Unit 1- The Particle Nature Of Matter
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
polyatomic ions
ions that are made of more than one atom
State symbols
solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq)
mole
the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
significant figures
All the digits that can be known precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
gas pressure
results from the force exerted by a gas per unit surface area of an object
Real Gases vs. Ideal Gases
1) real gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures.
2) real gases deviate from ideal behavior at low temperatures
3) at a given P/T, stronger IMA's will result in greater deviation from ideal behavior
4) at high P/low T, the larger the size of the molecules results in a greater deviation from ideal behavior
Combined Gas Law Equation
P1 V1 / n1 T1 = P2 V2 / n2 T2
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Pure substance
A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties
Elements
A molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions.
Compounds
two or more elements chemically combined
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture
homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
Atoms
smallest unit of matter, with a nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons and electrons orbiting the nucleus
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Ions
Atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to loss or gain of one or more electron
Avogardo's constant
6.02 x 10^23 particles
Significant Figure Rules
1. non-zeros are always significant; 2. zeros between two other sig figs are significant; 3. all final zeros after the decimal point are significant; 4. zeros used solely for spacing the decimal point are not significant unless a decimal point is present
Liquid vs aqueous
liquid is the melted physical state of a substance (as apposed to solid or gas)
aqueous means dissolved in water
Changes in states of matter
Condensation, Evaporation, Sublimation, Melting, Freezing
states of matter
solid, liquid, gas, plasma
exothermic reaction
a chemical reaction in which heat is released to the surroundings
endothermic reaction
A reaction that absorbs energy
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Endo: Heat absorbed H>0
Exo: Heat released H
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
Kelvin (K) scale
The temperature scale that assigns 0 K to the coldest temperature possible, absolute zero (-273 C), the temperature at which molecular motion stops. The size of the kelvin is identical to that of the Celsius degree.
Celcius to Kelvin
K=C+273
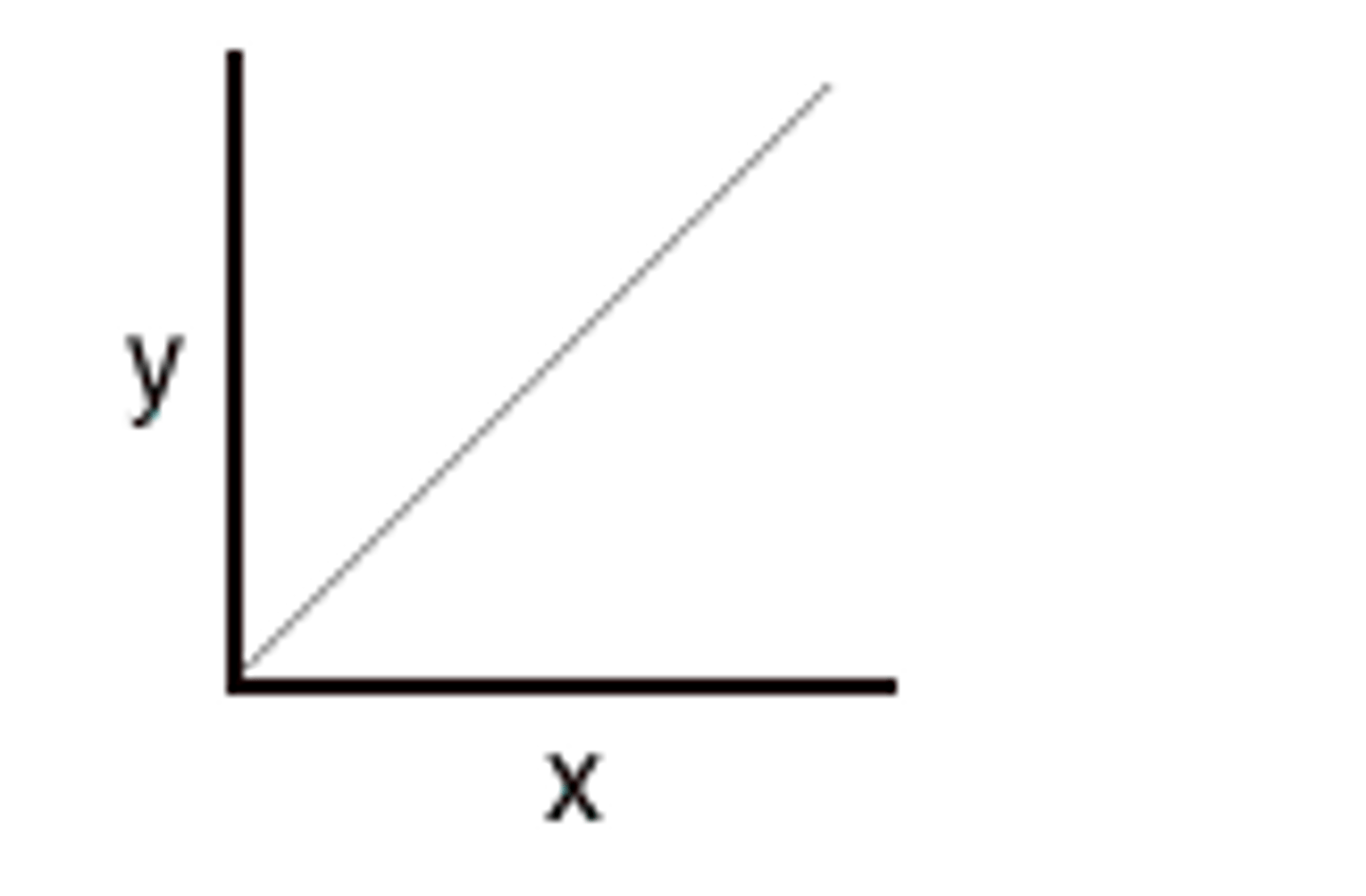
directly proportional relationship
as one amount increases, another amount increases at the same rate. (when x doubles, y doubles)
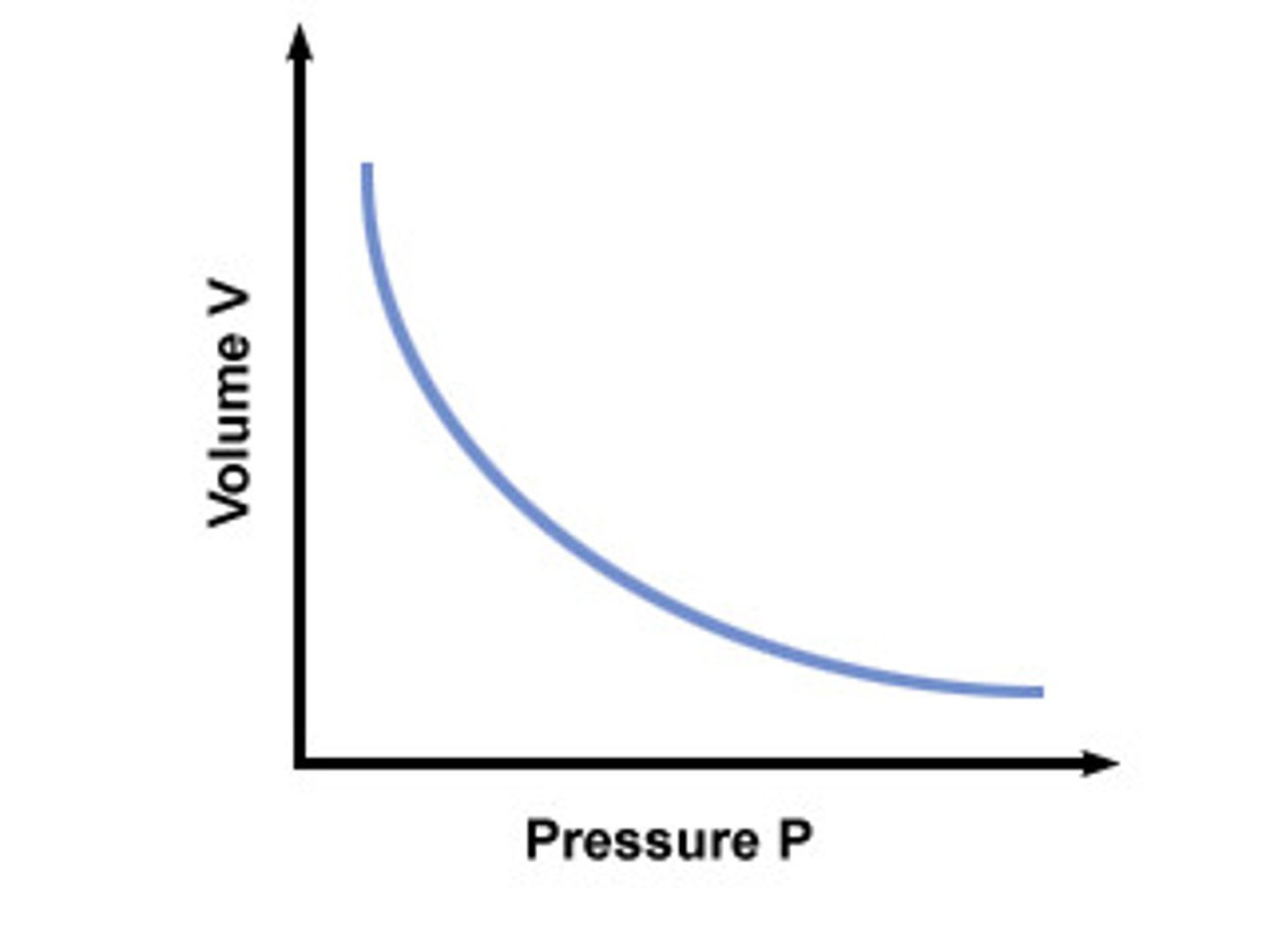
Inversely proportional relationship
a change in one quantity causes a change by the same factor, in the opposite direction, of another quantity. (when x doubles, y halves)
Assumptions of Ideal Gases
1. no interaction between gas molecules
2. collisions of gaseous molecules are perfectly elastic
3. gas particles move in continuous, rapid, random motion
4. no forces of attraction between gas particles
5. temperature of gases depend on average kinetic energy
pressure
the amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
kilopascals to pascals
x1000
Convert between the units of meters cubed, (m3) decimeters cubed (dm3), and centimeters cubed (dm3)
1 cubic metre (m^3)= 1000 cubic decimetre (dm3)
1 cubic metre(m^3)= 1,000,000 cubic centimetre (dm3)
Mole formula
moles = mass/molar mass
Density
mass/volume
empirical formula
a formula with the lowest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound
Avogadro's Law
V1/n1 = V2/n2
Molar mass of a gas
M= mRT/PV