pharmacolgy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Last updated 2:30 PM on 1/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Pharmacognosy
*study of the characteristics of natural drugs*
2
New cards
Pharmacodynamics
*study of the effects of the drugs on the body*
3
New cards
Pharmacokinetics
*study of the effects of the body on drugs*
4
New cards
Pharmacotherapeutics
*study of the of drugs and efficacy on treatment*
5
New cards
Prophylactic
*preventative measure*
6
New cards
Absorption
*process of converting a drug to a form the body can use*
7
New cards
Excretion
*elimination of a drug from the body*
8
New cards
Metabolism
*process of converting drug molecules into a simpler form called a metabolite*
9
New cards
Distribution
*process of transporting a drug to the site of action*
10
New cards
Generic name
*referred to as the official name*
11
New cards
Trade name
*brand or proprietary name given to a medication by the manufacturer*
12
New cards
Acupuncture
*procedure that uses needles and electrical currents to block pain*
13
New cards
What is an ampule?
S*mall sealed glass or plastic container that needs to be broken at the neck*
14
New cards
What is used to treat anaphylaxis?
*Epipen (epinephrine)*
15
New cards
Summarize the steps to reconstituting a medication:
*heck order, gather supplies, wash hands, cleans rubber stop of powder and diluent, inject air into vial of diluent, withdraw diluent, add to powder, palm roll to mix*
16
New cards
How can liquid vaginal medications be administered:
*via douche*
17
New cards
What is a salve?
*A type of ointment*
18
New cards
How long before another manufacturer can produce a drug that was originally made by another manufacturer?
20 years
19
New cards
What is the unit of measure for insulin
measured units and not mL
20
New cards
what is unique about an insulin syringe?
*syringe has no dead space*
21
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from plants
*digitoxin, codeine, quinine*
22
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from fungi or bacteria
*penicillin, cephalexin*
23
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from minerals
*potassium chloride, sodium chloride*
24
New cards
routes of injection
* Subcutaneous (under the skin)
* Intramuscular (in a muscle)
* Intravenous (in a vein)
* Intrathecal (around the spinal cord)
* Intramuscular (in a muscle)
* Intravenous (in a vein)
* Intrathecal (around the spinal cord)
25
New cards
subcutaneous route
a needle is inserted into fatty tissue just beneath the skin
26
New cards
intramuscular route
preferred to the subcutaneous route when larger volumes of a drug product are needed
\
Drugs are usually injected into the muscle of the upper arm, thigh, or buttock.
\
Because the muscles lie below the skin and fatty tissues, a longer needle is used.
\
Drugs are usually injected into the muscle of the upper arm, thigh, or buttock.
\
Because the muscles lie below the skin and fatty tissues, a longer needle is used.
27
New cards
intravenous route
a needle is inserted directly into a vein
\
inserted in a vein, usually in the forearm.
\
Intravenous administration is the best way to deliver a precise dose quickly and in a well-controlled manner throughout the body. It is also used for irritating solutions, which would cause pain and damage tissues if given by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection.
\
When given intravenously, a drug is delivered immediately to the bloodstream and tends to take effect more quickly than when given by any other route.
\
inserted in a vein, usually in the forearm.
\
Intravenous administration is the best way to deliver a precise dose quickly and in a well-controlled manner throughout the body. It is also used for irritating solutions, which would cause pain and damage tissues if given by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection.
\
When given intravenously, a drug is delivered immediately to the bloodstream and tends to take effect more quickly than when given by any other route.
28
New cards
intrathecal route
a needle is inserted between two vertebrae in the lower spine and into the space around the spinal cord. The drug is then injected into the spinal canal
29
New cards
\n Sublingual
A few drugs are placed under the tongue (taken sublingually)
30
New cards
buccal route
between the gums and teeth (buccally)
31
New cards
\n Rectal route
Many drugs that are administered orally can also be administered rectally as a suppository.
\
inserts through the rectum
\
A suppository is prescribed for people who cannot take a drug orally because they have nausea, cannot swallow, or have restrictions on eating, as is required before and after many surgical operations
\
ex. __acetaminophen__ (for fever), __diazepam__ (for seizures), and laxatives (for constipation)
\
inserts through the rectum
\
A suppository is prescribed for people who cannot take a drug orally because they have nausea, cannot swallow, or have restrictions on eating, as is required before and after many surgical operations
\
ex. __acetaminophen__ (for fever), __diazepam__ (for seizures), and laxatives (for constipation)
32
New cards
vaginal route
Some drugs may be administered vaginally to women as a solution, tablet, cream, gel, suppository, or ring.
33
New cards
ocular route
Drugs used to treat eye disorders (such as glaucoma, conjunctivitis, and injuries) can be mixed with inactive substances to make a liquid, gel, or ointment so that they can be applied to the eye.
34
New cards
otic route
Drugs used to treat ear inflammation and infection can be applied directly to the affected ears. Ear drops containing solutions or suspensions are typically applied only to the outer ear canal.
35
New cards
nasal route
If a drug is to be breathed in and absorbed through the thin mucous membrane that lines the nasal passages, it must be transformed into tiny droplets in air (atomized). Once absorbed, the drug enters the bloodstream.
36
New cards
\n Cutaneous route
Drugs applied to the skin are usually used for their local effects and thus are most commonly used to treat superficial skin disorders, such as __psoriasis__, __eczema__, skin infections (__viral__, __bacterial__, and __fungal__), __itching__, and __dry skin__
37
New cards
\n Transdermal route
Some drugs are delivered bodywide through a patch on the skin. These drugs are sometimes mixed with a chemical (such as alcohol) that enhances penetration through the skin into the bloodstream without any injection. Through a patch, the drug can be delivered slowly and continuously for many hours or days or even longer.
38
New cards
intramuscular injection sites
\-deltoid muscle of the arm
\-**Vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh**
\-**Ventrogluteal muscle of the hip**
\-**Dorsogluteal muscles of the buttocks**
\-**Vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh**
\-**Ventrogluteal muscle of the hip**
\-**Dorsogluteal muscles of the buttocks**
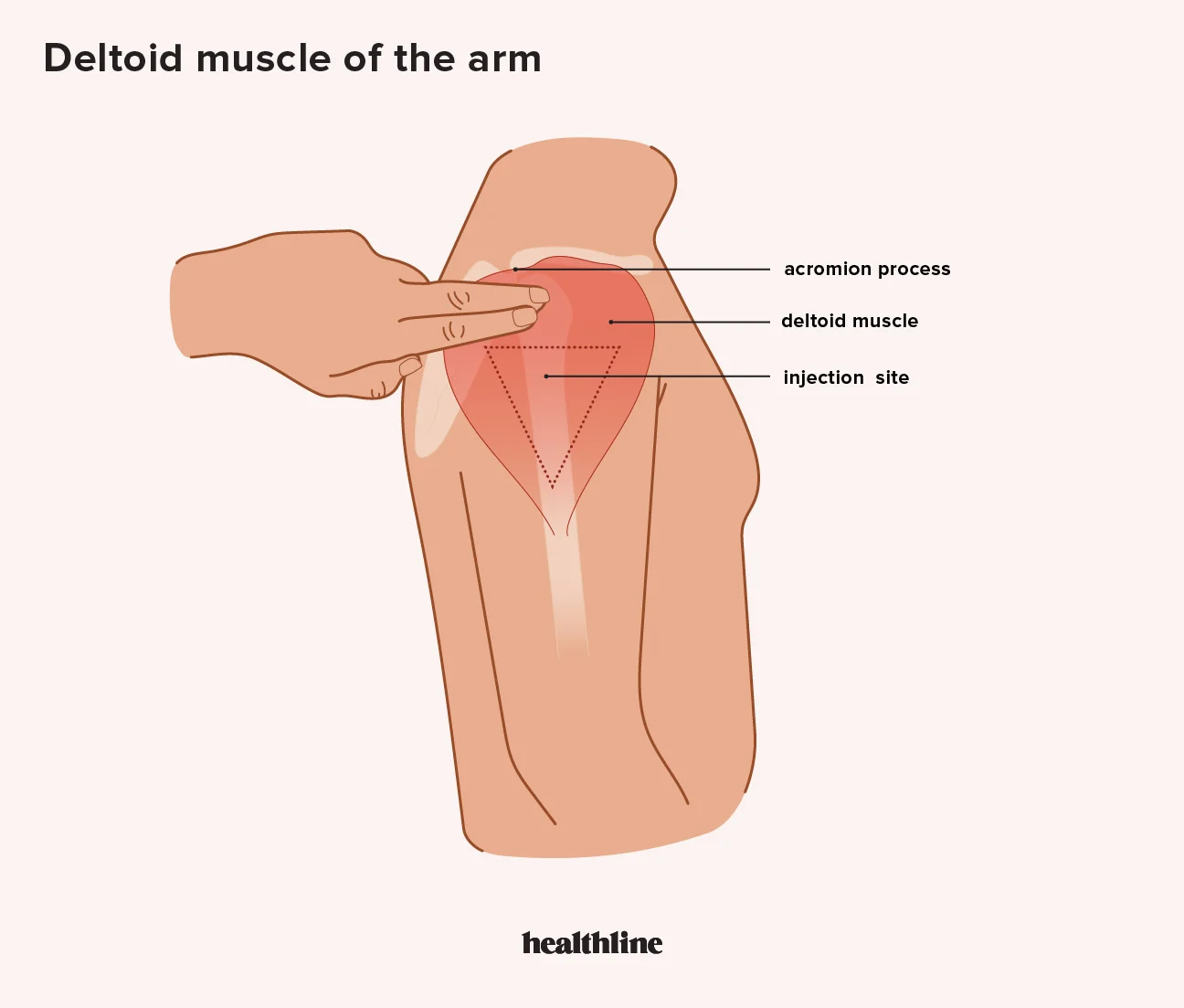
39
New cards
deltoid
To locate this site, feel for the bone (acromion process) that’s located at the top of your upper arm. The correct area to give the injection is two finger widths below the acromion process. At the bottom of the two fingers will be an upside-down triangle. Give the injection in the center of the triangle.
40
New cards
**Vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh**
Divide the upper thigh into three equal parts. Locate the middle of these three sections. The injection should go into the outer top portion of this section.
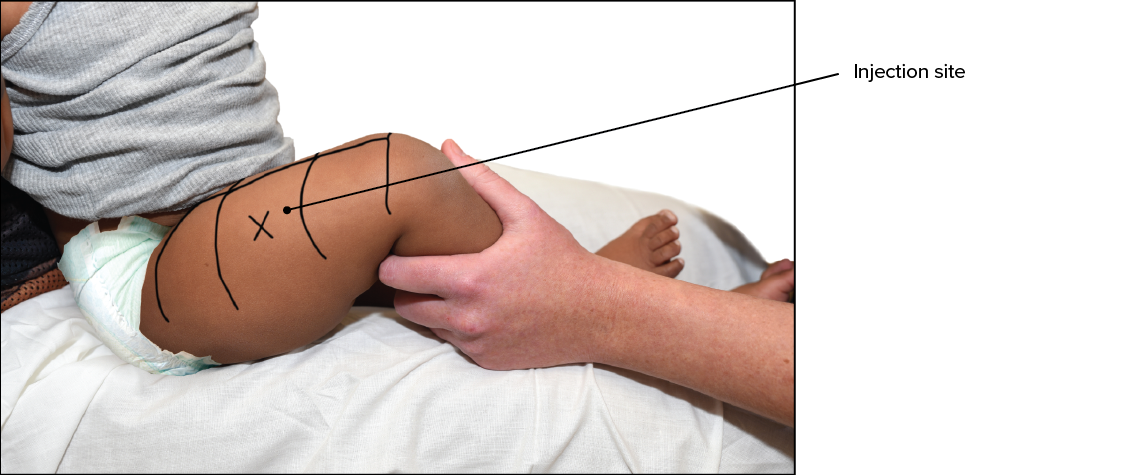
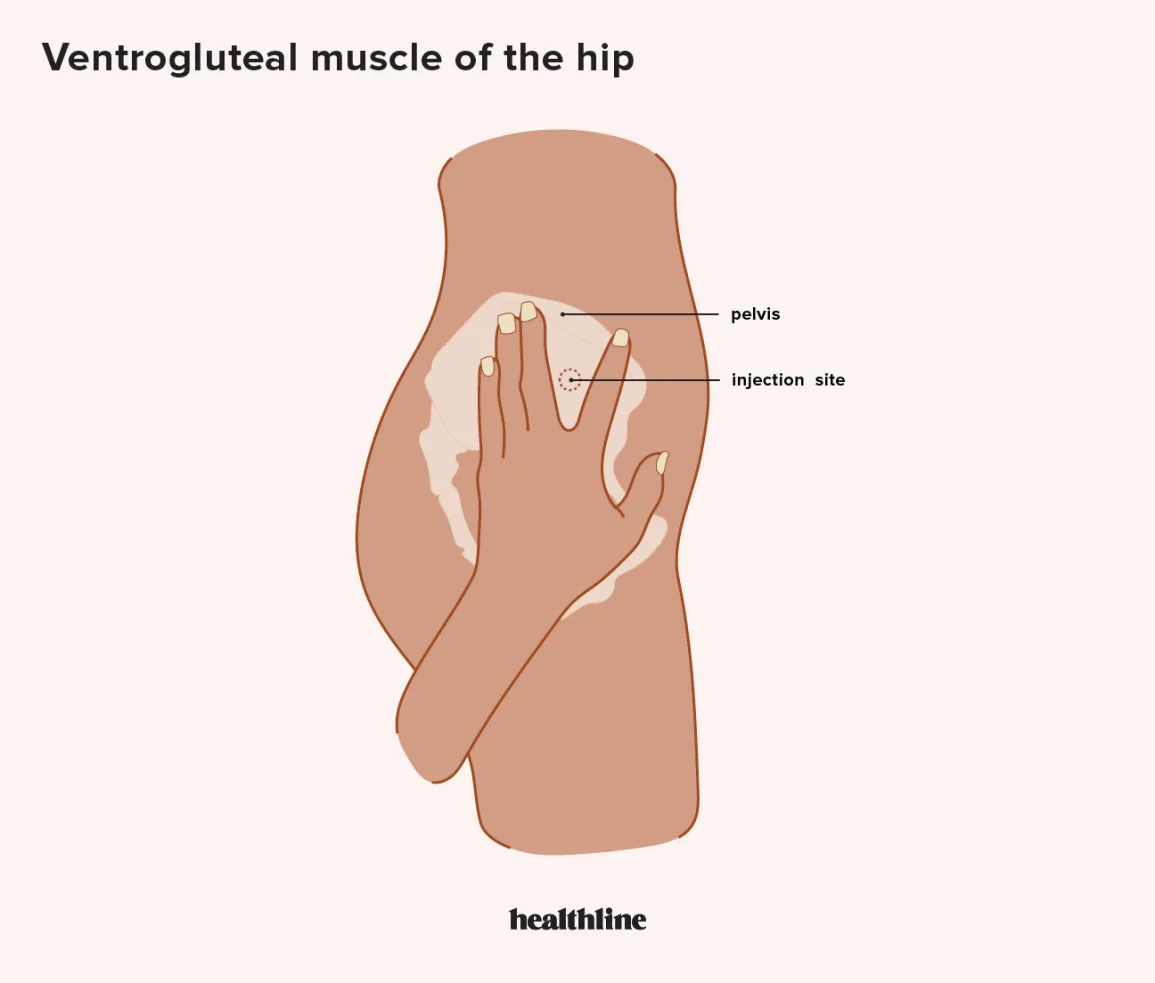
41
New cards
**Ventrogluteal muscle of the hip**
Place the heel of your hand on the hip of the person receiving the injection, with your fingers pointing toward their head. Position your fingers so your thumb points toward their groin and you feel the pelvis under your pinky finger. Spread your index and middle fingers in a slight V shape, and inject the needle into the middle of that V.
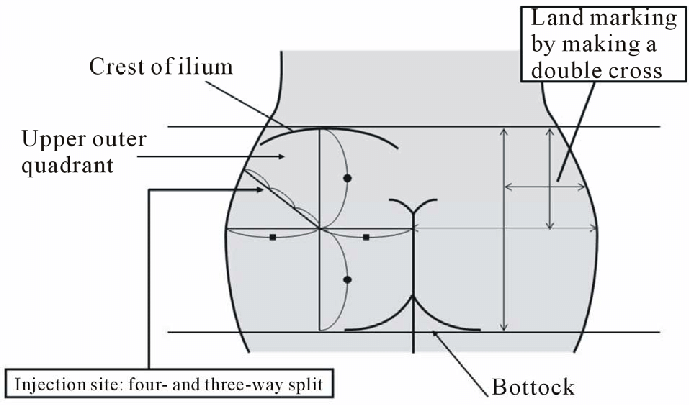
42
New cards
**Dorsogluteal muscles of the buttocks**
The first thing to understand about the dorsogluteal im site is where it is located. For a visual, you should divide the buttocks into four quadrants. To locate the site of injection you will simply find the upper and outer section of that grid. It is located high on the buttocks, near the thigh.
43
New cards
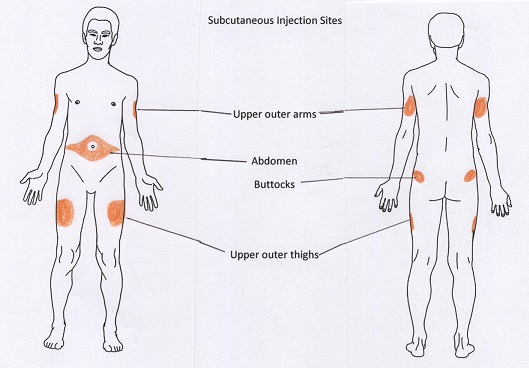
subcutaneous injection sites
* Upper arms. At least 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) below your shoulder and 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) above your elbow, on the side or back.
* Outer side of upper thighs.
* Belly area. Below your ribs and above your hip bones, at least 2 inches (5 centimeters) away from your belly button.
\-use for insulin
* Outer side of upper thighs.
* Belly area. Below your ribs and above your hip bones, at least 2 inches (5 centimeters) away from your belly button.
\-use for insulin
44
New cards
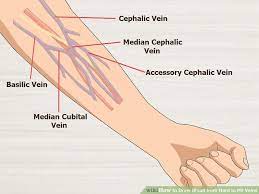
intravenous injection sites
veins on the forearms
45
New cards
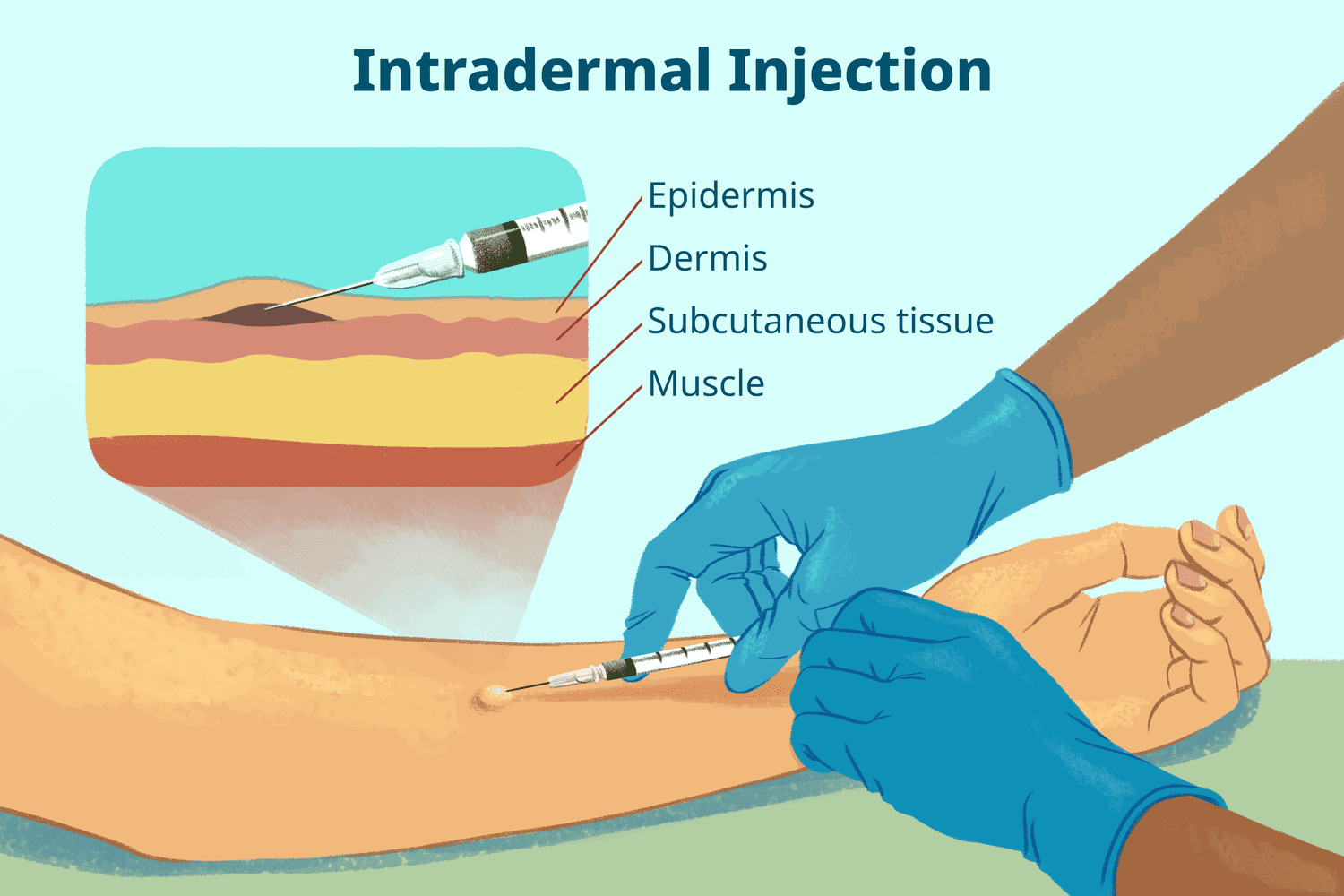
intradermal
are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB ), allergy, and local anesthesia tests.
46
New cards
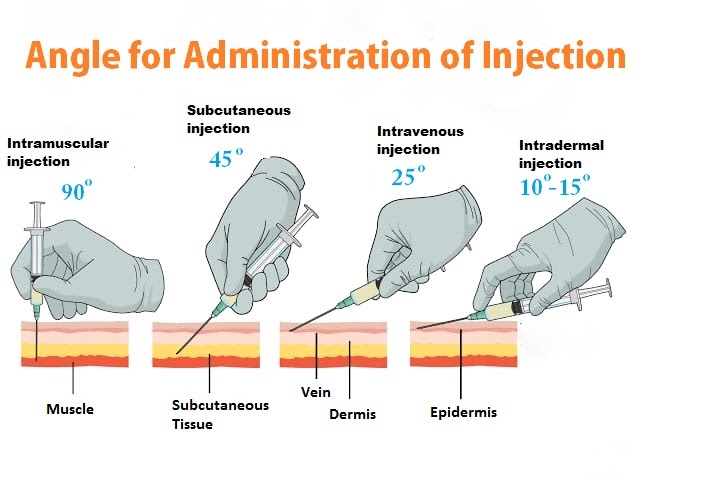
angles for injections
intramuscular - 90 degrees
subcutaneous- 45 degrees
intravenous - 25 degree
intradermal- 10-15 degree
subcutaneous- 45 degrees
intravenous - 25 degree
intradermal- 10-15 degree
47
New cards
ch 51 53
48
New cards
needle gauges
the bigger needle size, the smaller size of the actual needle
49
New cards
analgesics
drugs that relieves pain
*tylenol, percocet*
*tylenol, percocet*
50
New cards
***Antacids***
Drugs that relieve indigestion and heartburn by neutralizing stomach acid
tums
tums
51
New cards
*Diuretics*
*increases urine production): lasix (furosemide)*
52
New cards
*Antibiotics*
*(treat infection): amoxicillin*
53
New cards
*Antihypertensives*
*(decrease blood pressure): atenolol*
54
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from plants
*digitoxin, codeine, quinine*
55
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from fungi or bacteria
*penicillin, cephalexin*
56
New cards
Provide examples of medications derived from minerals
*potassium chloride, sodium chloride*
57
New cards
*Antihypertensives*
*(decrease blood pressure): atenolol*
58
New cards
*Anticoagulants*
*(reduces clotting): coumadin, heparin…*
59
New cards
*Prophylactic*
*(preventative medicine): birth control pills*
60
New cards
*Antiarrhythmics*
*(normalizes heartbeat): amiodarone*
61
New cards
Schedule I
*highest potential for abuse, no accepted medicinal use*
62
New cards
Schedule II
*high potential for abuse, includes meds such as morphine*
63
New cards
Schedule III
*lower potential for abuse, moderate potential to develop dependency*
64
New cards
Schedule IV
*lower potential for abuse, limited potential to develop dependency*
65
New cards
Schedule V
*lowest potential for abuse, very limited potential for dependency*
66
New cards
Inscription
*includes the name and amount of the drug*
67
New cards
Subscription
*instructions to the pharmacist dispensing the medication, may include authorization to substitute generic form*
68
New cards
Transcription
*includes patient instructions which generally follow the abbreviation Sig which means “mark”*
69
New cards
Signature
*prescriber’s signature*
70
New cards
Parenteral
*IM, SC, ID, IV*
71
New cards
Buccal
*cheek*
72
New cards
Sublingual
*under the tongue, must allow drug to dissolve completely before eating*
73
New cards
Transdermal
*applied to the skin usually in the form of a patch*
74
New cards
rectal
vaginal
vaginal
*placed in the rectum*
*placed in the vagina, such as a douche*
*placed in the vagina, such as a douche*
75
New cards
Topical
*salves or ointments, lotions. Salves and ointments are oil based and require more rubbing in.*
76
New cards
How many times do you check your order?
3 times
77
New cards
List at least 7 rights of medication administration.
Right person, right location, right dose, right time, right documentation, right route, right medication
78
New cards
IMD
90-degree angle bevel up
79
New cards
SC
45 degrees, bevel down
80
New cards
ID
15 degrees, bevel up
81
New cards
IMG
90 degrees, bevel up
82
New cards
How do you measure for a SC injection behind the arm?
3 inches above your elbow (cubitus) on the fatty tissue on the back of your arm.
83
New cards
Why would the z-track method of injection be used?
prevents leakage of irritating and discoloring medications into the subcutaneous tissue or the layers of the skin. It also may be used in elderly patients who have decreased muscle mass.
84
New cards
Why must you remove air from the syringe when drawing up a medication?
It helps remove air bubbles so you can give the accurate amount of medication.
85
New cards
Why would the needle be changed after drawing up a medication?
It decreases the risk of infection and different medications have different needles to draw up than to be injected
86
New cards
What information must be documented when administering an injection of medication or vaccine?
The expiration date, the manufacturing date, the lot number, the name of the person administering it, the dosage, the location, the time, the date, the route of administration, patient allergies, whether they have gotten the vaccine before, patient education
87
New cards
Absorption
the process of converting a drug from its dose form to a form the body can use.
88
New cards
Side effects
are unintended but fairly mild and common effects of a medication.
89
New cards
Adverse effects
are potentially more harmful, but less common effects.
90
New cards
Toxicology
is the study of the poisonous effects, or toxicity of drugs. This would include adverse effects and drug interactions.
91
New cards
DEA number
required for prescriptions of Schedules II, III, IV, and V medications only
92
New cards
NKDA (No known drug allergies)
should be asked before prescribing medication
93
New cards
Drugs that have local effects
are applied directly to the skin, tissues, or mucous membranes
94
New cards
Drugs that produce systemic effects
are administered by routes that allow the drug to be absorbed and distributed in the bloodstream.
\
\
95
New cards
patient rights
Right Reason – Know reason drug is being given
Right to Know – Patient should know reason as well
Right to Refuse – Patient does not have to take drug
Right Technique – Review technique before using
Right to Know – Patient should know reason as well
Right to Refuse – Patient does not have to take drug
Right Technique – Review technique before using
96
New cards
Sublingual medication
medication under the tongue
97
New cards
a sharps container should only be filled
2/3 full
98
New cards
parental
medication given by injection
99
New cards
z track method
is used by pulling the skin and subcutaneous tissue to the side before inserting the needle at the site.
100
New cards
intramuscular injection for pediatric patients
until the patient is two years ago