year one core studies
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Milgram Aim
To measure the level of obedience to an authority figure, when asked to administer electric shocks to another person.
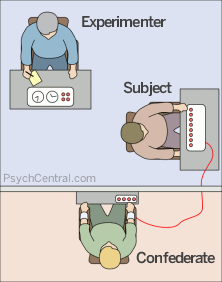
Milgram Sample
40 males aged between 20-50. newspaper article. $4.50.
Milgram Procedure
Participants were 'randomly' allocated to be the teacher. Asked to give an electric shock every time the learner got a question wrong. Increased by 15volts each times.
Milgram Results
100% reached 300v. 65% reached 450v. Signs of extreme stress.
Milgram Conclusions
People obey those of high authority. People will shift the blame to the experimenter.
Bocchiaro Aim
To investigate the rates of obedience, disobedience and whistleblowing in unethical situations.
Bocchiaro Sample
149 participants. (comparison group= 138). Volunteer sampling. Paid $7.
Bocchiaro Pilot studies
8 pilot studies, conducted to ensure the study was ethically sound.
Bocchiaro Procedure
Participants were told that a study into sensory deprivation was going to be carried out. They were put into a room with computers, a mail box and committee form. They were asked to write an enthusiastic statement about the study. They completed a personality test.
Bocchiaro Comparison group
These students were asked: 'what would you do?' 'what would they average student do?'
Bocchiaro Results
76.5% obeyed. 9.4% whistleblew.
Bocchiaro Conclusions
People tend to obey authority figures, even if it is unethical. The level of obedience was underestimated. Wanting to be good is taken over by situational factors.
Loftus & Palmer Aim
To investigate the effect of leading questions on eye witness testimony of car crashes.
Loftus & Palmer Sample
Experiment 1= 45 participants. Experiment 2= 150 participants, (3 groups)
Loftus & Palmer Procedure 1
Shown 7 films of car crashes. They were asked to write an account of the incident. Asked questions about the crash. 'How fast were the cars going when they verb'
Loftus & Palmer Verbs used
Hit Contacted Bumped Collided Smashed
Loftus & Palmer Procedure 2
Participants watched a clip of a car crash. Asked questions after the clip. Group 1= 'how fast were the cars going when they Smashed into each other?' Group 2= 'how fast were the cars going when they hit each other?' Control= were not asked about speed.
Loftus & Palmer Results
EXP 1
smashed = fastest speed estimates contacted = slowest All estimates were higher than the actual crashes EXP 2 More P's in 'smashed' said there was broken glass than in 'hit' and the control. Most P's correctly recalled no glass
Loftus & Palmer Conclusions
Misleading post event information can affect memory. Memories are formed of information from event and after event. Eye witness testimony is rarely accurate.
Grant Aim
To investigate that learning context and taking a test in the same environment has a positive effects on performance.
Grant Sample
8 psychology students as experimenters. 39 participants. Ages 17-56.
Grant Procedure
Instructions were read aloud. Participants were given an article to read. Told they would be tested on it. All participants wore headphones. 2 minute break between reading and testing. Short answer test followed by multiple choice test.
Grant Conditions
Reading/Testing: Silent/Silent Silent/Noisy Noisy/Noisy Noisy/Silent
Grant Results
Better results in silent/silent condition= 14.3. Shows reading and testing in the same environment produces Better results.
Grant Conclusions
Studying and testing in the same environment leads to enhanced performance. There are context-dependency effects for newly learned material. Students should study in silent conditions.Moray
Bandura Aim
To investigate if social behaviours can be acquired by observation and imitation.
Bandura Sample
72 children. 37-69 months. Stanford university nursery.
Bandura Procedure 1
Room 1- children sat at a table and watched models set up toys.
Aggressive models verbally/physically abused the bobo doll. Non-aggressive models assembled a tinker toy set quietly.
Bandura Procedure 2
Room 2- children taken into another room and allowed to play with attractive toys.
After 2 minutes the toys were taken away and told they were for other children.
Bandura Procedure 3
Room 3- Bobo doll, mallet, dart gun, tea set, cars and dolls.
Their behaviour was observed.
Bandura Results
Children in the aggressive condition showed more aggressive behaviours. Children imitated models of their own sex more. Male models exerted a greater influence.
Bandura Conclusion
Children imitate behaviours shown by adult models. Children learn behaviours through observation and imitation. Boys and Girls are more likely to learn verbal aggression from same sex models.
Chaney Aim
To test whether positive reinforcement of funhaler could improve medical compliance.
Chaney Sample
32 children. 1.5 to 6 years. Australia. Parents contacted by the phone.
Chaney Procedure
Parents helped in the use of funhaler. Asked to use the funhaler for 2 weeks instead on their normal one. Funhaler incorporates a number of features to distract the child.
Chaney Results
Improved parent and child compliance. 38% more parents found to have medicated their children when using the funhaler. 60% more children took the recommended cycles.
Chaney Conclusion
Improved adherence and satisfactory delivery characteristics.
Funhaler may be useful for management of young asthmatics. Improve measurements of clinical outcome.
Sperry Aim
To investigate the effects of hemispheric deconnection on perception and memory.
Sperry Sample
11 epileptic participants. Had undergone hemisphere deconnection.
Sperry Procedure Visual
Participants had 1 eye covered. Their central gaze on a fixed point of a translucent screen. Visual stimuli projected at 1/10th of a second. Everything projected on the left of the screen, passed via the LVF into the right hemisphere.
Sperry Procedure Tactile
There was a gap below the screen, so the participants could reach objects and not see their hands. Left hand processed by the right hemisphere.
Sperry Results Visual
Information presented to RVF could be described in speech and writing. Information in LVF was either not seen or just a flash. Participants could point with left hand to matching pictures.
Sperry Results Tactile
Objects placed in right hand could be described could be described in speech or writing. Left hand, unaware of holding anything. Each hand selected their own object.
Sperry Conclusion
People with split brain have 2 separate visual inner worlds. Lack of cross-integration where a second hemisphere does not now what the first has been doing. 2 independent streams of consciousness, perceptions and memories.
Casey Aim
To investigate the extent to which the ability to resist temptation at a preschool age affected the same pps in adulthood.
Casey Sample
Started with 562 participants. Exp 1- 59. Exp 2- 27.
Casey Systems
Cool system= cognitive control. Hot system= controlled by desires and emotion.
Casey Procedure 1
Tested whether individuals who were low delayers as children, would show less impulse control in suppression as adults. Cool version: genders.
Go task (press button)= One sex No-go task (withhold to press button)= Other sex 160 trials, presented in a pseudo-randomised order. Hot version: fearful and happy facial expressions.
Casey Procedure 2
fMRI was used to examine neural correlates of delay of gratification. Anticipated that low delayers would show diminished activity in the Right prefrontal cortex. Hot version similar to exp 1. 48 trials in pseudo-randomised order.
Casey Result 1
Participants all performed with high levels accuracy for the 'go' trails.
Cool= 99.8% Hot= 99.5% Low delayers committing more false alarms than high delayers in No-go trials. Low delayer performed more poorly on Hot task.
Casey Result 2
Hot go= 98.2% correct. Hot No-go= 12.4% false alarms. Low delayers= diminished recruitment of inferior frontal gyrus.
Casey Conclusion
The more temping the choice, the more predictive the individual differences in peoples ability to regulate their behaviour. Low delayers at age 4, have more difficulty as adults in suppressing responses.
Psychosexual stages
Oral- Mouth is the main focus of pleasure suckling.
first year of life. Anal- Pleasure of the anus as the child learns to retain and expel faeces at will. 1-3 years. Phallic- Involves strong attachment to opposite sex parent and rival from the same sex. 3-6 years.
Freud Sample
Little Hans. Case study.
Freud Procedure
Little Hans kept playing with his 'widler'. Hans liked being in bed with his mother. He was scared that his father would castrate him. He also had a fear of horses. Hans' father was a fan of freud and contacted him.
Freud Results
Subconscious fear for his father. Blinkers and dark around the horses mouth resemble his fathers glasses and moustache. Scared of a horse biting him, represents fear of being castrated. Hans was going through the phallic stage.
Freud Conclusion
His study provided support for:
His theory of psychosexual development. That boys in the phallic stage experience the Oedipus complex. The nature of phobias are the product of unconscious anxiety displayed onto harmless objects.
Baron-Cohen Aim
To test emotional recognition in people with and without autism.
Baron-Cohen Sample
16 high-functioning autistic participants. 50 normal participants. 10 Tourettes participants.
Baron-Cohen Procedure
Strange stories task:
Story comprehension, which concerns either characters mental or physical state. Eye task: Black and white pictures of the eye region. Choice between 2 mental state words to best describe what that person was feeling.
Baron-Cohen Results
Normal females performed significantly better than normal males. Normal and Tourettes participants performed higher than autism group. Autism made more errors on strange story task.
Baron-Cohen Conclusion
Autism participants do posses an impaired theory of mind. Theory of mind deficits are independent of general intelligence.