Psychology Sem 3 2026
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Definition of psychology
The scientific study of behavior (what can be observed) and mental processes (Thoughts, feelings and motives)
Psychology approaches (7)
Biological - neuroscience , genetics, structure, biochemistry
evolutionary - origins of behavior, adaptation, natural selection, reproduction, physical features
cognitive - cognition and mental processing, attention, perception, memory
humanistic - positive human values (ppl can choose their behavior)
psycho dynamic - unconscious mind, biological drives (s_xual, aggressive) and society demands,
behavioral - interactions with the environment (environmental determinants, deals with childhood)
sociocultural - needs cultural context (cultural environment)
4 goals of psychology
Describe
experiment
predict
change
Why is psychology a science
There is systematic scientific research
Independant and Dependant variables
IV - MANIPULATED VARIABLE
DV- MEASURED VARIABLE
Descriptive vs experimental
DESCRIPTIVE
find out something new
EXPERIMENTAL
determine the causation
cause and effect
What are the ethics
Research participants have rights
Their risk must be balanced against scientific merit of the study
Researchers MUST protect participants from physical/mental harm
the IRB
What’s validity, and what are the 2
Basically research confidence.
INTERNAL
does the DV truly change due the result of IV manipulation?
EXTERNAL - Applying it to the real world (if it be generalized)
The 2 groups
Control - placebo effect
experimental - manipulated IV
Bias types
Experimental biases
systematic biases
Research participant biases
Methods of DESCRIPTIVE research
NATURALISTIC
LABARATORY
SURVEY
CASE STUDY
The nervous system
CNS - brain and spineal cord
PNS -
SOMATIC - voluntary movement
AUTOMATIC - INvoluntary movement
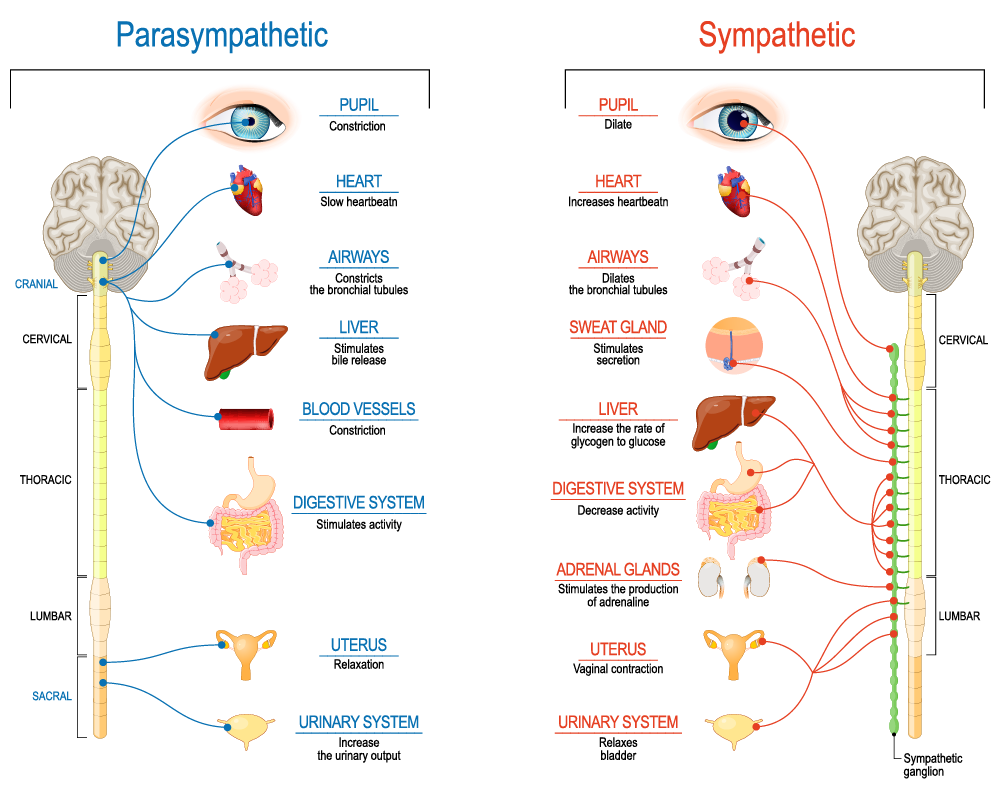
sympathetic’ - fight/flight, stress hormones
parasympathetic - rest and digest, calming down, peace
sympathetic vs PARAsympathetic
Sympathetic
pupils constrict
stimulates saliva
decreases ? heratrate
PARAsympathetic
pupils dilate
inhibits saliva
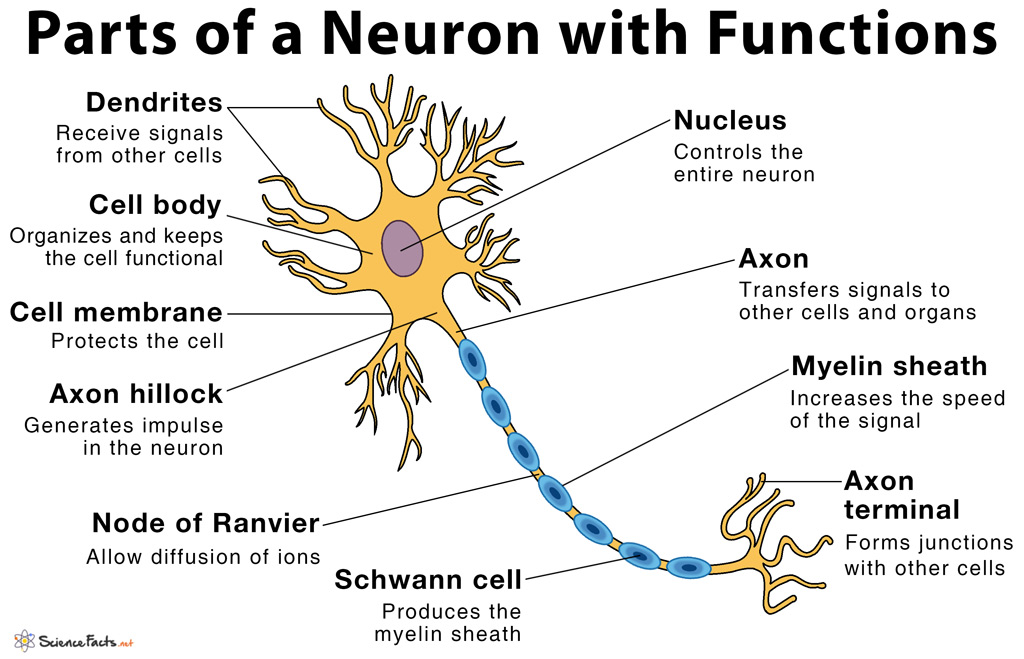
The parts of a neuron
the process of how neurons work
How do we study the brain?
1) Brain lesioning
2) Electrical recording (EEG)
electroencephalograph
Records brain activity
3) CT/CAT scans
Computerized Axial tomography
use XRAY to produce image of structure
4) PET scans
Positron emission tomography
requires radioactive tracer injection
track amounts of glucose in brain (activity)
5) MRI scans
Magnetic resonance imaging
uses magnetic/radiowave
shows clear brain images (no radiation or injections
6) fMRI scans
FUNTIONAL Magnetic resonance imaging
checks changes in oxygen levels in the brain
Neural development
The parts of the brain!! (as in the 3 sections) (what they include)
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
The brainstem
THE BRAINSTEM -
Alertness, basic survival functions, Breathing, heartrate, blood pressure
Medulla (oblongata)
the long chunk
controls refelxes, heart and breathing rate
Pons
links the medulla and the thalamus
sleep and arousal (as in)
if damaged = impaired alertness and disrupted sleep
cerebellum
the “other big chunk
motor coordination, balance, fine motor skills
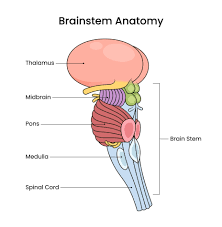
MIDBRAIN
rich in dopamine receptors (reward, pleasure, addiction)
Substantia Niagra
has dopamine producing neurons
input station of basal gangalia
bottom of the brain
dopamine into striatum
Reticular formation
stereotypical behavious like walking sleeping chewing, turning attention to something
THE FOREBRAIN (largest part)
The limbic system - part of the cerebral cortex
AMYGDALA
one on each side of the brain
emotional awareness and expression
detection of objects for survival/adaptation (food)
HIPPOCAMPUS
formation and recalling of memories
when damaged - alzeimers’s, retrograde and anterograde amnesia
THALAMUS
relay station for sensory information (doesnt process it )
Decide where the info goes
CEBERAL CORTEX
Part of the outer layer of fore brain
most recently developed part
divided info left and right
NEOCORTEX
Outermost , 80% of the cortex
Related to the size of social groups (bigger social group, bigger neocortex)
the 4 lobes of the brain
THE OCCIPITAL LOBE - sight
THE FRONTAL LOBE - intelligence, personality
PREFRONTAL - Planning, reasoning and self control
THE TEMPORAL LOBE - hearing (audio),memory and language processing
THE PARIETAL LOBE- Spatial location, attention, motor comtrol
Prefrontal cortex
most forward position of the frontal lobes involved with planning of behavior, attention, and judgement
Phineas Gage case
AREAS
Wernickes area
located in the temporal lobe
- processes speech comprehension
BROCA’s area
located In the Frontal lobe
production of speech
The area of each lobe
OCCIPITAL
at the back of the brain
TEMPORAL
above the ears
PARIETAL
FRONTAL
THE CORTEXES
Somatosensory
front of parietal lobe
processes body sensations
Motor
rear of frontal lobe
Controls voluntary movements
HEMISPEHERES
left hemisphere
verbal processing
speech
grammar
right hemisphere
spatial perception
visual recognition
emotion