8.1 acids and bases
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what’s an arrhenius acid
a substance that produces H+ protons when dissolved in water
what’s an arrhenius base
a substance that produces OH- ions when dissolved in water
what is a bronsted-lowry acid
a proton donor
what is a bronsted-lowry base
a proton acceptor
what is formed when HCL donates a proton to water
H3O+ + Cl-
What’s the significance of using a single arrow for HCL+H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
it’s irreversible because HCL is a strong acid
why can only one hydrogen be donated from CH3CH2OOH
only the hydrogen bonded to the electronegative oxygen can dissociate
CH3CH2COOH forms what when water is added
H3O+ + CH3CH2COO-
How does NH3 act as a bronsted-lowry base
it accepts a proton from water to form NH4+
NH3+H2O forms what
NH4+ + OH-
why can organic molecules with nitrogen act as bases
nitrogen has a lone pair that can accept a proton
what does amphiprotic mean
a substance that can donate or accept a proton
why is water amphiprotic
it can accept a proton to form H3O+ or donate a proton to form OH-
What’s an example of another amphiprotic substance
HCO3-
What’s a conjugate acid
the species formed after a base accepts a proton
What’s a conjugate base
the species formed after an acid donates a proton
what’s the conjugate acid in HX+Y→HY++X-
HY+
what’s the conjugate base in HX+Y→HY++X-
X-
Conjugate pairs when H2S reacts with water (H2S+H2O→H3O++HS-)
H2S/HS- and H3O+/H2S
what’s the rule about conjugate bases and acids
the conjugate base has one fewer H+ than the acid
what determines acid/base strength
the degree of dissociation in water
what makes an acid strong
when it dissociates 100% in water
name 3 common strong acids
HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
what are strong bases
metal hydroxides that dissociate completely
two examples of strong bases
NaOH and KOH
what makes an acid weak
when it partially dissociates in water
two examples of weak bases
CH3COOH and H2CO3
relationship between acid strength and conjugate base strength
strong acids have weak conjugate bases
what’s the self ionization of water
H2O+H2O<>H3O++OH-
what’s the ion product constant for water (Kw)
[H3O+][OH-]
value of Kw (constant for water) at 25 degrees Celsius
1.0×10^-14
in pure water at 25 degrees celsius what’s the molarity of [H3O+] and [OH-]
both are 1.0×10^-7 M
What happens if [H3O+] increases in the self ionization of water
[OH-] decrease to maintain kw at 1.0×10^-14
Why does adding solute not change Kw
Kw is temperature-dependent only, not concentration-dependent
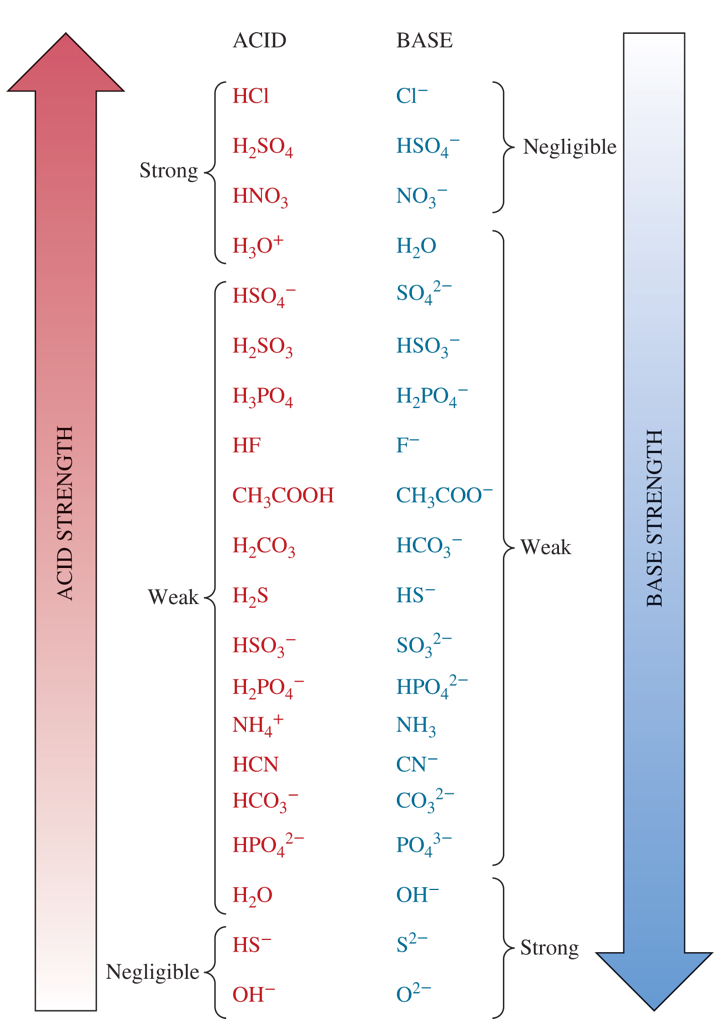
4 strongest acids from the chart
HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, H3O+
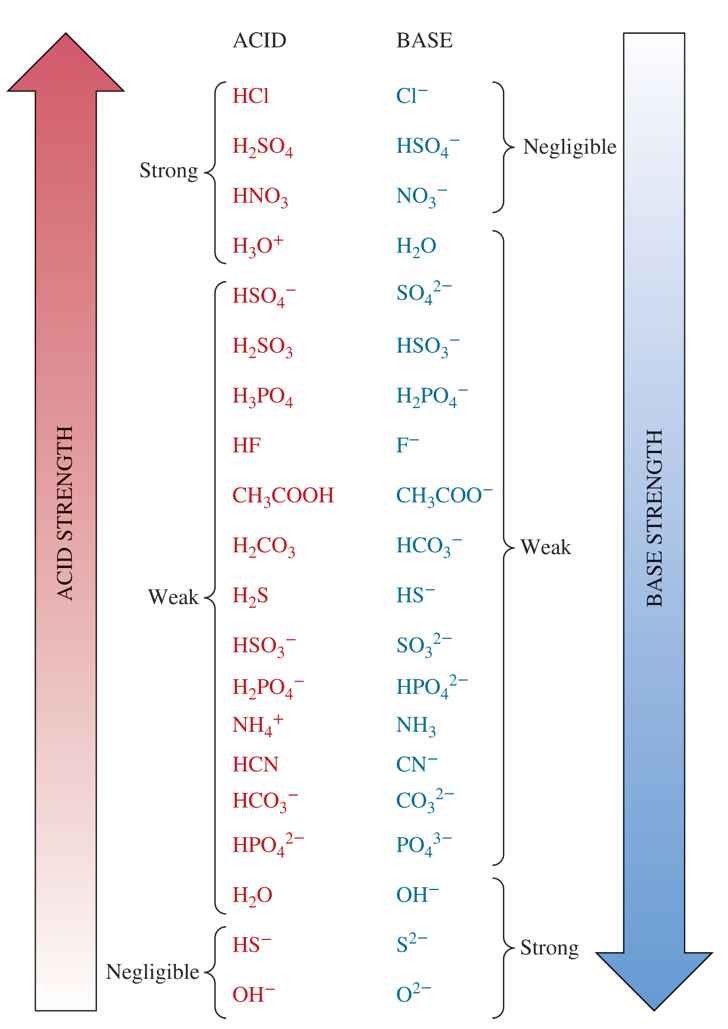
4 weak acids from the chart
HF, CH3COOH, H2CO3, H2S
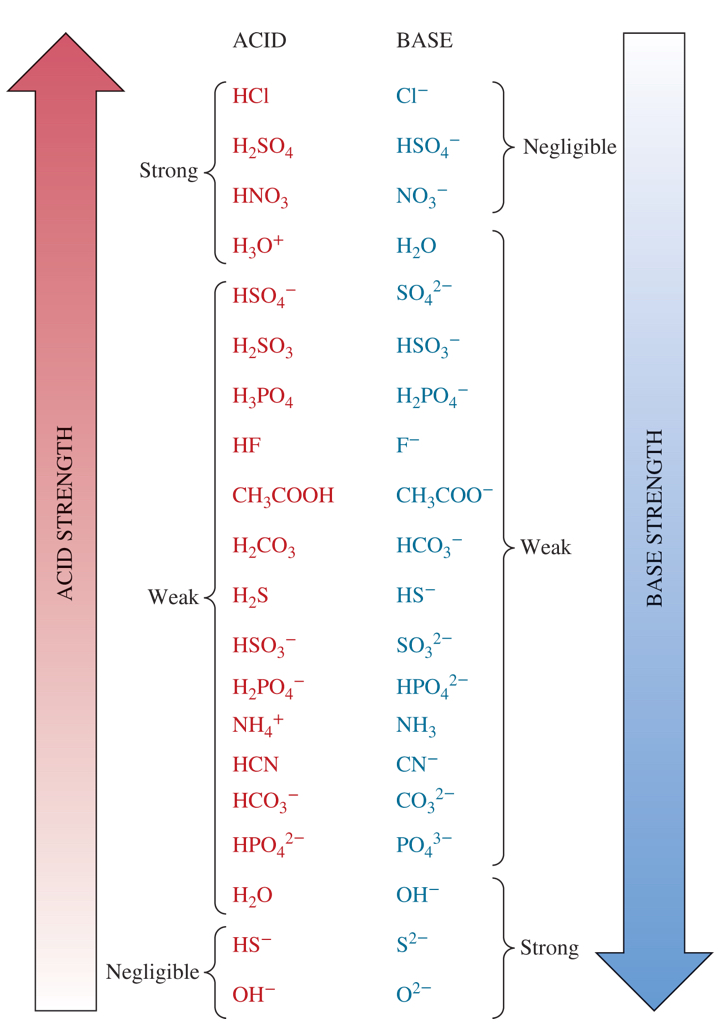
3 strongest bases from the chart
O²-, OH-, and S²-
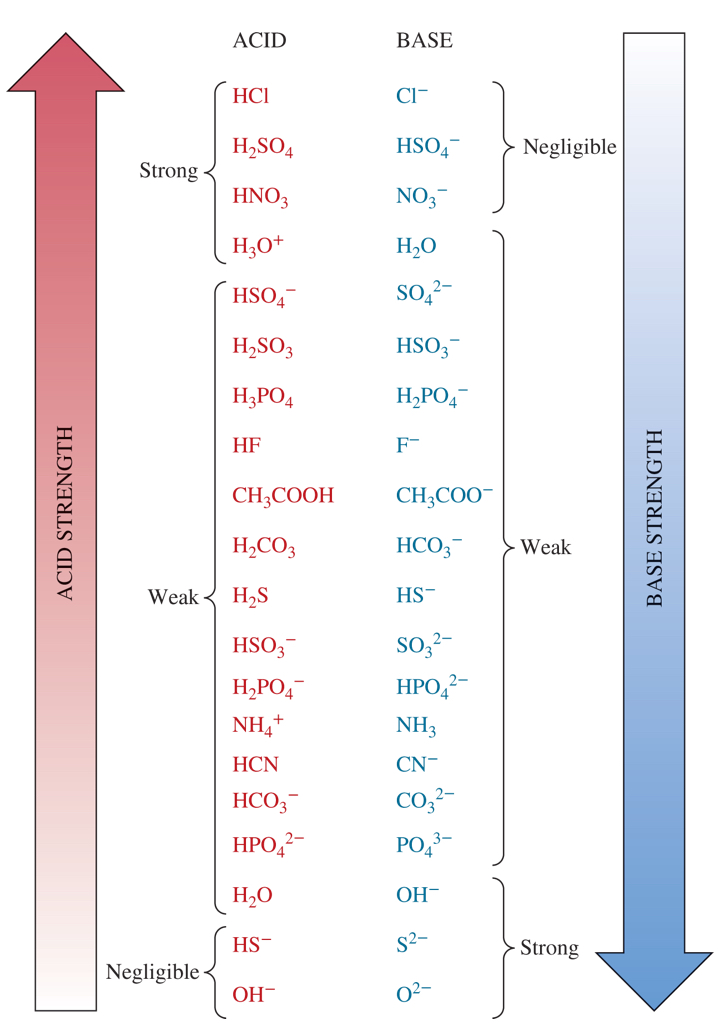
3 weakest bases from the chart
HCO3-,NH3,F-