Physiological Psychology Exam 3
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Biological rhythm: Circadian Rhythm
- 24 hours
Biological rhythm: Ultradian rhythm
- repeats more than once a day
Biological rhythm: Infradian rhythm
- repeat less frequently than once a day
Which mechanisms shows evidence that light influences our internal clock?
- The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus controls circadian rhythms
- it also detects light and entrains daily biological and behavior rhythms to the onset of light from the environment.
- in mammals, light information from the eyes reaches the SCN directly
Lesion studies of SCN?
demonstrate that its destruction disrupts circadian rhythms in sleep-wake cycles, temperature, and other physiological functions
Developmental shifts in circadian rhythm
- early months after conception, the fetus spends most of its time in REM sleep
- The newborn spends about 16 hours sleeping, over half is in REM
- humans sleep more during infancy than adulthood
- At puberty, most people shift their rhythm of sleep so they can get up later in the day
- over the years, we spend more of our daily hours awake
Course of sleep stages
- Awake
- Stage 1 (NREM)
- Stage 2(NREM)
- Stage 3(NREM)
- REM sleep
- Repeat
Stage 1: NREM
This is the lightest stage of sleep, a transition between wakefulness and sleep, where you might feel like you're drifting in and out of consciousness.
Stage 2: NREM
This stage is characterized by a further slowing of brain waves and a drop in body temperature, heart rate, and breathing, preparing you for deeper sleep
Stage 3: NREM
This is the deepest stage of sleep, where your body repairs and restores itself, and it's harder to wake someone in this stage
REM sleep
During this stage, your brain activity resembles wakefulness, and you experience vivid dreams, with eye movements and temporary paralysis of the muscles
Sleep impacts on learning and memory
- sleep during the interval between learning and recall improves retention
- Consolidation of declarative memory tasks and complicated motor skills seems to benefit from SWS
- REM sleep is not absolutely necessary for learning
What is one biological function of sleep related to energy?
Rest and recovery: conserve energy and repair
How does sleep affect brain function?
Memory and learning
What hormones are regulated during sleep?
Cortisol and growth hormones
What effect does sleep have on cardiovascular health?
Lowers blood pressure and slows heart rate
How does sleep influence immune function?
Production and activation of immune cells to fight illnesses
What role does sleep play in metabolic regulation?
Regulates blood sugar and breaks down fat for energy storage
How does sleep contribute to emotional regulation?
Mood stability
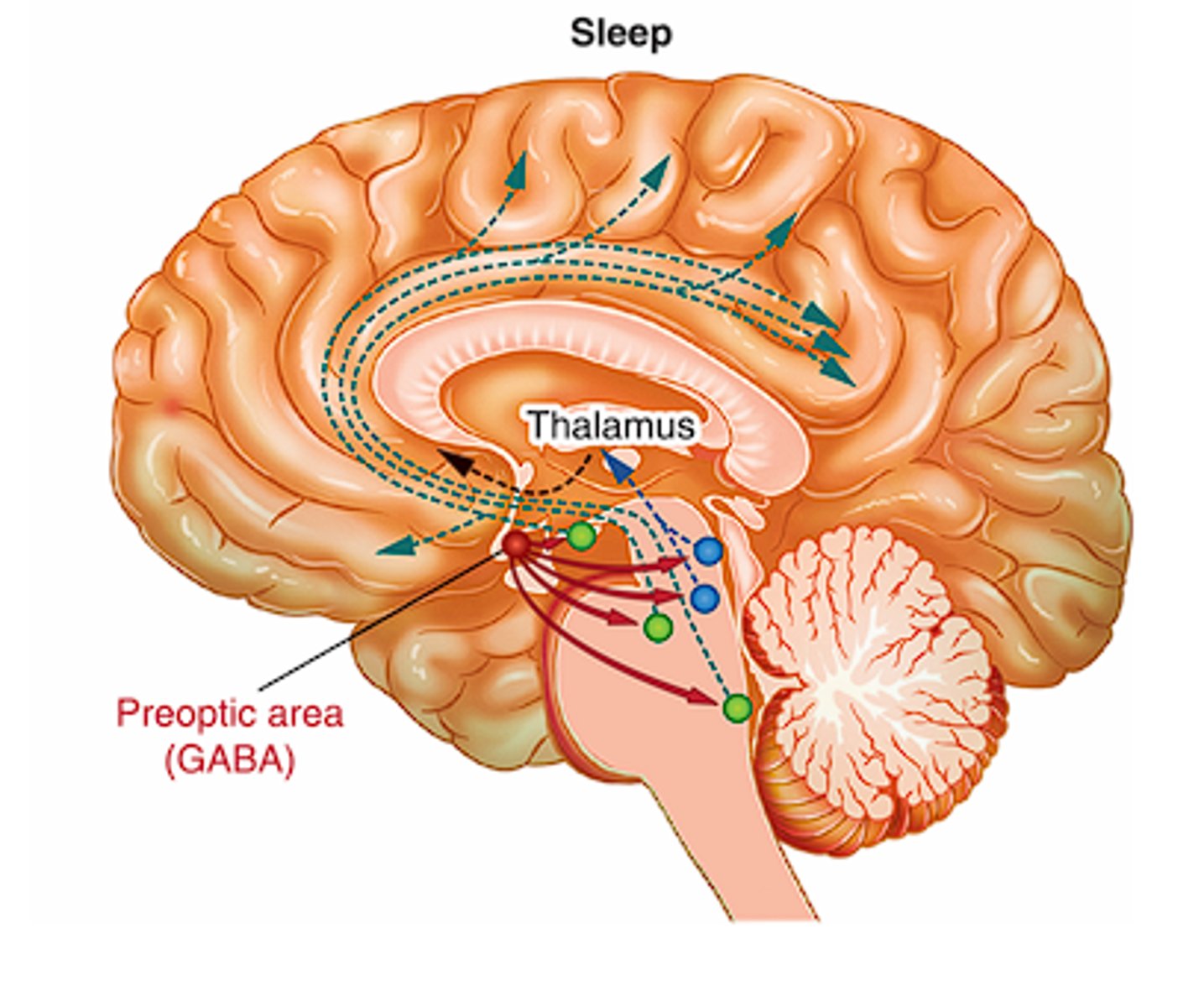
Sleep onset mechanisms: Non-REM Circadian
- The SCN activates neurons in the preoptic area of the hypothalamus
Sleep onset mechanisms: Non-REM Homeostatic
- build up of adenosine during waking hours
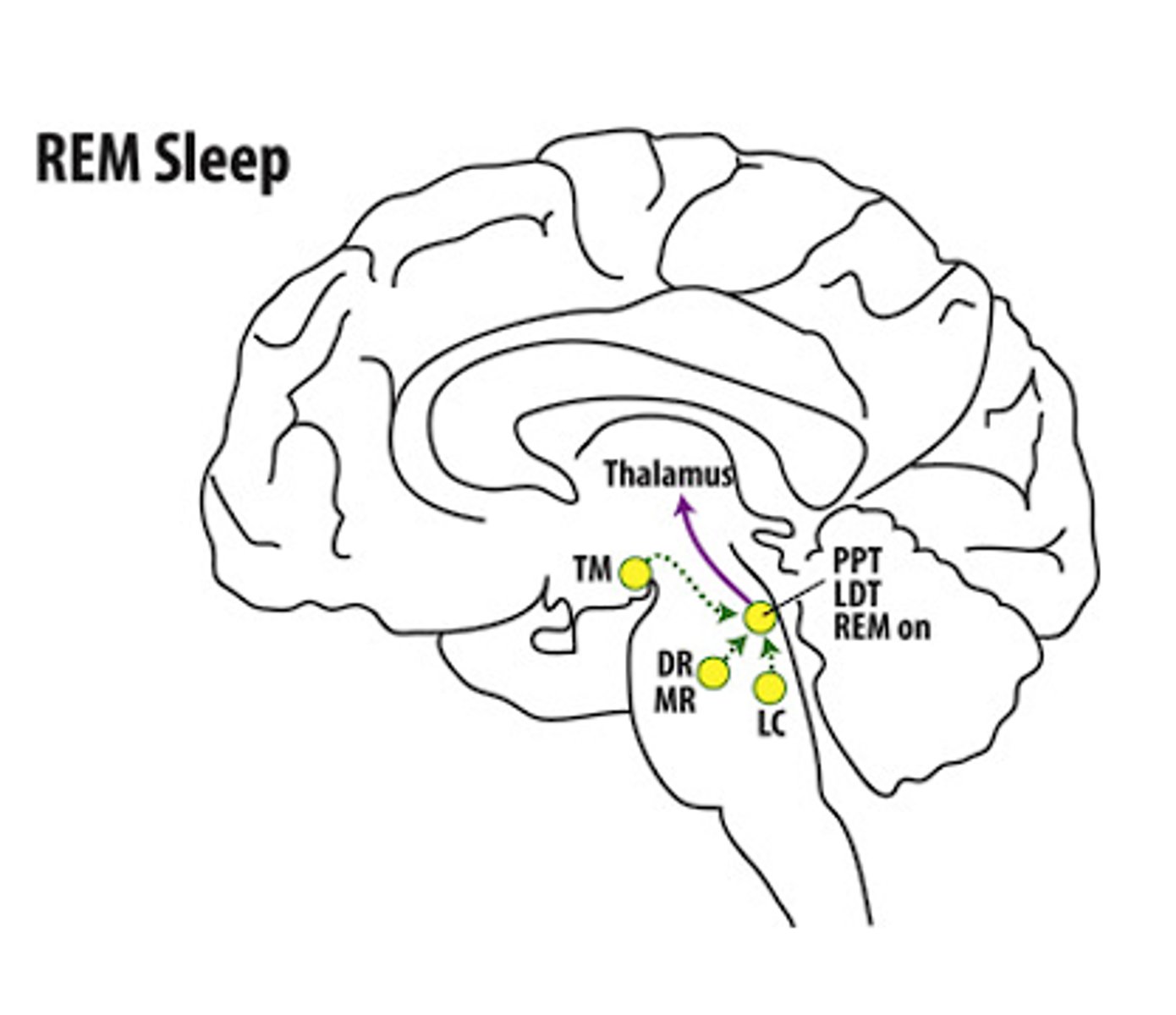
Sleep Mechanisms: REM sleep
- an area of the pons, near the locus coeruleus, is responsible for REM sleep
- they inhibit motor neurons to keep them from firing, disabling the motor system during REM sleep
- sleep paralysis connection
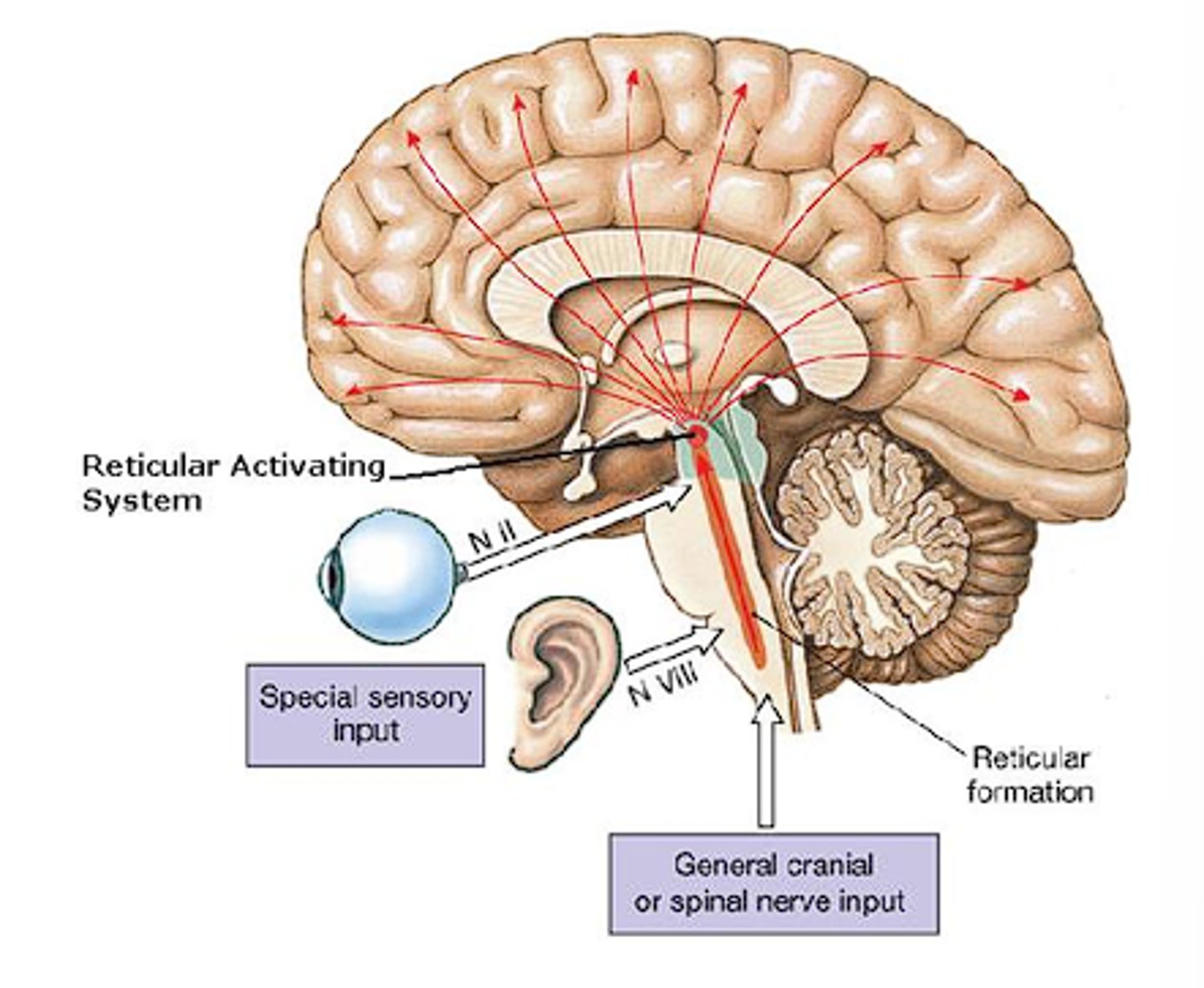
Waking Mechanisms
- the reticular formation wakes up the forebrain via the thalamus
- Ach
- NE
Systems involved in dreaming
- Posterior activation
- Frontal inactivation
- Sympathetic NS
Insomnia
an inability to sleep, is the most common sleep disorder
Sleep-onset insomnia
is a difficulty in falling asleep and can be caused by situational factors, such as shift work or jet lag
Sleep-maintenance Insomnia
is a difficulty in staying asleep and may be caused by drugs or neurological and psychiatric factors
Hypnotic Drugs
Medications for insomnia
Insomnia prevalence
- more common in women, elderly people, people with chronic disorders, and people with mental health disorders
- about 30% of adults suffer from insomnia
Insomnia risk factors
- irregular sleep/work patterns
- stress, anxiety, depression
- poor sleep hygiene
- chronic pain
- medications
- gender, age, socioeconomic status
Cause of narcolepsy
loss or absent orexin neurons in the hypothalamus that project to other sleep system centers: the basal forebrain, the reticular formation, and the locus coeruleus
What is a symptom of narcolepsy related to daytime alertness?
Intense sleepiness during the daytime
What is cataplexy in narcolepsy?
- Symptom of Narcolepsy
- A sudden loss of muscle tone while awake
What is sleep paralysis?
- Symptom of Narcolepsy
- A condition that occurs after waking or just before sleep
What are hypnagogic hallucinations?
- Symptom of narcolepsy
- Dream-like experiences while awake
Sleep hygiene: timing suggestions
- set a bedtime that is early enough for you to get at least seven hours of sleep
- If you don't fall asleep after 20 minutes, get out of bed
- Keep a consistent sleep schedule even on weekends and vacations
Sleep hygiene: room and bed suggestions
- Use your bed only for sleep and sex
- Make your bedroom quiet and relaxing. Keep the room at a comfortable, cool temp. establishing relaxing bedtime rituals
Sleep hygiene: awake time suggestions
- Don't go to bed unless you are sleepy
- Limit exposure to light in the evenings
- exercise daily and maintain a healthy diet
- avoid consuming caffeine in the late afternoon or evening
- Avoid consuming alcohol before bedtime
- reduce fluid intake before bedtime
Homeostasis
is the action of a system to maintain internal stability when faced with a disturbance of its normal condition
Homeostatic System: Thermoregulation
the regulation of body temperature
Homeostatic System: Endotherms
generate their own heat through internal processes
Homeostatic System: Ectotherms
get most of their heat from the environment
Homeostatic System: Negative Feedback
- These loops counteract a change such as in temp or blood pressure
- Set point = desired value
- Set zone = range of tolerance in a system
Homeostatic System: Redundancy
- Monitored by more than one mechanism
- EX: rat hypothalamus, lesions in the preoptic area, impaired physiological responses to cold, but not behavioral
Homeostatic System: Behavioral regulation of temperature
- change exposure of the body surface
- change external insulation
- change surroundings
- endotherms use internal processes to generate a fever
Allostasis
behavioral and physiological adjustments to maintain an optimal (versus unchanging) functioning of a system in the face of changing environmental stress
Set point
desired value
Set Zone
range of tolerance in a system
Selection advantages of endothermy
- the ability of an organism to generate and regulate its own body heat
- the increased capacity to sustain a high level of muscular activity
- high degree of thermal independence from environmental temperature
Brain anatomy related to temperature regulation
The hypothalamus receives input from thermoreceptors (internal and externa)l and initiates responses to maintain a stable core temperature
Isotonic solution
A solution with the same concentration of water and solutes as inside a cell, resulting in the cell retaining its normal shape because there is no net movement of water.
- EX: Physiological saline
Osmotic pressure
is the force that pushes or pulls water across the membrane
Osmotic Thirst
a thirst for water may be triggered by high extracellular solute concentration, or very salty fluids
Osmotic Thirst pathway: Drinking
1. Detection by OVLT (osmosensory neurons)
2. Preoptic area
3. Hypothalamic thirst network
4. Drinking
Osmotic Thirst pathway: water conservation
1. OVLT (osmosensory neurons)
2. Preoptic area
3. supraoptic nucleus, paraventricular nucleus
4. Vasopressin release
5. Water conservation
Osmotic Thirst behavior
Drinking
Vasopressin
hormone that stimulate the body to retain water
Aldosterone
hormone that stimulates the body to retain NA+
Hypovolemic thirst
low extracellular volume from a loss of bodily fluids, loss of salt and ions but concentration has not changed
Hypovolemic thirst: Water conservation
1. Kidney Baroreceptors
2. Release Angiotensin II
3. Subfornical organ
4. preoptic area
5. supraoptic nucleus, paraventricular nucleus
6. Vasopressin release
7. Water conservation
Hypovolemic Thirst: Drinking
1. Cardiac Baroreceptors
2. Brainstem
3. Preoptic area
4. Hypothalamic thirst network
5. Drinking
Baroreceptors
in blood vessels and the heart to detect a drop in pressure
Hypovolemic thirst behavior
- thirst
- drinking
- water conservation
- salt hunger
Angiotensin II (AII)
- released by the kidneys
- increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels
- causes release of vasopressin and aldosterone
Short-Term forms of energy storage
- Glucose (carbohydrates)
- stored in the liver as glycogen
- when their is a drop in glucose in the blood stream glycogen gets turned back into glucose for energy
Long-Term forms of energy storage
- Fat
- Triglyceride
- Triglycerides get broken down into free fatty acids, which can be used by cells outside the brain
- The brain relies on glucose not fatty acids
Leptin
- Origin: Adipose tissue
- Effect: reports status of long-term energy reserves to the brain
Ghrelin
- Origin: empty stomach
- Effect: stimulates food intake when high
CCK
- Origin: Intestines
- Effect: Suppresses appetite when released
GLP-1
- Origin: Intestines
- Effect: Suppresses appetite when released
Signaling pathway of appetite
1. Ghrelin hunger signals are sent through the vagus nerve
3. Receptors in the arcuate nucleus detect the ghrelin hunger signal
4. Activate the Lateral Hypothalamus (LH)
5. Activation triggers food-seeking and eating
Signaling pathway of satiety
1. Vagus nerve sends satiety signals to the solitary nucleus
2. The message is sent to the arcuate nucleus
3. Arcuate nucleus activates the paraventricular nucleus
4. The activation produces satiety
Effects of endocannabinoids on appetite
- influence the mesolimbic DA reward system
- act directly on hypothalamic appetite regulation
- inhibit satiety signals from the gut
The _____ nucleus of the hypothalamus receives both "stop and go" signals from the periphery regarding hunger
arcuate
People in the westernmost part of a time zone go to bed _______ than those in the easternmost part of the same time zone
later
Which hormone sends the brain a satiety signal via the Vagus nerve?
CCK
Heart rate is an example of a ______ rhythm
ultradian
During a sleep study, we would expect the EMG to appear most flat during ____
REM
Adenosine quantities build up when we have not slept in a while and increase sleep drive
true
Children secrete growth hormones during REM cycles
false
Posterior and prefrontal regions of the brain are activated when we dream
false
"Sleep on" neurons may be found in the _____ and secrete the neurotransmitter _____
locus coreleus; GABA
Which part of the brain helps endotherms regulate body temperature?
Preoptic nucleus (POA)
Blood donation is an example of an event that could trigger hypovolemic thirst
true
When hypovolemic thirst occurs, the posterior pituitary gland secretes _____ to slow urine production
angiotensin II