1. OVERVIEW OF METHODS USED IN HISTOLOGY
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
microscope
is an instrument that magnifies an image and allows visualization of greater detail than is possible with the unaided eye
simple and compound
Two types of microscope
Resolving power
is the ability of a microscope lens or optical system to produce separate images of closely positioned objects
bright-field microscope
The microscope used by most students and researchers is the ______________________
– light source
– condenser lens
– stage
– objective lens
– ocular lens
The bright-field microscope has the ff parts:
bright-field microscope
in this type of microscope the object/specimen appear dark in bright background
-scanning - 40x
-LPO - 100x
-HPO - 400x
-OIO - 1000x
types of objective lens and their total magnification
phase contrast microscope
it enables examination of unstained cells and tissues and is especially useful for living cells.
interference microscope
differential interference microscope
Two modifications of the phase contrast microscope are:
interference microscope
(modifications of the phase contrast microscope)
allows quantification of tissue mass
differential interference microscope
(modifications of the phase contrast microscope)
(using Nomarski optics), which is especially useful for assessing surface properties of cells and other biologic objects.
there is a buldging on the specimen and it it embosed.
dark-field microscope
is useful in examining autoradiographs, in which the developed silver grains appear white in a dark background.
dark-field microscope
Clinically it is useful in examining urine for crystals and in demonstrating specific bacteria particularly Treponema pallidum and spirochetes
Treponema pallidum
the bacterium the causes syphilis
Fluorescence microscope
is used to display autofluorescent molecules such as vitamin A and some neurotransmitters
Fluorescence microscope
Widespread application is in the detection of antigens or antibodies immunocytochemical staining procedures
antibody
if we’re looking for antigen; we use ____________ to detect
antigen
if we’re looking for antibody; we use ____________ to detect
Fluorochrome Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)
most common stain used in fluorescence microscopy
green
Fluorochrome Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC) emits the color ________
confocal scanning microscope
allows visualization of a biologic specimen in three dimensions. It combines components of a light optical microscope with a scanning system to dissect a specimen optically
ultraviolet microscop
e uses quartz lenses with an ultraviolet light source. The image depends on the absorption of UV light by molecules in the specimen. results are usually recorded photographically.
ultraviolet microscope
• is useful in detecting nucleic acids, specifically the purine and pyrimidine bases of the nucleotides.
• It is also useful for detecting proteins that contain certain amino acids
• Also use to determine quantitatively the amount of DNAand RNAinindividual cells.
polarizing microscope
is a simple modification of the light microscope in which a polarizing filter (the polarizer) is located between the light source and the specimen, and a second polarizer (the analyzer) is located between the objective lens and the viewer
polarizing microscope
It uses the fact that highly ordered molecules or arrays of molecules can rotate the angle of the plane of polarized light.
it is important in disease to differentiate crystal arthritis
transmission electron microscope
scanning electron microscope
two kinds of EMs
TEM
light passes through the specimen. uses the interaction of a beam of electrons with a specimen to produce an image
scans the surface, if there are appendages. the electron beam does not pass through the specimen but is scanned across its surface
viro: nano : electron microscopy
viro: ______: ________
bact : _______ : _________
bact : micro : bright field
1. Fixation
2.Dehydration
3. Clearing
4. Infiltration
5.Embedding
6. Trimming
7. Section-Cutting
8. Staining
9. Mounting
10. Labeling
enumerate histopathologic techniques:
Fixation
(histopath techniques)
• To avoid tissue digestion by enzymes present within the cells or bacteria
• To preserve cell and tissue structure
Fixation
(histopath techniques)
Small pieces of tissues are immersed in a solution called fixative after removal from the body.
10% neutral buffered formalin
(histopath techniques)
best general fixative that is used in fixation
20:1
(histopath techniques)
ideal fluid to tissue ration in fixation
Dehydration
(histopath techniques)
Tissue is transferred through a series of increasingly concentrated alcohol solutions called as dehydrating agents , ending in 100%, which removes all water.
alcohol-ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
(histopath techniques)
common agent in dehydration
10:1
(histopath techniques)
ideal ratio in dehydration
Clearing/Dealcoholization
(histopath techniques)
Alcohol is removed in the tissue by immersing in a clearing agent.
Clearing/Dealcoholization
(histopath techniques)
it nakes he specimen clear and higher refractive index
xylene
(histopath techniques)
common agent in clearing
10:1
(histopath techniques)
ideal ratio in clearing
Infiltration / Impregnation
(histopath techniques)
Tissue is then placed in melted paraffin until it becomes completely infiltrated with the substance.
-paraffin / melted paraffin
-celloidin
-gelatin
-ester wax
(histopath techniques)
common agent used in infiltration
25:1
(histopath techniques)
ideal ratio in infiltration
Embedding/ Casting
(histopath techniques)
The paraffin- infiltrated tissue is placed in a mold with melted paraffin and allowed to harden
false
true or false
the same medium is used in infiltration of tissue is the same medium used for embedding.
Trimming
(histopath techniques)
The resulting paraffin block is trimmed to expose the tissue for sectioning (slicing) on a microtome. Furthermore, it is used to fit to the tissue block holder of microtome.
tissue block
(histopath techniques)
the product in embedding / casting is called
Section-Cutting
(histopath techniques)
Tissue block is sliced into thin films using a microtome which are placed on glass slides and allowed to adhere, deparaffinized, and stained
tissue ribbon
(histopath techniques)
product in section-cutting
-rotary
-base-sledge
-rocking
-sliding
-freezing (cryostat) = used in enzyme; doesn’t need preserving: frozen section
(histopath techniques)
types of microtome
Staining
(histopath techniques)
to make various components conspicuous and permit distinctions to be made between them
basophilic
(histopath techniques)
Cell components with a net negative charge (anionic) stain more readily with basic dyes and are termed
acidophilic
(histopath techniques)
Cationic components have affinity for acidic dyes and are termed as
hematoxylin and eosin
(histopath techniques)
common agent in staining
hematoxylin
(histopath techniques)
is a stain used for negatively charges or basic specimens. it dyes the DNA or nucleus blue to black.
eosin
(histopath techniques)
is a stain used for acidic or positively charged specimens. it dyes the cytoplasm pale pink
Mounting
(histopath techniques)
Stained tissue slides are mounted with a cover slip using a mounting media.
canada balsam = derived from Abies balsamea
(histopath techniques)
commonly used mounting media
Labeling
(histopath techniques)
Tissue slides are labeled on the frosted areas with assigned tissue numbers or codes
pencil
(histopath techniques)
in labeling use
a. marker
b. pencil
Autoradiography
•is a method of localizing newly synthesized macromolecules in cells or tissue sections
•It makes use of a photographic emulsion placed over a tissue section to localize radioactive material within tissues
Cell and Tissue Culture
allows the direct observation of the behavior of living cells under a phase contrast microscope
Cell culture
has been widely used for the study of the metabolism of normal and cancerous cells and for the development of new drugs.
false
true or false
all microorganism can grow in petra dish
Enzyme Digestion
can be used to confirm the identity of the stained material such as glycogen, DNA, or RNA
periodic-acid-schiff
diastase or amylase
give the stain and enzyme to identify glycogen
fuelgen stain (red)
DNAse
give the stain and enzyme to identify DNA
basic dyes (methyl green-pyronin)
RNAse
give the stain and enzyme to identify RNA
DNAse, 0.2 M Tris Buffer, pH 7.6, distilled water
reagents needed in enzyme extraction of DNA
potassium dichromate
in enzyme extraction of DNA avoid the fixative ___________
RNAse, distilled water
reagents used in enzyme extraction of RNA
potassium dichromate and mercuric chloride
in enzyme extraction of RNA avoid the fixative ___________
Enzyme Histochemistry
used to diagnose storage diseases and answers the question “why is there accumulation?”, thus it uses cryostat
phosphatases, dehydrogenases, and peroxidases
enumerate enzyme classes:
Perls' Prussian blue reaction
for iron (used to detect the iron storage diseases hemochromatosis and, hemosiderosis)
PAS-amylase and alcian blue reactions
for glycogen and glycosaminoglycans (to detect glycogenosis and mucopolysaccharidosis
Immunohistochemistry
based on specific reactions between an antigen or antibodies labeled with visible markers, often fluorescent compounds for light microscopy and gold articles for TEM.
direct immunohistochemistry
indirect immunohistochemistry
two types of immunohistochemistry
Direct immunohistochemistry
uses primary antibody
Indirect immunohistochemistry-
uses secondary antibody. the secondary antibody is labeled
polyclonal antibodies
monoclonal antibodies
Two types of antibodies used in immunocytochemistry:
polyclonal antibodies
mixture of heterogeneous which are usually produced by different B cell clones in the body of an immunized animal
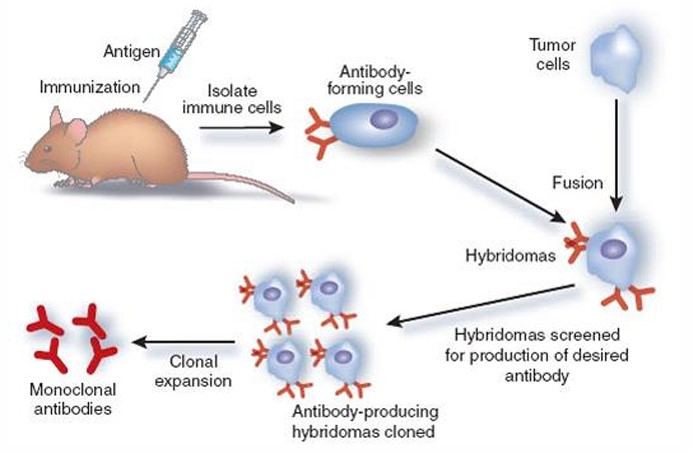
monoclonal antibodies
are generated by identical B cells which are clones from a single parent cell (immortalized antibody-producing cell lines)
monoclonal
polyclonal
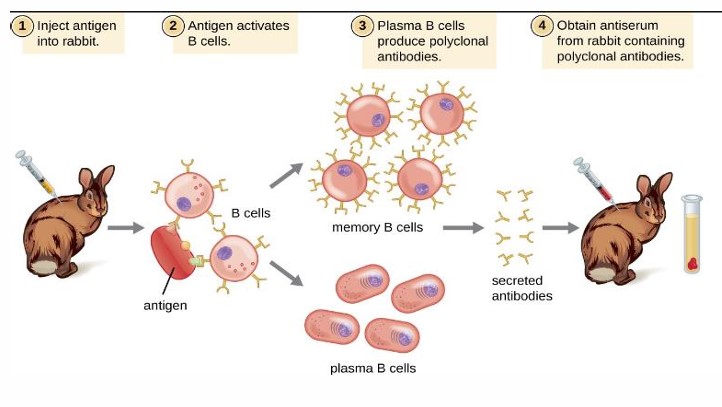
advantages polyclonal antibody
• Short production time and low cost.
• Highly stable
• High affinity Tolerant of minor changes of antigen.
• are less sensitive to antigen changes
disadvantages of polyclonal antibodies
• Prone to batch variability.
• Multiple epitopes make it important to check immunogen sequence for any cross-reactivity.
advantages of monoclonal antibodies
• Highly specific recognition of only one epitope of an antigen
• Immortal hybridoma cell lines have the ability to produce unlimited quantities of antibodies
• Minimal cross-reactivity
disadvantages of monoclonal antibodies
• it takes time and requires high technical skills.
• They can produce large amounts of specific antibodies but may be too specific to detect in across a range of species.
• Vulnerable to the change of epitope
Hybridization
allows the specific identification of sequences of DNA or mRNA by hybridizing the sequence of interest to a complementary strand of a nucleotide probe
In situ hybridization (ISH)
solution of nucleic acid are applied directly to cells and tissue sections
– Oligonucleotide probes
– Single- or double-stranded DNA probes
– RNA probes
Several nucleotide probes used in in situ hybridization
– radioactive isotopes
– digoxigenin
– biotin
Labels used for complementary probes: