fast enough to overcome the forces of attraction - bubbles of gaseous particles are formed throughout the liquid
14
New cards
Evaporation
In a liquid, a few of the faster particles, near the surface of the liquid, will have enough energy to overcome the forces of attraction and form a gas
15
New cards
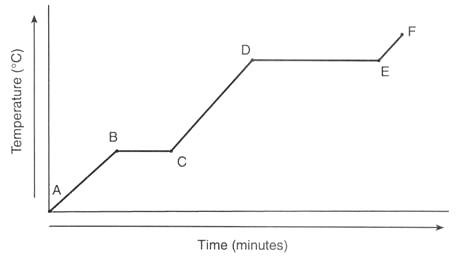
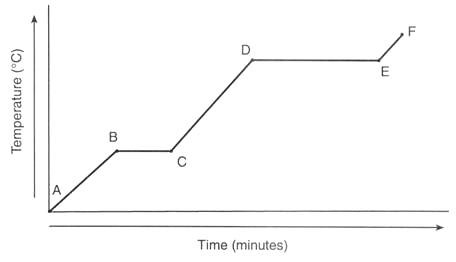
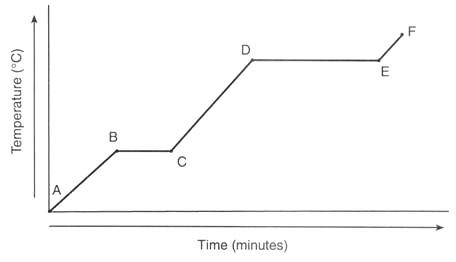
A to B heating curve
Water is solid
Temperature increases
Particles are vibrating faster
Temperature increases
Particles are vibrating faster
16
New cards
B to C heating curve
Melting
Temperature stays the same
Particles are overcoming the forces of attraction
Temperature stays the same
Particles are overcoming the forces of attraction
17
New cards
C to D heating curve
Liquid
Temperature is increasing
Particles are moving with more kinetic energy
Temperature is increasing
Particles are moving with more kinetic energy
18
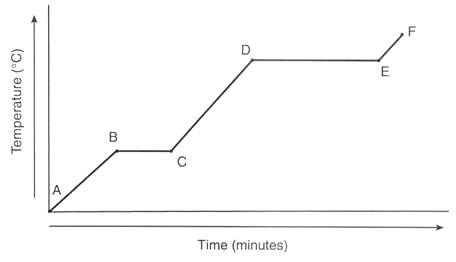
New cards
D to E heating curve
Change of state - boiling or evaporating
Liquid to gas
Temperature stays the same
Particles are overcoming the forces of attraction
Liquid to gas
Temperature stays the same
Particles are overcoming the forces of attraction
19
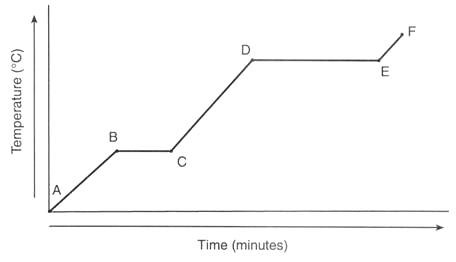
New cards
E to F heating curve
Gas
Temperature increases
Particles are gaining more kinetic energy
Temperature increases
Particles are gaining more kinetic energy
20
New cards
The heat put into the system is used to either:
Increase the temperature
Change the state
Change the state
21
New cards
Increasing temperature in heating curve
Substance remains in the same state
22
New cards
Changing state in heating curve
Substance remains at the same temperature
Heat energy is used to overcome the forces that hold the molecules together (N.B. the molecules remain the same structure - their spacing changes)
Heat energy is used to overcome the forces that hold the molecules together (N.B. the molecules remain the same structure - their spacing changes)
23
New cards
Diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until a uniform mixture is produced
24
New cards
What is the kinetic theory of matter?
Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms and molecules) that are in constant motion
25
New cards
High temperature and diffusion
The higher the temperature, the faster the particles will move
26
New cards
Diffusion in states of matter
Faster in a gas than in a liquid
The particles diffusing will collide with fewer particles in a gas than a liquid
The particles diffusing will collide with fewer particles in a gas than a liquid
27
New cards
HCl and NH3 demonstration
The white smoke ring forms closer to the HCl side because HCL is heavier than NH3 and so moves slower down the glass tube
28
New cards
Element
Made up of only one type of atom
29
New cards
Compound
Two or more elements chemically combined / bonded
30
New cards
Mixtures
Two or more different atoms or molecules not chemically bonded together
31
New cards
Atom
The smallest particle
32
New cards
Molecule
Two or more atoms (either the same element or different element) chemically bonded together