Pedigrees
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Why is it important to predict risk or affected/carriers
→ it is important to know how genetic diseases are inherited in humans
Predict risk of being affected:
for family members of affect individuals
Screening + treatment
Predict risk of being carriers:
for family members of an affected
Risk to unborn child
Reproduction choices
Pedigrees
→ graphical representation of a family tree
useful in calculating risk (affected or carrier) for well known disorders
First step in establishing the mode of inheritance of a new disorder
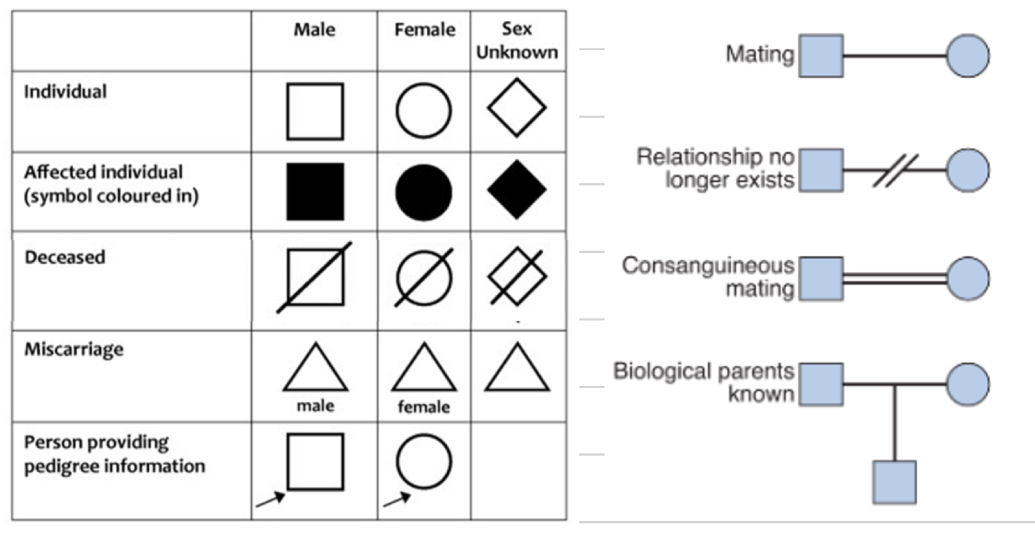
Pedigree symbol meanings
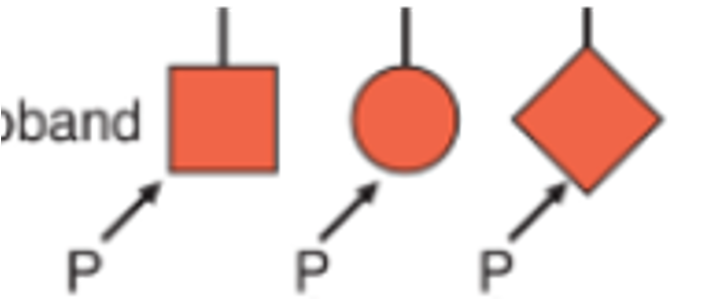
Probands
individuals affected by a genetic condition or who is concerned they are at risk
Usually first person in a family to bring concern to healthcare professionals
Denoted by an arrow with a P
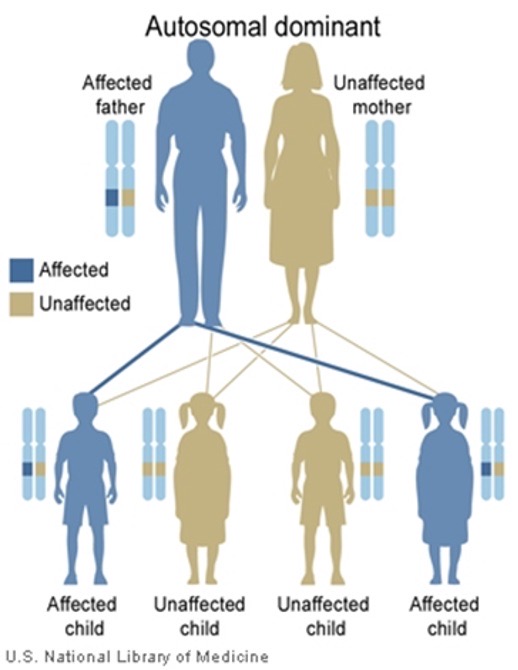
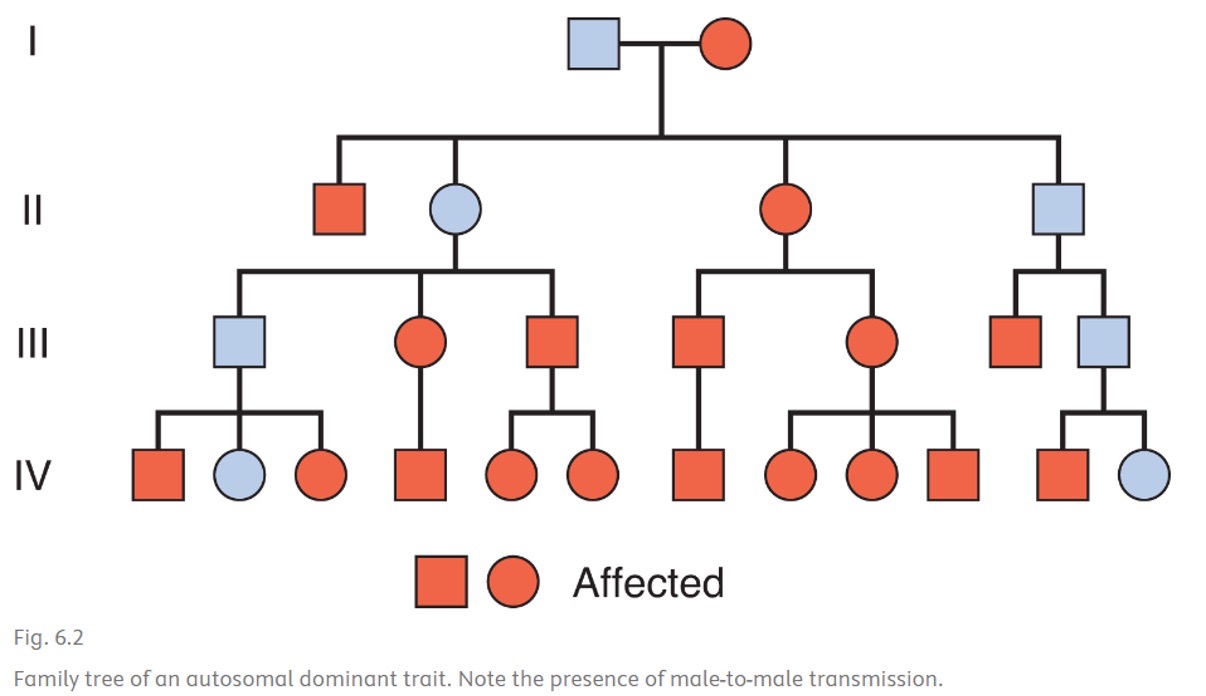
Autosomal dominant inheritance
50% risk in offspring
Transmission by females and males and both are equally affected
Affected individuals have affected parent
Teds to occur in every generation
Autosomal dominant pedigree
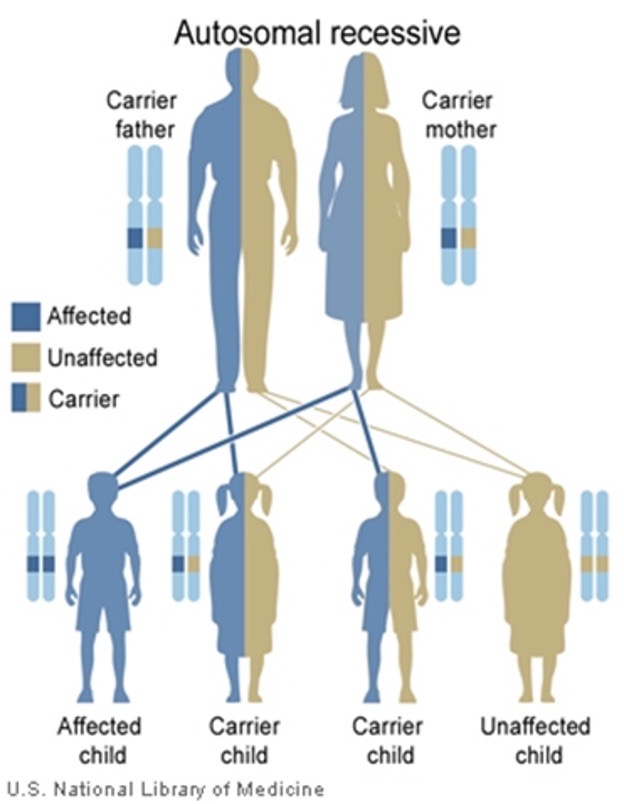
Autosomal recessive inheritance
25% risk in offspring with 2 carrier parents
Males and females equally affected
Usually no previous family history
Increased risk if parents are related
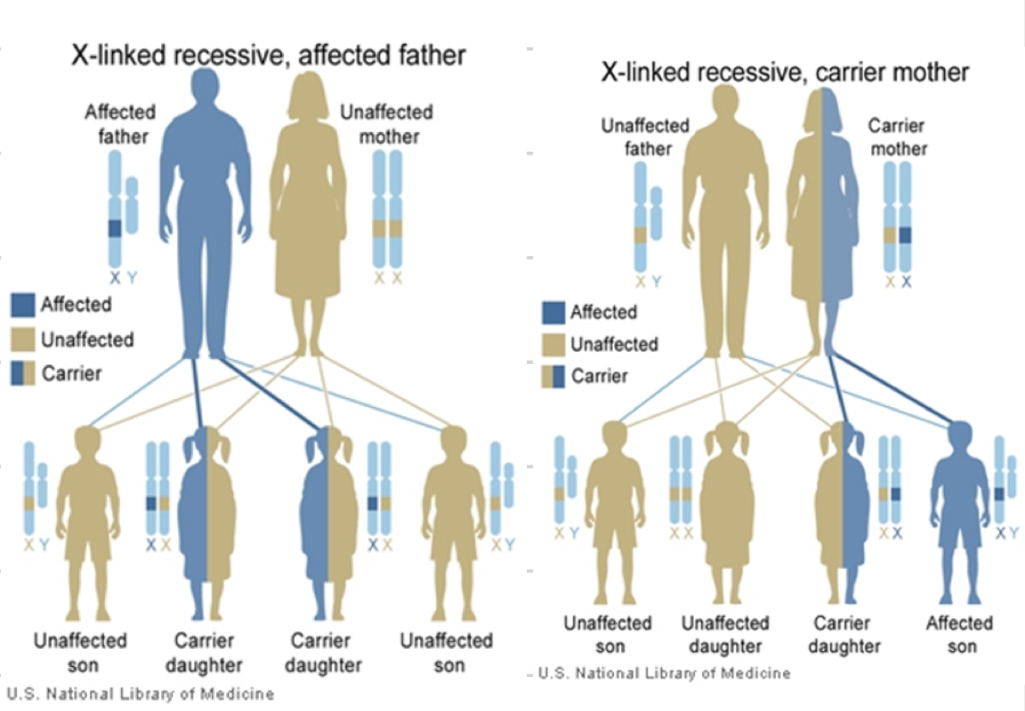
X-linked recessive
No male-to-male transmission
Males affected almost exclusively
Transmitted through unaffected female carriers
All daughters of an affected male are carriers
E.g. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
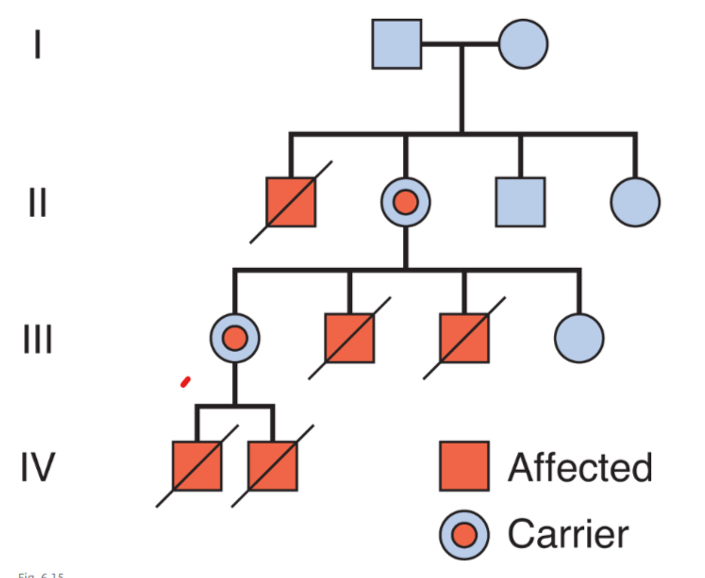
X-linked pedigree
X-linked dominant
males and females affected (often more females)
Females usually less severely affected due to 2nd X
Males transmit to ALL daughters and never sons
Affected females transmit to 50% of her offspring
E.g. incontinnentia pigmenti
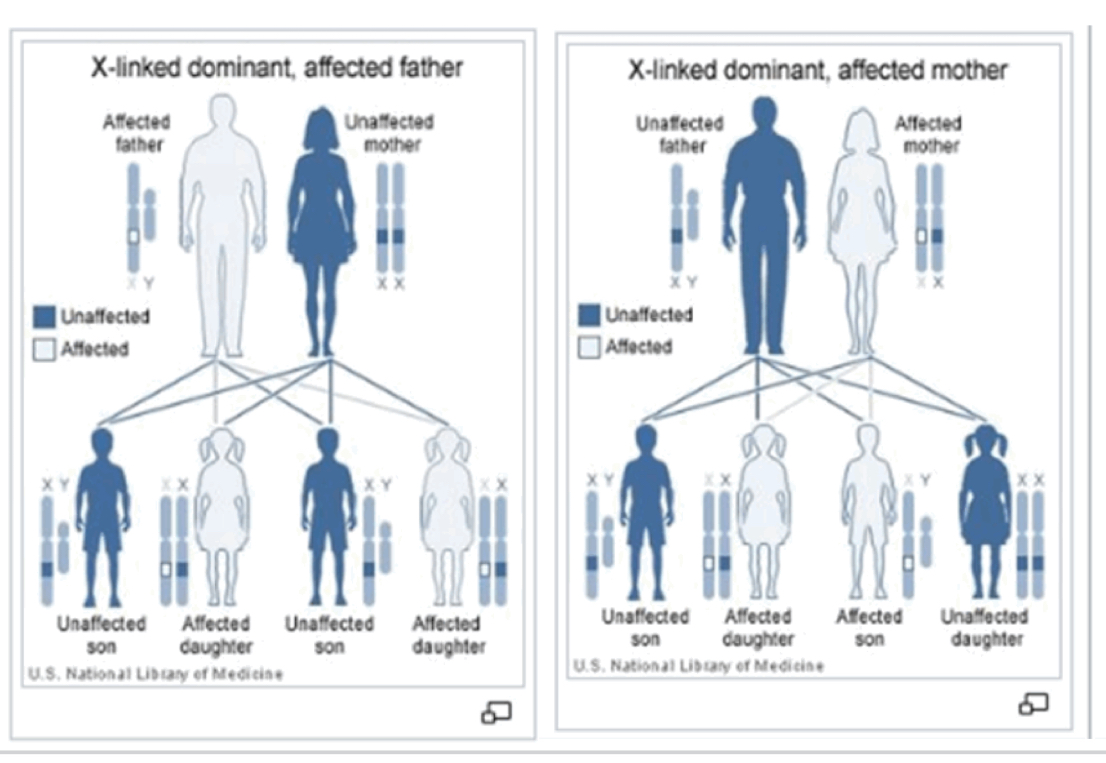
Incognentia pigmenti
some alleles result in death before birth
Females XX : skin abnormalities, hair loss, small/few teeth, eye problems, intellectual disability/neurological problems
Males XY : lethal in utero in most males
X-linked dominant
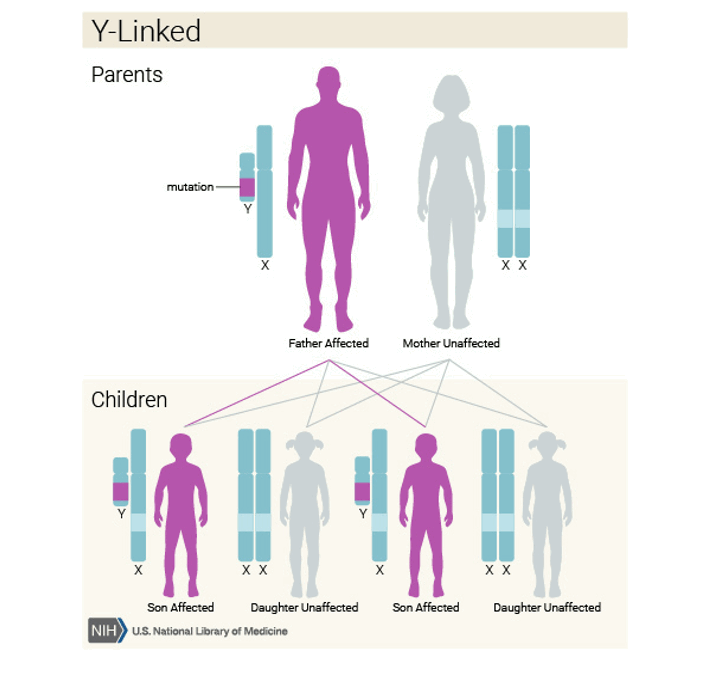
Y linked inheritance
affected males only
Affected males transmit to all their sons
Because there are so few genes on Y, only a few speculative cases have reported this
Some mutations cause infertility = no inheritance
Affected males ONLY have affected sons
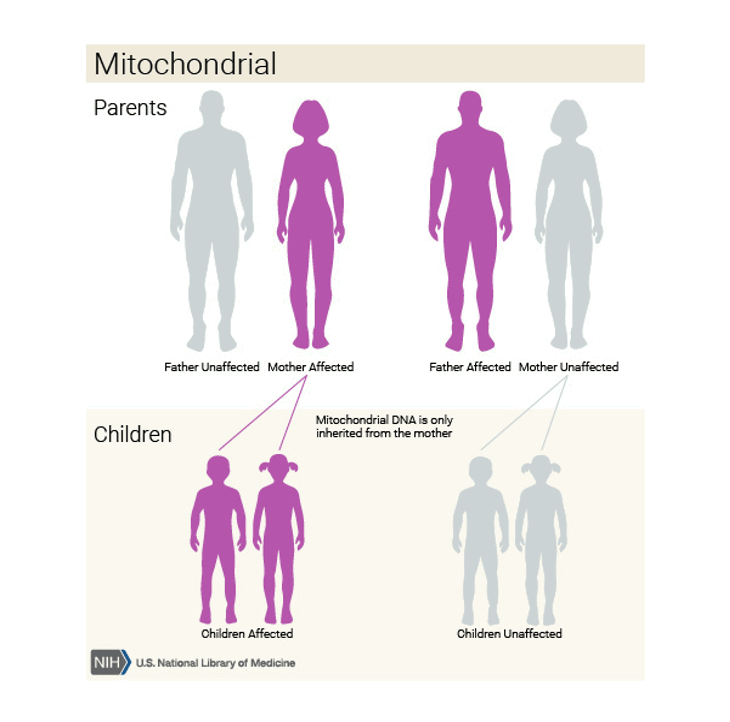
Mitochondrial inheritance
Conditions can appear in every generation of a family
Can affect males and females
Fathers don’t pass onto offspring - only females pass on as eggs but not sperm contain mitochondria
Can pass on a mixed population→ different children inherit different no.s of mitochondria with the disease mutation:
Homoplasmy
Heteroplasmy = mix of mitochondrial types
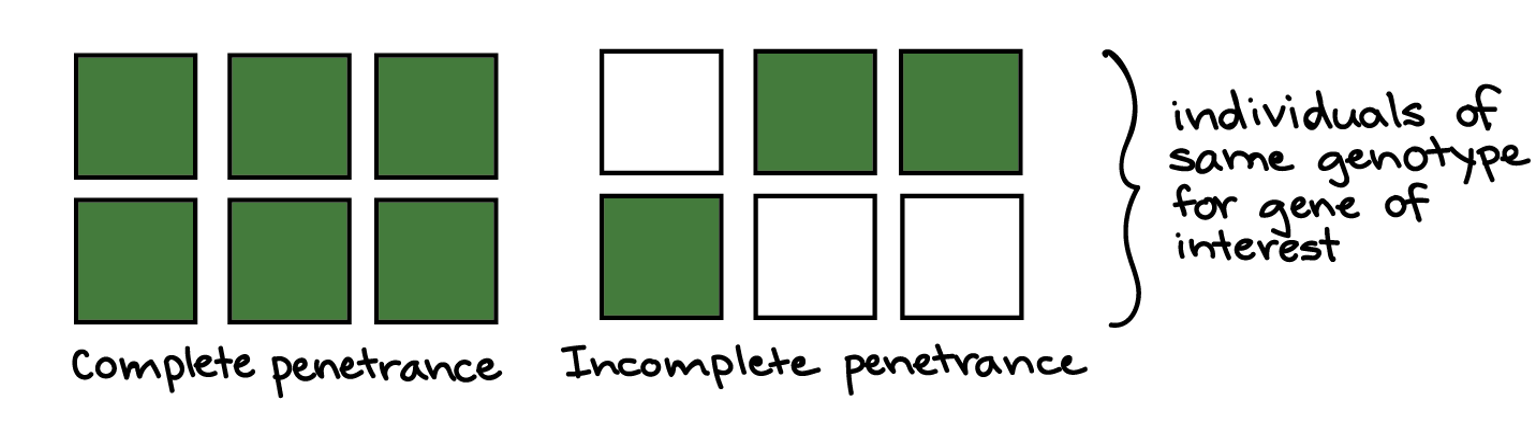
Penetrance
→ % of people with the genotype that express the phenotype
complete penetrance = all individuals have the phenotype
Incomplete penetrance = individual genotype may not develop a phenotype
E.g BRCA1 = 80% lifetime risk
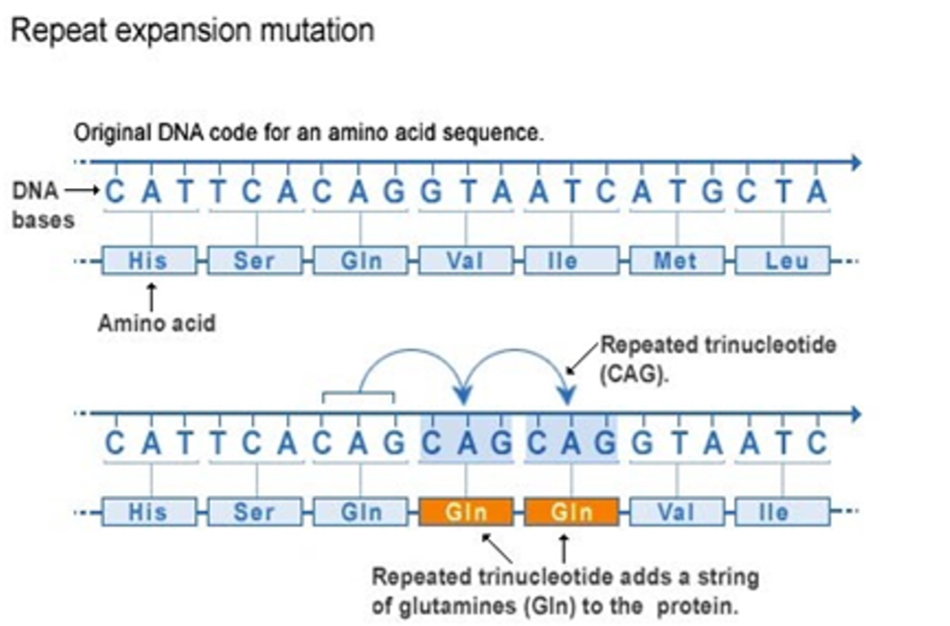
Anticipation in trinucleotide repeats
→ genetic disorder by a trinucleotide (codon) repeat
signs and symptoms become more severe and appear at an earlier age as the disorder is passed from one generation to the next
Typically occurs with disorders caused by an unusual mutation called trinucleotide repeat expansion
Anticipation - mechanism
Expansion due to ‘slippage’ during DNA replication, above a threshold where the gene stops functioning normally
People with the same disease genotype may have stronger or weaker forms of the disorder, or never develop it
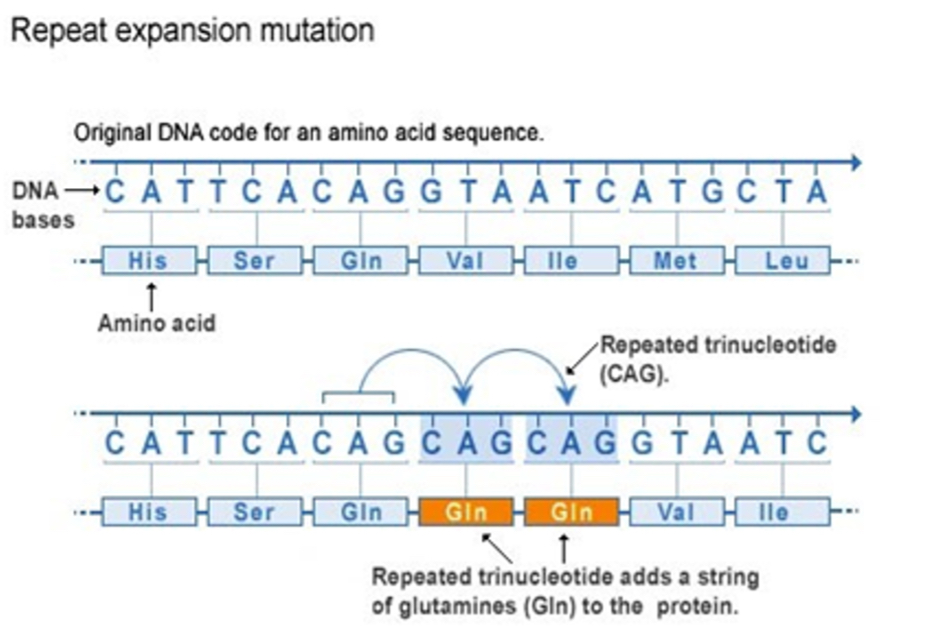
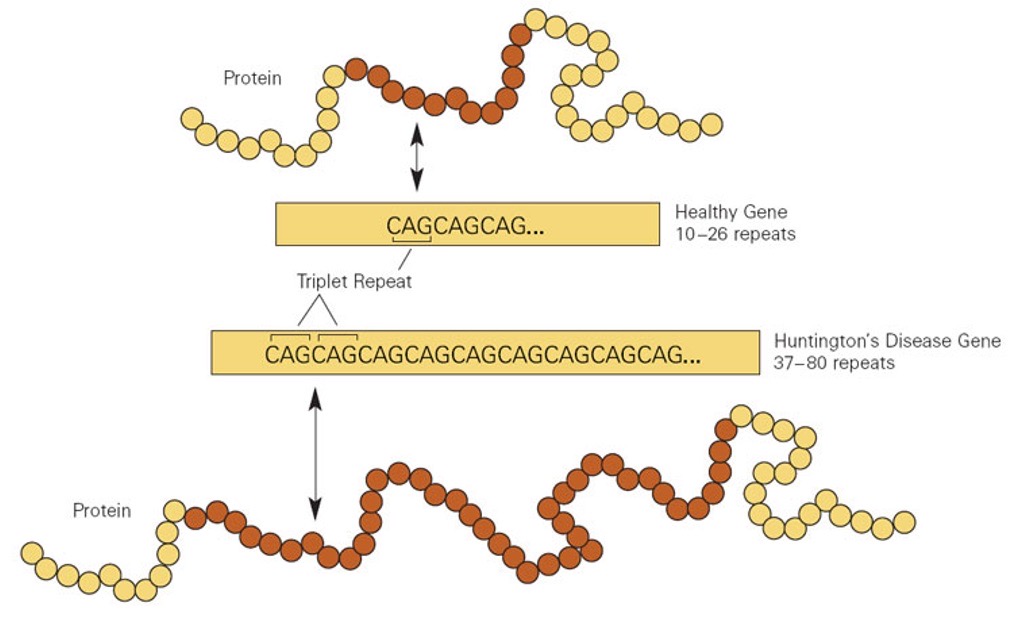
E.g. Huntington’s, fragile X syndrome
Huntington disease
more CAG repeats in the HTT gene, which makes aa glutamine
27-35 repeats = no disease but prone to repeat instability
36-55 =-19 common in patients with Huntington’s
60+ repeats = juvenile onset
Detecting anticipation
Use PCR with one fluorescent primer and one standard primer
Bind either side of the repeat region
Capillary electrophoresis - exact size(s) of alleles and number or repeats detected using laser