Parasitology Week #1/2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
geographic distribution of malaria
-eradicated from US and most of europe now
-still kills more people per year than any other communicable disease except TB
-most cases in US are from travelers or refugees
-mostly due to P. falciparum
-mostly in africa!!
-more people die today from it than 30 years ago!!
-vivax has the widest distribution and most common in our lab
-ovale is only in africa really
clinical significance of malaria
FOUR MAIN Plasmodium INFECT HUMANS:
-vivax
-malaria
-faciparum
-ovale
**all cause malaria
-MOSQUITO!!
-malaria paroxysm (sudden fever) is due to rupture of RBCs and release of merozoites, malaria metabolites, and endotoxins
-Falciparum is life-threatening so we are 7 days a week 24/7
-can cause liver and spleen damage due to malarial pigment (HEMOZOIN)
-PBS doesn't correlate to how much parasite in the body
-falciparum is the most severe leading to cerebral malaria
-falciparum can also cause blackwater fever (massive intravascular coagulation because of antibody to RBCs made leading to black urine)
life cycle picture of parasite
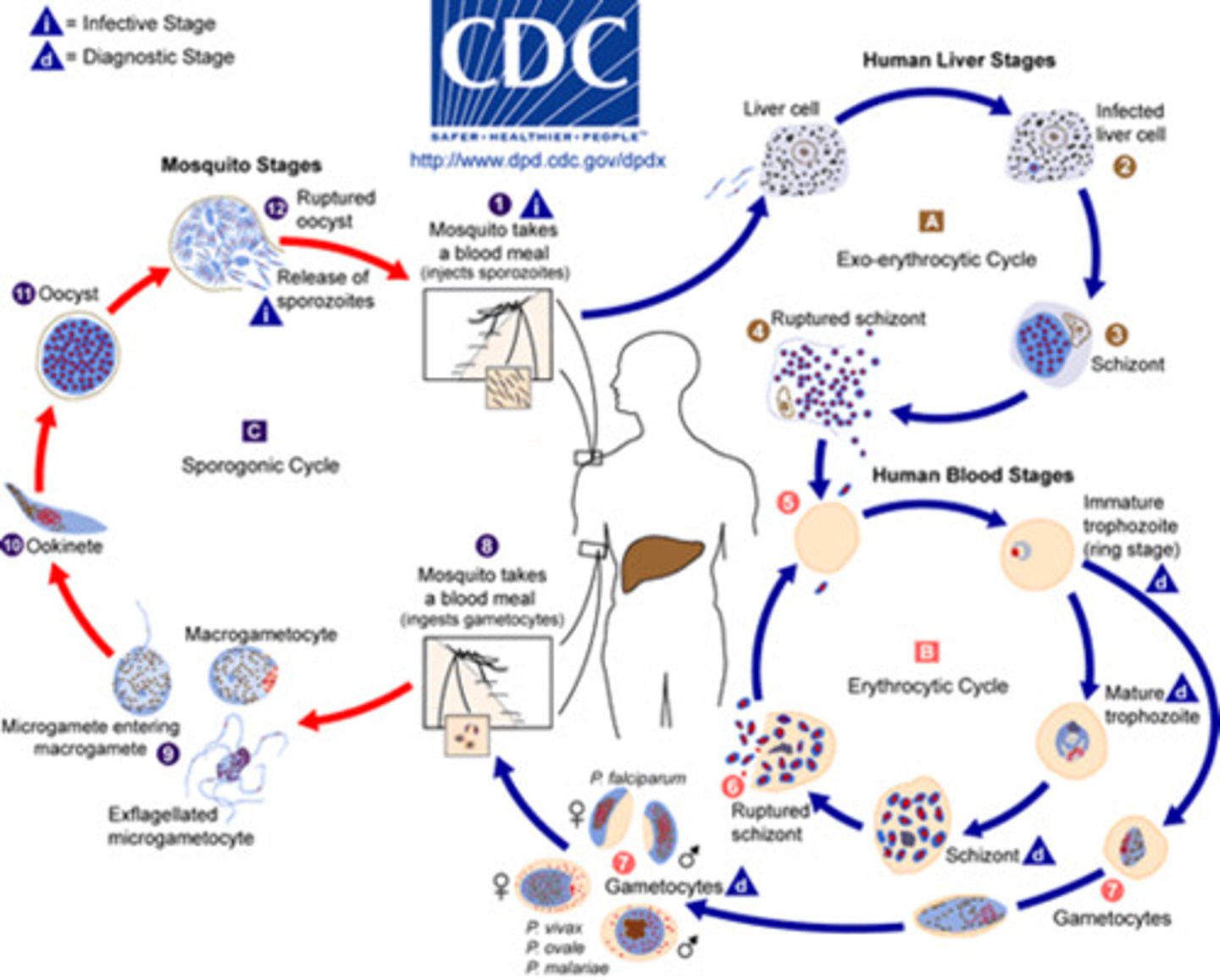
life cycle of the parasite in humans
-what stages are seen in PBS
-asexual life cycle
-begins with sporozoites injected into bloodstream by a bite from mosquito
-the sporozoites invade hepatocytes and undergo exoerythrocytosis to form liver schizonts
-each liver schizont holds thousands of free merozoites that go into PBS
-the merozoites infect RBCs
-early trophozoites (ring form) develop into mature trophozoites with an increase in their cytoplasm
-the young feed on hemoglobin and the metabolism from this creates a malarial pigment called HEMOZOIN!!
-trophozoites then mature into schizonts which contain merozoites
-schizonts rupture and release merozoites where they invade OTHER RBCs
-after many generations, some trophozoites develop into macrogametocytes or microgametocytes which help with the sexual phase of malaria in the mosquito
-sporozoites are produced within a cyst and released into the body cavity where they go to the salivary glands so SPOROZOITES are what are injected into the wound of humans where they go to our liver cells and start the asexual life cycle in humans
-BUT: ONLY THE ASEXUAL phase occurs in HUMANS!!!
key peripheral blood characteristics of each plasmodium species
-which makes distorted RBCs that appear oval and fimbriated?
-GIEMSA stain
-THICK: detect parasites
-THIN: speciation
-no anticoagulant
-prefer fingle or ear stick
-as fresh as possible
THIN: feather edge like heme
THICK: drop of blood size of dime and scratch the blood into the slide
recognize following life cycle stages and identify the plasmodium species they are associated with
§ Band form (MALARIAE)
§ Banana shaped gametocyte (FALCIPARUM)
§ Basket form (MALARIAE)
§ Ameboid trophozoite (VIVAX)
§ Ring form (MANY, MOSTLY FALCIPARUM)
§ Schizont with merozoites
§ Basophilic stippling (VIVAX, OVALE (all stages though))
§ Hemazoin (ANY?)
malarial parasites can look like what on PBS
-platelets
-Howell-Jolly bodies
plasmodium falciparum in PBS vs other plasmodium species
only rings!!!
life cycle stages of P. falciparum that is DIAGNOSTIC for this species
only RINGS!!!!
maurer's clefs possibly
importance of treatment malarial smears as STAT
-why speciation is critical for effective treatment of malaria
malaria falciparum is the worst one and all are treated a little differently!!
clinical symptoms of blackwater fever
-massive hemolysis after acute malaria that have hemoglobinuria, anemia, jaundice, fever
-DARK URINE SEEN!
caused by P. falciparum
principle of thick smear for parasites
-how is a thick smear made
-what power is used to look at
-what parasites are screened for?
POWER?
stain used to examine blood smears for parasites
GIEMSA!
hemazoin
malarial pigment from when a young trophozoite is eating hemoglobin
which plasmodium species have a LIVER PHASE that can persist and lie dormant?
-VIVAX!
-lies dormant until some event like immmunosupression is triggered
Plasmodium vivax
-widest distribution
-tertian life cycle = 48 hours (fevers every 48 hours)
-invades YOUNG RBCs and will take shape of the growing organism within
-trophozoite form grows within the cell and becomes ameboid (fingers reaching to the edges of the cell containing vacuoles)
-it will fill the RBC until it becomes a mature schizont which has about 12-24 merozoites inside (usually 16 which helps to identify)
-SHUFFNER'S DOTS: fine pink stippling of RBCs
-all stages from ring to gametocytes can be seen in PBS
-more pale appearance
-cells will be enlarged compared to nearby ones if parasite present
Plasmodium malariae
-all stages can also be found in PBS (like vivax)
-QUARTAN malaria cause life cycle is 72 hours
-infects older RBCs (not reticulocytes)
-since walls are more fixed in old cells, the parasite does NOT enlarge the cells
-BAND OR BASKET APPEARANCE!!! trophozoites
-mature schizonts have 6-12 merozoites (daisy or rosette looking)
-more vibrant color
-no relapse bc no liver phase like vivax
-ring form is a bit thicker
-no stippling present
-lowest parasitemia present
Plasmodium ovale
-very similar to vivax SO PRODUCES THE DOTS, RBCS WITH FIMBRIATED EDGES, but only has 8 merozoites usually!!!
-less severe and replases less
-young RBCs
-48 hour life cycle
-CELLS BECOME OVAL SHAPE!! with frayed irregular edges (fimbrionated)
-RBCs are stippled even in ring stage (with vivax only stippling in advanced stages)
-mature schizont has 8 merozoites (12-14 in vivax)
-heavy stippling in all stages!!
Plasmodium falciparum
-most aggressive and fatal
-RBCs of all ages
-schizogony occurs in spleen, liver, BM, etc. so very rare to see early rings --> gametocytes
-ischemia (low oxygen to tissues) because of plugging of vessels bc of parasitized RBCs prodcues a wide range of symptoms
-blackwater fever and cerebral malaria!!
-RBC rosettes (infected RBC surrounded by 3+ uninfected RBCs)
-MANY RING FORMS!!! with very high parasite load
-only rings seen!!!!
-no distortion of RBCs
-Signet rings: look like thye are pasted to the outside of the cell
Babesia
-vector of transmission
-morphology on smear
-geographic distribution
-TICKS
-similar to malaria
-Microti is main species in the US
-nantucket fever from microti
-dark staining nuclei
-ring form is the most common so can be confused with P. falciparum
-CAN BE EXTRACELLULAR!!!!
-MALTESE CROSS (not common but diagnostic)
-will never have hemozoin
-schizonts and gametocytes are NEVER present so this would indicate P. falciparum
-the rings often vary in size while malarial ones don't
-usually no antibiotics needed
-lag time between transmission of infection is about 50 hours so remove ticks ASAP!
BLOOD AND TISSUE #2 LECTURE
protozoa vs worms
PROTOZOA: unicellular
WORMS: multicellular
eosinophilia is only seen with
WORM infections not protozoa!
hemoflagellates (protozoa) and filarial worms (round worms = nematodes) are transmitted by
ARTHROPOD!
Hemoflagellates
-Leishmania species
-Trypanosoma cruzi
-Trypanosoma brucei
MOTILE VS NONMOTILE
motile = in blood
nonmotile = in tissues
Leishmania species
-amastigote: non-motile stage
-amistigote found in macrophages!
-SAND FLIES!
-mostly South America!
-promastigote: motile stage in blood (not as often seen i guess)
VISCERAL:
-fever, panctopenia, hepatosplenomegaly
-fatal if not treated with antimony (also toxic)
CUTANEOUS:
-lesions
MUCOCUTANEOUS:
-in the nose or mouth
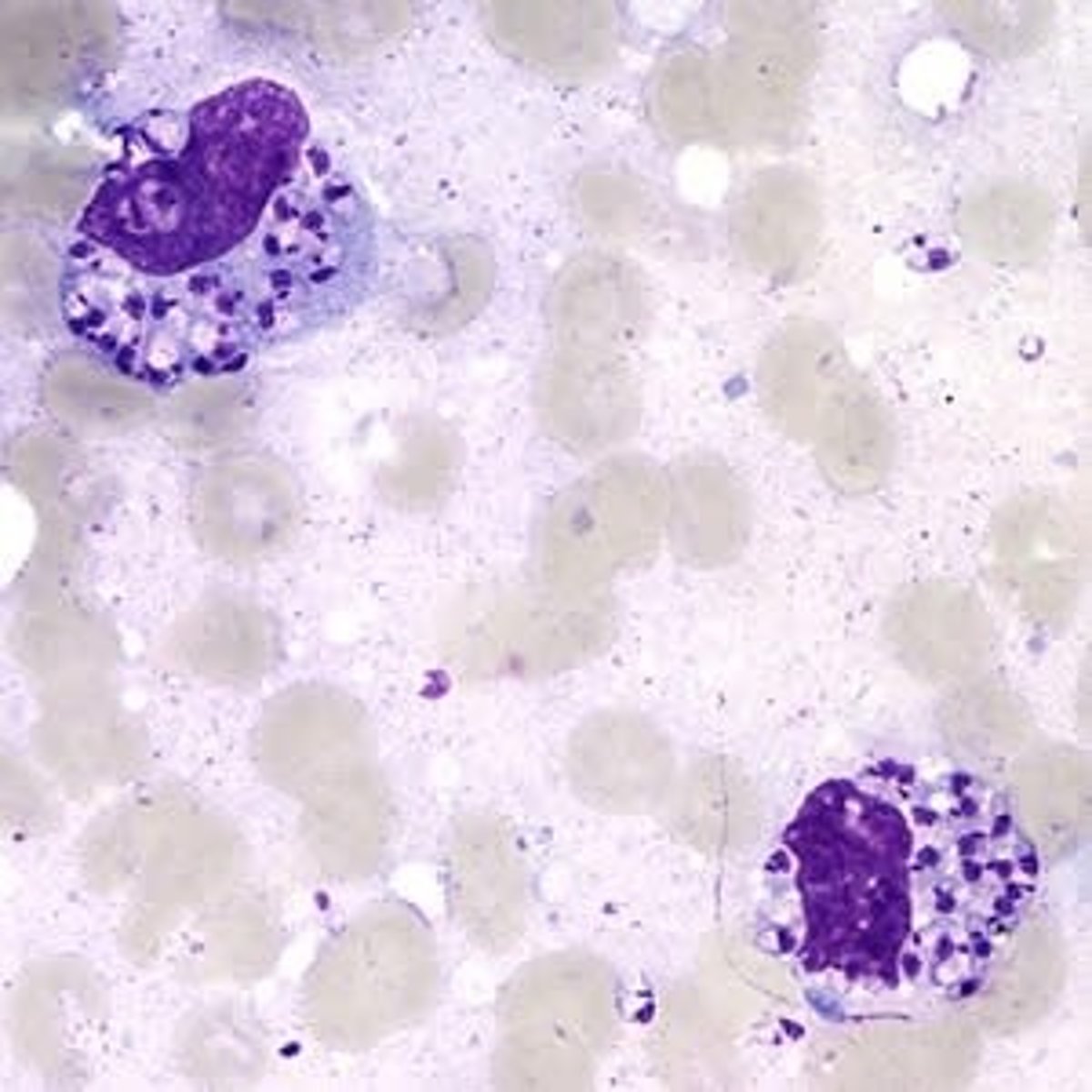
Trypanosoma cruzi
AMERICAN TRYPANO (south and central america)
-trypomastigote in blood
-causes CHAGAS disease!!!
*mostly asymptomatic
*ACUTE: romana's sign (eye swelling)
*CHRONIC: mega-syndromes
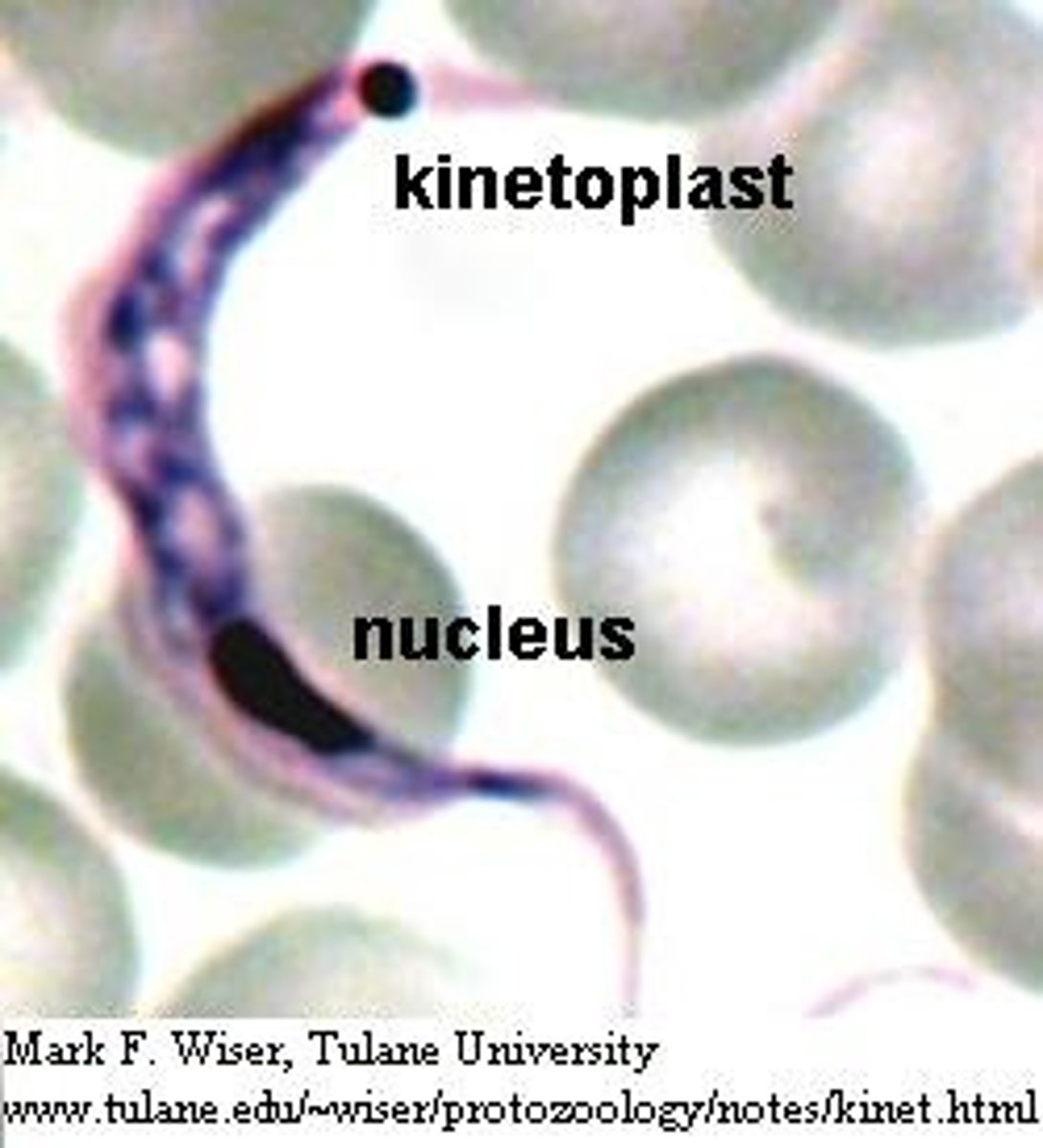
-C SHAPE!
-undulating membrane
-flagella, large, bulging kinetoplast that fills the posterior portion
-KISSING BUG is the vector
-more C shaped and the kinetoplast iS MUCH BIGGER!!!!!
kinetoplast
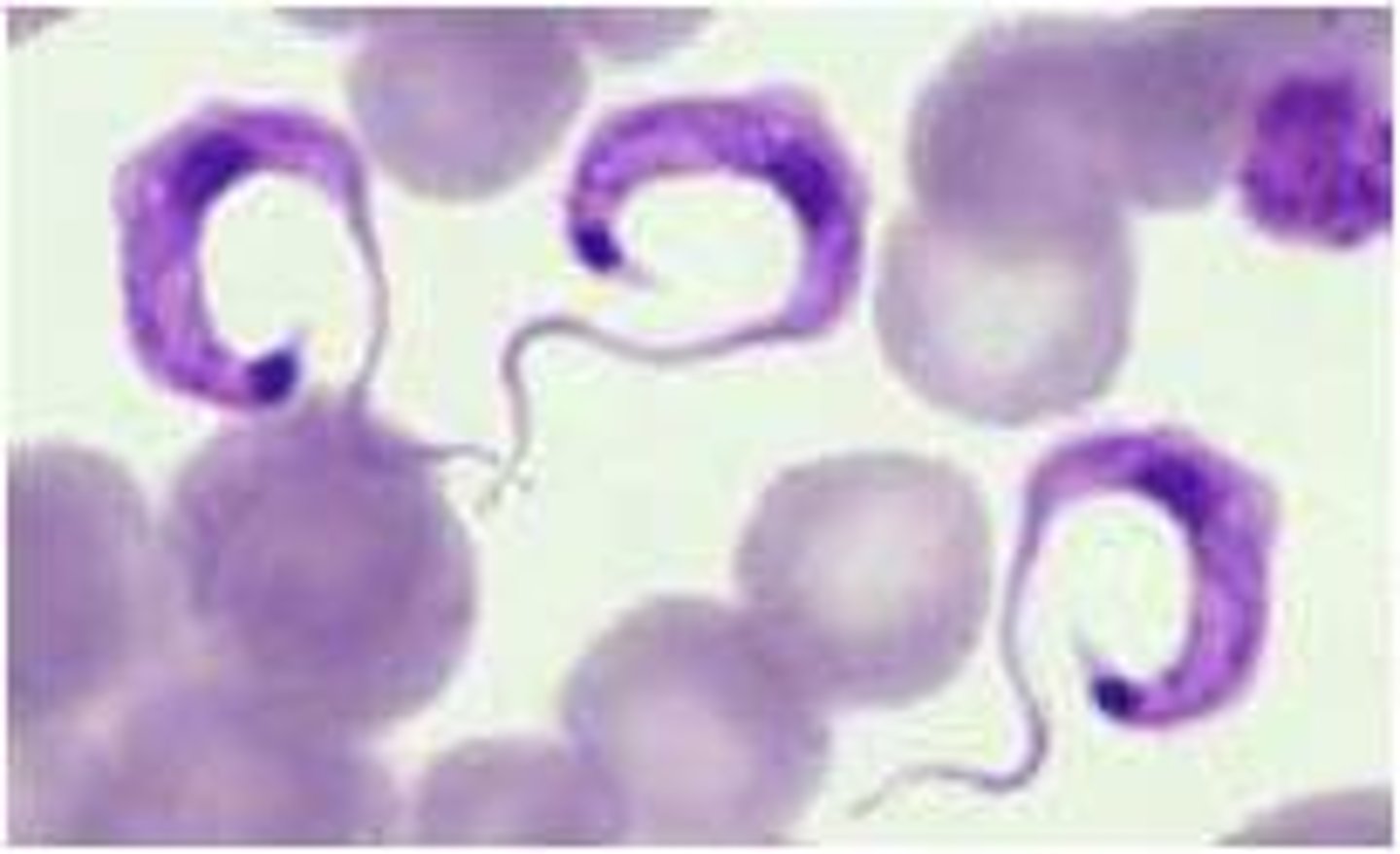
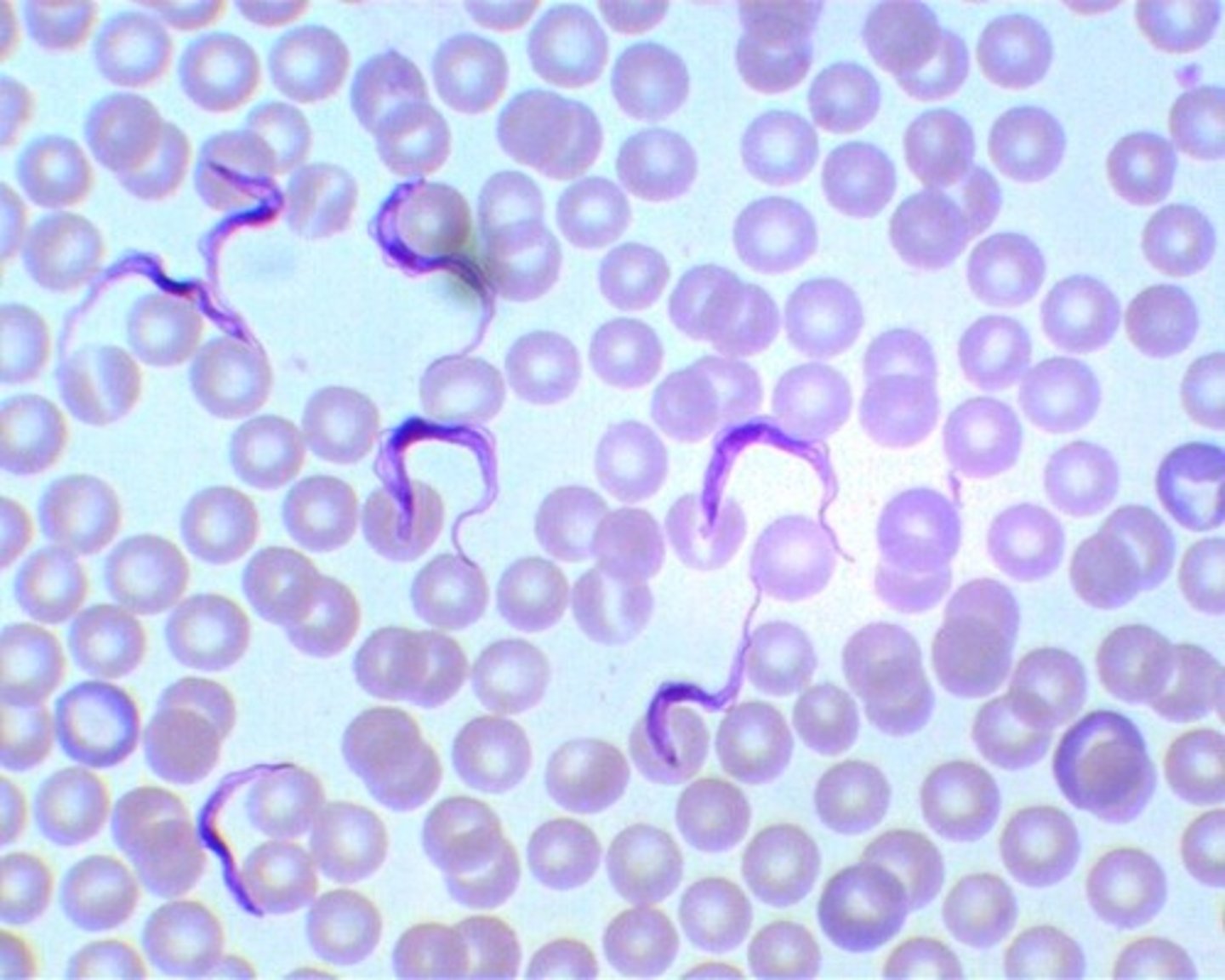
Trypanosoma brucei
-AFRICAN TRYPANO!!!
shape of kinetoplast here is small, compact dot
-african sleep sickness!!!
-transmitted by Tsetse fly
-early (no CNS): CHANCRE and enlarged lymph nodes
-late (CNS) eventually you get inflammation of the brain and brain tissues
-tx is highly toxic to us
-in picture you can see flagellum
-kinetoplast kinda
Filariasis
-macroscopic round worms and their offpsring (microfilariae)
-transmitted by mosquitos, black flies, deer flys, and midges
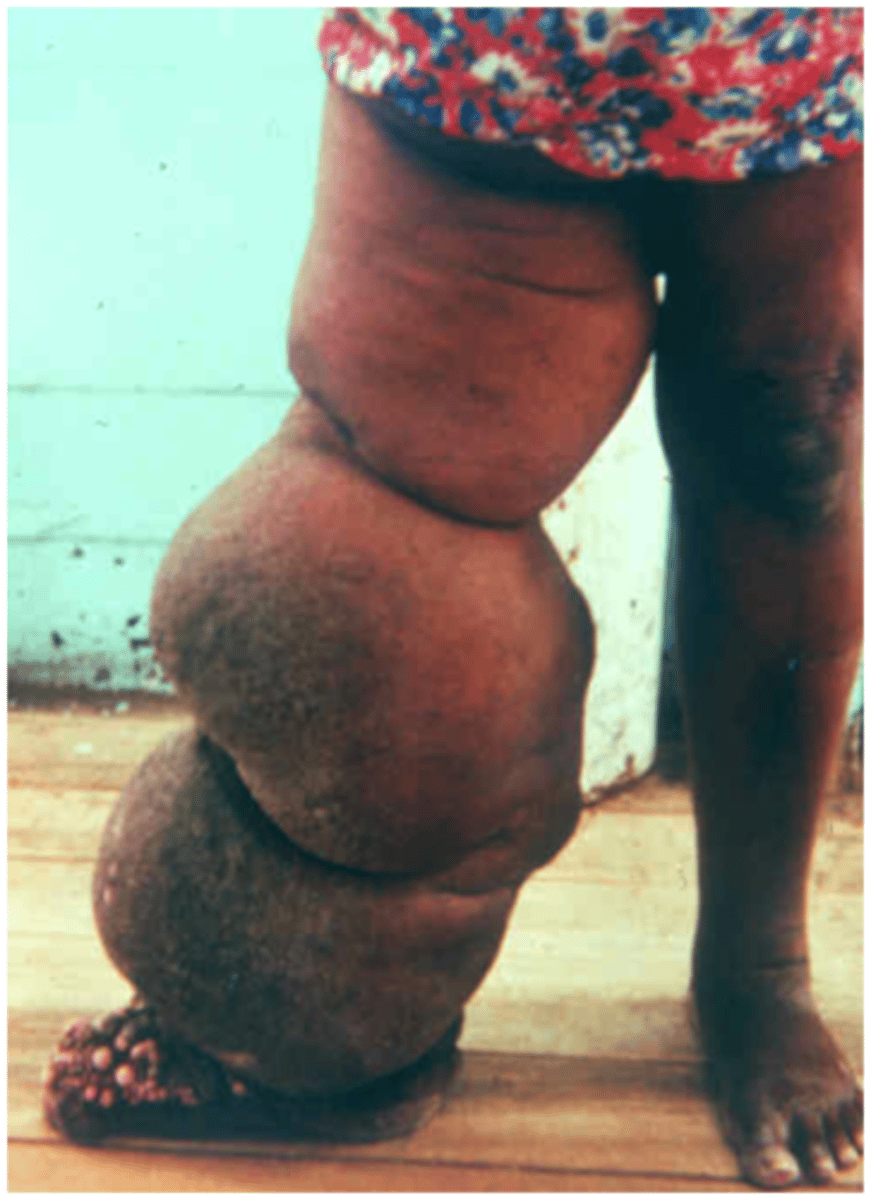
Lymphatic filariasis
-wuchereria bancrofti
-brugia species
-MOSQUITOS
-adult worms infiltrate the lymph tissues
-larvae (microfilariae) are seen in the blood!!!
-found in blood around midnight!!!
ADD HOW TO DIFFERETIATED BASED ON THE IDENTIFICATION OF SHEATH, ETC WHEN SHE TALKS ABOUT IT!!!
Migrating eye worm
-loa loa
-found in blood around 12pm!!
-DEER FLY *CHRYSOPS*
-
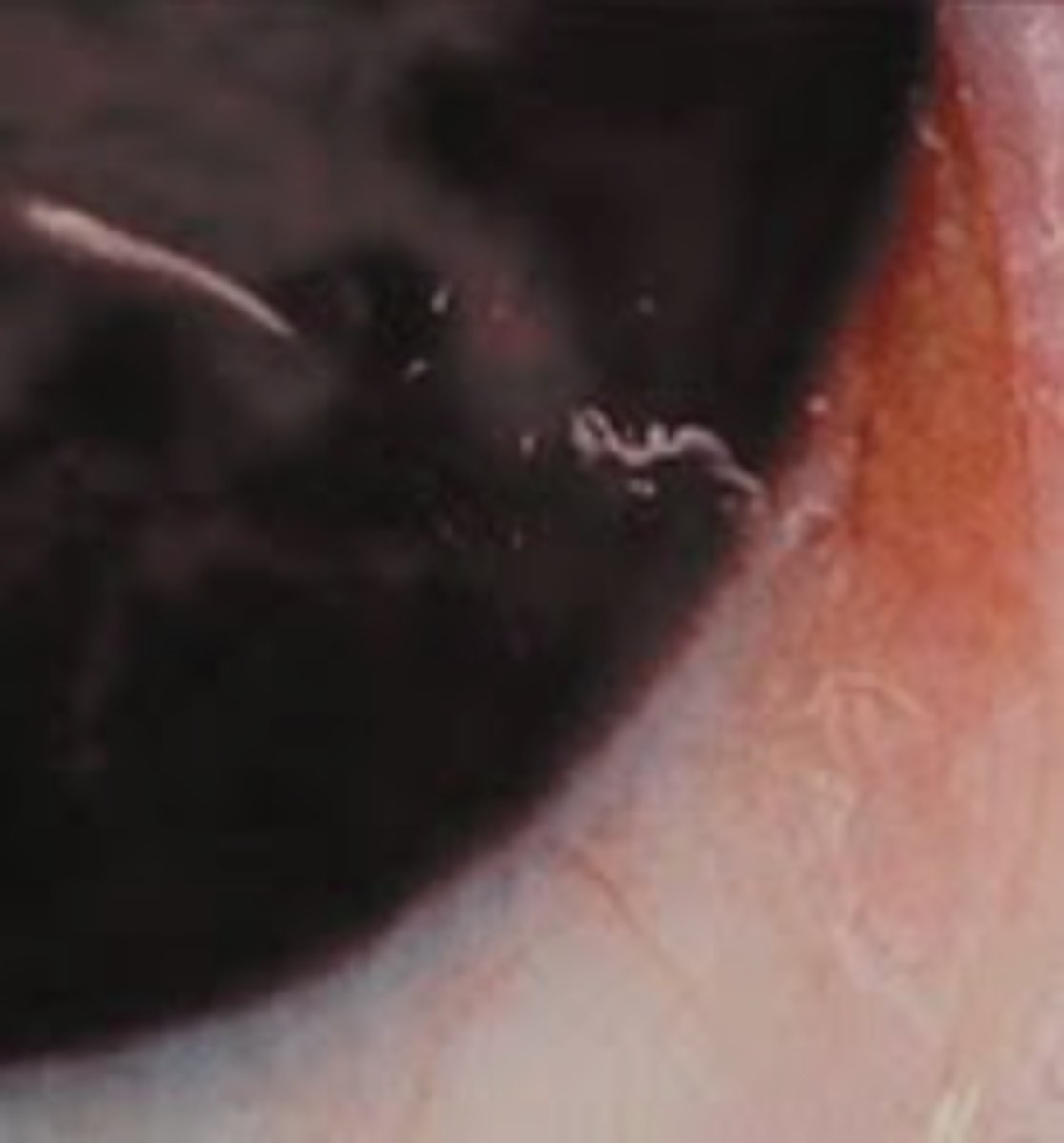
skin/tissue filaria
-onchocerca volvulus
-RIVER BLINDNESS
-from a BLACK FLY!
-fast flowing rivers in africa and central america
-DON'T LOOK AT BLOOD BUT AT SKIN SNIPS!!!
Starting BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS #3
Protozoa: Toxoplasma gondii
-life cycle
-host
-modes of transmission
-what it looks like in tissue/key characteristics (tissue cysts with bradyzoites)
-protozoan
-sexual: only in cats (definitive host)
-asexual: mammals/humans (intermediate host)
-you get it from undercooked cow meat and CHANGING THE LITTER BOX!! OR BY ORGAN TRANSPLANT!!
-immunocompetent: mild, could look like mono
-congenital is when pregnany and very bad
-immunocompromised worse
-look for tissue cysts to diagnose maybe called BRADYZOITES? (or free tachyzoites)
-you look for the crescent shaped trophozoites coming out of a cell usually
-the tachyzoites are inside of cysts that ruptures and release the free tachy or trophozoites
-it causes MULTIFOCAL BRIAN LESIONS IN AIDS PATIENTS!!
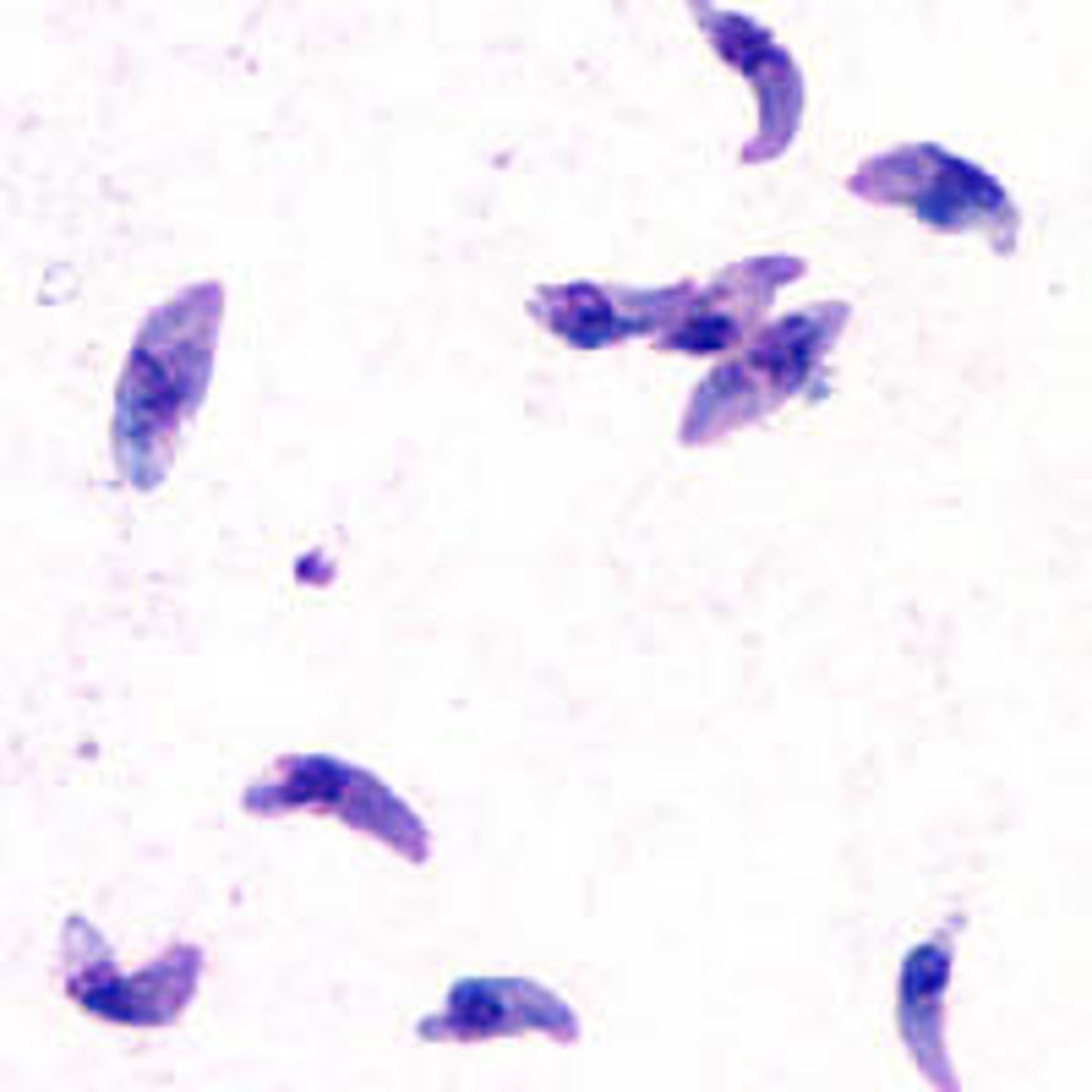
Free Living Amebae
*N. fowleri
*Acanthamoeba spp.
*Balamuthia mandrillaris
-which affect humans
-organism --> Disease?
-mode of transmission
-trophozoites and cyst stages key microscopic features
-protozoa that live in soil or water
-exist in nature as trophozoites or cysts
-free living and don't need humans but a few can affect us
-involve the CNS and the eye (for acanth only)
CNS:
-primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is for Naegleria
-secondary: granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) is for Acanth and Balamuth
acanth has a crinkly edge to the cyst and double walled; and lacy cell with a nucleus for the troph form with a vacuole that expands to eat the bacteria
PAM (Primary amebic meningoencephalitis)
-Naegleria fowleri
-infects healthy children swimming in infected water
-"brain eating ameoba"
-WARM, STAGNANT FRESH water
-ALWAYS FATAL!!!
-can see motile trophozoites (this is the only form that is seen in humans)
-goes to MENINGES and the brain so CSF can be a sample type
-look in CSF for this and see what the picture shows
-we use PCR at mayo though
-primary cause it goes right from the nose to the brain
GAE (granulomatous amebic encephalitis)
-*Acanthamoeba spp.
-*Balamuthia mandrillaris
-from skin to brain!!!
-immunocompromised
-all types of water
-both trophozoite and CYST seen in humans
**Acanthamoeba spp. can also cause Amebic Keratitis which is much more prevalent!
-biospy tissue for cysts and trophozoites
-PCR
-just goes to the brain and really only in immunocompromised!
-secondary because it goes to the blood first before brain!
Amebic Keratitis
-cornea infection
-contact wearers
-biopsy tissue
Acanthamoeba spp
principle and procedure:
-Formalin-Ethyl Acetate Concentration Method
-stool
-look for eggs or parasites
-CONCENTRATES the stool for part 2!
FORMALIN: decontaminate, less infectious
ETHYL-ACETATE: traps particulate matter/debris
ova and parasite examination:
-main components (direct exam, exam of fixed and concentrated specimen, wet prep, and permanent stain)
1: direct exam of fresh stool (not part of CDC required part, mayo doesn't do)
*motile trophozoites and motile larvae only in fresh, unfixed stool
2: exam of fixed spcimen: CONCENTRATED
*removes fecal debris
*wet prep at 10x and 40x
*IODINE: highlights protozoa features (mayo doesn't do)
*uses centrifuge to concentrate/sedimentation
3. exam of fixed specimen: UNCONCENTRATED
*permanent TRICHROME stain!!
*confirms wet prep findings in part 2
*100x!!!
types of stains used to examine the permanent smear preparation
-iron hematoxylin stain
-trichrome stain**more common now
why we collect 3 fecal specimens every other day before ruling out an infection
parasites are sporadically made so this ensures we see the parasite
why ELISA tests for Giardia intestinalis and Cryptosporidium are preferred over the 'ova and parasite' exam in the US
-more specific, quicker!
-some things can be destroyed in an O&P
differentiate debris vs organic matter in direct exams from parasites
STARTING INTESTINAL PROTOZOA
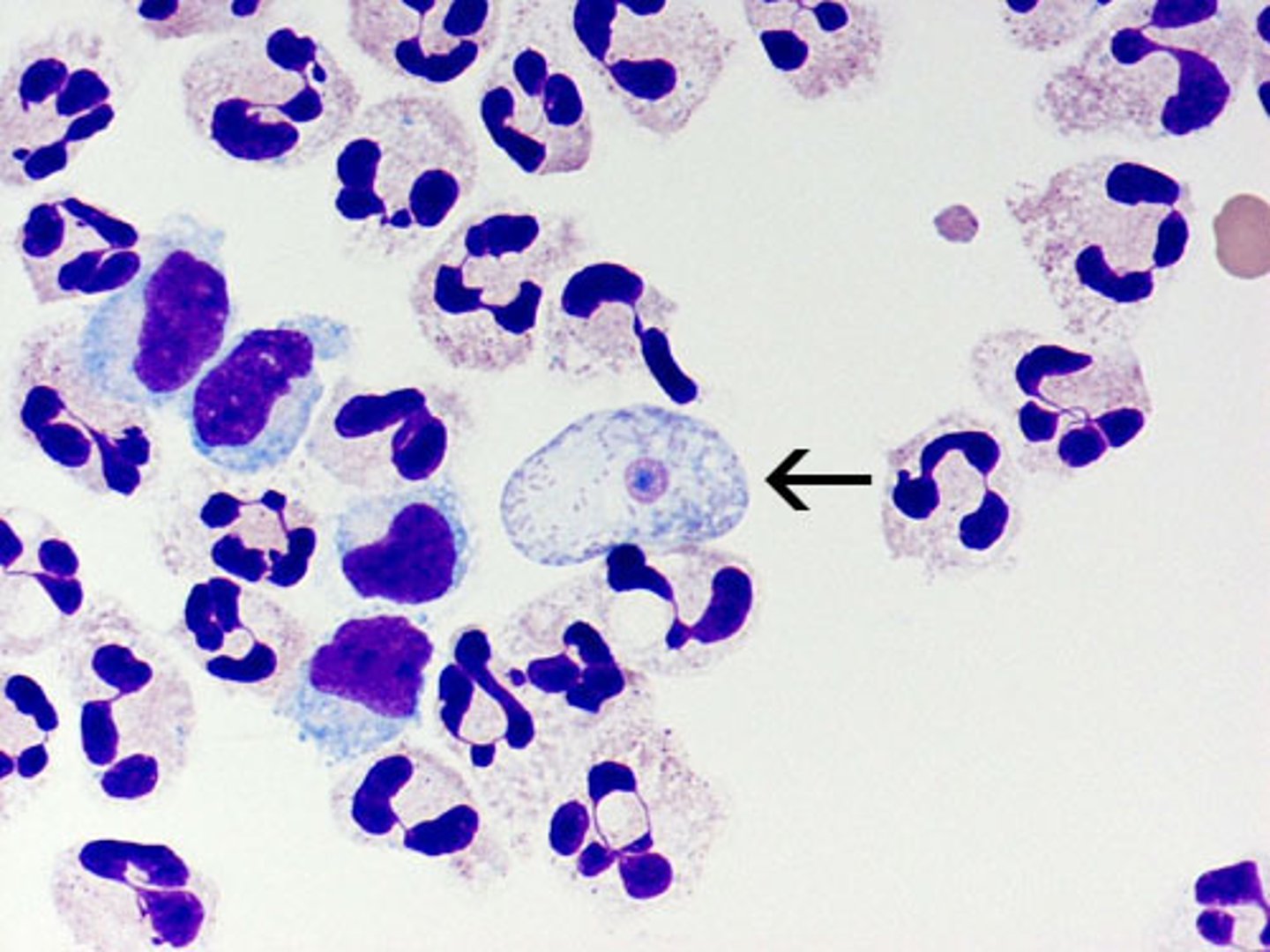
Amebae: Entamoeba histolytica
-clinical significance
-cyst and trophozoite forms
-key morphological characteristics
-unique from other entamoeba because it invades the gut!
-this is the only amebae to really cause infections in humans!!!!
-can be asymtomatic
-can be invasive and cause Amebic Dysentery (blood diarrhea + mucus) or go to liver and other organs
-BLOODYYYYY DIARRHEA
-AMEBIC DYSENTERY --> FLASK SHAPED ULCERS IN THE INTESTINE
-Dissemination to the LIVER produces necrotic tissue that looks like ANCHOVY PASTE!
-Exactly the same look as E. dispar unless ingested RBCs meaning histolytica!!
-E. dispar is COMMENSAL but looks the exact same!
-DIRECTIONAL MOTILITY in fresh specimens
-nucleus is ring + dot shape
*karyosome is like a nucleolous so it has a ring of black and then a black dot (pictured)
-mature troph has 1 nucleus with central karyosome
-mature cyst has 1-4 nuclei
-chromatoid bodies (pictured like black coal)
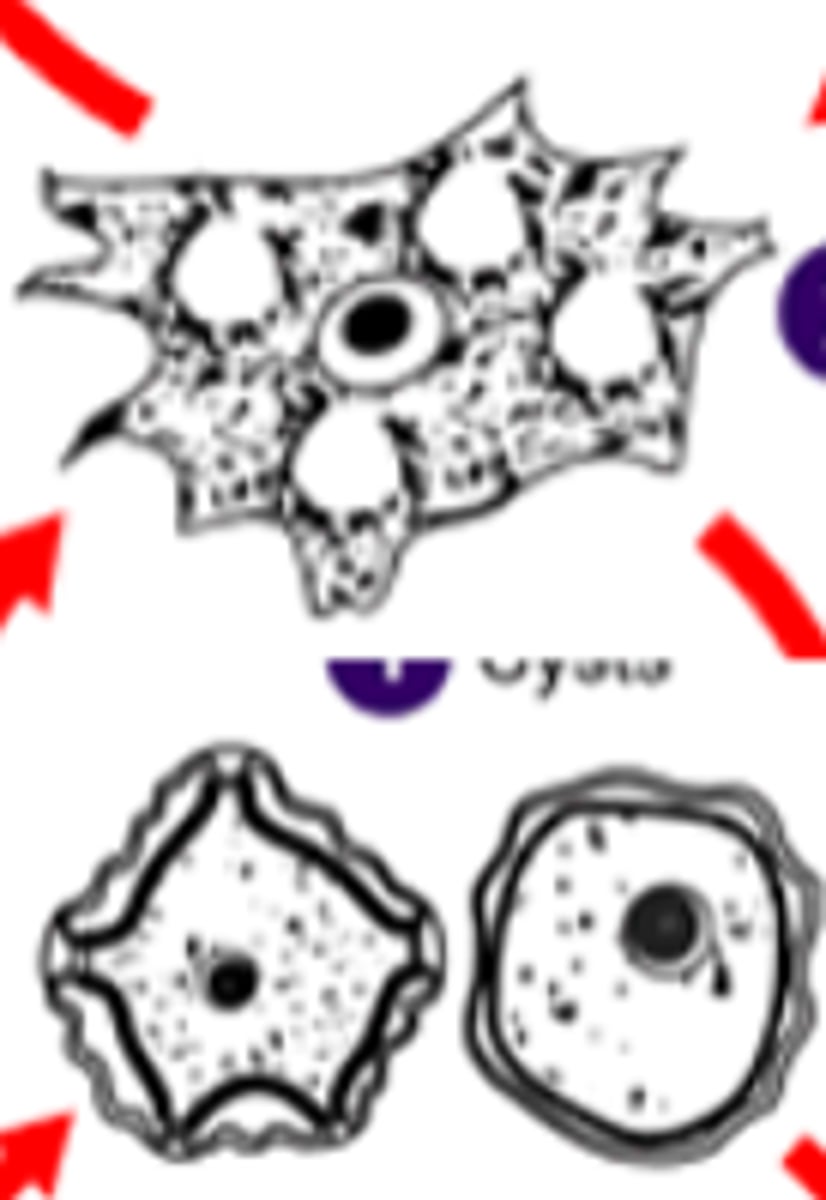
Amebae: non-pathogenic amebae
-significance of finding non-pathogenic amebae in a fecal specimen
-fecal contamination marker!!!
-Entamoeba harmtanni and Entamoeba coli are both commensal!
-Hartmanni cysts have 1-4 NUCLEI!!!!! just like histo but just SMALLER!!
-E.coli has 5-8 NUCLEI!!!! and larger than cyst!!
-E.coli's ring is more thick/thing, not so even with an accentric karyosome that looks like it's kinda bleeding inside of the nucleus
*E.coli also has slow UNDEFINED MOTILITY!
*make a chart with SIZES cause will be on practical?!
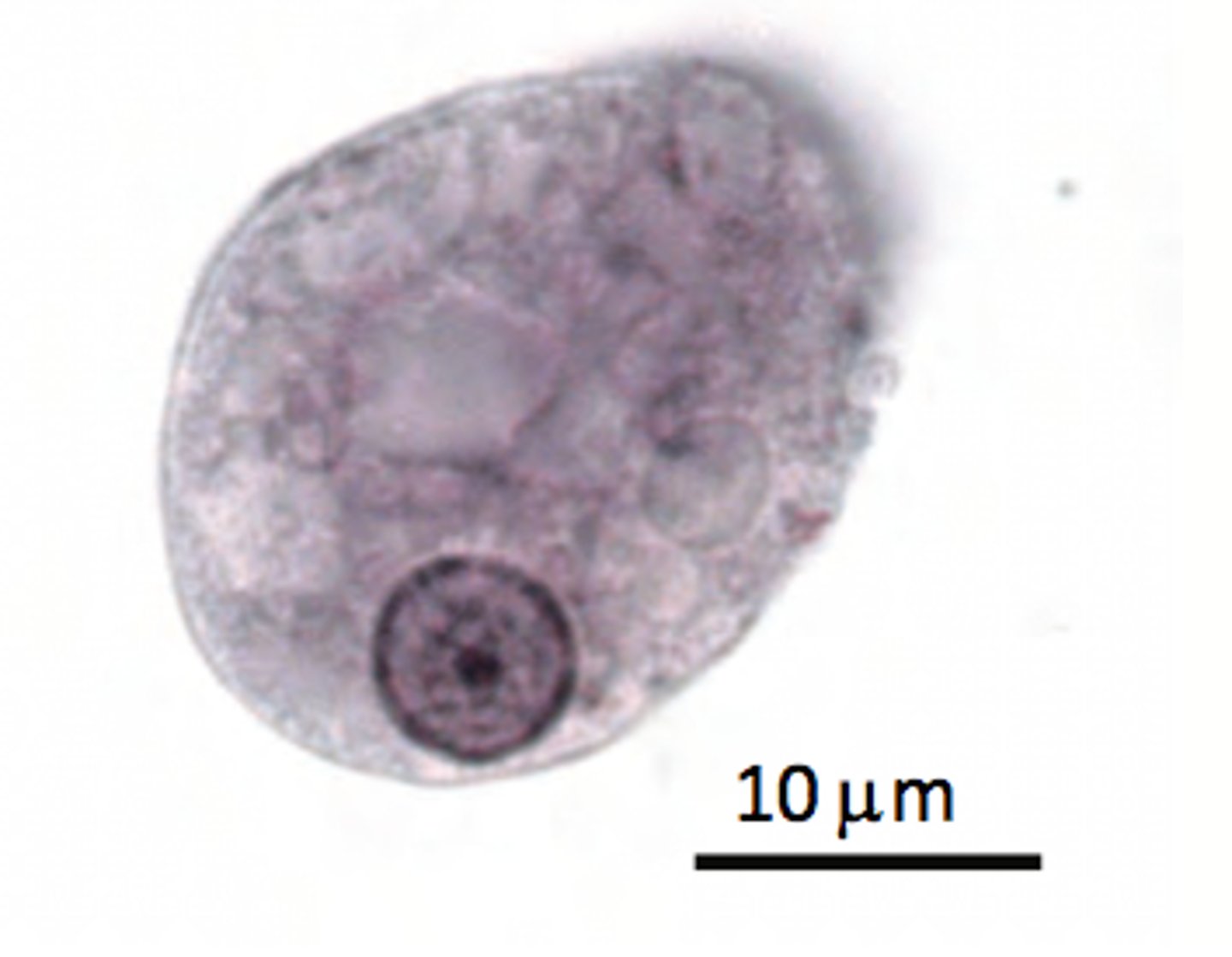
Amebae: ciliated amebae (Balantidium coli)
-how to identify microscopically!
-Balantidium coli (B.coli) is the only CILIATED one that causes disease in humans
-invasive intestinal parasite
-bloody diarrhea
-pigs!!!
-largest protozoan to affect humans too and the only ciliated one!
-kidney bean shaped nucleus in the cyst and the trophozoite has CILIA!
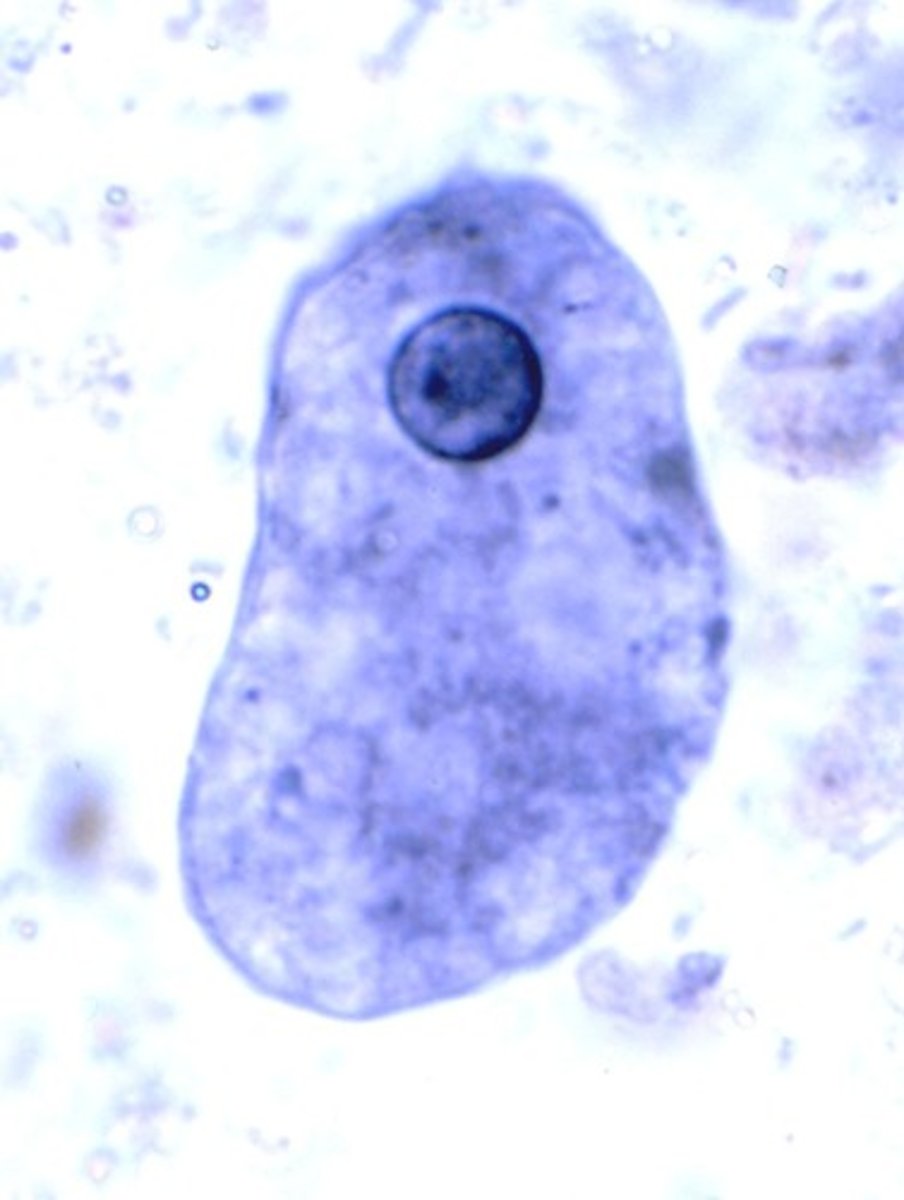
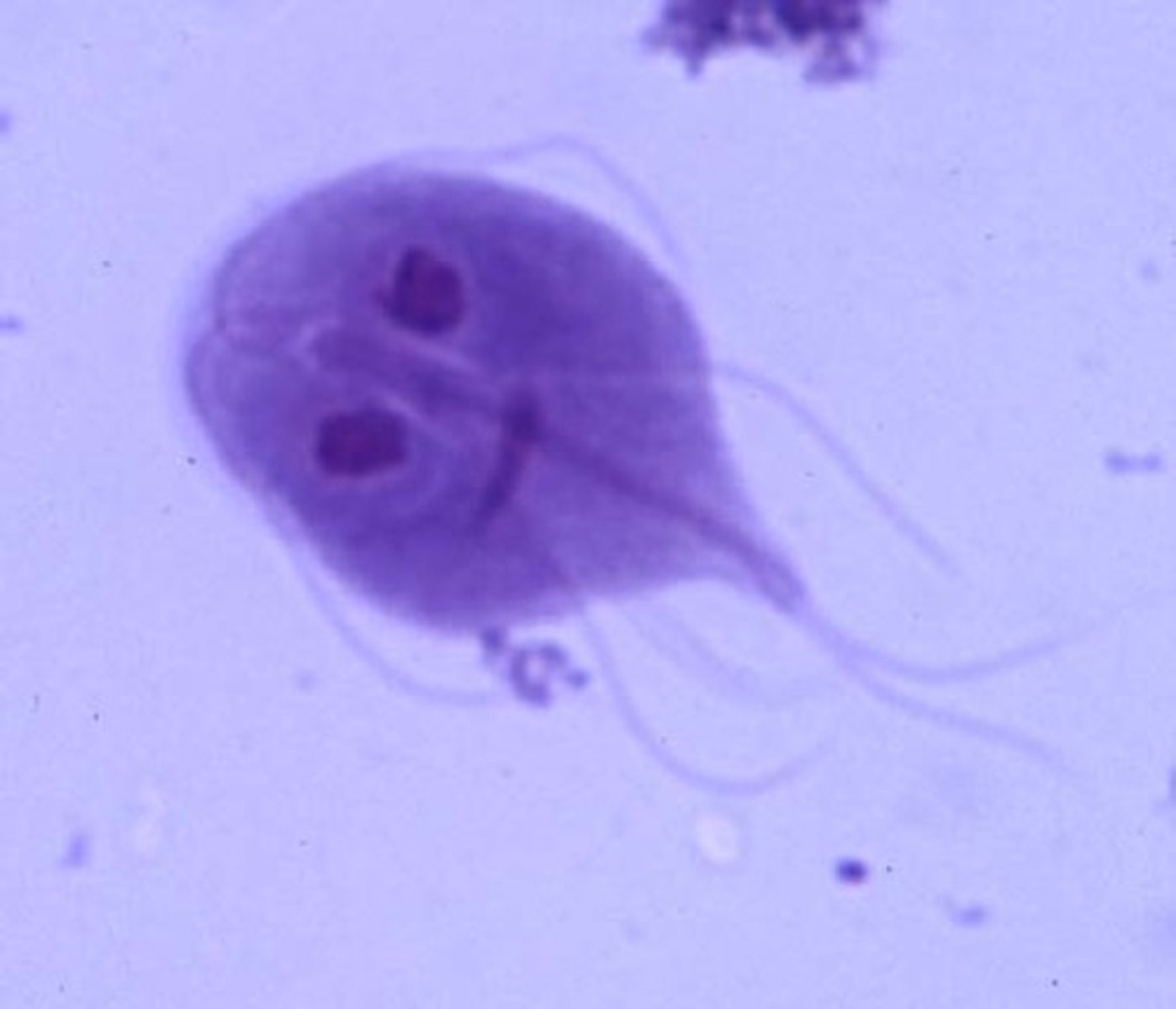
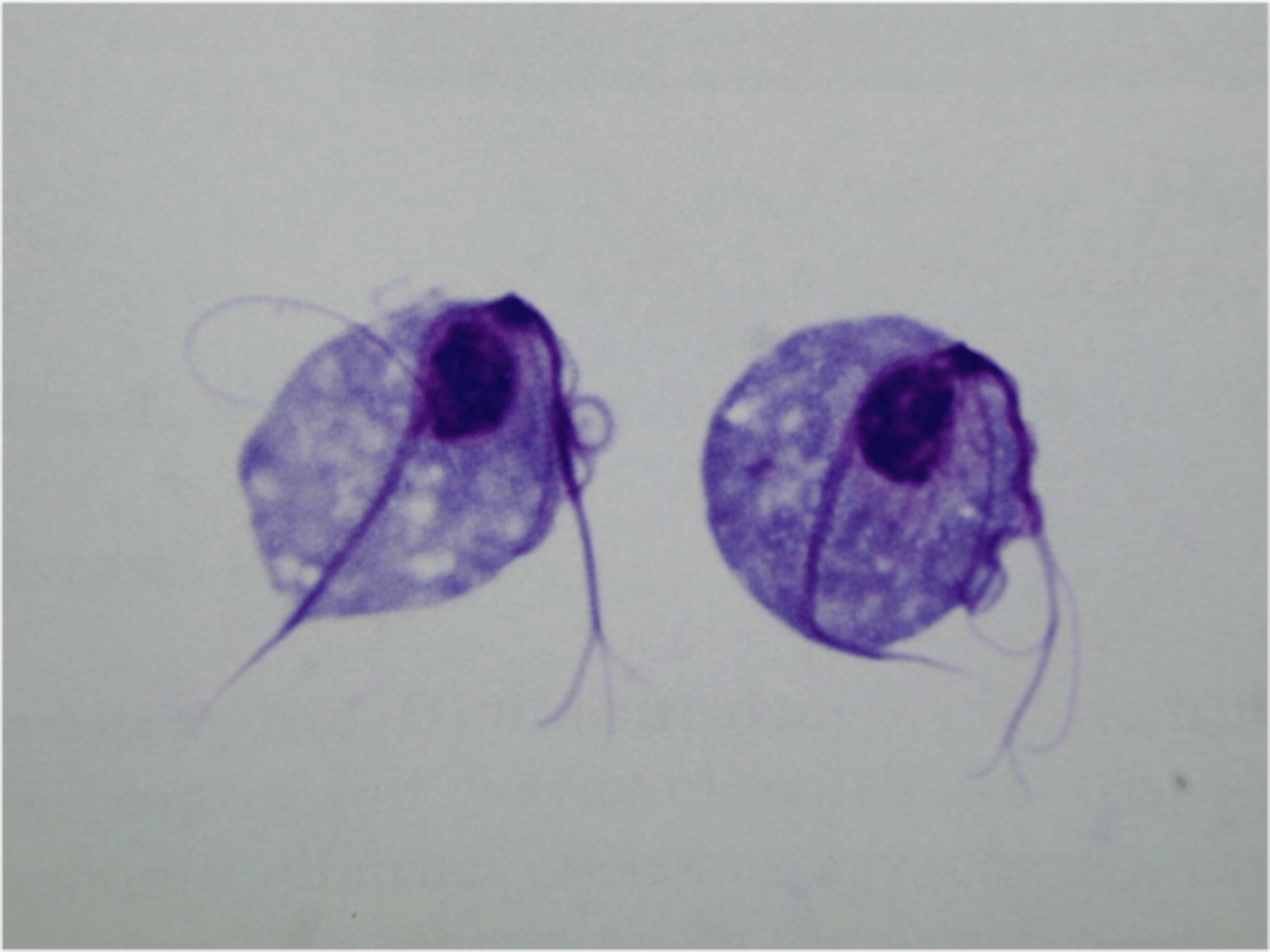
Flagellates: Giardia intestinalis (lamblia)
-cyst form in microscope
-trophozoite form in microscope
-MODES of transmission
-most common fecal parasite
-get from water mainly like hikers!
-trophozoite pictured
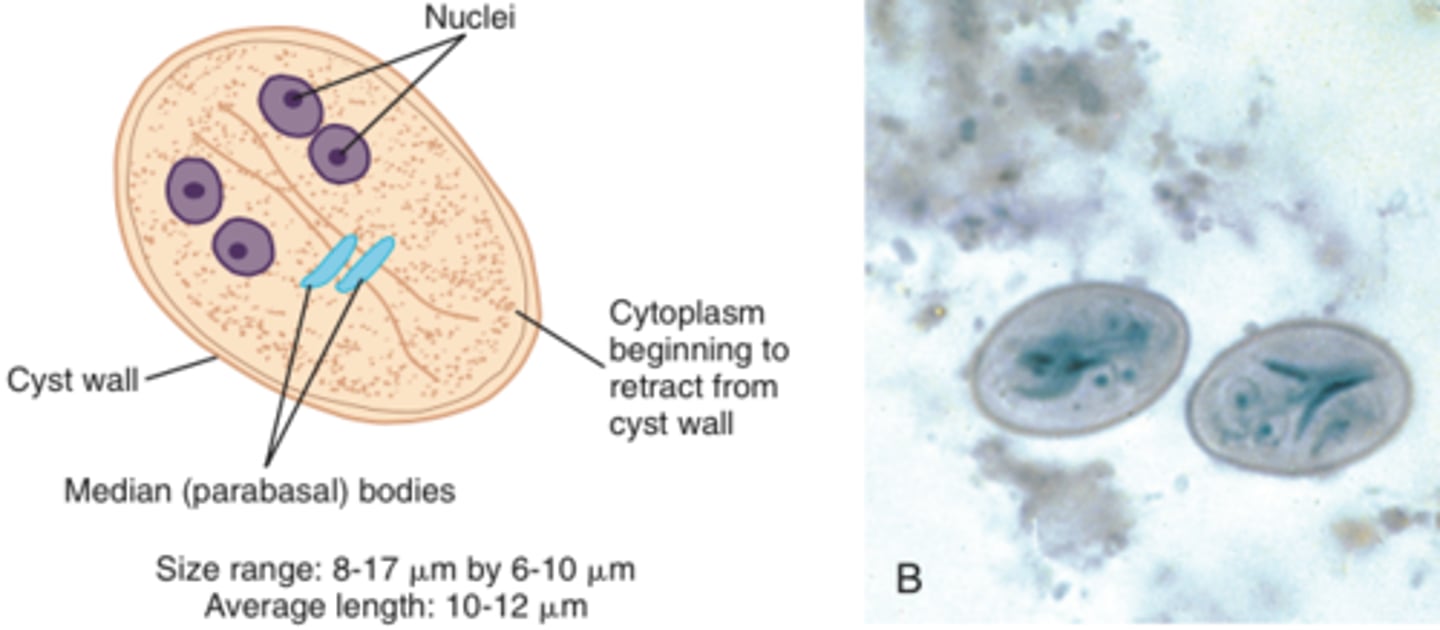
-the cyst form has a long line and curved bodies inside!
-tear drop with 2 NUCLEI, axoneme (up and down) and median bodies (curved things)
-in the eggs you can still usually see median bodies and axoneme
-has a 'sucker' that sticks to bowel
-cysts resistant to chlorine
-2 nuclei (comes from beaver with 2 big teeth)
-affects all ages
-person to person, food, etc!
-only need 10 to cause disease
-resistant to chlorine and other disinfectants
-the trophs bind to bowel lining and stop absorption leading to watery diarrhea
-WATERY DIARRHEA
-FOUL SMELLING FATTY FECES!!
-FALLING LEAF MOTILITY
-usually need 6+ stool samples so we use antigen detect and PCR now instead
*only need 10 to be infected
Giardia intestinalis cyst
pictured
Flagellates: Blastocystis hominis, and Chilomastix mesnili
-also flagellates!
-other flagellates but not pathogenic
-marker of fecal contamination
-Chilomastix mesnili cysts under microscope because of LEMON-SHAPE (cyclops like)
-Endolimax nana cyst looks like a BALL AND SOCKET! and racetrack shape. BLOT LIKE KARYOSOME!!!! BLOT LIKE!! and no PERIPHERAL CHROMATIN!! meaning it's jsut a dot? like a bowling ball!
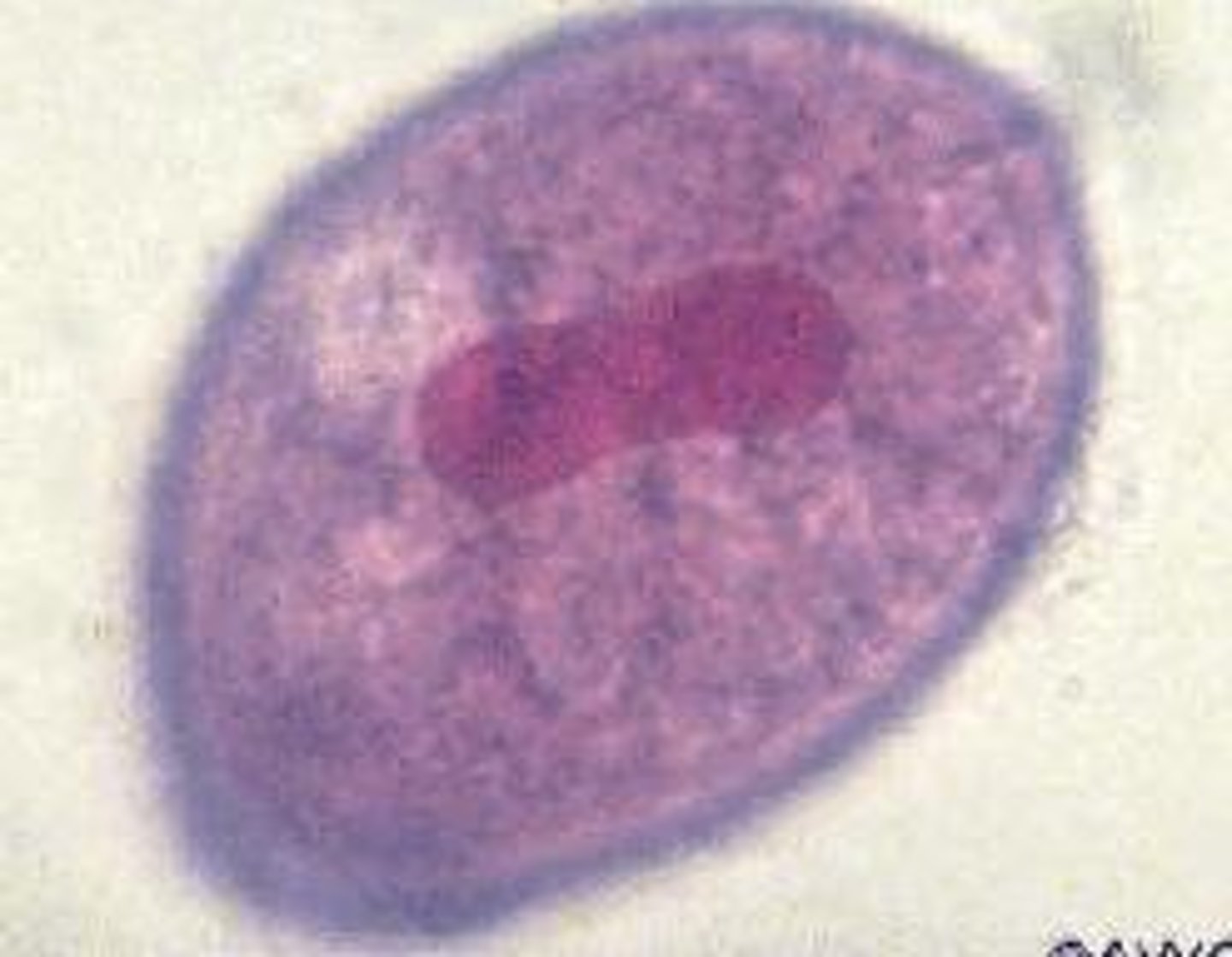
Dientamoeba fragilis (flagellate)
-internalized flagella
-best seen with permanent stains
-SEGMENTED NUCLEUS/KARYOSOME!! like a fist
-IBS????
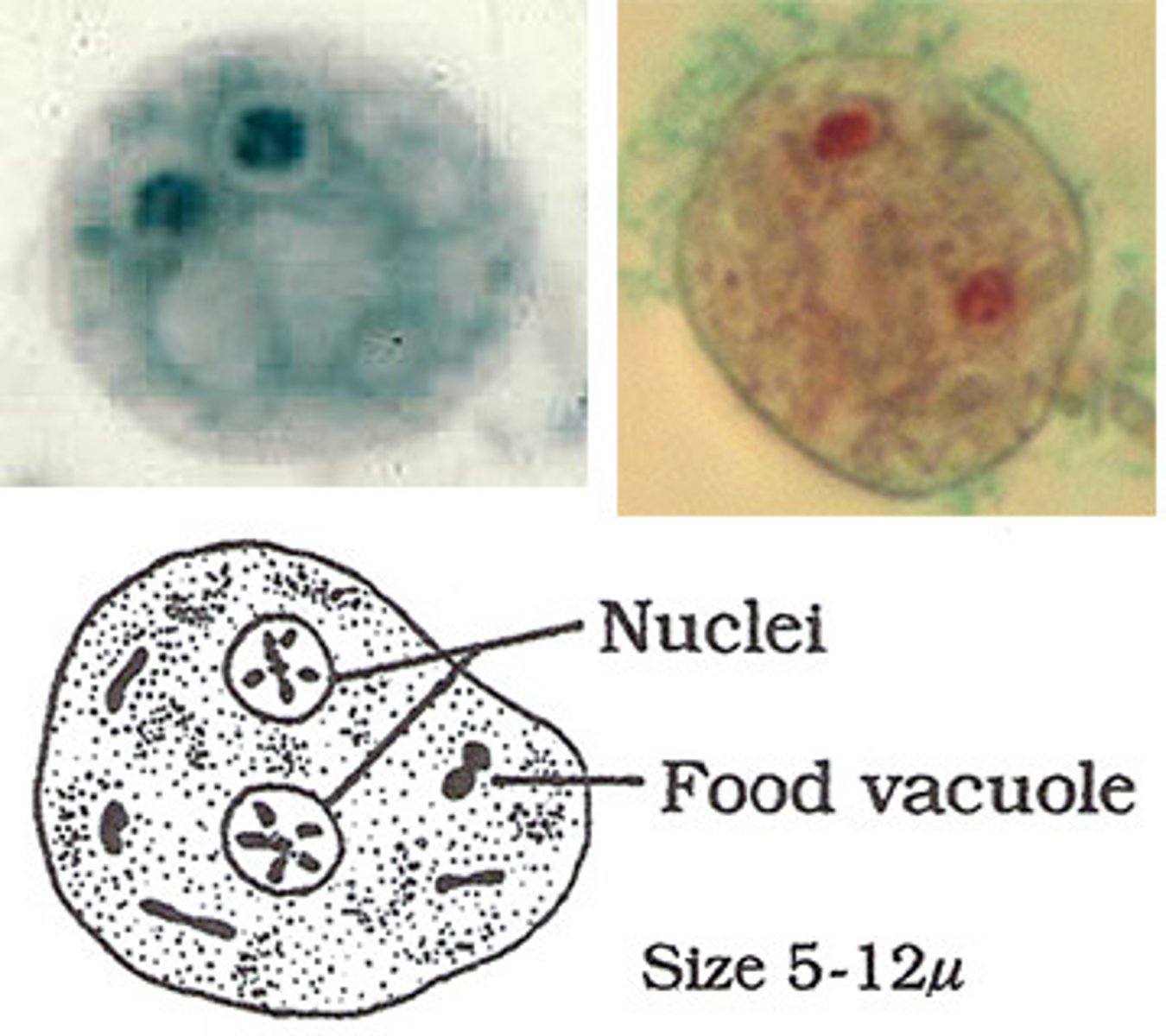
Blastocystis hominis
-very common
-IBS?
-central vacuole taking up most of the cell and nuclei pushed to outside!
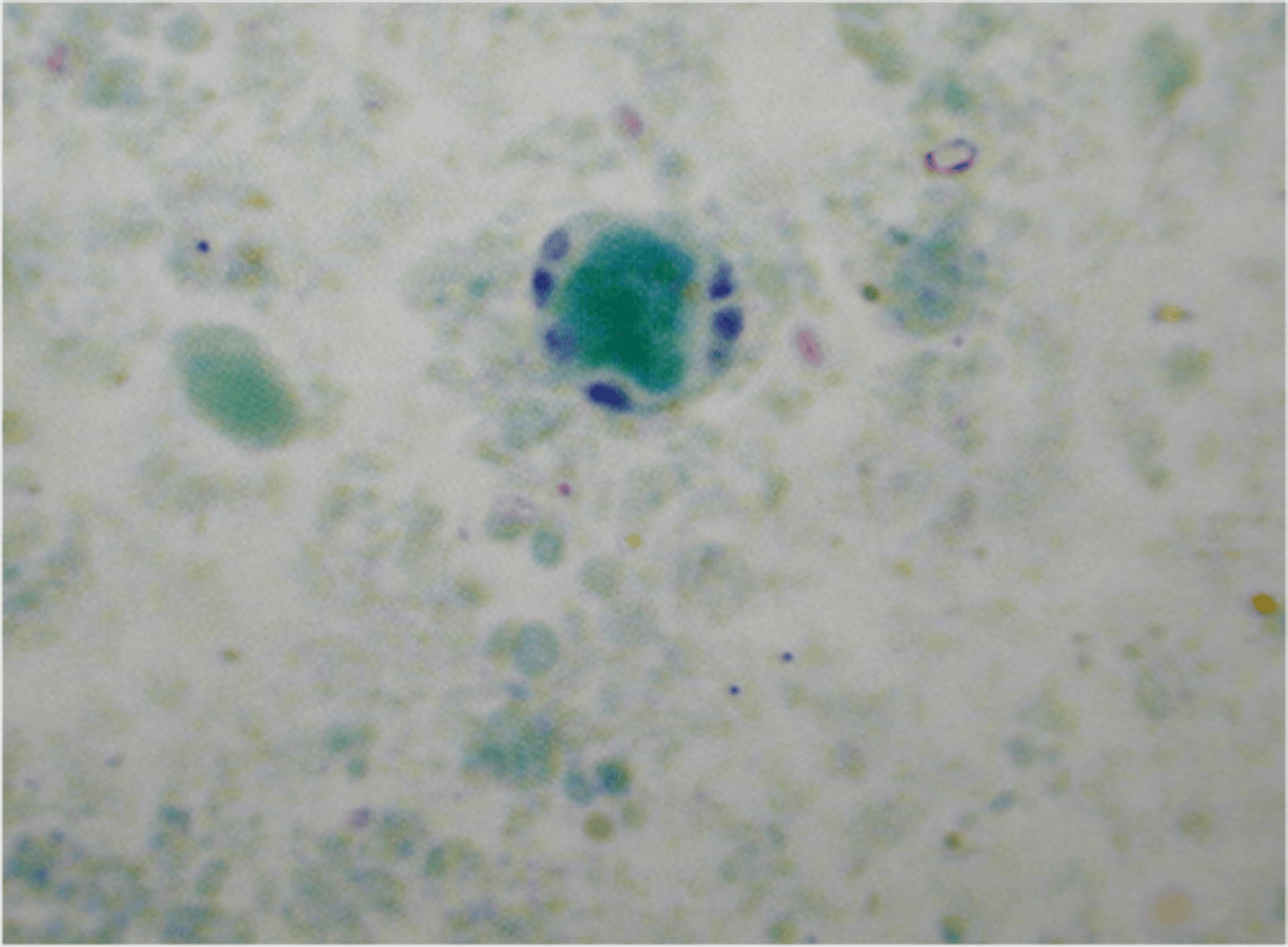
Flagellates: Trichomonas vaginalis
-most common non-viral STD
-trophozoite can't survive outside urogenital system (delicate)
-trophozoites have the protruding axostyle (like axoneme in giardia but sticks out so called axostyle)
-no cyst stage!
-asymptomatic or can lead to STRAWBERRY CERVIX!
-JERKY motility!!!!!
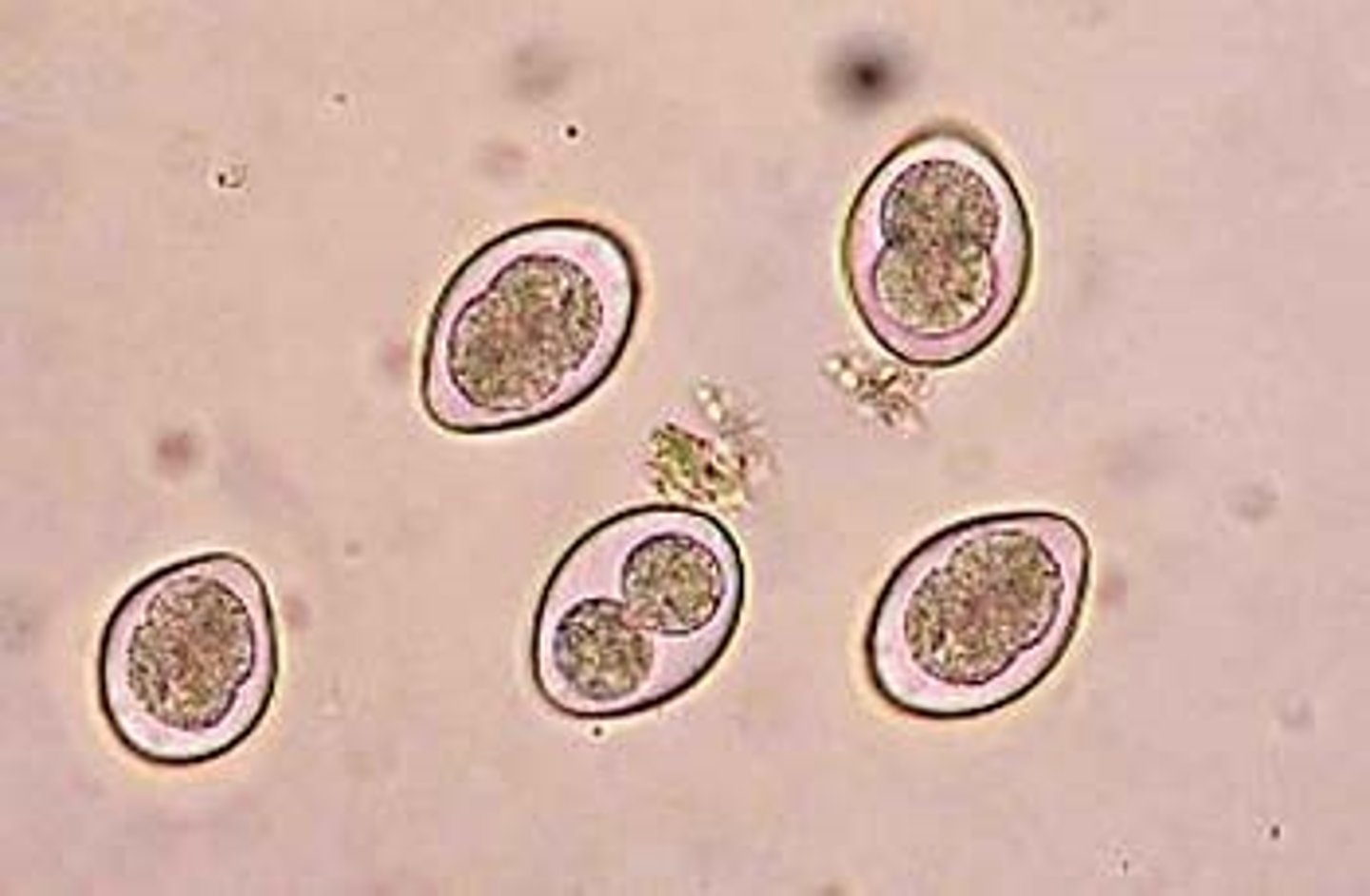
Coccidia
-which cause disease?
-clinical significance
-mode of transmission
-microscopic features in tissue
-stain procedure to examine smears for coccidia
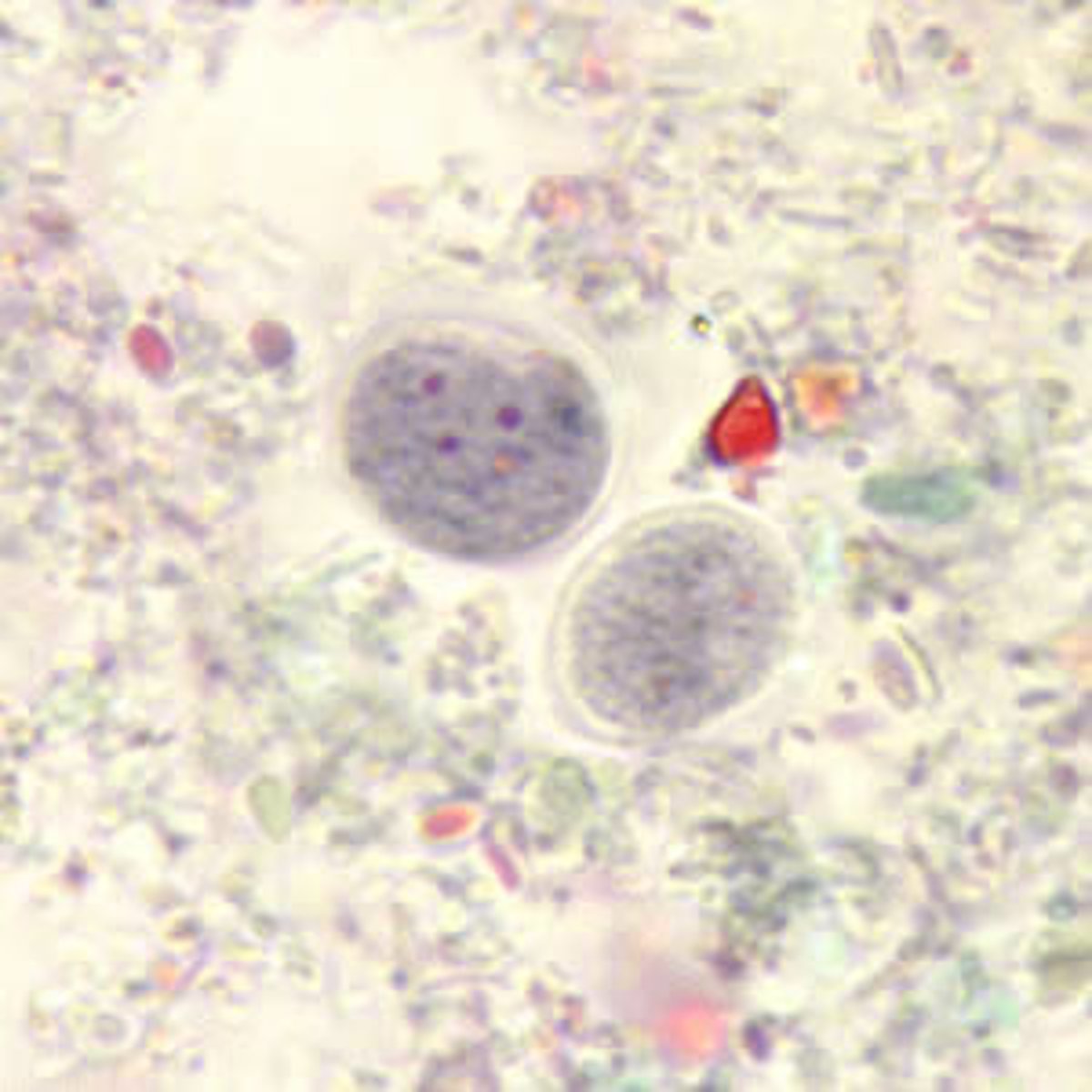
-cystoisospora (biggest)
*pictured i think
-cyclospora (middle)
*8-10 microns (bigger than RBC)
*only in humans ever!
*looks like destroyed bubble wrap dot to me
-cryptosporidium (smallest)
*c. parvum and hominis
*waterborne
*only need 100
*smaller than an RBC 4-6 microns
*from other animal poo
-watery diarrhea
-ingestion of fecally contaminated food or water
-modified acid stain: oocysts stain positive (RED) in tissues!
SEROLOGY IS BEST FOR
-chagas (american trypanosoma)
-T. gondii
-Entamoeba histolytica!