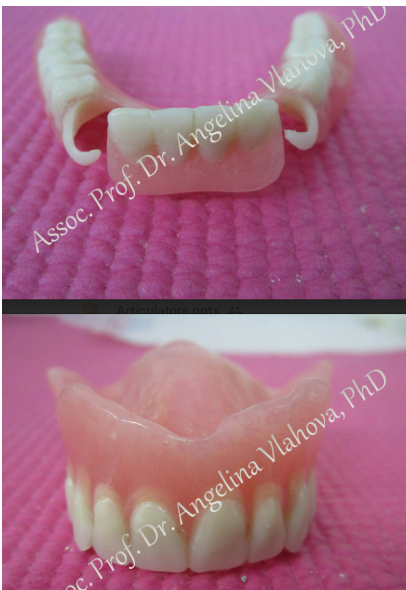
4.4 artifiical teeth set-up etc
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What does the occlusion rim provide?
guideline (midline, high lip line, canine guidnace)
proper placement of occlusal plane
proper lip support
correct jaw relationship
what are factors affecting setting of upper anterior teeth?
alveolar ridge resorption
esthetics
phonetics
what is alveolar ridge resorption?
In anterior maxilla it occurs upwards and backwards
In anterior mandible it occurs downwards and backwards (lingually)
Anterior teeth in maxillary dentures are placed forward and inferiorly
how is alveolar ridge resorption minimised/prevented in anterior teeth placed in maxillary denture?
teeth are placed forward and inferiorly
What is importance of aesthetics when setting upper anterior teeth?
lip support by teeth is important
amount of tooth showing about 1mm
What is speech (phonetics) affected by setting of upper anterior teeth?
speech affected, contour + bulk of palate affected
Central incisor - incisal edge in contact with horizontal plane
Lateral incisor - incisal edge is 1-2 mm higher than plane
Canine - its cusp is in contact with horizontal plane
what is the inclination of central incisor compared to sagittal plane and vestibularly?
long axis is parallel to sagittal plane
vestibular inclination is around 5-8 degrees
what is inclination of lateral incisors compared to sagittal plane and frontal plane?
inclination to sagittal plane is between 10-20 degrees
inclination to the frontal plane is approx 8 degrees
what is the inclination of canines compared to sagittal plane?
inclination to sagittal plane is about 7-10
there is axial rotation of crown as well
from frontal view, only mesial part of crown should be visible
what should be the only part visible of canines from frontal view?
mesial part of crown
what are the factors to remember when arranging posterior teeth?
neutral zone
position on ridge
balanced occlusion
what is neutral zone (arrangement of posterior teeth)?
potential space between lips/cheek and tongue
area where forces between them as equal, providing equilibrium
ensures denture stability
how does position on ridge affect arrangement of posterior teeth?
posterior teeth placed on ridge crest are vital for lower denture stability
Maxillary dentures, teeth may be placed outside ridge crest if needed
how is balanced occlusion important in arranging posterior teeth?
bilateral, simultaneous contact of anterior and posterior teeth in various positions, ensuring proper chewing and stability
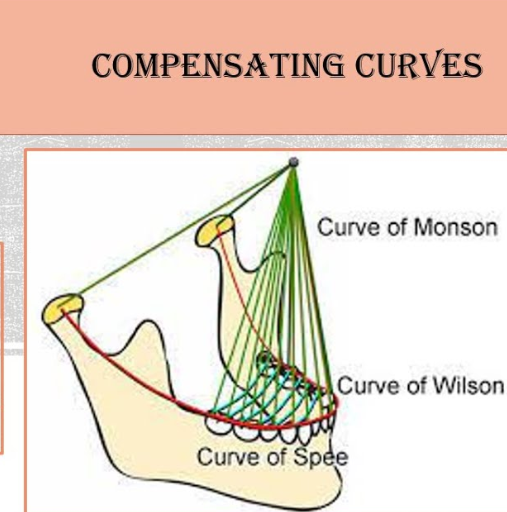
what is the compensating curve?
anteroposterior and mediolateral curving within alignment of artificial teeth used for balance occlusion development
Arc introduced in complete removable dental prostheses to counteract opening influences during mandibular excursive movements.
Necessary for balanced occlusion, involves curve of spee (posterior teeth) and curve of monson
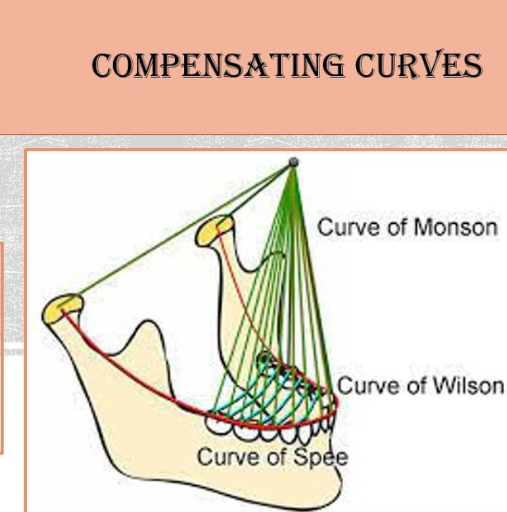
what is curve of spee?
occlusal alignment of teeth
median plane from mandibular canine cusp tip through premolar and molar buccal cusp tips to anterior border of mandibular ramus, ending at anterior portion of mandibular condyle
essential for balanced occlusion
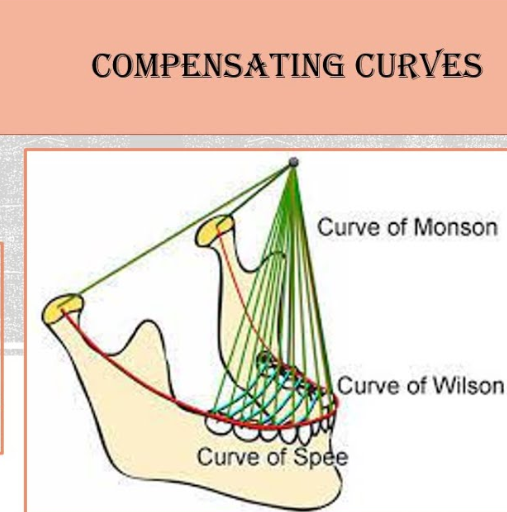
what is curve of monson?
each cusp and incisal edge conforms to a segment of an 8-inch diameter sphere, centred around region of glabella (in between eyebrows)
Crucial for balanced occlusion, aid in lateral and protrusive mandibular excursive movements
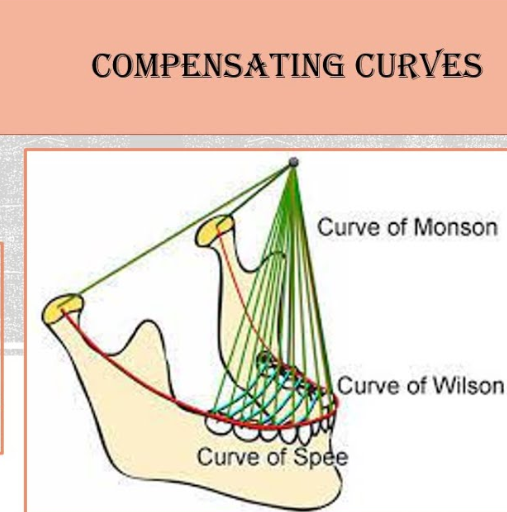
what is curve of wilson?
represents mediolateral curve in occlusion theory
Lower arch - it’s concave due to lingual inclination of right and left molars, allowing corresponding cross-aligned cusps to fit into circle’s circumference
Upper arch - it’s convex due to buccal inclination of long axes of upper teeth. Essential for spherical occlusion theory, maintaining balanced occlusion
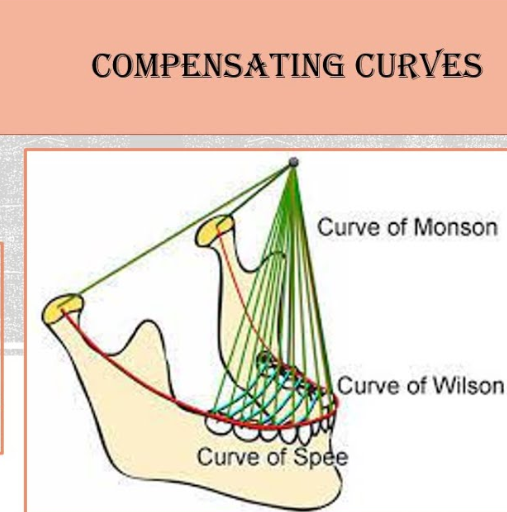
what is NEEDEDD for balanced occlusion?
anteroposterior curve of posterior teeth (curve of spee)
mediolateral curve (curve of monson)
what is the anteroposterior curve?
on middle plane
tip of lower canine and follows outer cusps of premolars and molars
continues to front border of lower jaw and ends at frontmost part of jaw joint
also known as curve of spee
what is mediolateral curve?
curve formed by alignment of teeth when viewed from front
helps ensure proper contact and distribution of forces during biting and chewing
how should maxillary posterior teeth be aligned?
make contact in two ways:
posterior teeth buccal surfaces make contact with a straight line drawn from labial surface of canine backwards
Angle between vestibular surfaces of canines and premolars and molars is 155 degrees
how is alignment of mandibular teeth done?
They are set to occlude with maxillary teeth in anteroposterior and mediolateral curves
how are upper/lower posterior teeth positioned?
buccal cusps of upper posterior teeth overlap those of lower
Palatal cusps of upper posterior teeth contact with central fossae of mandibular teeth
what are the rules for distal teeth arrangement?
1st premolar - contact with horizontal plane with vestibular cusp only
2nd premolar - contacts horizontal plane with both vestibular and lingual cusps
1st molar - contacts horizontal plane with mesiolingual cusp (mesiobuccal cusp 0.5mm, distolingual cusp 1mm, distobuccal 1.5mm over horizontal plane )
2nd molar - 1mm over horizontal plane
Lower
1st molar - mesiobuccal cusp of 1st upper molar in contact with groove between mesiobuccal and distobuccal surface of lower 1st molar
1st premolar/2nd premolar/2nd molar - vestibular cusp in contact with central groove of antagonist
steps of flasking
mix gypsum with proper water/powder ratio
fill lower part of flask, place model (make sure not to exceed edge of flask)
use soap water/isodent/other materials for isolation after hardening
Put upper part of flask and fill with gypsum
after hardening, put flask in boiling water for 5 mins
open flask and remove plasticised base plate and wax
properly isolate denture
what occurs in polymerisation?
mix acrylic resin (Polymer+monomer)
stages of polymerisation:
wet sand phase
sticky (threads) phase
plastic (working) phase
elastic (gummy) phase
put acrylic in empty space, close flask and press it
Two options for high-temperature polymerisation cycle:
long cycle - gradually heat flask in room temperature water, reach 60 degrees for 1 hour, then 100 degrees for 30 minutes, followed by slow cooling
Short cycle - boil water for 30 minutes, don’t exceed 100 degrees as monomer evaporates at 100.3 degrees
After cooling, remove denture from gypsum, clean/polish should be done to ensure smooth polished finish
what are immediate removable partial dentures?
any removable dental prosthesis fabricated for the placement immediately following removal of natural teeth
what are examples of immediate removable partial dentures?
Kemeney denture
Pelots RPD
Immediate removable partial dentures
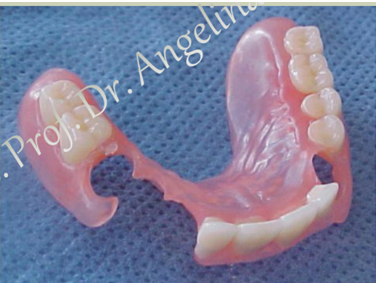
Kemeney denture
plastic toot-alveolar clasps
main indication: abutment teeth mobility
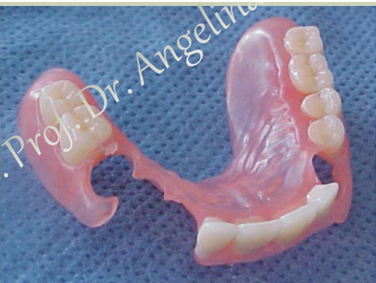
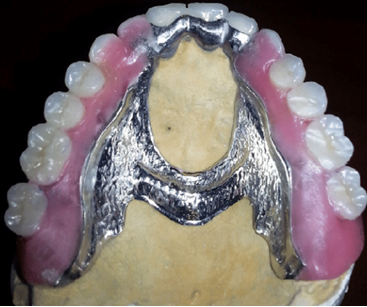
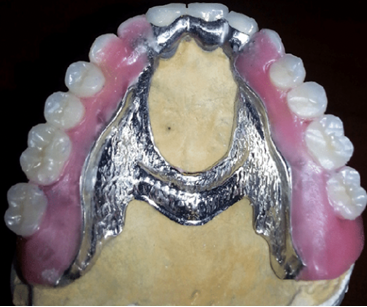
Pelots RPD
plastic alveolar clasps
mobility of teeth, retentive
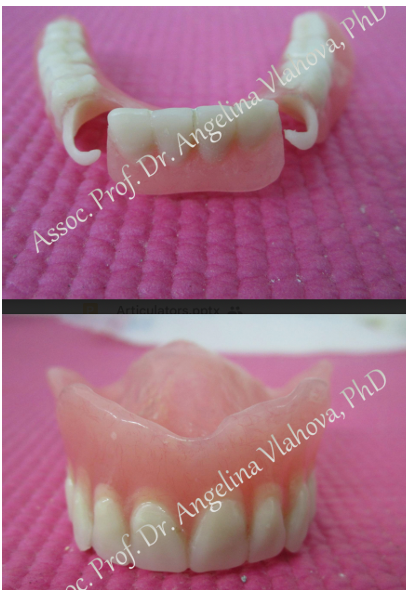
Immediate removable partial dentures?
any removable dental prosthesis fabricated for placement immediately following removal of natural tooth/teeth
Alveolar ridge in upper frontal area