Lecture 2: Vertebrates from egg to embryo
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Define notochord
Early form from of spinal cord.
What makes an animal a vertebrate?
Head, dorsal nerve chord, notochord.
Do all vertebrates all develop the same way?
All start off as single egg then lots of division gives rise to variation. Then reaches stage where they look similar across diff species but then followed by more differences as variety of structure + function between species is established.
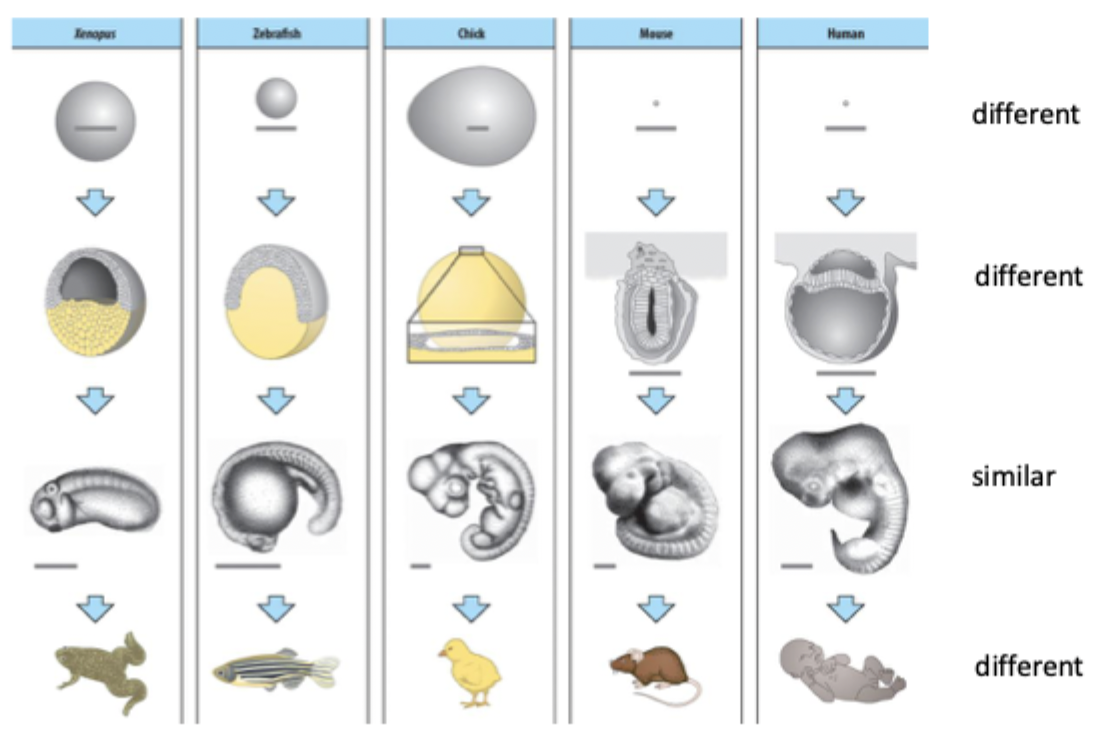
Define pharyngula stage
Stage where vertebrae embryos are similar, has some conserved characteristics like pharyngeal pouches + somites. Is likely conserved due to genetic bottleneck.
Define metameric structures
Repeating modules, similarities
Define segmentation
Formation of metameric structures, from diff segments, easily seen in insects but also present in humans.
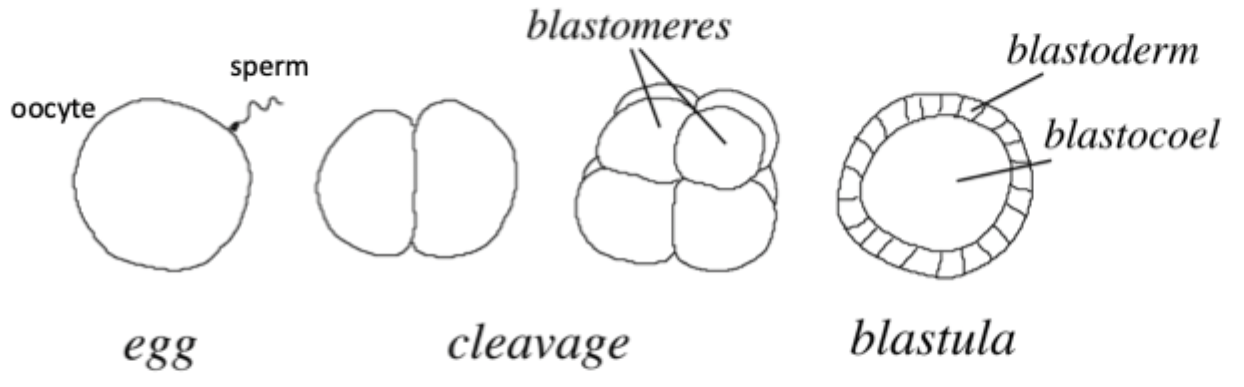
Define blastula
Made of blastomeres on outside which forms blastoderm + inside cavity called blastocoel.
What is the doubling time during early cell proliferation?
Half an hour.
Describe egg activation after sperm entry
Wave of free Ca2+ ions travels across egg, Ca2+ is released from intracellular stores (e.g mitochondria), Ca2+ acts in proteins that control the cell cycle to initiate cleavage, oscillations in Ca2+ levels during early development synchronises cell division.
How is it shown that only Ca2+ is needed to trigger division?
When Ca2+ is added to a frog egg in early development = starts dividing = only Ca2+ needed.
Which phases are NOT seen in the cell cycle of an early embryo + why?
No G1 or G2 as cells are dividing very rapidly = transcription suppressed.
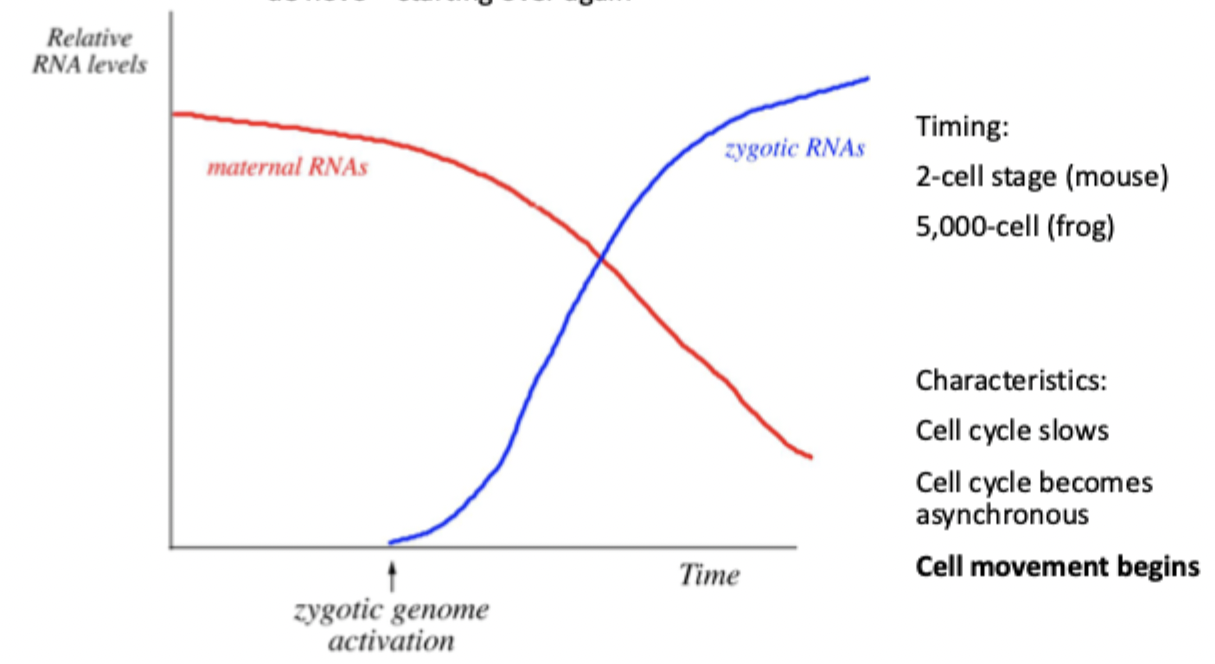
Due to no G1 or G2 phases in early embryo cell cycle, what does the early embryo rely on instead?
Maternal stores of RNA + protein so DNA synthesis + growth can be started. Is maternal because there is no room for RNA + proteins in sperm.
Define zygotic genome activation
When early embryo runs out of maternal RNA + protein, zygotic RNA (genes from mother + father) is activated. Cell cycle slows, lose synchrony + cell movement begins.
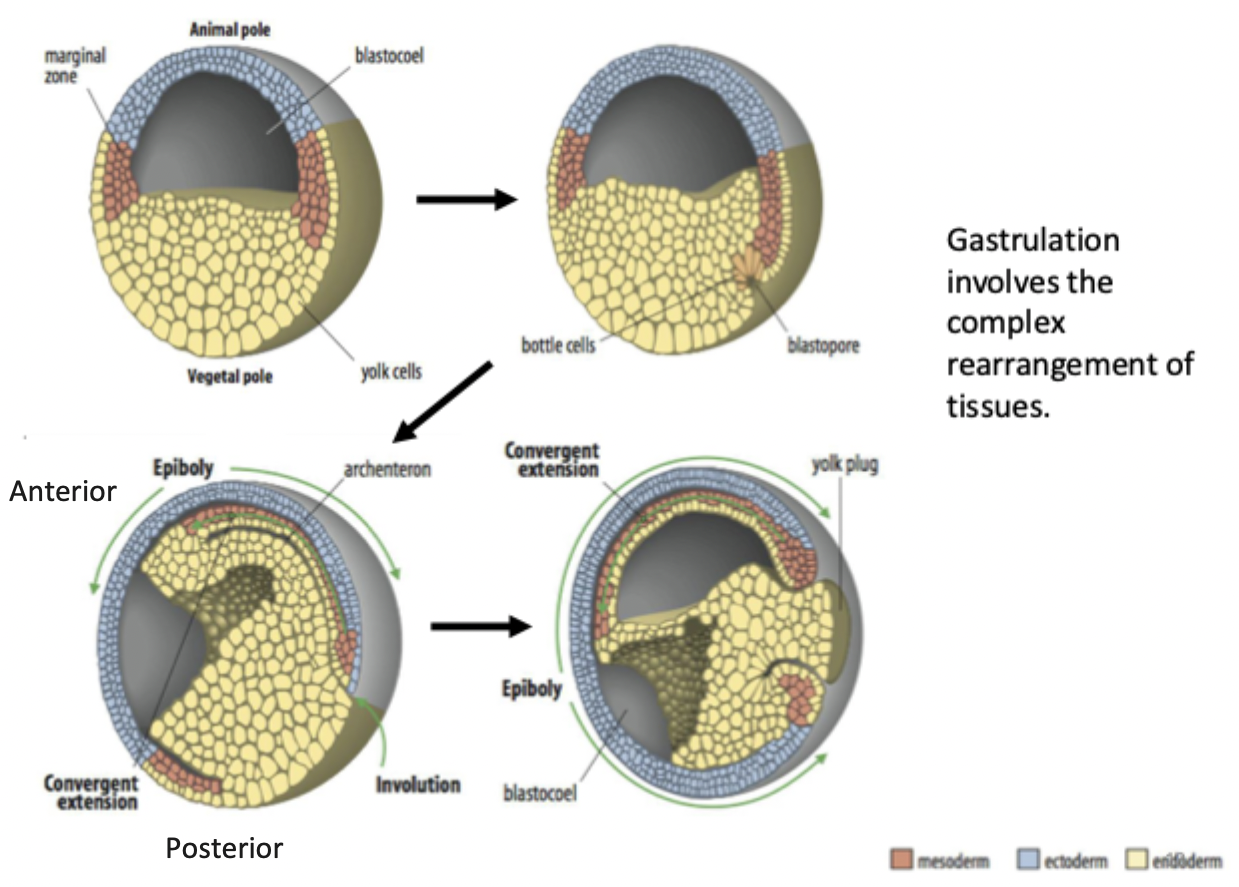
Define gastrulation
Formation of the 3 germ layers, cells move inside of the embryo to form the endoderm and the mesoderm, cells that stay on the outside form the ectoderm. Anterior/posterior, dorsal/ventral axes is established. Cell get specified into 3 linages = cell fate more restricted.
What type of cells are derived from each of the 3 germ layers?
Ectoderm: neurons, glia, epidermis + pigment cells.
Mesoderm: muscle, cartilage, bone, dermis, kidney, heart, blood.
Endoderm: lungs, gut, giblets etc.
What happens if gastrulation is unsuccessful?
Embryo will abort.
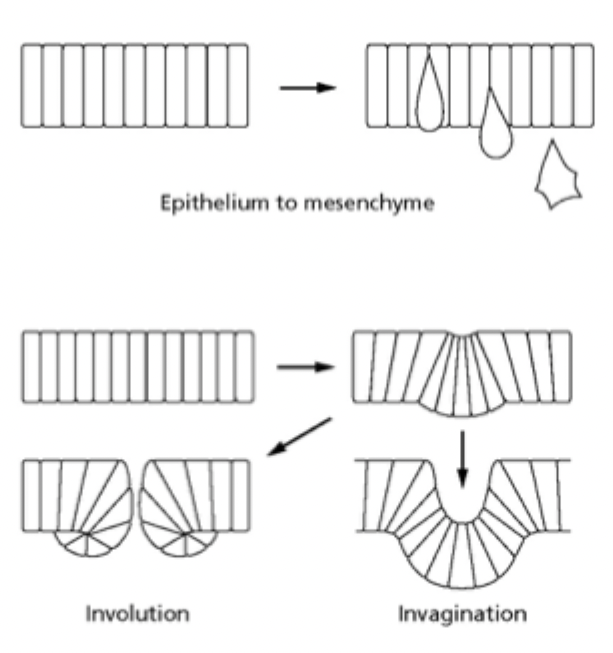
Describe epithelial cells
Structured + often cuboidal, can migrate but often move en masse as a sheet or cluster. Joined by junctional complexes = stops pathogens getting in + keeps fluid in. One of earliest cell types to form. Can change to mesenchyme or form hole (involution) or form cavity (invagination) = caused by cell shape changes.
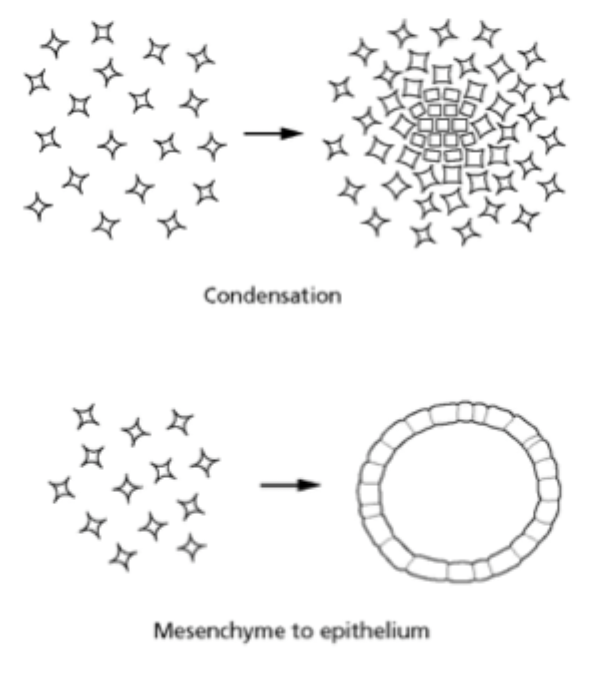
Describe mesenchymal cells
Amorphous (random shapes/not alike) + don’t stick to each other as separated by EC proteins or ECM outside cell = can move around + pass each other easily. Can group together to form condensation or organise into epithelium = not just fixed to being mesenchyme.
What is cell shape change brought about by?
Cytoskeletal rearrangements.
What does migration and cell death give rise to?
Changes in tissue shape.
Define morphogenesis
How an organism goes from being a ball of cells to having complex structures.
Define somitogenesis
Somites form from anterior to posterior. Are temporary structures. Form following gastrulation in the mesoderm. When somites are formed they become specified to become diff cell types. 1 somite = 1 vertebrae, off by ½ = 0.5 each gives rise to posterior vertebrae + anterior of neighbouring vertebrae.
What are muscles segmented from?
Somites.
What does the neural tube arise from?
Ectoderm after gastrulation.
State the stages of development of vertebrates from egg to embryo
Early cleavage → gastrulation → somitogenesis/pharyngula/neurulation.