Lecture 4 - Software Estimation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Software Engineering, Friedrich L. Bauer
Software engineering is the establishment and use of sound engineering principles to obtain economically software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines.
What is software estimation, and why is it important?
Software estimation forecasts the effort needed for a project, determining its cost and duration. The goal is to approximate the resources needed to complete the project while meeting functional and non-functional requirements.
How does software estimation differ in traditional and Agile development?
Traditional estimation occurs in the early project phases, helping in contract negotiations and predicting effort and cost before implementation. It provides the best possible estimate based on available information.
Agile estimation is incremental, estimating individual requirements throughout development. Developers are allocated efficiently, and cost estimates are revised multiple times.
Cone of Uncertainty
The Cone of Uncertainty shows how estimation accuracy improves over time. Early in a project, estimates can vary by a factor of 4x or 0.25x due to limited information. As the project progresses, uncertainty decreases, especially within the first 20-30% of the timeline. In Agile, estimates are regularly updated to reflect new insights.
Primary Cost Categories in Software Estimation
Development costs (producing the software). - Personnel costs (largest portion). - Other costs (office materials, documentation, business trips, -CASE tools (Hardware and System Software for Development). Note: Offshore models may increase travel and communication costs.
Sneed’s Devil’s Square
The Devil’s Square describes the interdependence of quantity, quality, development duration, and cost.
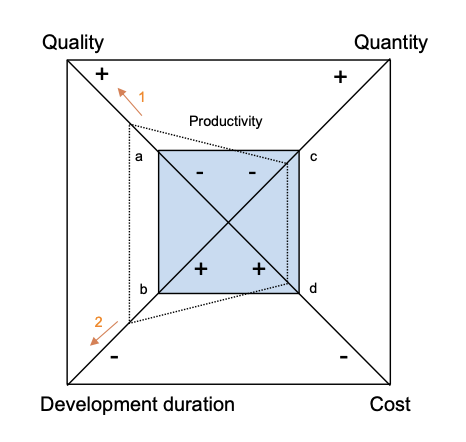
Example: Improving quality and shortening development time requires reducing product scope if costs remain unchanged. Productivity is assumed constant for a given organization and resources.
How is quantity measured in software development, and why is it difficult to estimate early? Quality?
Quantity is measured by Lines of Code (LOC) and functional and data scope, which may vary by complexity. It is unknown in the planning phase since project size and effort are difficult to predict early.
Higher quality requirements increase effort. There is no single definition of quality, as it depends on different characteristics. Key performance indicators (KPIs) help measure specific quality aspects.
How does team size affect productivity in software projects? Brook’s Law
Productivity depends on multiple factors, including team motivation and learning ability. As team size grows, communication links increase quadratically, making coordination harder. According to Brook’s Law, adding more people to a late project delays it further due to increased overhead and training time.
How does team size impact development time and productivity?
✔ More project members reduce development time but increase communication effort, which lowers productivity.
✔ Too few members limit the division of work, causing delays.
✔ An optimal team size balances development efficiency and coordination overhead to maximize productivity.
How are cost and time estimated in software development?
Cost and time estimation is based on Lines of Code (LOC), where the scope of the software is divided by programming productivity (LOC per person per month/year). The result is measured in Person Years (PY) or Person Months (PM) (1 PY ≈ 9-10 PM). System size is the most critical factor affecting estimation accuracy. Rules of thumb: 350 LOC/year.
What are the main methods and strategies for software effort estimation?
Effort estimation methods include:
✔ Comparison Methods – Based on similar past projects (e.g., analogy, relation methods).
✔ Algorithmic Methods – Use mathematical models (e.g., Function Point Method).
✔ Key Figure Methods – Use of cost extrapolation of individual units (e.g., multiplication or percentage-based methods).
Two main strategies are:
Top-Down – Estimate total effort based using mathematical algorithms based on the on functional requirements.
Bottom-Up – Each expense item is estimated separately, then summed up to get the total project effort
📌 Note: Estimation is not exact; some uncertainty always remains.
What is the Function Point Method, and how is it used in effort estimation?
The Function Point Method is a combined relation and weighting method developed by IBM (Albrecht, 1979). It estimates effort based on the functionality of a system and is widely used in industry.
Main Steps:
Categorize requirements (e.g., input, output, database)
Classify them by complexity (simple, medium, complex)
Enter data into a calculation form
Evaluate influencing factors
Calculate total Function Points (FP)
Convert FP into person-months (PM) using a table
Update empirical data for future project
What are Requirements of Function Point Method
✔ Can only be applied once project requirements are known
✔ Must be done by experienced staff
✔ Evaluates the entire product from the client’s perspective
✔ Needs training and guidelines to reduce subjective judgment
✔ Actual effort must be measured for future estimates
What are Advantages and Limitations of Function Point Method
Advantages:
✔ Based on requirements, not Lines of Code
✔ Adaptable to technologies, domains, and company needs
✔ Iterative refinement (from Lastenheft to Mockups)
✔ Early estimation possible
✔ Structured, easy to learn, time-efficient
✔ Tool support available
✔ Offers good accuracy
Limitations:
✘ Estimates only total effort (phases need separate % conversion)
✘ Originally personnel-intensive and hard to automate
✘ Very function-focused
✘ Influencing factors may blur product/project distinctions
How is estimation handled in the Scrum Framework? Two methods
Scrum uses two estimation techniques:
Story Point Estimation – For each item in the Product Backlog, estimating relative effort.
Time Estimation – In days, for each task in the Sprint Backlog.
The Product Backlog and its Refinement
The Product Backlog is a prioritized list of everything needed in the product. It is the single source of requirements, managed by the Product Owner
Product Backlog Refinement The act of adding detail, estimates, and order to items.
Product Owner and the Development Team collaborate on the details of Product Backlog items.
User Stories
A user story is the unit with which software features are estimated and developed, defined by the Product Owner while the estimates are made by the Scrum Team.
Planning Poker
A method where each team member independently estimates effort using story points. - Avoids groupthink and ensures fair participation in estimation.