OChem 8A - Ch4
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
isomers- arrangement of isomers in space
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures
falls into two main classes:
constitutional isomers
stereoisomers
Constitutional isomers
differ in the way their atoms are connected
ex) ethanol and dimethyl ether have same formula C2H6O but their atoms are connected differently - (the oxygen in ethanol is bonded to a carbon and to a hydrogen, whereas the oxygen in dimethyl ether is bonded to two carbons).
Cis-trans isomers / geometric isomers result from…
restricted rotation
what causes restricted rotation in cis-trans isomers?
cyclic structure or a double bond
cis isomer
compound with the substituent (in example H) on the same side of the double bond
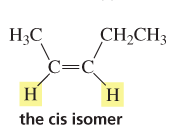
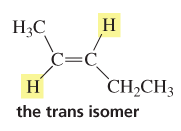
trans isomer
compound with the substituents (H in example) on opposite sides of the double bond
cis and trans have ___ molecular formula and ___ bonded atoms but ____ configurations.
same, same, different;
differ in the way atoms are oriented in space
trans isomers have dipole moments of ____ and why?
0 because of the dipole moments their individual bonds cancel
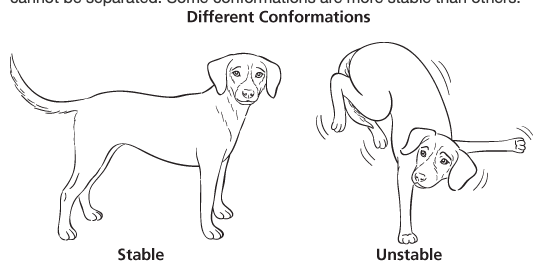
conformations / conformers
different spatial arrangements of the same compound (ex: anti & gauche conformers)
they cannot be separated
some conformers are more stable than others
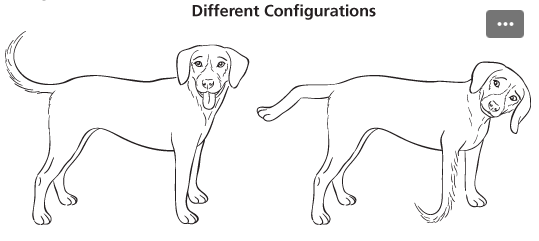
configurations/ stereoisomers
different compounds (ex. cis and trans isomers)
can be separated from each other
bonds have to be broken to interconvert compounds with different configurations
priority depends on
atomic number - relative priority depends on the atomic numbers of the artoms bonded directly to the sp2 carbon. the greater atomic number higher priority.
If there is a tie (same two atoms attached to sp2 carbon) consider the atomic # of atoms attached to tied atoms
if an atom is doubly bonded to another, treat it as if it were singly bonded to two of those atoms
if an atom is triply bonded, treat it as if it were singly bonded to 3 of those atoms
cancel atoms that are identical in the two groups; use the remaining atoms to determine the group with higher priority
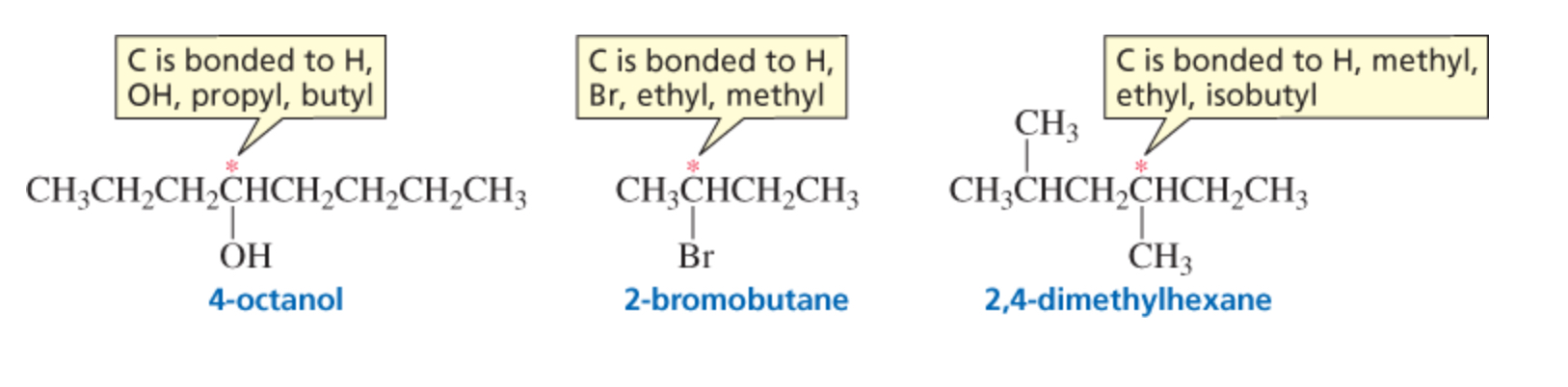
chiral
nonsuperimposable mirror image
ex) hand, ear, seat config. in a car
achiral
object is the same as its mirror image → superimposable
a chiral molecule has…
an asymmetric center - an atom bonded to four different groups
(only sp3 carbons can be asymmetric centers)
enantiomers
molecules that are non superimposable mirror images of each other
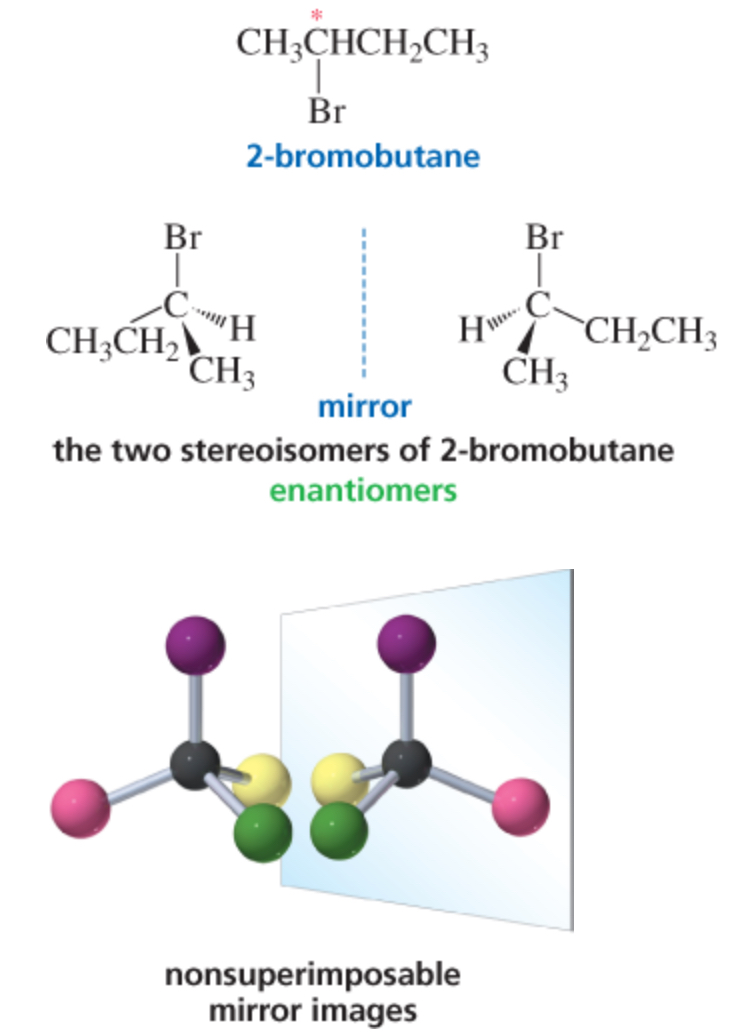
enantiomers = chiral
each member of a pair of enantiomers is chiral because it has a non superimposable mirror image (like the hand, ear, car seats img)
how to see if a molcule is achiral
mirror image is superimposable
check by rotating the molecule clockwise
R is
to the right - clockwise
S is
to the left - counterclockwise
(latin root → sinister for left)
if lowest priority isn’t on hatched switch it with the hatched bond and if it was moved once is the opposite (if after switch it was R it was originally S)
Recognizing pairs of enantiomers
determine configurations
if one is R and other is S then enantiomers
if both R or S they’re identical compounds.
chiral compounds are what optical activity
optically active - rotates the plane of polarization
(+)= clockwise rotation
(-) = counterclockwise rotation
achiral compounds are what optical activity
optically inactive - does not rotate the plane of polarization
2n = max number of stereoisomers
n= number of asymmetric centers
meso compound
has asymmetric centers but achiral, superimposable on mirror image
has two or more asymmetric enters and a plane of symmetry
“in the case of cyclic compounds, the cis isomer will be a meso compound and the trans isomer wil be a pair of enantiomers”