Enthalpy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Define enthalpy (H)
Refers to all the heat energy that is stored in a chemical system at a constant pressure
What is enthalpy change?
Change in heat energy of a substance at a constant pressure
What happens in an exothermic reaction?
Energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings
Products have less energy than reactants
Reaction profile form an exothermic reaction
Enthalpy change in an exothermic reaction is always negative
As energy is given out
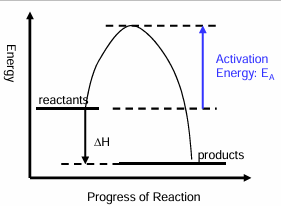
Define activation energy
Minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to take place
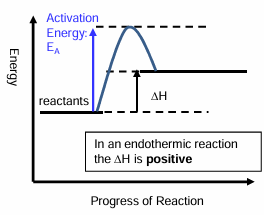
What happens in an endothermic reaction?
Energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system
The products have more energy than the reactants
Reaction profile for an endothermic reaction
In an endothermic reaction the enthalpy change is positive
What happens to the bonds in the reactant molecules for a chemical reaction to take place?
Bonds in the reactant molecules are broken
This requires energy
How are products formed in a chemical reaction?
Bonds are made
Energy is released
What are enthalpy changes always measured under?
Standard conditions
What are the standard conditions?
Standard temperature = 25 degrees (298K)
Standard pressure = 100Kpa
Standard concentration = 1mol dm-3
Define standard enthalpy change of combustion
When 1 mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen
With all substances in their standard states
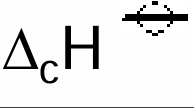
Define standard enthalpy change of formation
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
All elements being in their standard rates
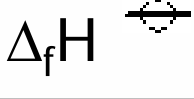
Measuring the standard enthalpy change of combustion via an experiment
Use a balance to measure starting mass of a spirit burner and fuel (ethanol)
Use a thermometer to measure starting temperature of water in the metal calorimeter
Remove cap of spirit burner and immediately light the wick (do not leave spirit burner uncapped when not lit as fuel will evaporate)
Stir water with thermometer, to ensure thermal energy is distributed
After several minutes extinguish the flame by putting the cap back on
Read temp on thermometer and measure the final mass of the spirit burner
Starting mass-final mass=total mass combusted
What equations are required to workout enthalpy change
Enthalpy change = q/1000 divided by mole of fuel
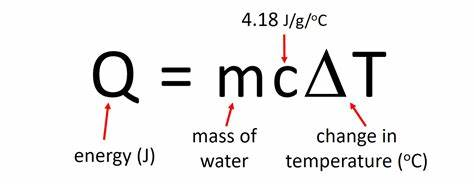
Why may published values of enthalpy change be higher than experimental values?
Spirit burner being left uncapped- fuel will evaporate making it seem like more fuel was burnt
Heat energy released does not pass into water- some heat energy transferred to calorimeter and air
Not all the fuel underwent complete combustion-incomplete combustion releases less thermal energy
Experiment not carried out under standard conditions
Measuring enthalpy change through another experiment (polystyrene cup)
In this experiment there is a reaction between Mg and CuSO4 (solution) which is exothermic
Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 + Cu
Weigh the Mg powder
Copper sulphate must be in excess. The equation shows Mg and CuSO4 react in a 1:1 ratio
For CuSO4 to be in excess we must add less than 0.1 moles of Mg. E.g 0.05 moles
Measure 100cm3 of CuSO4 in a polystyrene cup which is an insulator
Place the cup inside a glass beaker so it doesn’t tip over
Place the thermometer in the solution.
Need to ensure solution is the same temp as the room, as the experiment must be conducted under standard conditions
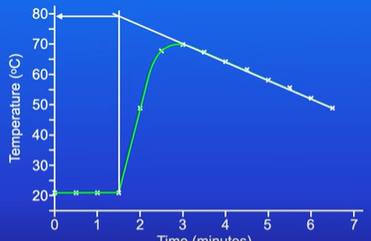
Take temp readings every 30 seconds until there is a constant temprature
Then add Mg powder and stir it in with thermometer
Take temp readings every 30 seconds for a period of time like 15 minutes
Plot a graph with temp on y axis and time on x
Explain the results
Once temp reaches a maximum it decreases due to thermal energy being lost to surroundings
These heat losses would have taken place throughout the reaction
Extrapolate the line to show what the temp would’ve been if there was no cooling
use equations to workout enthalpy change
Why can we use 100cm3 as the mass of the solution heated (CuSO4) even though its not in grams?
CuSO4 was dissolved in water making it an aqueous solution
It can be assumed that 1g = 1cm3 as density of this solution is similar to water
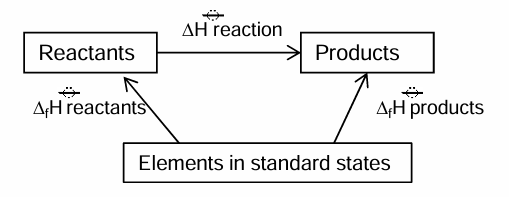
What is Hess’s law
Enthalpy change is independent of route taken
Enthalpy cycle that uses standard enthalpy change of formation
Arrows face upwards
Enthalpy cycles using standard enthalpy change of combustion
Arrows face downwards
Define average bond enthalpy
Energy required to break 1 mole of a specific bond in a molecule in its gaseous state
Energy needed to break a bond is the same amount of energy…….
released when forming a bond