Biological Molecules 🧬🧫
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Biological Macromolecule
A large molecule that is necessary for life that is built from smaller organic molecules
Organic Molecules
Any molecule that consists of carbon, it can be joined with hydrogen and other elements
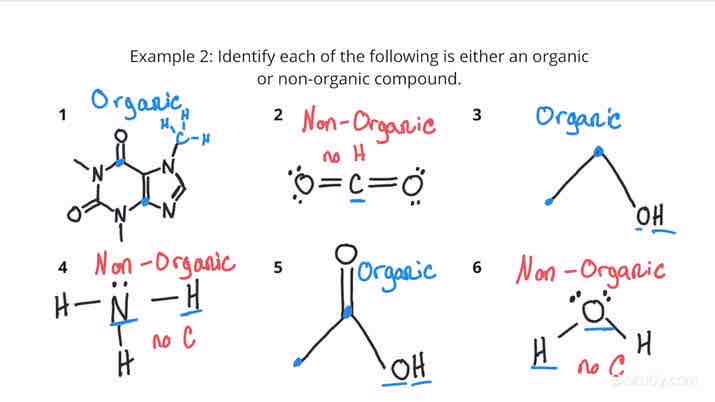
Inorganic Molecule
A molecule that consists of no carbon atoms
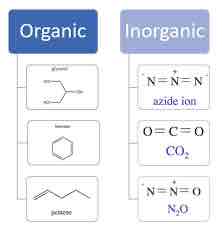
Nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids; contains a pentose sugar, one or more phosphate groups, and a nitrogenous base
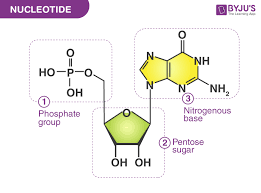
Chitin
Type of carbohydrate that forms the outer skeleton of all arthropods that include crustaceans and insects; it also forms fungi cell walls
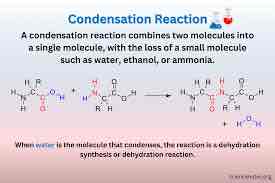
Dehydration Synthesis
(AKA condensation) A reaction that links monomer molecules, releasing a water molecule for each bond formed
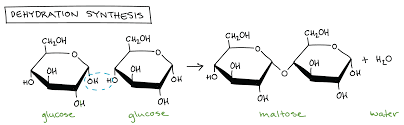
Monomer
Smallest unit of larger molecules that are called polymers.
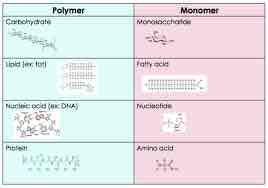
Polymer
Chain of monomer residues that covalent bonds link; polymerization is the process of polymer formation from monomers by condensation
Polypeptide
Long chain of amino acids that peptide bonds link
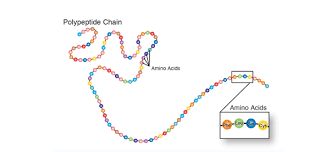
Protein
Biological macromolecule comprised of one or more amino acids
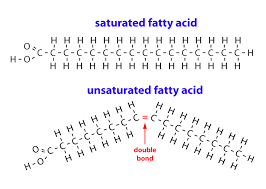
Saturated Fatty Acid
Long-chain hydrocarbon with single covalent bonds in the carbon chain; the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized
Covalent Bond
Interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. This binding is caused from electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons
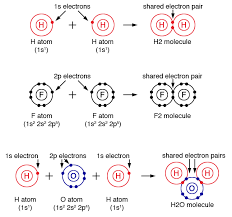
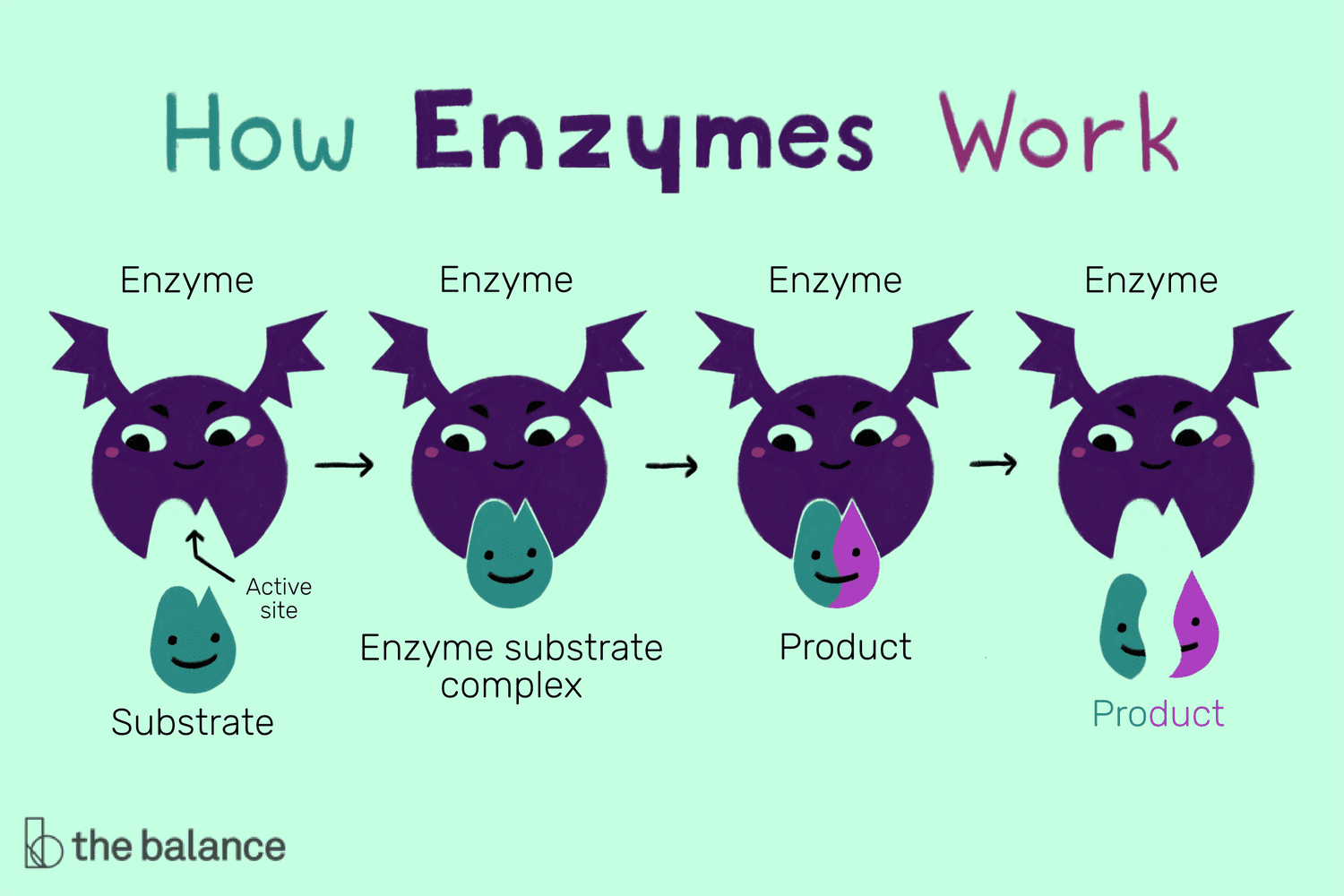
Enzyme
Catalyst in a biochemical reaction that is usually a complex or conjugated protein
Glycogen
Storage carbohydrate in animals; made of connected glucose molecules
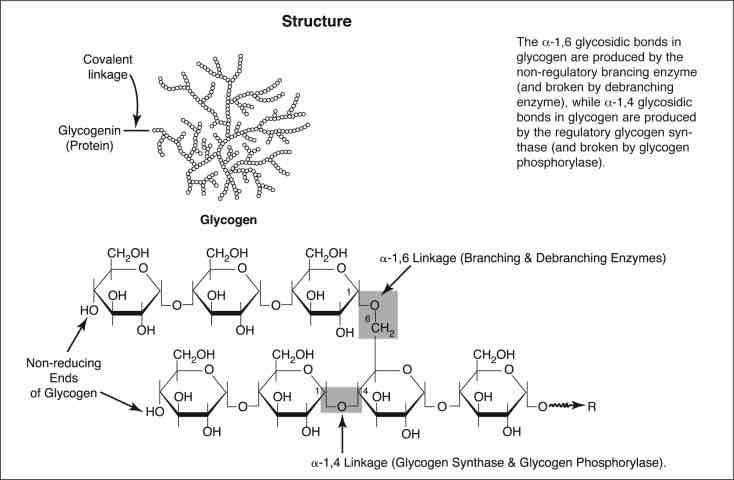
Glycosidic Bond
A bond formed by a dehydration reaction (Condensation) between two monosaccharides with eliminating a water molecule.
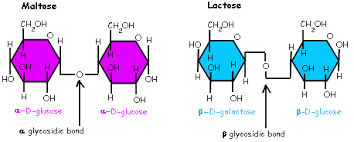
Hormone
Chemical signaling molecule, usually protein or steroid, secreted by endocrine cells that act to control or regulate specific physiological processes.
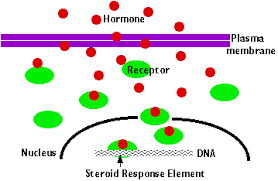
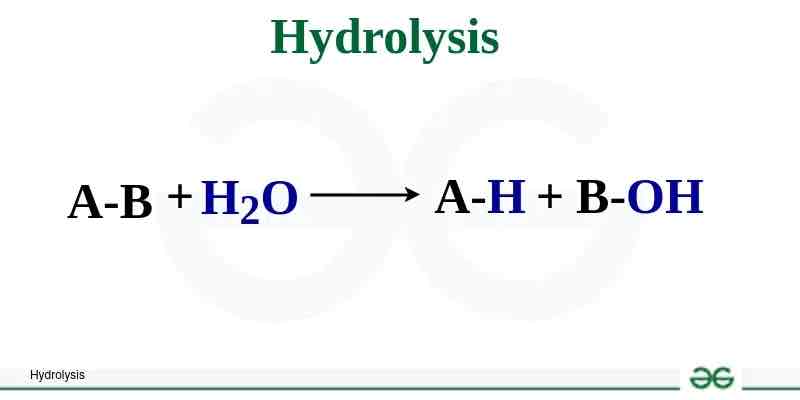
Hydrolysis
Reaction that causes breakdown of larger molecules into smaller molecules by utilizing H2O
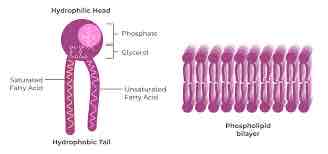
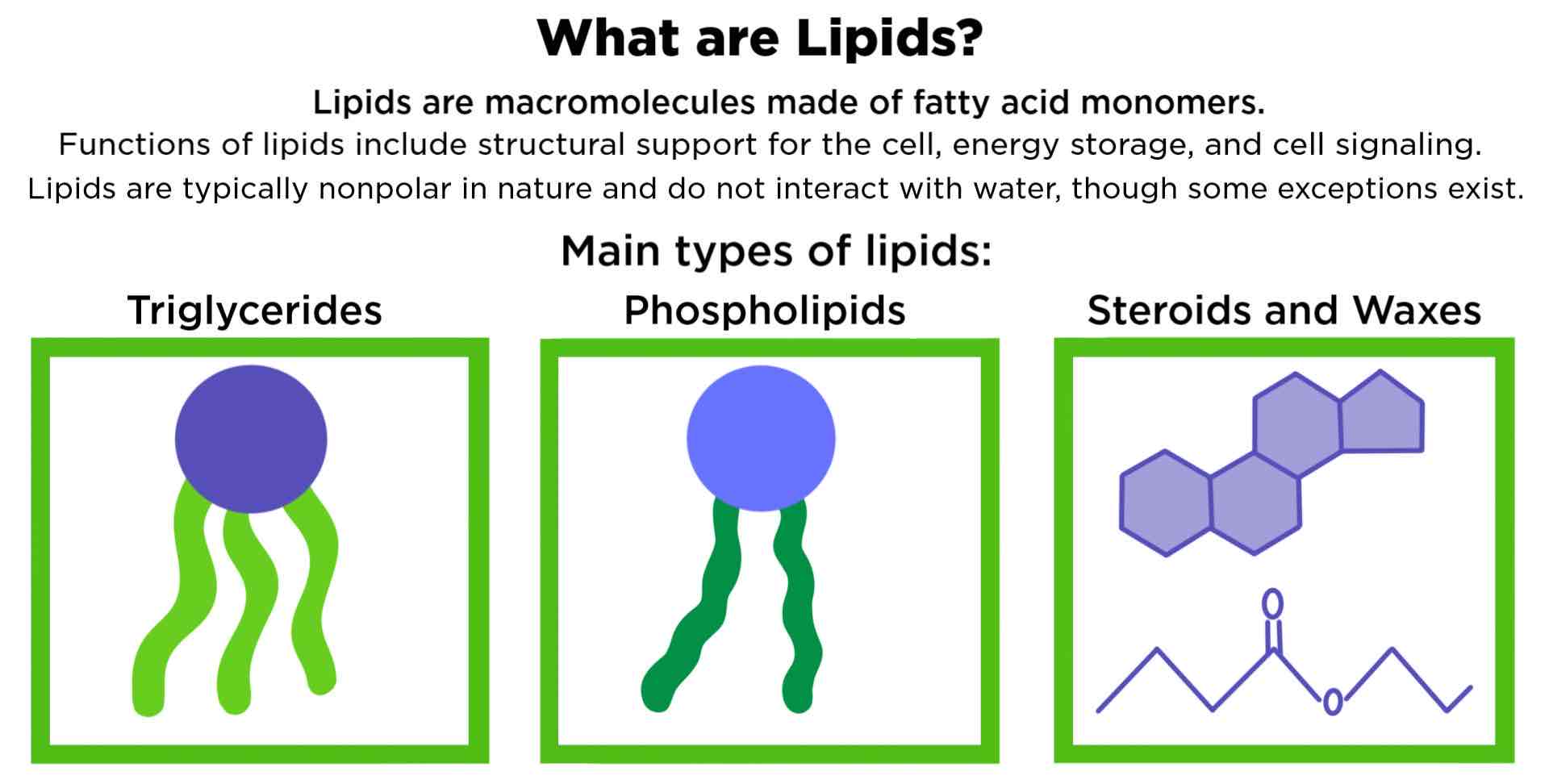
Lipid
Macromolecule that is non polar and insoluble in water
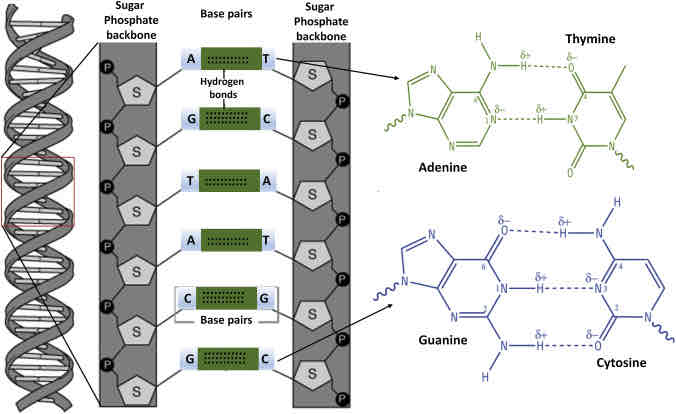
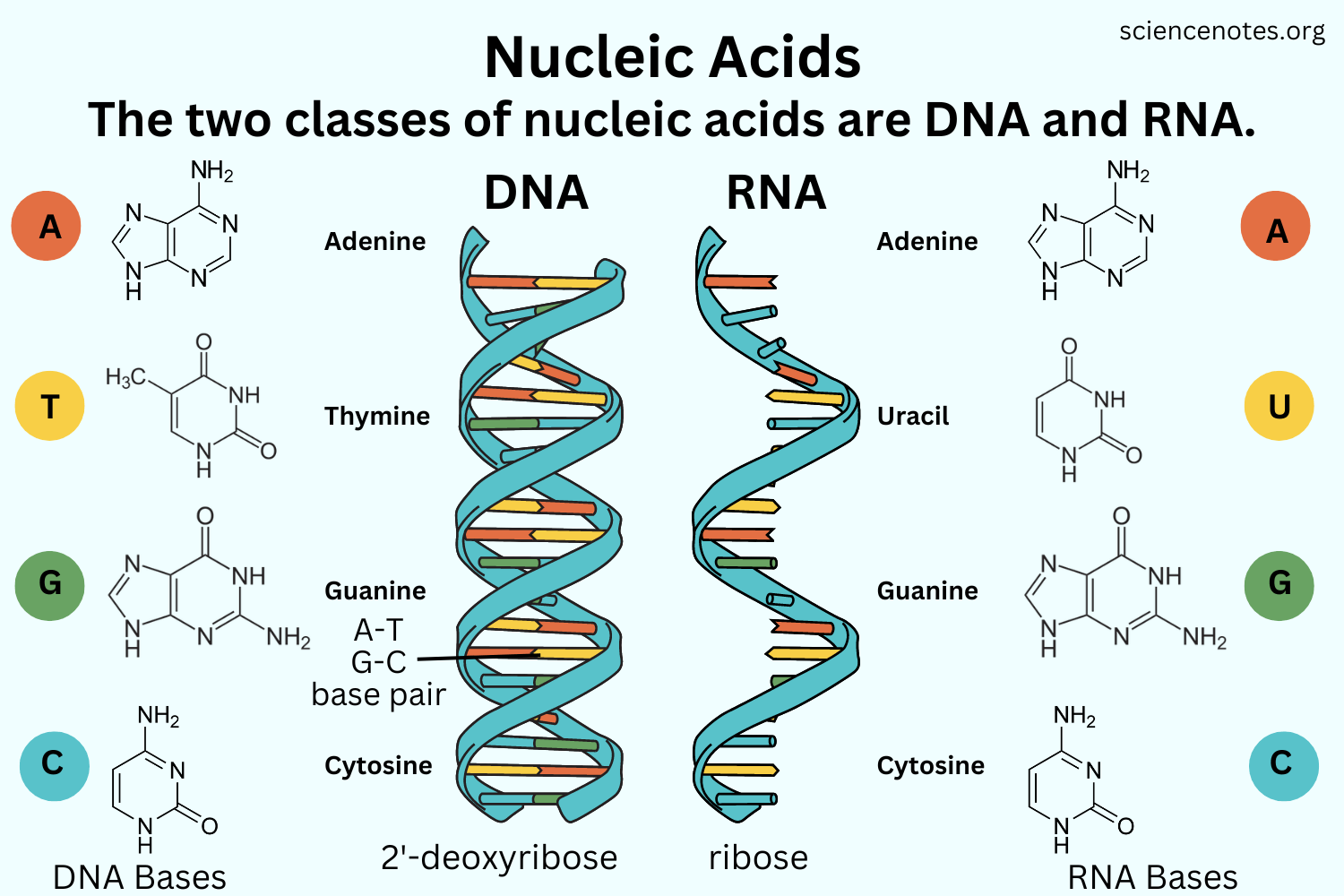
Nucleic Acid
Biological macromolecules that carries the cells genetic blueprint and carries instructions for the cells rings forming a planar structure

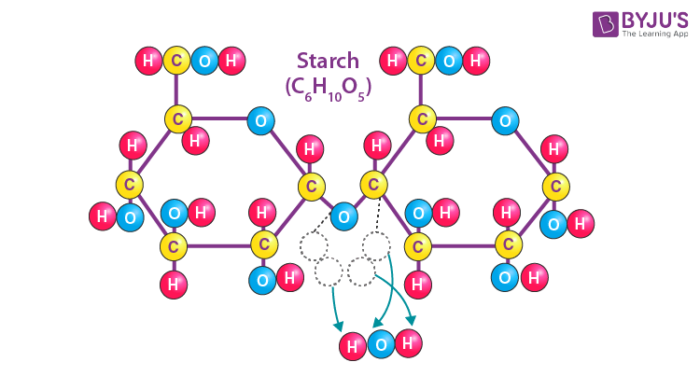
Starch
Type of carbohydrate that plant cells store energy in the form of glucose
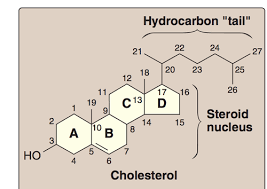
Steroid
Type of lipid comprised of four fused hydrocarbon acids to the site of protein synthesis on the ribosome
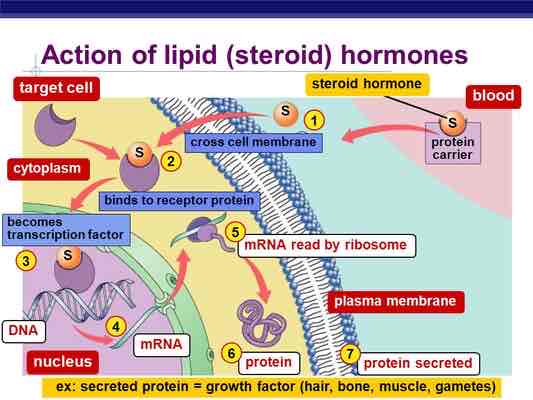
Translation
Process through which RNA directs the proteins formation
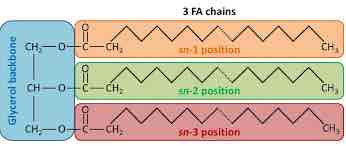
Triacylglycerol (triglyceride)
Fat Molecule; consists of three fatty acids linked to a a glycerol molecule

Unsaturated fatty acid
Long-Chain hydrocarbon that has one or more double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
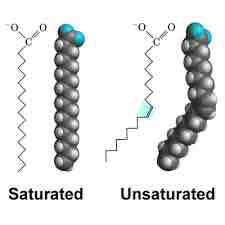
Wax
Lipid comprised of a long-chain fatty acid that is esterified to a long chain alcohol; serves as a protective coating on some feathers, aquatic mammal fur, and leaves
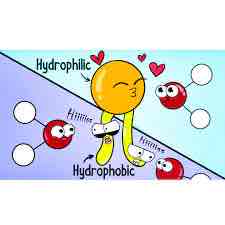
Hydrophilic
Polar molecules; charged sections of a molecules will interact with water. (Loves)
Hydrophobic
Non polar areas of a molecule

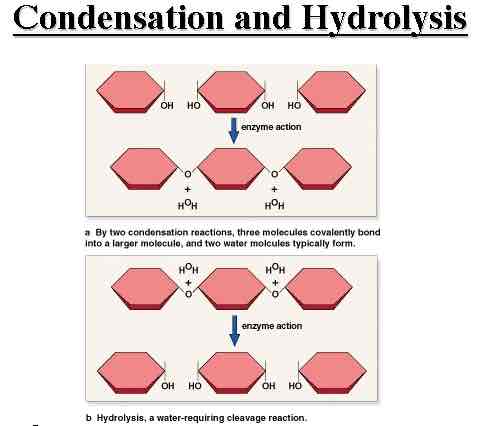
How does condensation occur?
A molecules will remove H+ and the other removes OH-, combining the other elements. (Removing water)
Condensation Characteristics
Puts monomers together
Results in water in the products
Hydrolysis Characteristics
Taking macromolecules apart
Requires water in the reagents (Reactants)
What are the 4 Main Types of Macromolecules?
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Protein
Nucleic acid description and monomer
Information storage and expression
Monomer: ATCG; Nucleotides
Examples of Nucleic Acids?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), Ribonucleic acid (RNA),
Carbohydrate Description and Monomer
Chemical formula (CH2O)n
Energy Storage
Soluble in water
Structural support
Monomer: Monosaccharide- “one””sugar”
What are examples of Carbohydrates?
Glucose, Sucrose, Starch, Cellulose
Lipids Description
Hydrophobic
Defined by properties

Protein Description and Monomer
3-D shape=Function
Monomer: Amino Acid
What are examples of proteins?
Enzymes, Signals hormones, Transport (Channels, pumps), Immune (antibodies)