OSCE Exam
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Impression tray
a device that is used to carry, confine, and control impression material while making an impression without deformities
Factors the effect alginate setting time (3)
1)Water temperature
2)Mixing time
3)Water-powder ratio
How does water temperature affect the alginate setting time?
increasing water temperature speeds up setting time while decreasing water temperature slows setting time
How does mixing time affect the alginate setting time?
longer mixing time speeds up setting time
How does water-powder ratio affect the alginate setting time?
increasing water slows the setting time
What is the average setting time for alginate?
1-3 minutes
Steps for alginate impressions (5)
1)Mix water and powder (45 minutes) (3 scoops of water and powder)
2)Fill impression tray evenly
3)Insert tray into patient mouth (2-minutes set time but 3-minutes in patient mouth)
4)Remove tray with quick hard snap
5)Clean off contaminants (blood)
Steps for stone casts (10)
1)Prepare impression: rinse and remove excess moisture
2)1st Mix stone: use type III microstone w/water and mix with spatula
3)Vacuum mix: 20-30 seconds
4)Pour stone: start with small amounts slowly (prevent air bubble)
5)Vibration: using table helps prevent voids
6)Base form: create a sturdy base and form tripod shape (not on vibration table)
7)2nd Mix stone: use another bag of type III microstone to vacuum mix
8)Patty: use second bag of mix to create a patty
9)Set and separate: let dry for 45 minutes and then separate from plate
10)Trim: wait 24 hours (dry trimmer) and 2 hours (wet trimmer)
Type III Microstone
used to make out stone dental casts and has a water/powder ratio of 40mL/140mg
What do voids in stone casts represent?
they represent air bubbles that can be produced from improper pouring or insufficient vibration of stone. Additionally, they can form from debris (tissue/blood) on the impression not being removed
What do positives in stone casts represent?
Air bubbles in the impression tray or imperfections that lead to raised areas in the stone
What does blue represent on the digital scan heat map? Green? Red?
blue: no contact
green: moderate contact
red: high contact
Kinematic Facebow
Precisely locates the actual hinge axis; more accurate but time-consuming.
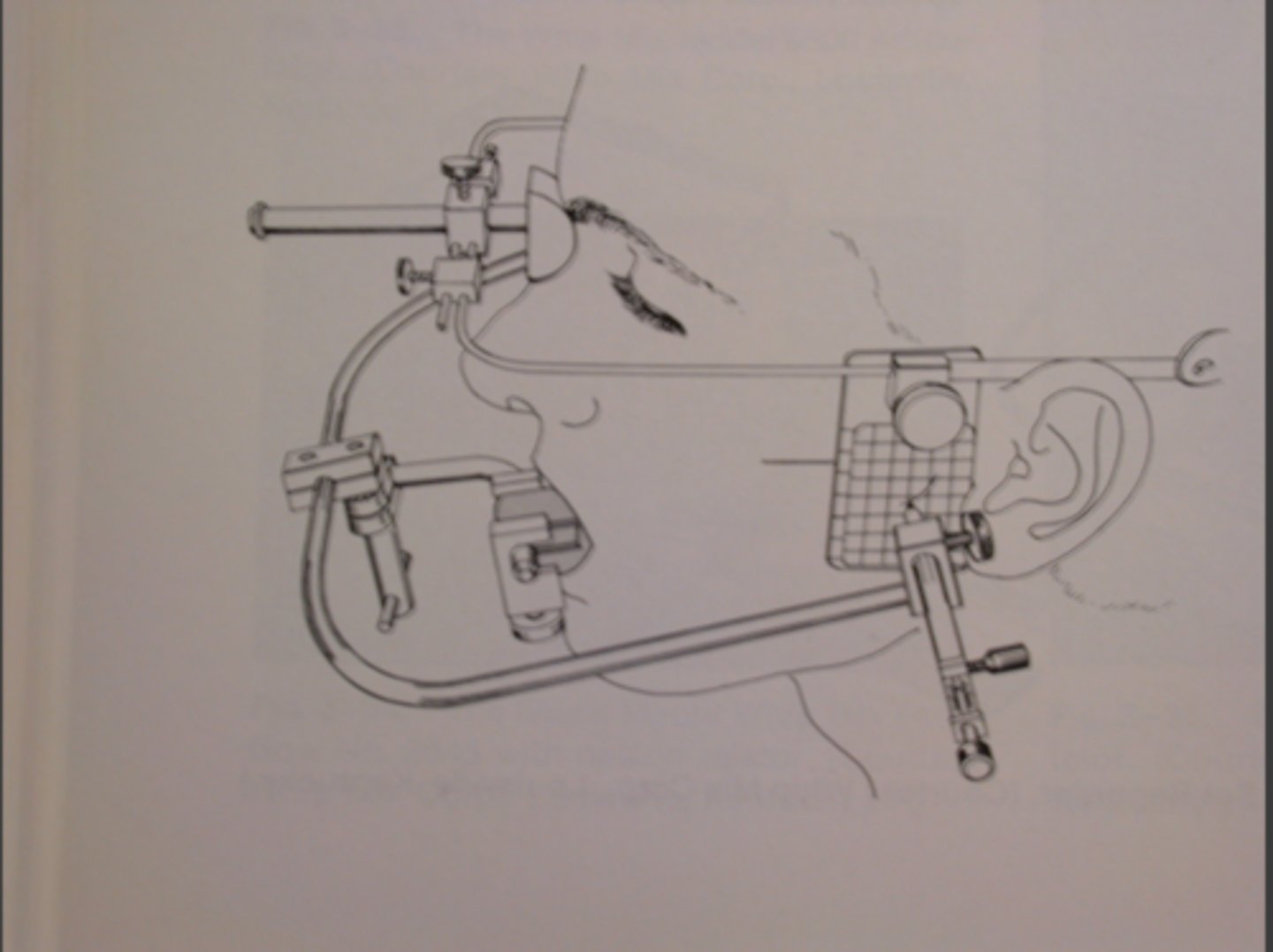
Arbitrary Facebow
estimates the position of the transverse hinge axis by using average anatomical landmarks (ear canal)
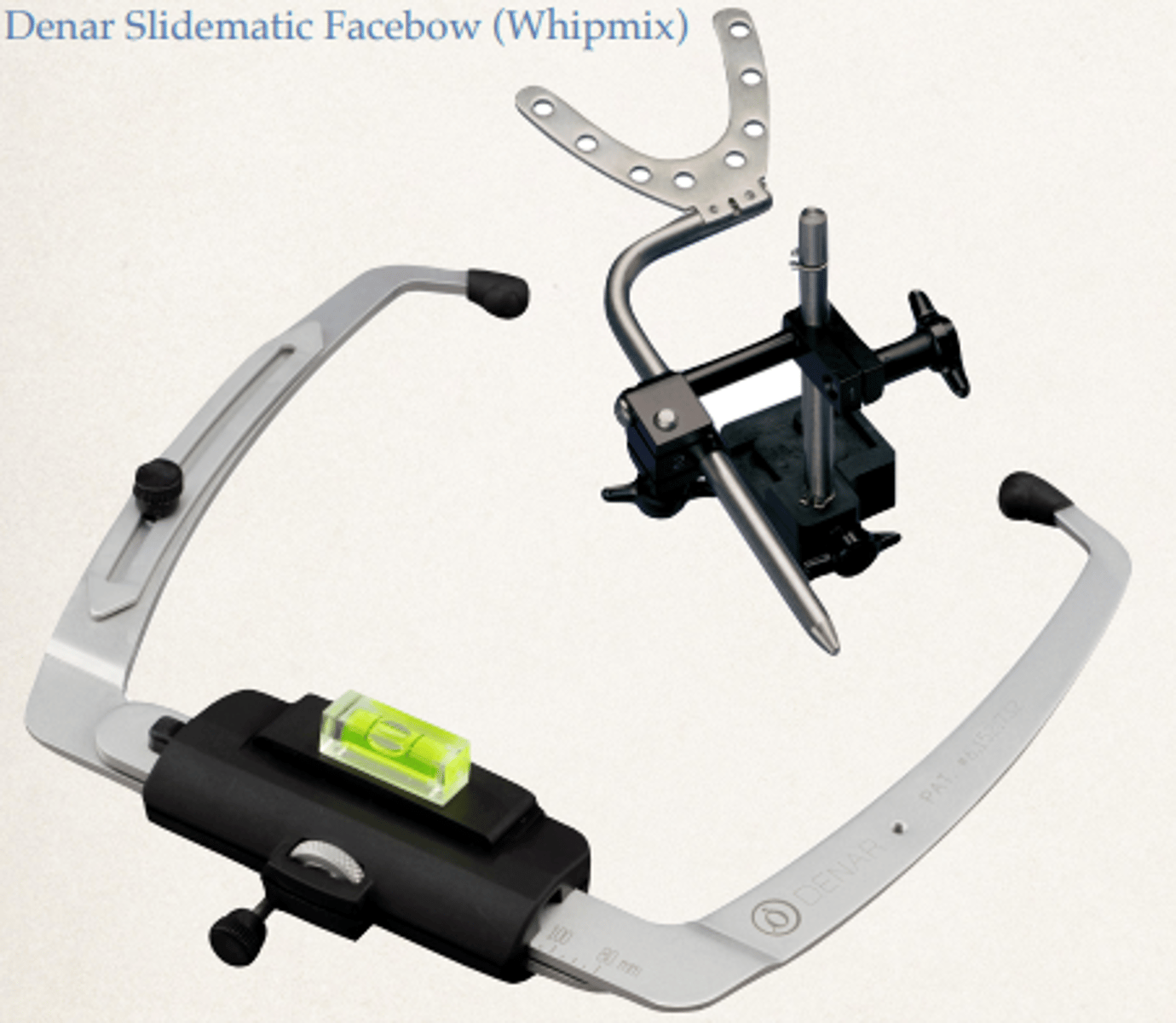

What facebow did we use in sim clinic?
arbitrary facebow because it can be used for quick and functional mounting of the articulator with slight discrpencies
Third point of reference
this is a point that helps you find the transverse hinge axis based on what the average position of it is in most humans, usually infraorbital notch or another facial landmark (43mm above #7 incisal edge in humans)
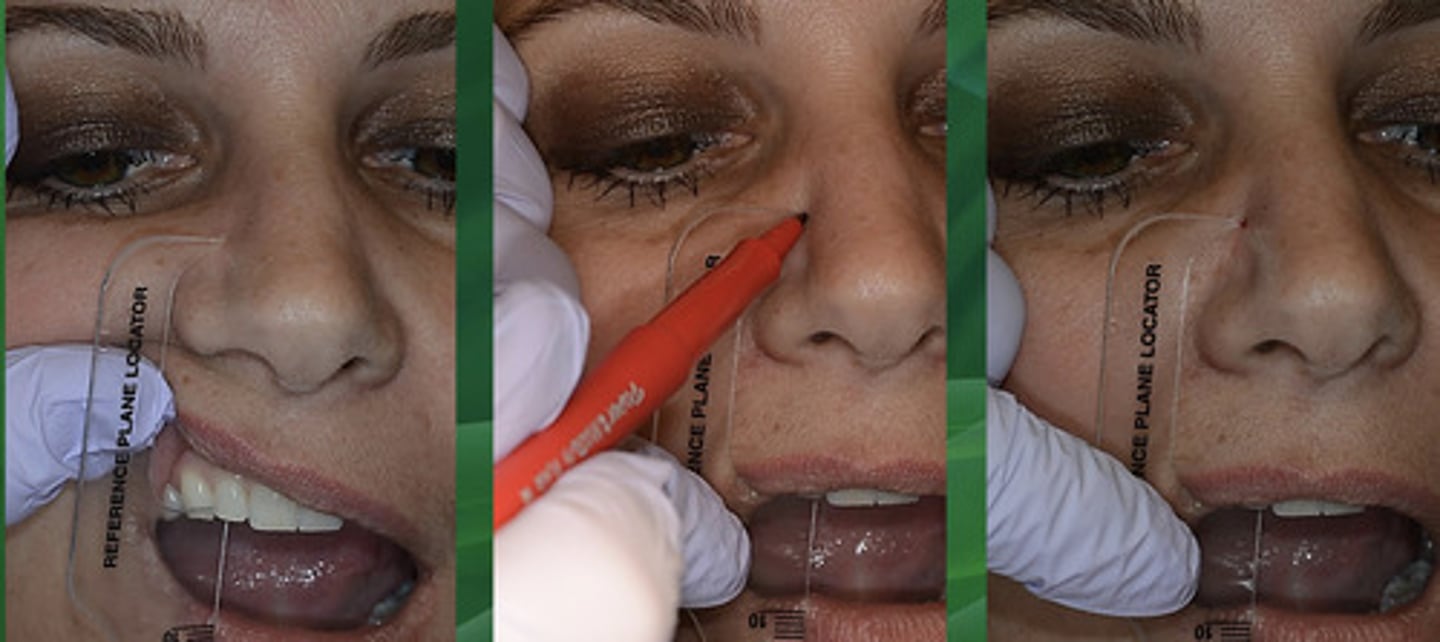
What is the purpose of finding the third point of reference?
it helps stabilizes the facebow and orients it in space relative to the patient's craniofacial structure
What is the purpose of taking a facebow record?
it is taken to transfer the spatial relationship of the maxilla between the temporal mandibular joint (TMJ) to the articulator
Steps for facebow record
1)Make 3rd point of reference 43 mm above #7
2)Make registration of occlusal surfaces using bite fork
3)Trim registration so only cusps are present
4)Place trimmed bite fork on registration on maxillary teeth
5)Make sure "21" faces you
6)Place facebow into earholes
7)Make sure bow is centered, horizontally parallel to eyes, and anterior reference pointer at the same level as the 3rd point of reference
Three criteria to confirm accuracy of facebow record
1)Horizontal part is parallel to pupillary line
2)Centered on face
3)Anterior reference point is set at the same level as the 3rd reference point
Why do we place indices on our stone casts?
provide reference points for repositioning the cast if it becomes detached from the articulator and it helps retention of the gypsum to the cast
Why do we soak stone casts before mounting?
it prevents dehydration and promotes surface stability when mounting
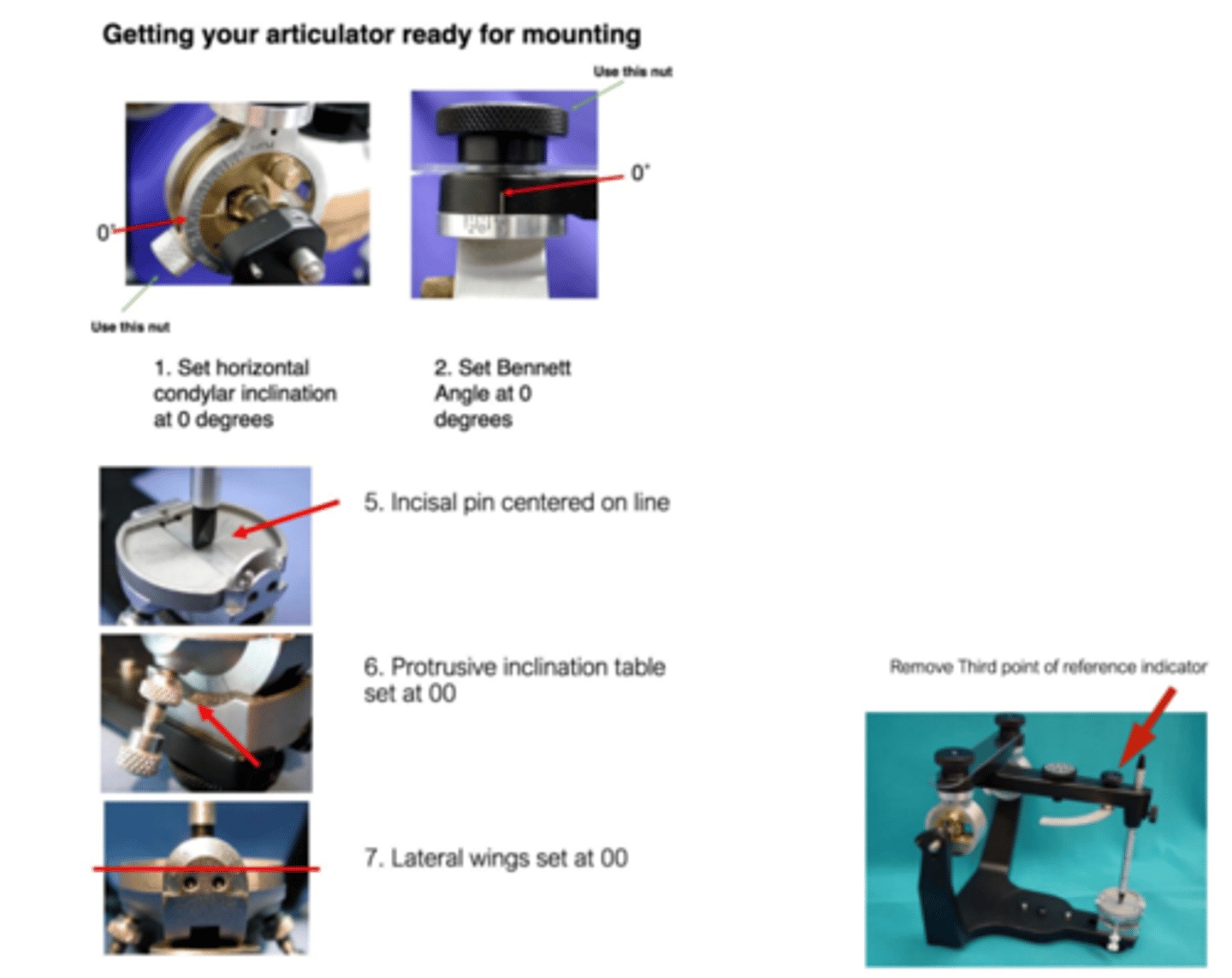
What articular settings should you use before mounting?
set horizontal condylar inclination to 0 degrees, bennet angle to 0 degrees, protrusive inclination table to 0 degrees, lateral wings to 0 degrees, incisal pin centered on the line, and remove third point of reference indicator
When do you use MIP to mount cast?
used when the patient has well defined occlusion and its stable (has all their teeth)
What do perforations represent in the MIP record represent?
they are areas of heavy contact (test with shimstock)
Centric relationship record
captures the position of the condyles in the most stable position (used for people without teeth)
How do you measure centric relationship?
bimanual manipulation or use a leaf gauge to guide the mandible to CR before taking the record
What are common errors for mounting and how do you correct them?
1)Incorrect vertical dimensions (adjust pin to black line and center it)
2)Improper articulation (make sure condylar ball is locked posteriorly)
Accufilm
this material is 21 micros thick so not as sensitive, but it marks where there are contacts
Shimstock
this material is 12 microns thick and very sensitive for contacts, but doesn't mark
Canine guidance
lateral excursive movements guided by the canines
Group function
lateral excursive movements guided by the canines, premolars, and molars
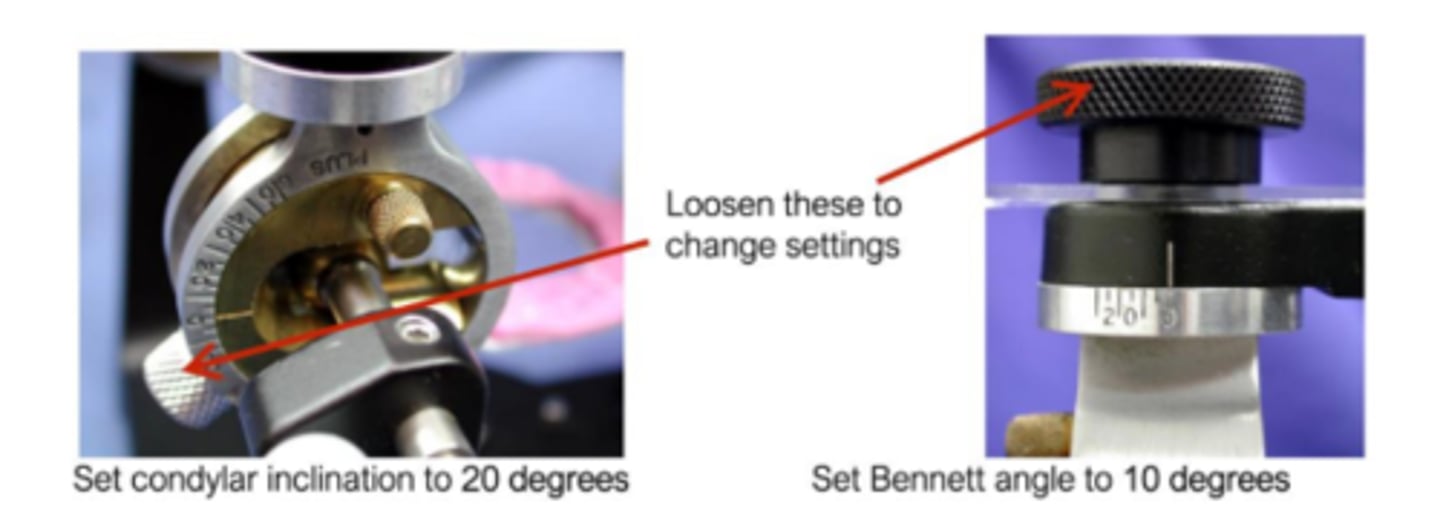
How do you set condylar guidance on articulator?
Bennet angle to 10 degrees and condylar inclination to 20 degrees
Centric cusps
used for massification and maintain facial heights
Ex/Maxillary lingual cusp and mandibular buccal cusp
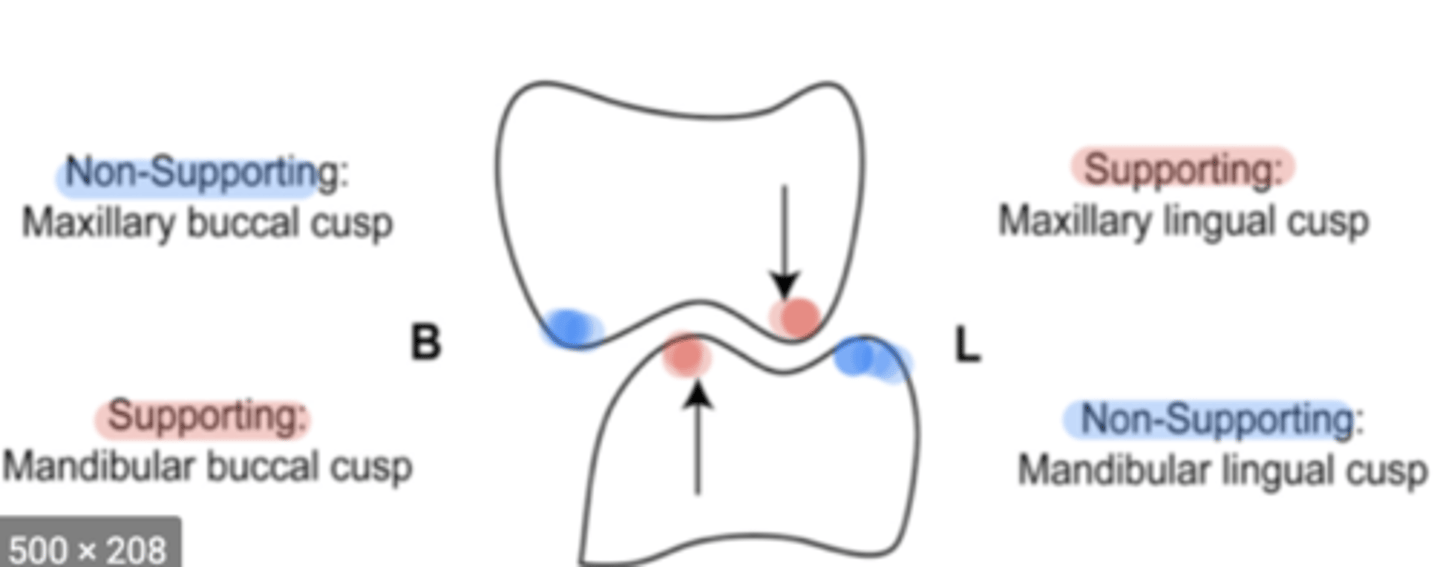
Non-centric cusps
used to minimize tissue impingement and maintain bolus/food on occlusal surfaces
Ex/maxillary buccal cusp and mandibular lingual cusp
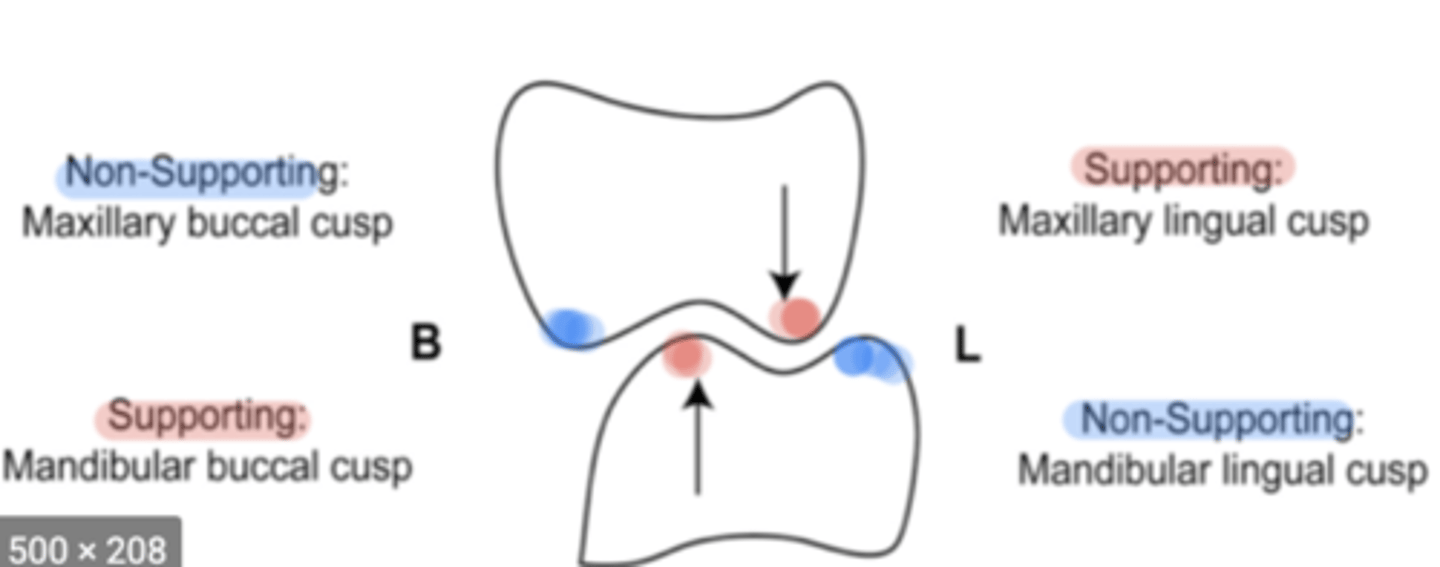
Laterotrusion
outer incline maxillary lingual cusp against inner incline mandibular lingual cusp AND/OR inner incline maxillary buccal cusp against outer incline mandibular buccal cusp (inner vs outer)
Mediotrusion
inner incline maxillary lingual cusp against inner incline mandibular buccal cusp (inner vs inner)
Protrusion
distal incline maxillary cusp against mesial incline mandibular cusp