Cycles (carbon + nitrogen)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Decomposition (2)
Breakdown of the dead remains/material of other organisms
by organisms such as bacteria or fungi
Carbon cycle: why is carbon important?
Is a component of all major biological molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, DNA, vitamins and other molecules all contain carbon.
Carbon cycle diagram
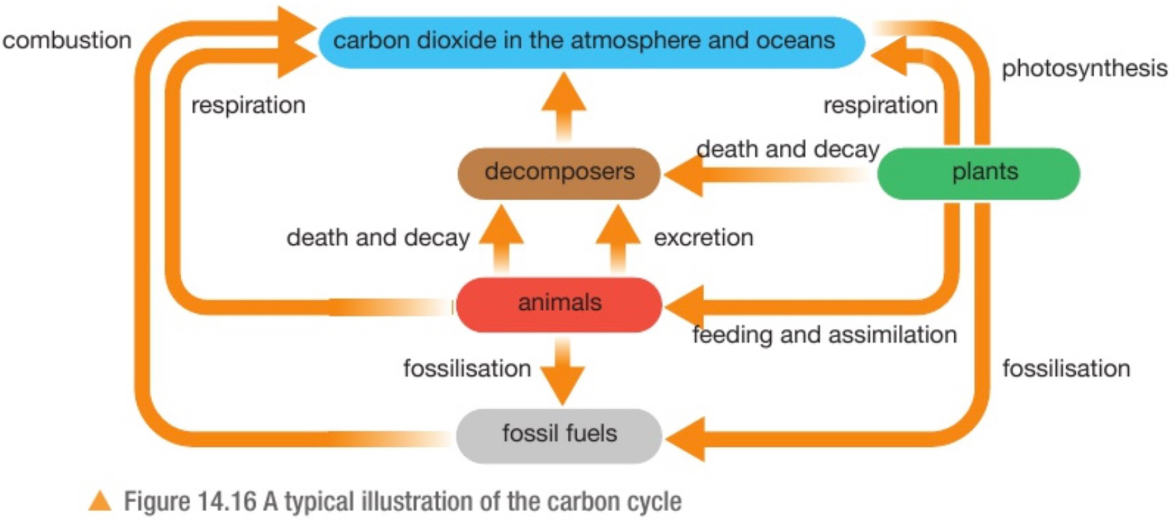
Processes during the carbon cycle
Photosynthesis: ‘fixes’ carbon atoms from CO2 into organic compounds
Feeding and assimilation: pass carbon atoms along food chains
Respiration: releases CO2 as organic compounds (glucose) is broken down to release energy
Fossilisation: sometimes they do not decay fully (soil is too acidic) and fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) are formed
Combustion: burning fossil fuels releases CO2
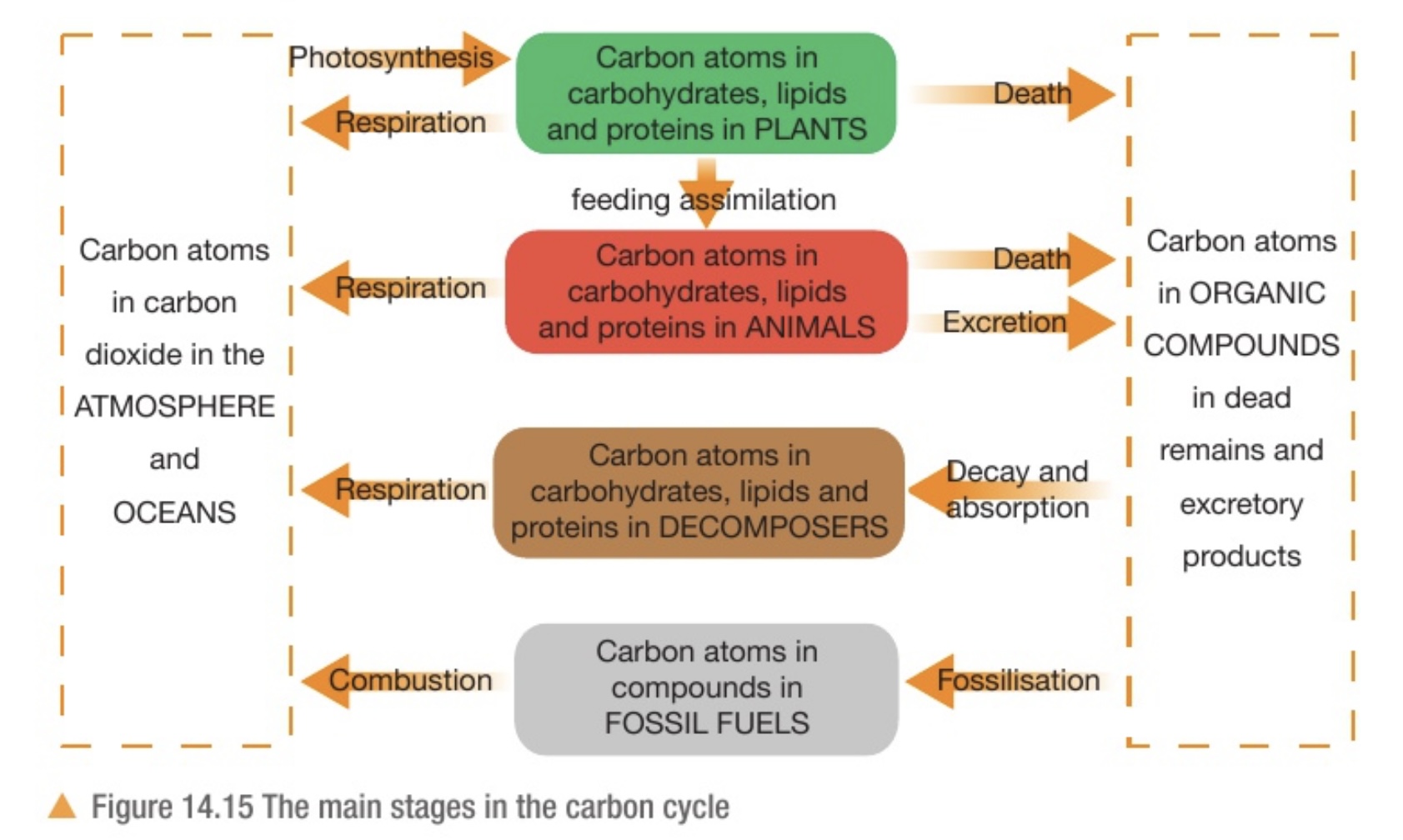
Nitrogen cycle diagram
Here excretion is about urea not faeces. Faeces mainly contain undigested food while most of the nitrogenous matter is excreted in urine (with the urea).
Plant roots can absorb the nitrates
Bacteria involved in nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixing bacteria, decomposers (bacteria), nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
Convert nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3). Ammonia gas dissolved in water forms ammonium ions (NH4+) which are the ones used by the plant
Textbook:
Free in soil: Ammonia is used by nitrogen fixing bacteria to make proteins and amino acids. When they die NH3 is released back into soil.
In root nodules: also make ammonia but this is converted by the plant into amino acids and other organic nitrogen compounds. Death and decomposition of plant returns the nitrogen into soil as ammonia.
Decomposers
Break down dead remains/material containing protein, DNA, vitamins and excreted nitrogenous waste products (urea) and turn them into ammonia. The ammonia dissolves in water to form ammonium ions
Nitrifying bacteria
Convert ammonium ions (in decaying matter) into nitrite (NO2^-) and then into nitrate (NO3^-)
Denitrifying bacteria
Convert nitrate (NO3^-) into nitrogen (NO2). Denitrification reduces amount of nitrate in soil and does no benefit to living organisms
Textbook: use nitrates as an energy source and convert them into nitrogen gas.
What are the two ways which nitrogen fixation can occur?
Lightning: there is so much energy in a bolt of lightning that it’s enough to make nitrogen react with oxygen in the air to give nitrates
Nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil and the roots of legumes
Explain how burning biomass returns nitrogen to the atmosphere (3)
(biomass) contains proteins / amino acids / DNA / RNA
They are nitrogen containing compounds (1)
produce nitrous oxides / oxides of nitrogen when burned / eq (1)