ENVR CHAP 18
5.0(2)Studied by 16 people
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Last updated 3:15 PM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Integrated waste management
variety of strategies for both waste reduction and waste management designed to deal with the waste we produce.
2
New cards
Composting
Partially decomposed organic plant and animal matter used as a soil conditioner or fertilizer.
3
New cards
Municipal Solid Waste
solid materials discarded by homes and businesses in or near urban areas.
4
New cards
Cradle to Cradle design
Reusing parts over and over in other products. Thinking of solid wastes and pollution as potentially valuable materials and chemicals
5
New cards
The 4 R’s
Refuse–don’t use it
Reduce–use less of it
Reuse–use it over and over
Recycle
Reduce–use less of it
Reuse–use it over and over
Recycle
6
New cards
Hazardous waste
hazardous (toxic) waste: any liquid, solid, or containerized gas that can catch fire easily, is corrosive to skin tissue or metals, is unstable and can explode or release toxic fumes, or has harmful concentrations of one or more toxic materials that can leach out. These substances are usually byproducts of manufacturing processes.
7
New cards
Waste Reduction
reducing the amount of waste produced; wastes that are produced are viewed as potential resources that can be reused, recycled, or composted.
8
New cards
Open Dump
fields or holes in the ground where garbage is deposited and sometimes covered with soil. They are rare in developed countries, but are widely used in developing countries, especially to handle waste from megacities.
9
New cards
Sanitary Landfill
waste-disposal site on land in which waste is spread in thin layers, compacted, and covered with a fresh layer of clay or plastic foam each day.
10
New cards
Incineration
burning waste
11
New cards
burning solid waste - trade offs
waste to energy incineration
advantages - reduces trash volume, produces energy concentrates hazardous substances into ash for burial, sale of energy reduces cost
advantages - reduces trash volume, produces energy concentrates hazardous substances into ash for burial, sale of energy reduces cost
12
New cards
burning solid waste disadvantages
expensive to build, produces a hazardous waste, emits some CO2 and other air pollutants, encourages waste production
13
New cards
Phytoremediation
using plants to remediate sites by removing pollutants from soil and water
14
New cards
Bioremediation
the use of either naturally occurring or deliberately introduced microorganisms or other forms of life to consume and break down environmental pollutants, in order to clean up a polluted site.
15
New cards
Upcycling
Recycled form more useful than original item
16
New cards
Industrial solid waste
solid waste produced by mines, factories, refineries, food growers, and businesses that supply people with goods and services.
17
New cards
Pre-consumer waste
Pre-consumer waste is basically any material that is discarded before it reaches the consumer. It might be material trimmings, faulty items, overstock raw materials, excess inventory — basically anything that doesn't make it to the consumer that is brought back into the manufacturing process to be given a new life
18
New cards
E waste
used electronics that are nearing the end of their useful life, and are discarded, donated or given to a recycler. Though “e-waste” is the commonly used term, EPA considers e-waste to be a subset of used electronics and recognizes the inherent value of these materials that can be reused, refurbished or recycled to minimize the actual waste that might end up in a landfill or improperly disposed in an unprotected dump site either in the US or abroad.
19
New cards
*What happens to electronic (e waste) that is not buried or incinerated in the US?*
An undetermined amount of used electronics is shipped from the United States and other developed countries to developing countries that lack the capacity to reject imports or to handle these materials appropriately. Without proper standards and enforcement, improper practices may result in public health and environmental concerns, even in countries where processing facilities exist.
20
New cards
What happens to electronic (e waste) that is not buried or incinerated in the US?
We have serious concerns about unsafe handling of used electronics and e-waste, in developing countries, that results in harm to human health and the environment. For example, there are problems with open-air burning and acid baths being used to recover valuable materials from electronic components, which expose workers to harmful substances. There are also problems with toxic materials leaching into the environment. These practices can expose workers to high levels of contaminants such as lead, mercury, cadmium and arsenic, which can lead to irreversible health effects, including cancers, miscarriages, neurological damage and diminished IQs.
21
New cards
Why can’t all plastics be recycled? Why are plastics a problem in the waste stream?
\
Plastics have categories based on their resin components
Not all plastic categories are as recyclable as the others
The book cites that 7% of plastics are recycled in the US – but that number is lower in 2023, it’s closer to 3%
Plastic recyclability is also dependent on facilities designed to recycle that particular type of plastic – if there are not facilities in the region, then all plastics of that particular category will be discarded and not recycled
Plastics have categories based on their resin components
Not all plastic categories are as recyclable as the others
The book cites that 7% of plastics are recycled in the US – but that number is lower in 2023, it’s closer to 3%
Plastic recyclability is also dependent on facilities designed to recycle that particular type of plastic – if there are not facilities in the region, then all plastics of that particular category will be discarded and not recycled
22
New cards
What type of waste (category) is the largest percentage of solid waste in the US?
paper
23
New cards
List several types of hazardous waste. What types of household waste is also considered hazardous waste?
3 types of hazardous waste:
3 types of hazardous waste:
Organic compounds
Toxic heavy metals
Radioactive waste
Toxic heavy metals
Radioactive waste
24
New cards
Household Hazardous waste:
Cleaning products, Disinfectants ,Drain, toilet, and window cleaners Spot removers ,Septic tank cleaners, Paint Products, Paints, stains, varnishes, and lacquers, Paint thinners, solvents, and strippers, Wood preservatives, Artist paints, Dry-cell batteries (mercury and cadmium), Glues and cements, Pesticides Weed killers, Ant and rodent killers, Flea powders, Gasoline, Used motor oil, Antifreeze, Battery acid Brake and transmission fluid
25
New cards
Which industrialized nation has refused to sign the International Basel Convention to reduce and/or control movement of hazardous e-waste across international boundaries?
\
USA
International treaty (not ratified by the United States) drafted as a result of hazardous waste from developed nations being shipped overseas to developing countries. It requires that developing countries must give full permission to accept the hazardous waste.
USA
International treaty (not ratified by the United States) drafted as a result of hazardous waste from developed nations being shipped overseas to developing countries. It requires that developing countries must give full permission to accept the hazardous waste.
26
New cards
What are the tradeoffs of using incinerators of waste to generate electricity?
reduces trash volume, produces energy, concentrates hazardous substances into ash for burial, sales of energy reduces cost
27
New cards
What are the disadvantages of using incinerators of waste to generate electricity?
expensive to build, produces a hazardous waste, emits some CO2 and other air pollutants, encourages waste production
28
New cards
Why is trash in landfills slow to decompose?
It doesn’t move
It is compacted and buried
It has no oxygen
It is compacted and buried
It has no oxygen
29
New cards
What is the function of vertical pipes found in landfills?
\
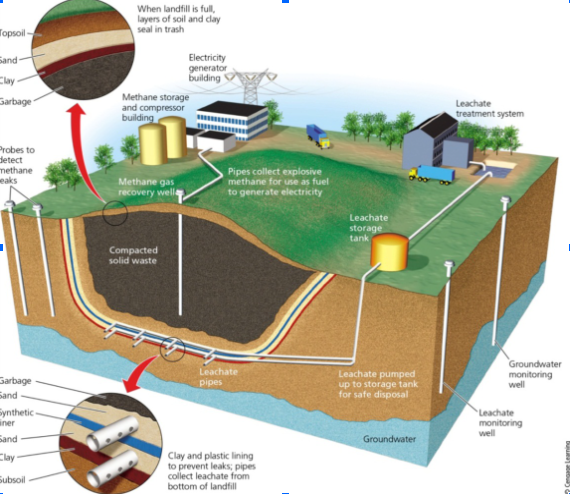
30
New cards
What types of items can be composted to use in a soil-enriching compost?
Biodegradable materials
Food scraps
Food scraps
31
New cards
E-waste can be recycled to extract what types of materials?
Metals
Gold
Copper
Glass
Lithium
Gold
Copper
Glass
Lithium
32
New cards
Solvents, pesticides, PCBs and dioxins are organic hazardous wastes – why are they classified as organic?
Organic compounds are carbon-containing compounds
33
New cards
What type of material (paper, metal, wood, plastic, glass??) makes up most of the municipal waste in the US?
paper
34
New cards
What type of waste storage method is the most commonly used storage method for hazardous waste in most countries in the world? (burial at sea, above ground tanks, inside plants and warehouses, land burial OR gasification???)
land burial