developmental care, positioning, and postural alignment
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Physiological flexion
typical vs atypical tone
typical tone
Reflexes intact and assimilating
typical vs atypical tone
typical
prone clearance to bilateral side
typical vs atypical tone
typical
Equal flexor in arms/legs
typical vs atypical tone
typical
Symmetry
typical vs atypical tone
typical
Trunk alignment during prone suspension
typical vs atypical tone
typical
Key developmental milestones related to feeding:
3 mos
5-7 mos
7-8 mos
9 mos
19-20 mos
3 mos: Trunk and neck stabilization, Midline head and hand orientation
5-7 mos: Reaching, grasping, picking up objects (e.g., cup, pellet)
7-8 mos: Efficient finger feeding in most infants
9 mos: Cause-effect play (e.g., ringing a bell) = purposeful chewing skills emerge
19-20 mos: Use of tools (stick to get toy), Feeding skills like using a spoon and cup with minimal spillage
preference for one side of the body • Increased hip/knee flexion, extensor posturing
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone
Finger splaying, thumb adduction
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone
Hypotonia indicated by slipping through axillary hold, extended limbs and in supine
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone
early “rolling”
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone
Asymmetries in posture, reduced movement on one side (suggests hemiplegia or early CP)
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone
signs of seeking stability outside of the trunk
typical vs atypical tone
atypical tone

noonan syndrome

costello syndrome

russell-silver syndrome
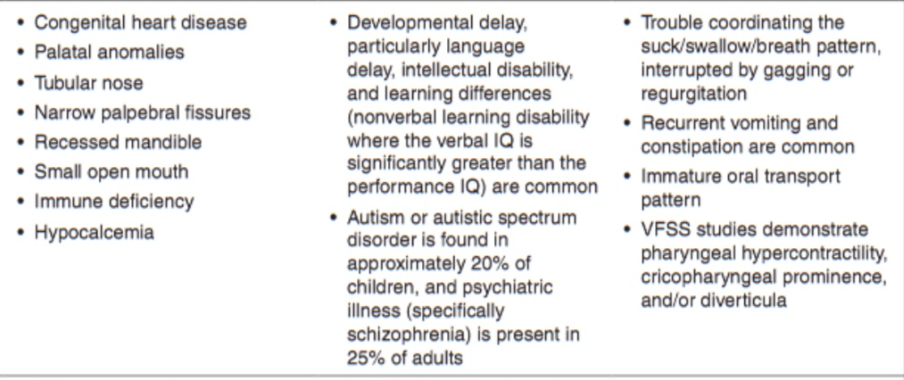
DiGeorge syndrome

Opitz G/BBB syndrome

Prader-Willi Syndrome

Coffin-Siris syndrome

Mobius syndrome

hemifacial microsomia syndrome

pierre robin (nonsyndromic)

trisomy 18

angelman syndrome