DNA to protein
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
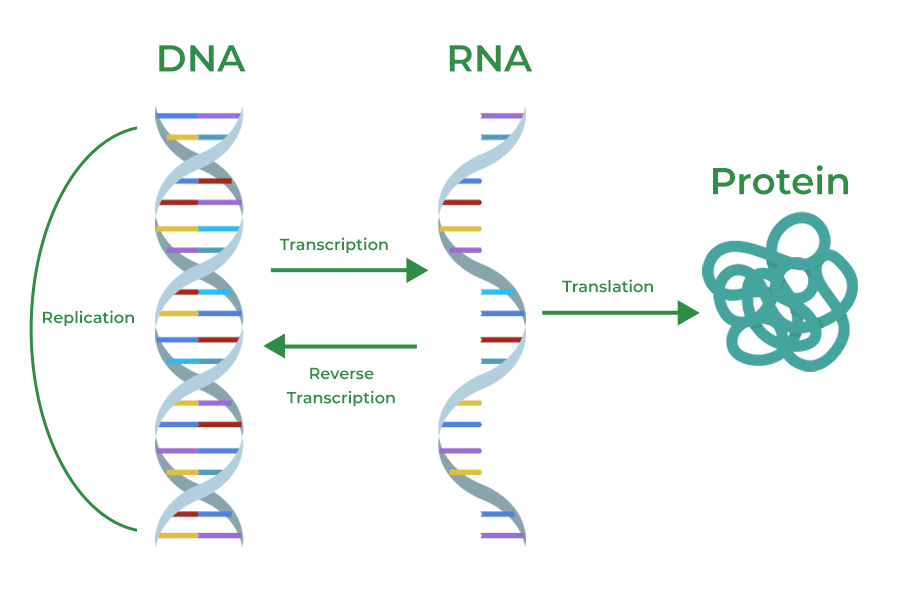
Central dogma
→ describes the genetic flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins
how genetic instructions stored in DNA are used to build proteins
Ensures preservation and accuracy of info transferred
Protein production = costly in energy, and the 3D structure is unsuitable template
Transcription
→ transfer of genetic information from DNA to mRNA
3 key steps: initiation, elongation and termination
catalysed by RNA polymerase
eukaryotes have 3 different RNA polymerases
Prokaryotes = only 1 RNA polymerase
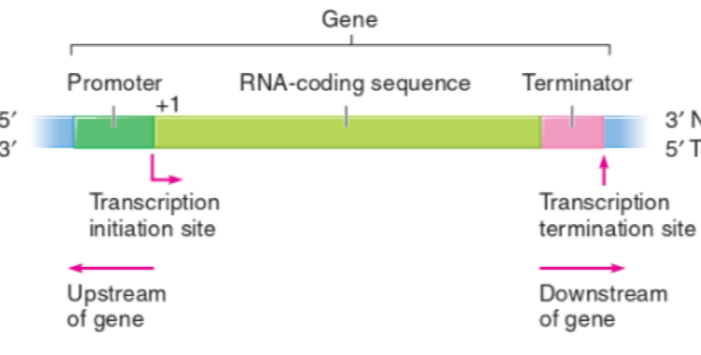
Location of points along a gene for transcription
Promoter = upstream of sequence
transcription initiation site
Terminator = downstream of gene
termination site for transcription
RNA polymerase types
RNA polymerase 1 = rRNA
2 = mRNA and some reg.ncRNA
3 = tRNA, rRNA and some reg.ncRNA
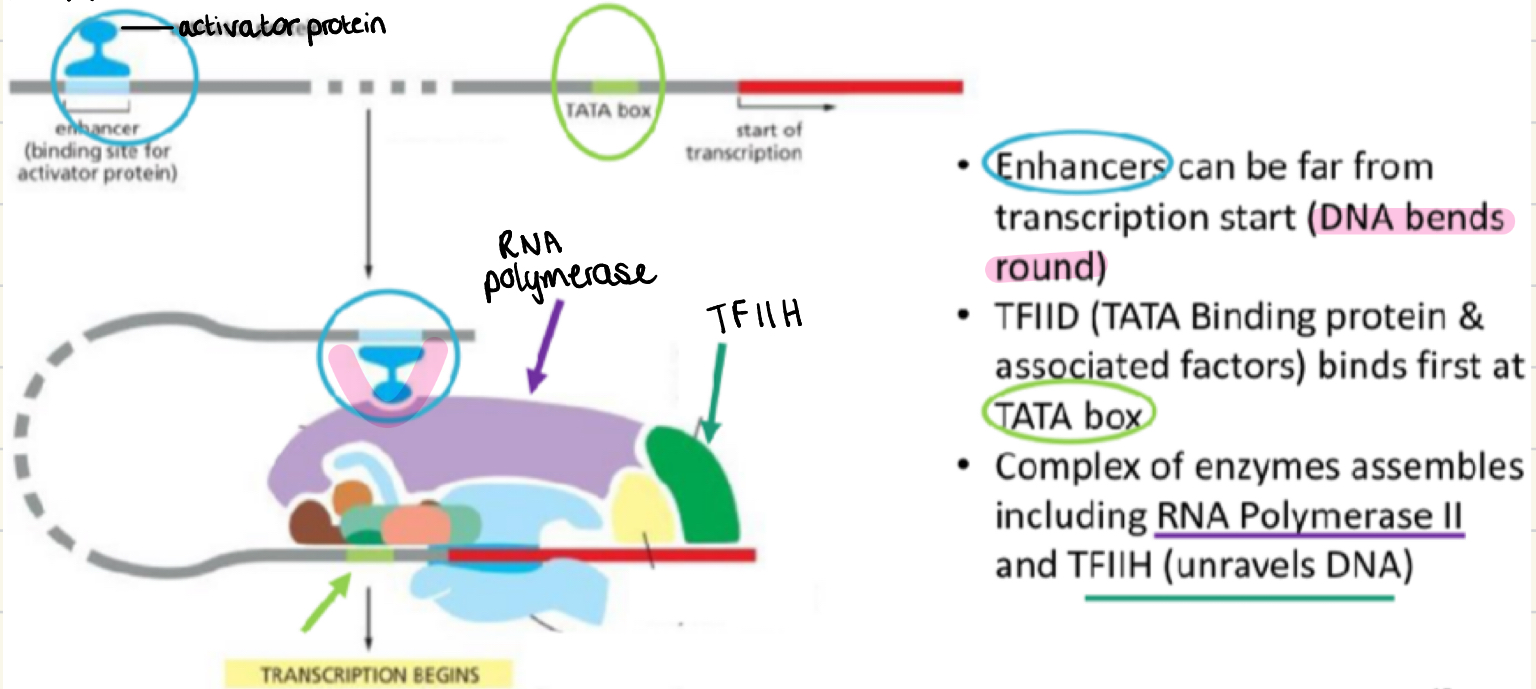
Transcription initiation eukaryotes
enhancers can be far from transcription start - DNA bends round)
TFIID (TATA binding protein and factors) binds first at the TATA box
Complex of enzymes assembles including RNA polymerases Prokaryotes 2, and TFIIH (unravels DNA)
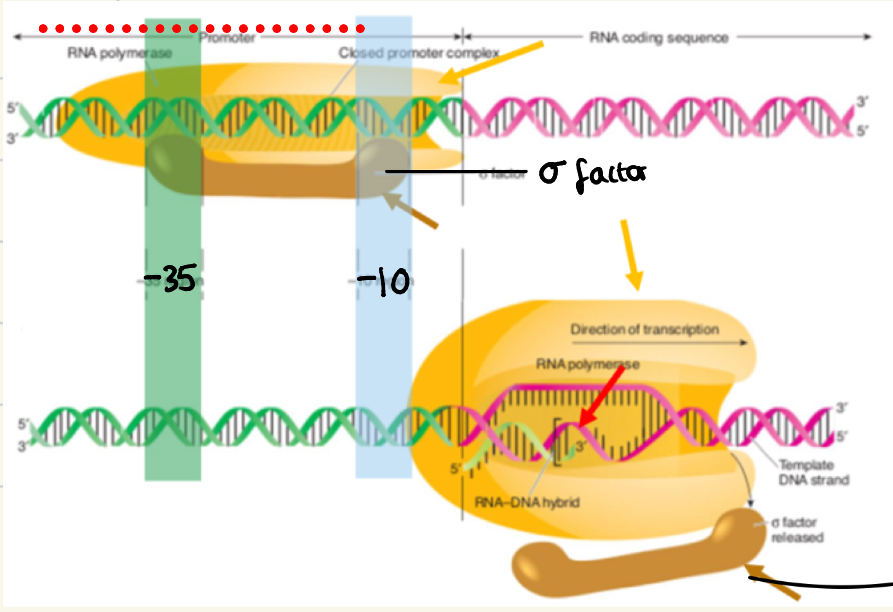
Transcription initiation prokaryotes
sigma (o) factor binds at the -35 and -10 promoter regions
Allows RNA polymerase to bind, then change conformation (opens)
DNA strand is opened, DNA-RNA hybrid forms and (o) factors dissociates
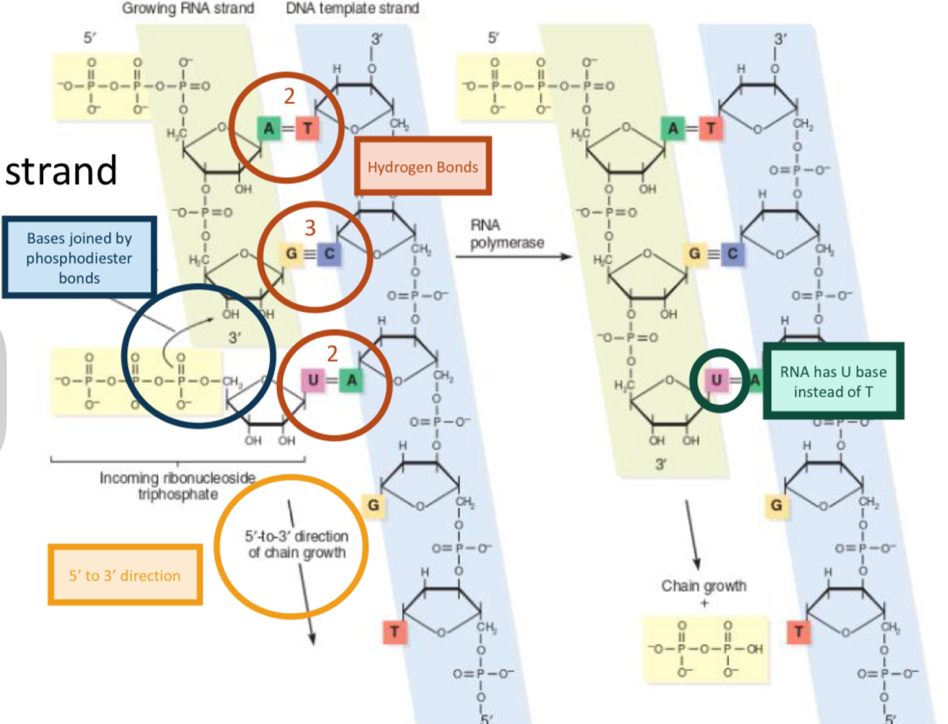
Elongation of RNA strand
Growth from 5’ to 3’ end
hydrogen bonds form between bases
Bases joined by phosphodiester bonds
RNA has U instead of T, so Adenine binds to U
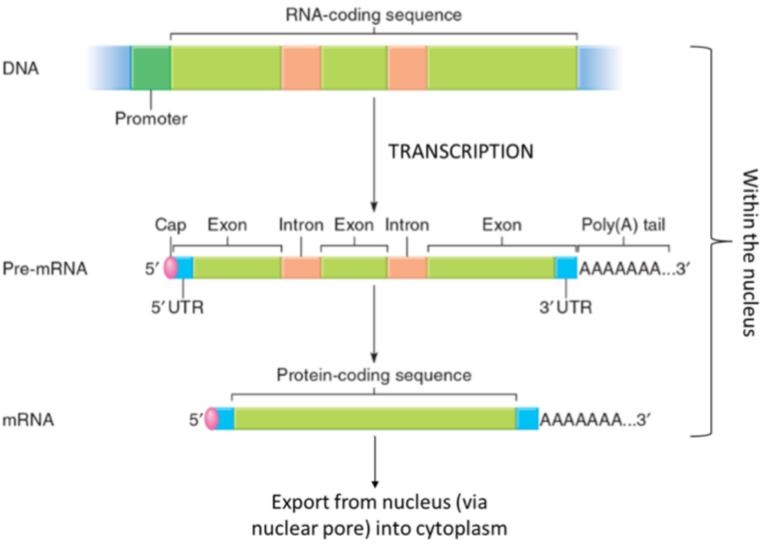
MRNA processing in eukaryotes
eukaryotic termination is not fully understood
Conserved sequence that recruits cleavage factors, dissociates on its own
(Pre-)mRNA transcript is altered before leaving the nucleus
introns spliced out
5’ cap added
Poly-A tail
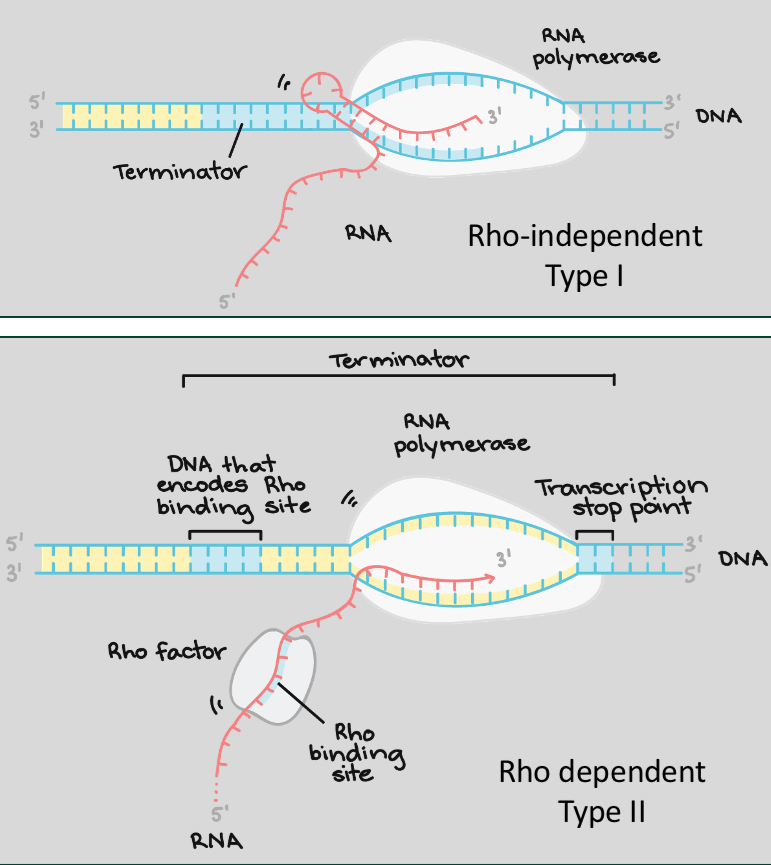
Transcription termination prokaryotes
2 mechanisms of termination:
Formation of hair pin, Rho independent
Rho factor
both prise open the transcription complex, terminating the process
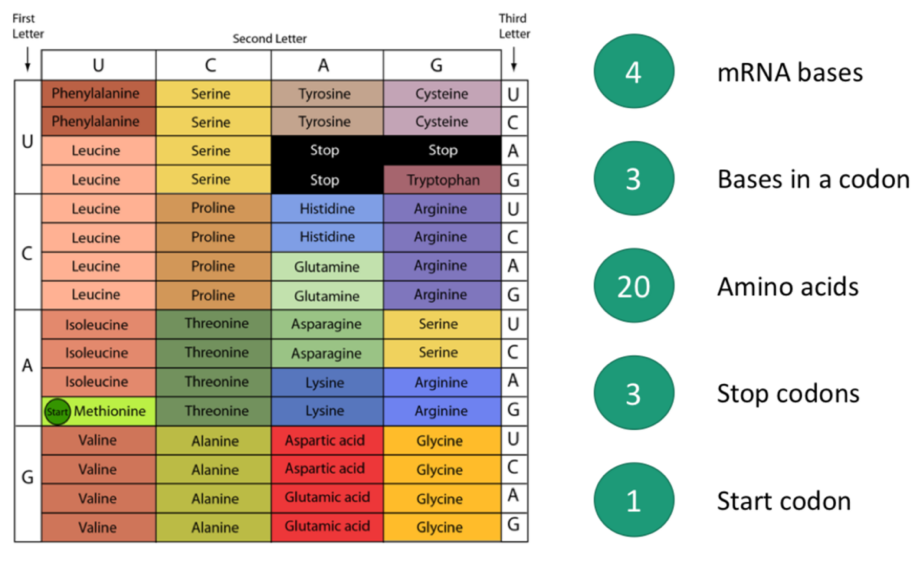
How many codons are stop/start etc.
3 bases per codon
20 amino acids
3 stop codons
1 start codon (methionine AUG)
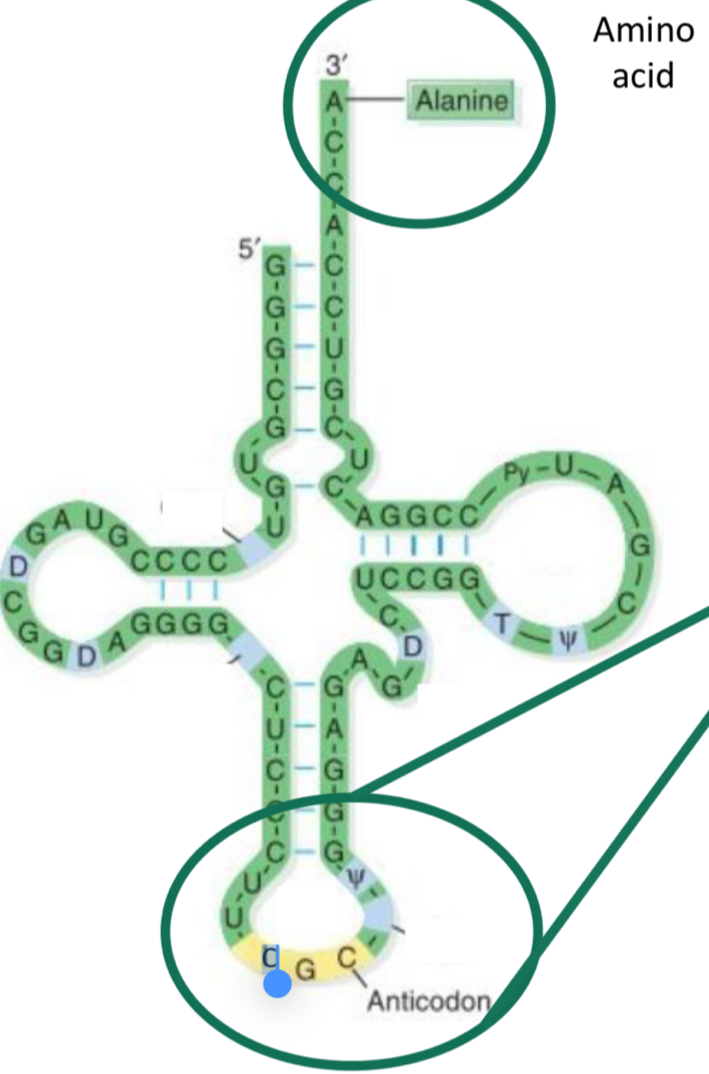
TRNA molecule
each has an anticodon which is complementary to the codon on mRNA
Has an amino acid attached when it binds
Some flexibility in 3rd nucleotide in a codon = base wobble (allows cell not to have all the tRNAs available)
Cross shape
What so the reading frame
polypeptide only reads between the start and stop codons
In groups of 3 = corresponding AA
Mutations can shift the reading frame
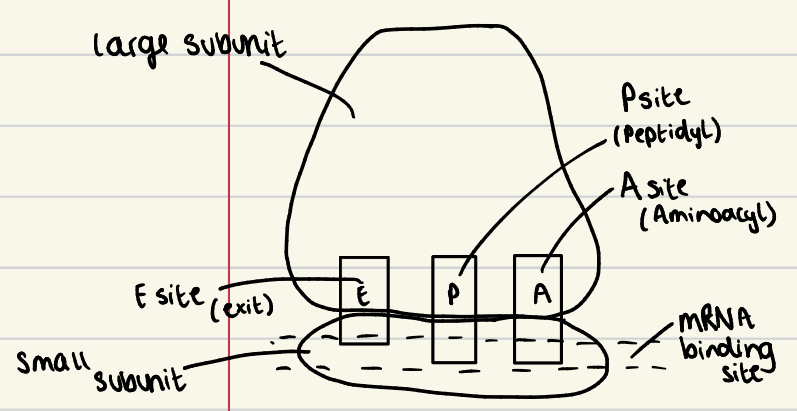
Ribosome structure
large and small subunit
E, P and A sites (in that order)
E = exit
P = peptidyl
A = aminoacyl
Small subunit contains the mRNA binding site/area
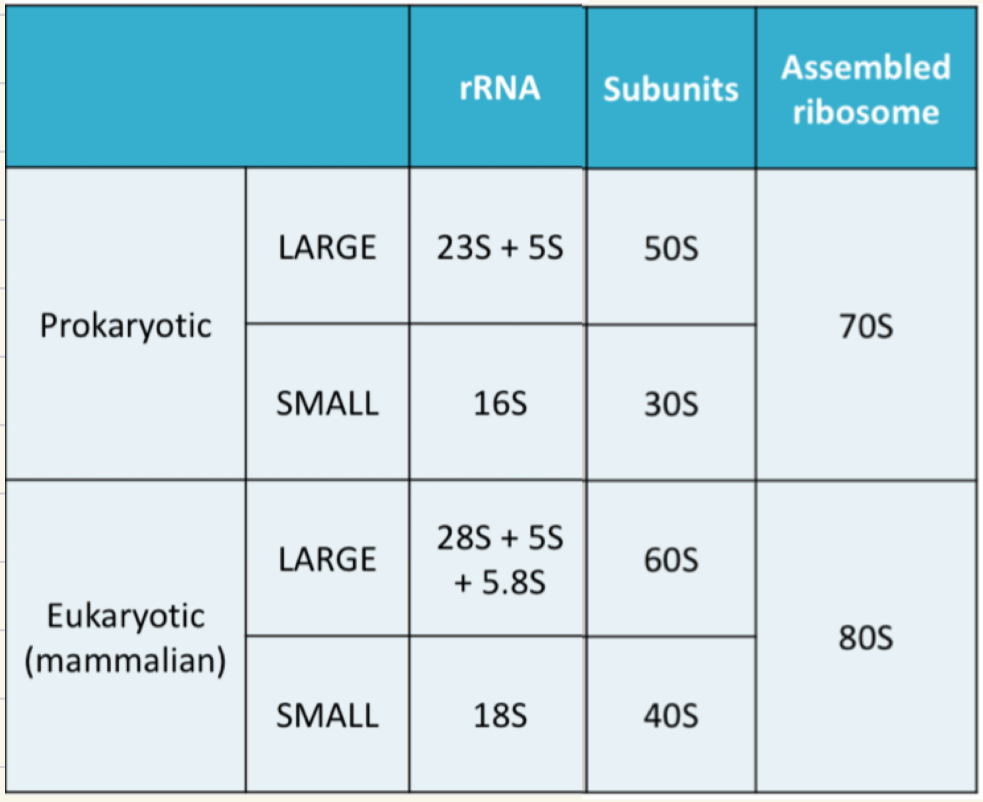
Ribosome measurements in pro/eukaryotes
Ribosomes are made of proteins and rRNA
subunit differences can be utilised in drug design.
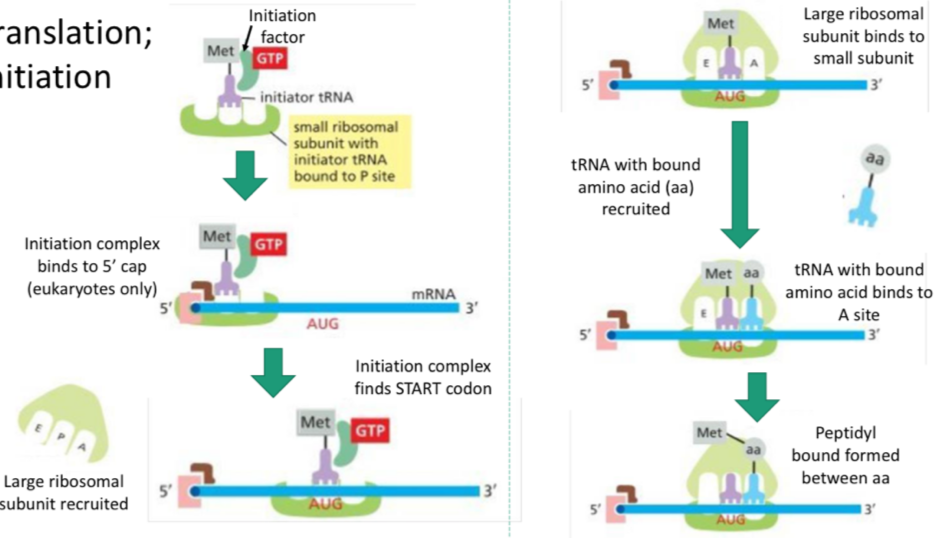
Translation: initiation
Initiation factor (protein) and a tRNA with the start codon and an AA (methionine) arrives, the small subunit binds the tRNA to the P site.
Initiation complex binds to 5’ cap (eukaryotes)
Large subunit recruited, initiation complex finds start codon
Large subunit binds to small, and another tRNA recruited with the next anticodon
Second tRNA binds to A site and peptidyl bond forms between the AAs
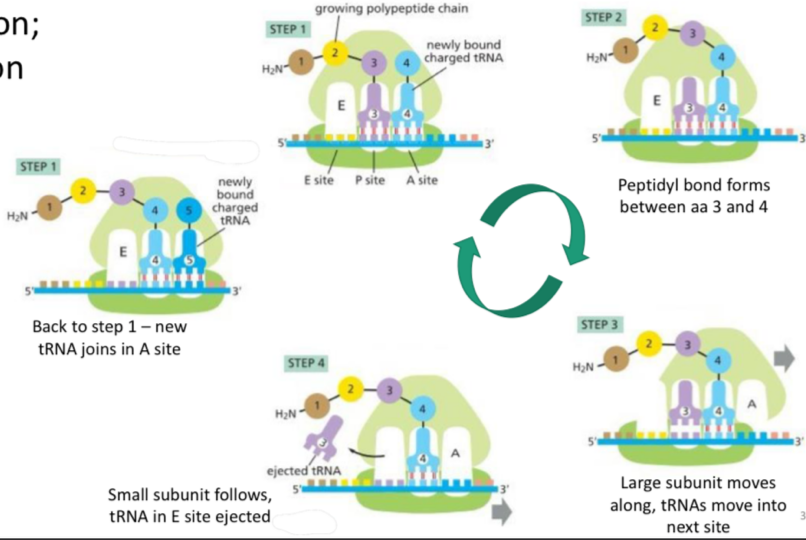
Translation: elongation
A new tRNA joins the A site, peptidyl bonds keep forming
Peptidyl bond forms between AA 3 and 4
Large subunit moves along, so 3 is in E site and 4 is in P site
Small subunit follows, tRNA in E site is ejected
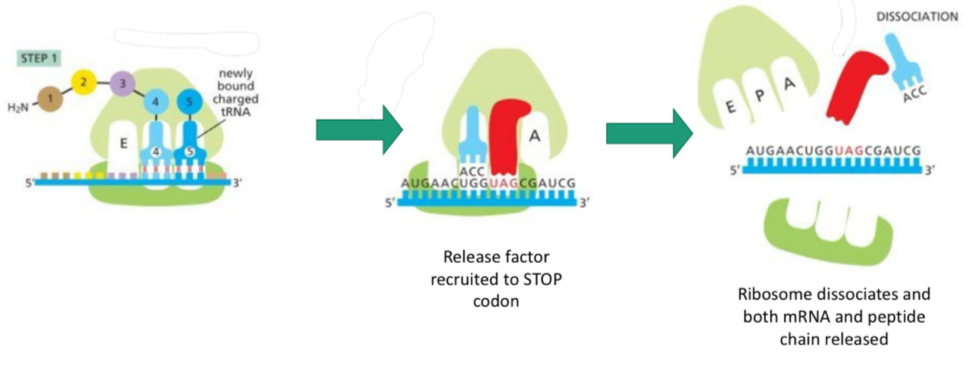
Translation: termination
Another tRNA binds, forms a bond etc
Release factor recruited as STOP codon is read
Ribosome dissociates ad both mRNA and peptide chain released