CM lect 5: Hemolytic Anemia Hemoglobinopathies 2026
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
heme
made of iron and protoporphyrin
globin
protein that binds/transports o2
Hb A
Adult hemoglobin
-Alpha chain: chromosome 16, 2 genes each (FOUR total), disrupted by DELETION
-Beta chain: chromosome 11, 1 copy each (TWO total), usually disrupted by POINT mutation
Hb A2
2 alpha chains, 2 delta chains
Hb F
2 alpha chains, 2 gamma chains
-At birth, newborn has 60-80% HbF
-Eventually (around 6 mos, by 1 yoa), switch in production from HbF -> HbA
-Gamma replaced by beta
thalassemias
What disorder:
Problems w/ synthesis of GLOBIN chains
-Thought to protect carries from plasmodium falciparum MALARIA
Def in alpha chains = alpha thalassemia
Def in beta chains = beta thalassemia
-Severity depends on how many chains are absent
-RBC will be MICROCYTIC and can appear target-like
alpha thalassemia
What disorder:
-Etiology: gene DELETION
-asian and african descent
-Manifests in BOTH fetal and adult, b/c alpha chains are common among HbF and HbA
¼ genes: carrier state, asymptomatic
2/4 genes: trait/minor, mild symptoms
¾ genes: moderate to severe, HbH disease
4/4 genes: HYDROPS FETALIS -> incompatible w/ life
Hb H disease
What disorder:
-alpha thalassemia with ¾ genes deleted
-HbH = tetramer of BETA chains
-May require episodic transfusion
-May have EXTRAMEDULLARY HEMATOPOIESIS
hydrops fetalis
What disorder:
-Complete LACK of alpha chains -> severe anemia -> hydrops fetalis
-Hb BARTS: tetramers of GAMMA globin
-Fetus develops: anemia, organomegaly, hypoalbuminemia, heart failure, ASCITES, effusions, etc.
-often fatal in utero
-Confirm diagnosis: chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, fetal blood sampling
-management/tx: intrauterine infusion therapy, chronic transfusions, phototherapy
beta thalassemia
What disorder:
-More common in MEDITERRANEAN ancestry
-Caused by gene MUTATIONS
-Will manifest in first year of life as gamma chains in HbF are replaced by beta in HbA
-Two genes:
½ mutated: minor, mild, carrier ‘trait’
2/2 w/ SOME being made: intermedia
2/2 w/ NO production: major, COOLEY anemia
-erythroid hyperplasia
beta thalassemia trait
What disorder:
½ mutated beta genes: minor, mild, carrier
-May have mild anemia w/ microcytosis -> may be mistaken for IRON def anemia
monitor and observe, folic acid, transfusions as needed
management of beta thalassemia minor/intermedia
beta thalassemia intermedia
What disorder:
2/2 mutated beta genes with some beta globin production
-varying degrees of anemia, transfusion requirements
beta thalassemia major (cooley’s anemia)
What disorder:
2/2 mutated beta genes w/ NO production of beta chains/HbA
-Symptoms occur 6-12 mos after birth
-Clinical manifestation: severe anemia, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, EXTRAMEDULLARY HEMATOPOIESIS
protein electrophoresis, high performance liquid chromatography, genetic testing
dx of beta thalassemias
scheduled RBC infusions, increased risk of HEMOCHROMATOSIS (may need iron CHELATION therapy), splenectomy, stem cell transplant, induction of Hb F, gene therapy
management of beta thalassemia major
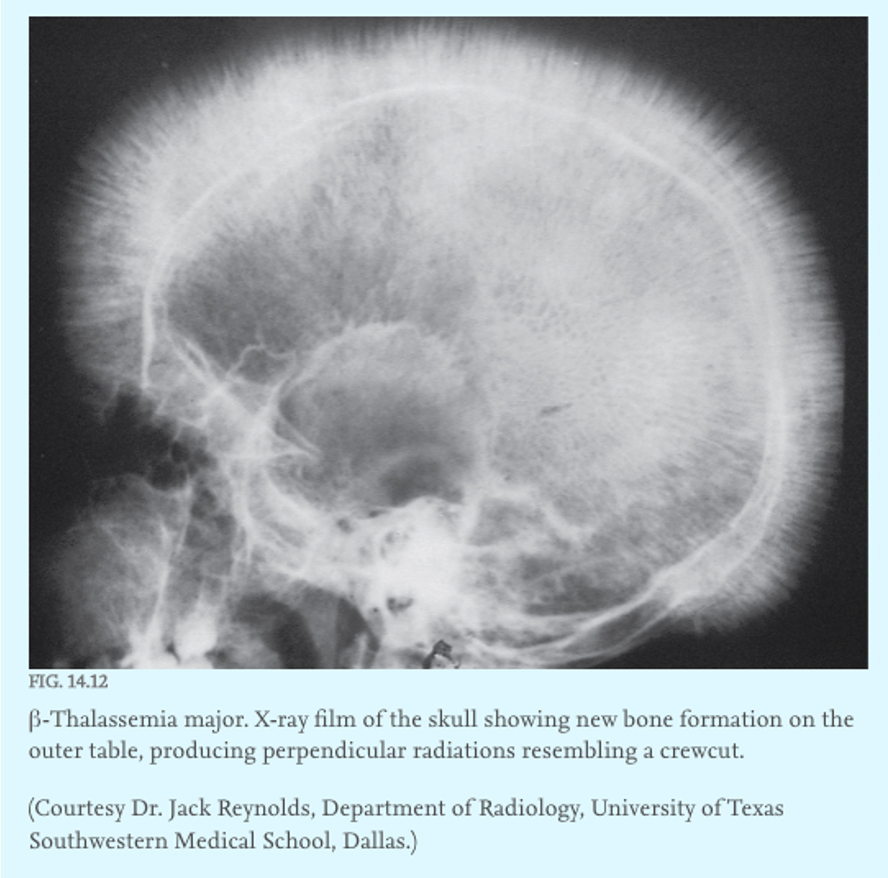
erythroid hyperplasia
what symptom:
-Erythroid hyperplasia: thickened bone marrow, FACIAL bone changes, increased fracture risk, and ectopic hematopoiesis
sickle cell trait
What disorder:
HETEROZYGOUS; inherited one HbS gene from one parent and a normal HbA gene from the other
-Do not have clinical symptoms, unless subject to severe STRESS
Dehydration, hypoxia, strenuous athletic training
Most pts have NORMAL life expectancy
-Rare: splenic infarction, strokes, or sudden death
-At risk for sickling of the RENAL MEDULLA -> painless HEMATURIA from medullary infarction
-Selective advantage for malaria
sickle cell disease
What disorder:
Point mutation in beta globin gene -> chronic hemolytic anemia w/ vaso-occlusion episodes and vasculopathy
-Can cause chronic organ damage and cause premature mortality
-Etiology: AR; intra- and extravascular hemolysis
HbS: VALINE instead of normal GLUTAMIC ACID on position 6 on chromosome 11
HbS under LOW O2 -> polymerizes and distorts -> sickle shape -> risk of vaso-occlusion and hemolysis
Clinical severity of disease depends on the amount of HbF, as HbF as HIGH AFFINITY for O2 and does NOT sickle
HYDROXYUREA increases HbF production
MSK pain, swollen digits, fatigue, SOB, weakness, chest and abdominal pain
scleral icterus, pale conjunctiva, jaundice, lethargy, fever, splenomegaly, hematuria
presentation of sickle cell disease
sickled cells seen on peripheral smear
labs of sickle cell disease
dactylitis, bone deformities, SPLENIC enlargement/splenic infarction, vaso-occlusive crisis, ACUTE CHEST syndrome, stroke, pulmonary HTN, priapism
complications of sickle cell disease
osteonecrosis, hemosiderosis, infarctions, marrow hyperplasia, osteomyelitis (SALMONELLA)
bone effects of sickle cell disease
RBC sequestration, infarction, INVOLUTION, loss of immune function against encapsulated bacteria (AUTOSPLENECTOMY)
spleen effects of sickle cell disease
supplemental O2, IV fluids, pain management
tx for vaso-occlusive crisis
acute chest syndrome
What disorder:
Pulmonary vaso-occlusive crisis
-Triad: chest pain, pulmonary infiltrates, arterial hypoxemia
-Often very difficult to distinguish b/w this and PNEUMONIA -> so tx w/ antibiotics
-If necessary, exchange transfusion to replace at least HALF of pt’s HbSS blood w/ normal HbAA blood
acute chest syndrome
Most COMMON cause of death in children and adults w/ HbSS
newborn screen, HPLC, hgb electrophoresis
diagnosis of sickle cell disease
Prophylactic and chronic: folic acid, vaccinations, HYDROXYUREA, daily penicillin until 5 yoa
management of sickle cell disease
Higher level of care: hospital for IV fluids, Abx, O2, blood transfusion, exchange transfusion, HSC transplant
acute tx of sickle cell disease
hydroxyurea
only drug approved for sickle cell disease
-Increase in NO -> increase in cGMP -> increase in globin synthesis -> HbF
-decreased transfusions, painful crisis, mortality, and hospitalizations