Data Models in Database Systems
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Data Modeling
Process of creating a specific data model.
Data Model
Simple representation of complex real-world data.
Database Designer
Professional who creates data models and databases.
Communication Tool
Data models facilitate understanding among stakeholders.
Database Blueprint
Overall design based on an appropriate data model.
Entity
Person, place, thing, concept, or event in data.
Attribute
Characteristic or property of an entity.
Relationship
Association among entities in a data model.
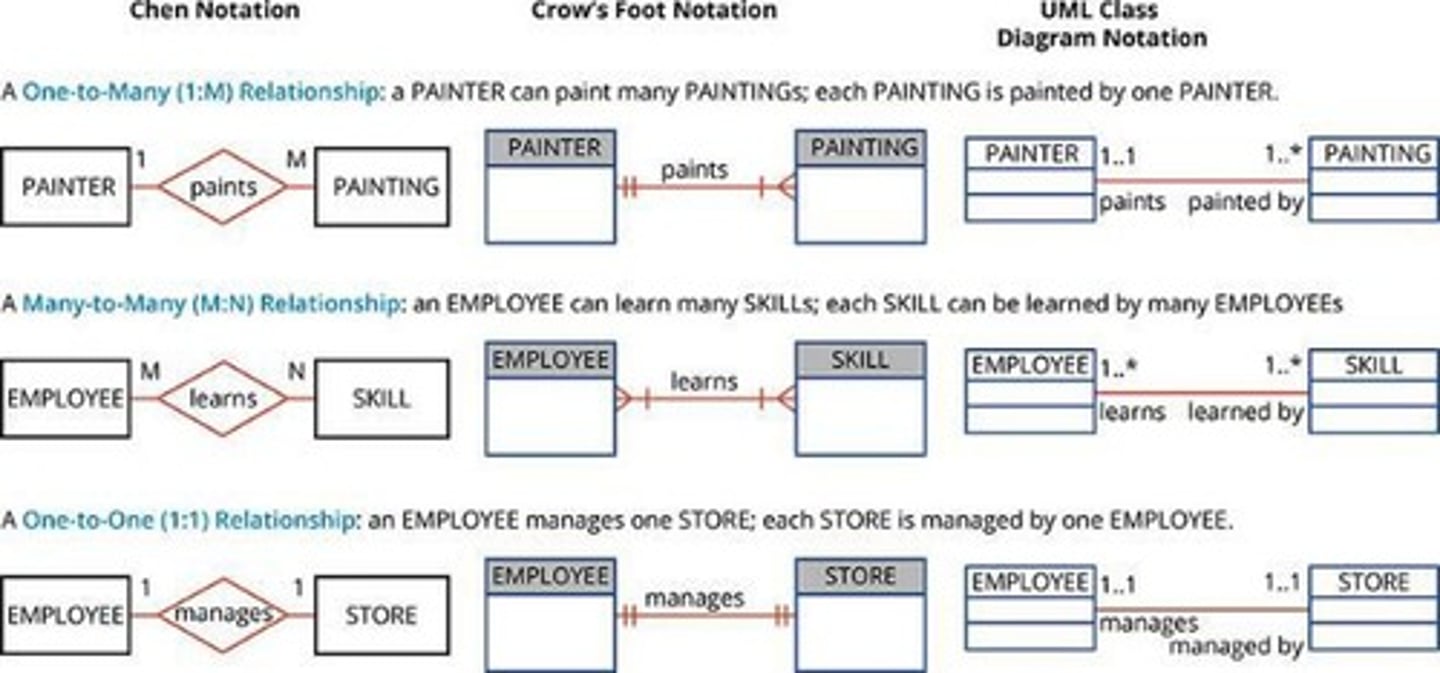
One-to-Many Relationship
One entity relates to multiple entities (1:M).
Many-to-Many Relationship
Multiple entities relate to multiple entities (M:N).
One-to-One Relationship
One entity relates to one entity (1:1).
Constraint
Restriction placed on data to ensure integrity.
Data Integrity
Accuracy and consistency of data over its lifecycle.
Salary Constraint
Employee salary must be between 6,000 and 350,000.
Final Mark Constraint
Student's mark must be between 50% and 74% to pass.
Iterative Process
Data modeling involves repeated refinement and improvement.
Data Transformation
Converting raw data into meaningful information.
Application Programmer
Developer who creates applications to manage data.
End User
Person who interacts with the database application.
Progressive Process
Data modeling evolves through successive stages.
Data Modeling Constructs
Tools and frameworks used in database design.
Business Rule
A precise description of organizational policies.
Entity
An object of interest in a database.
Attribute
A characteristic that describes an entity.
Relationship
Association between two entities in a database.
Tuple
A row in a relational database table.
RDBMS
Relational Database Management System for data management.
ER Model
Entity-Relationship model for database design.
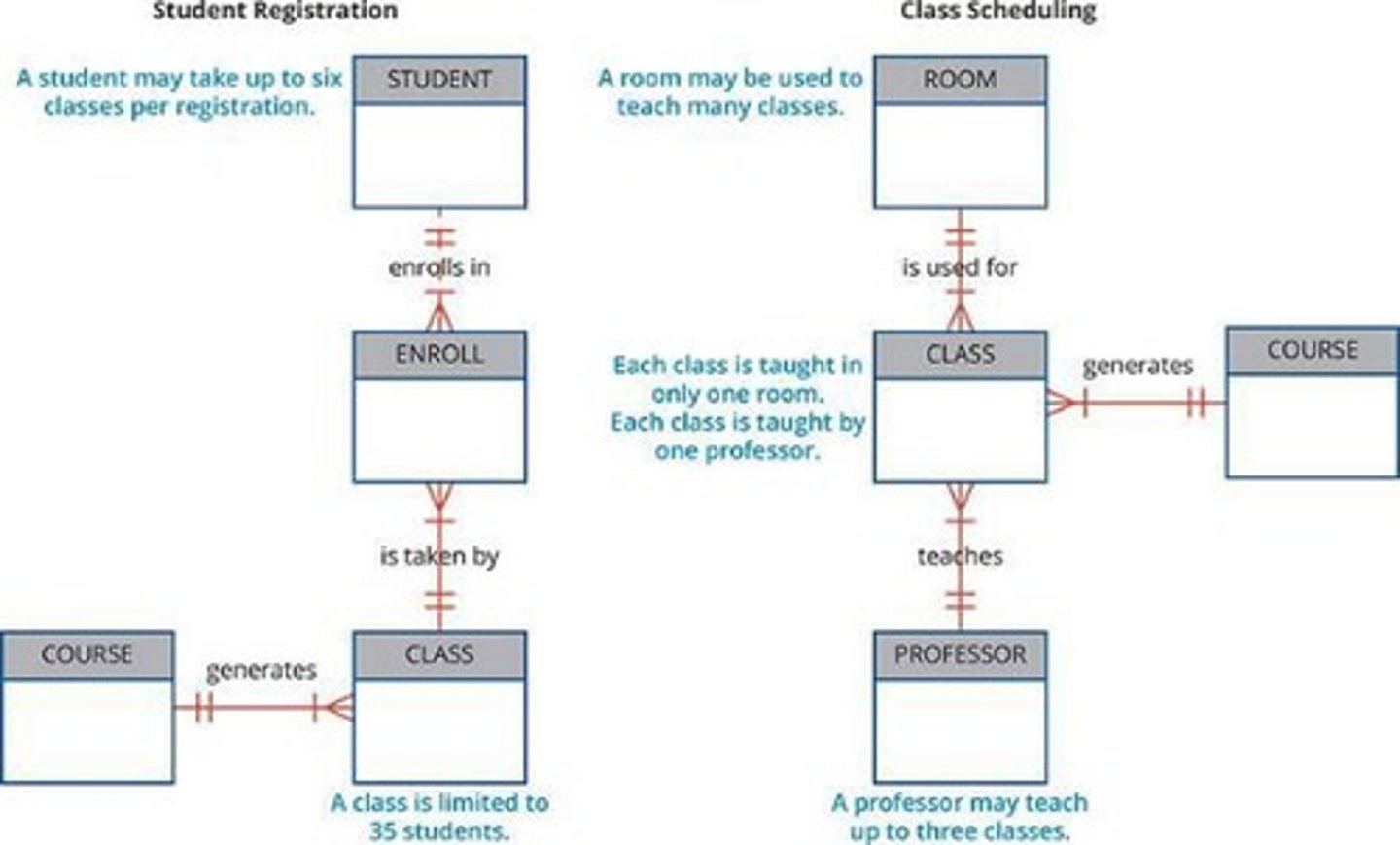
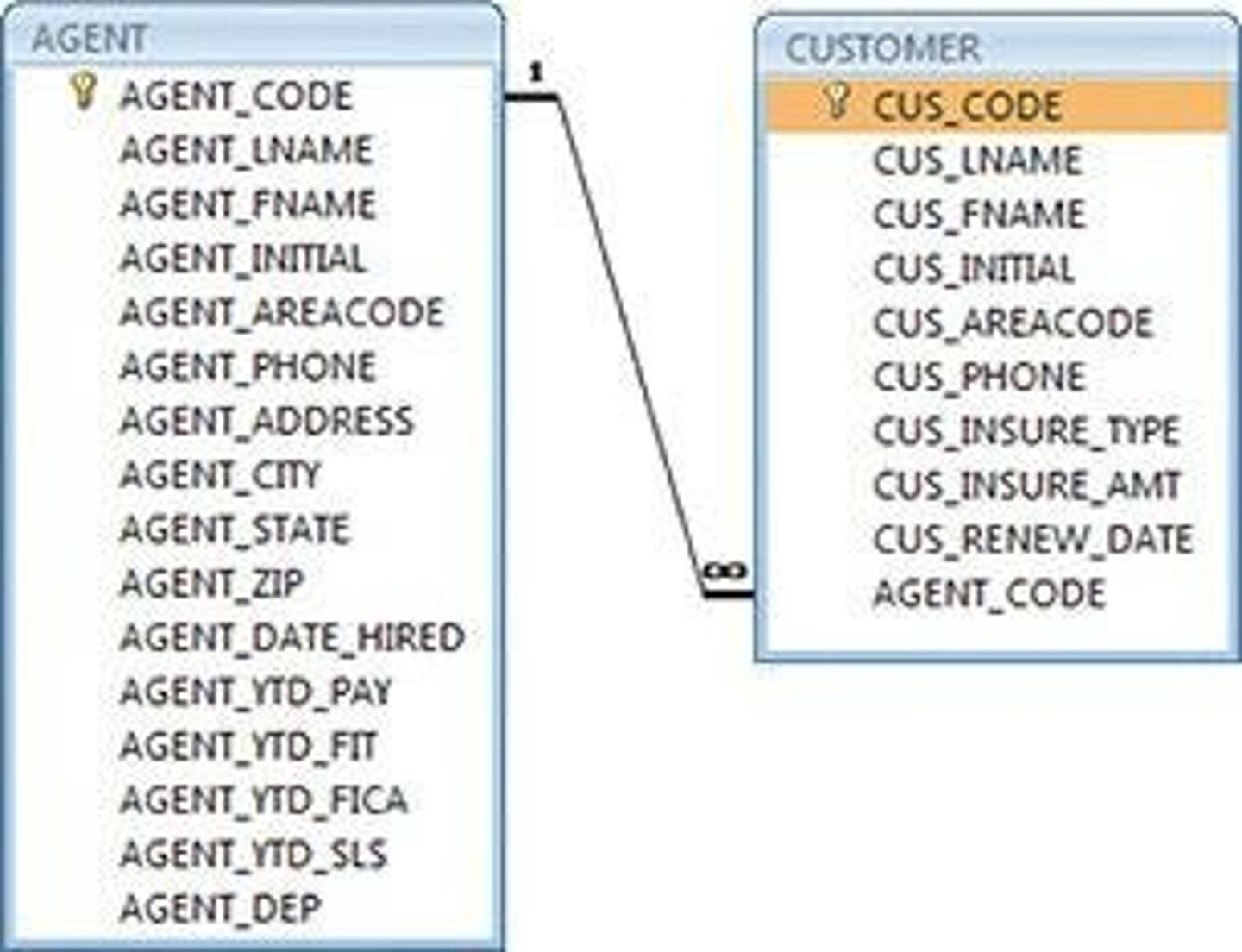
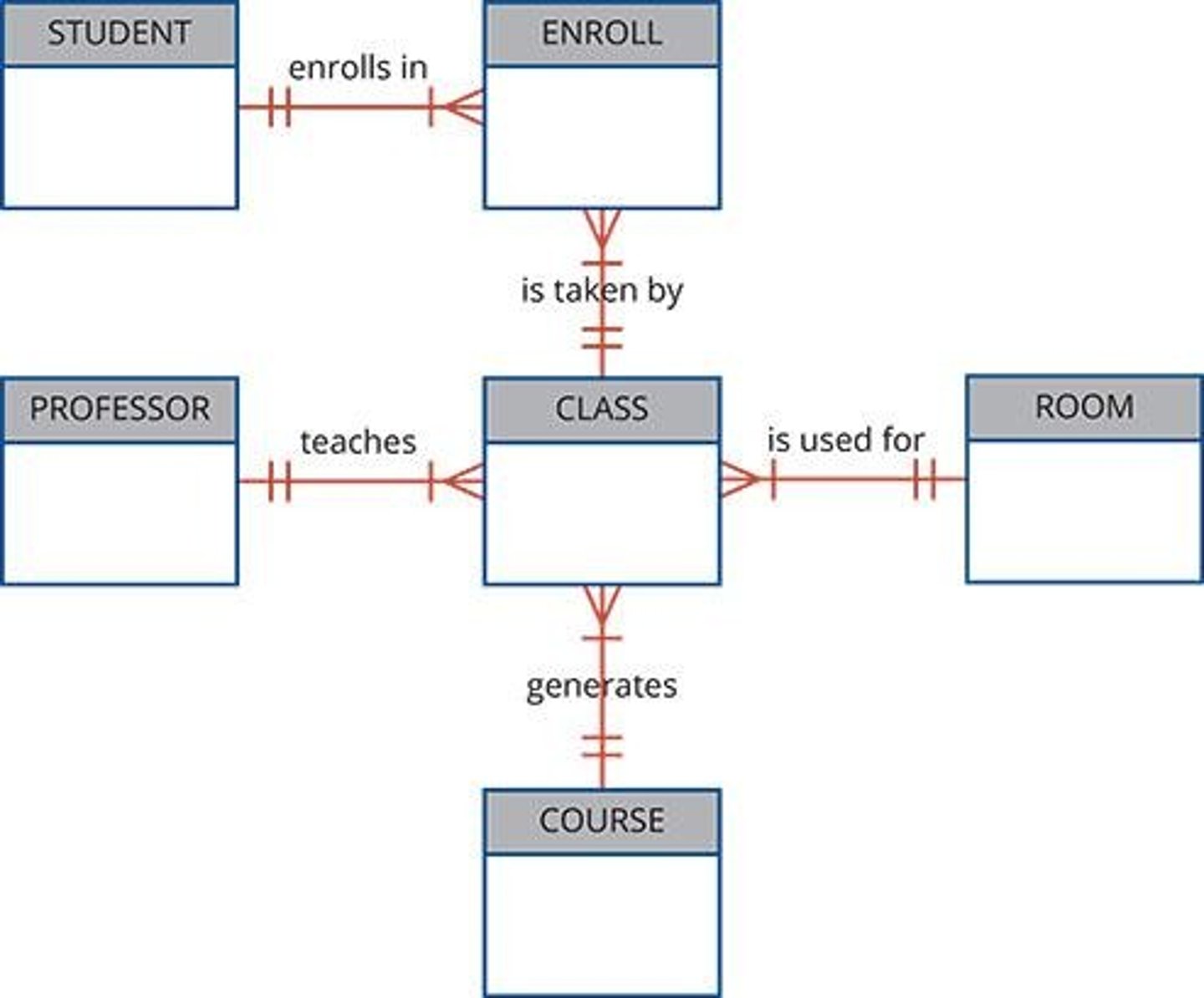
ERD
Entity Relationship Diagram representing database components.
Naming Convention
Descriptive naming for entities and attributes.
One-to-Many Relationship
A single entity relates to multiple entities.
Hadoop
Java-based framework for distributed data storage.
NoSQL
Database system for structured and unstructured data.
Big Data
Management of large volumes of data.
3 Vs of Big Data
Volume, velocity, and variety of data.
SQL Engine
Executes queries in SQL-based databases.
External Model
User's view of the data environment.
Conceptual Model
Global view of the entire database.
Internal Model
Database representation as seen by DBMS.
Physical Model
Lowest level describing data storage methods.
Logical Design
Creating a conceptual data model.
Data Abstraction Levels
External, conceptual, internal, and physical models.
Generate Relationship
Association where one entity produces another.
Fault Tolerance
System's ability to continue operation despite failures.
Data Model
Framework for organizing and structuring data.
Data Constraints
Rules that limit the type of data.
Communication Tool
Facilitates dialogue between users and designers.
Data Model Components
Entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints.
Data Security Constraints
Rules ensuring data protection in databases.
Physical Independence
Changing physical model without affecting internal model.
Data Model
Simple representation of complex data structures.
Database Designer
Professional who creates and manages databases.
Entity
Person, place, thing, or concept for data.
One-to-Many Relationship
One entity relates to multiple entities.
Many-to-Many Relationship
Multiple entities relate to multiple entities.
One-to-One Relationship
One entity relates to exactly one entity.
Constraint
Restriction placed on data for integrity.
Business Rule
Policy or principle defining data usage.
Entity Relationship Model (ERM)
Graphical representation of entities and relationships.
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
Visual tool for modeling database components.
Hadoop
Open-source framework for distributed data storage.
Big Data
Large-scale data management and analysis movement.
Tuple
Row in a relational database table.
Attribute in Relational Model
Column representing data characteristics.
External Model
End users' view of the data environment.
Physical Model
Describes data storage on physical media.
Data Integrity
Accuracy and consistency of data over time.
Mapping Business Rules
Translating rules into data model components.
Naming Conventions
Standardized naming for entities and attributes.
Data Environment
Overall structure and organization of data.
Data Blueprint
Framework guiding database design and implementation.
Communication Tool
Facilitates understanding between users and designers.
ER Notations
Different graphical representations in ER modeling.
Logical Independence
Changing internal model without affecting conceptual model.
Data Management Tools
Software for organizing and handling data.
Data Modeling Constructs
Frameworks used in the data modeling process.