Equine Prioplasms, Entomology, Acarology, Nematocera, Brachycera, and Cyclorrhapha
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What two types Equine Prioplasm?
Babeisa caballi and Theileria equi
How do you differentiate B. caballi and B. equi?
B. caballi - large prioplasms, usually paired
T. equi - small prioplasms, can be found in tetrads
How is Equine Prioplasm transmitted?
Ticks
True or False: Africa, the middle East, and Central and South American are endemic with Equine Prioplasm while the United States is non-endemic but can have sporadic outbreaks.
True
What ticks transmit B. caballi?
Dermacentor nitens and Dermacentor albipictus
What ticks transmit T. equi?
Dermacentor variabilis, Amblyomma cajennense, and Rhipicephalus microplus
What are the clinical signs of Equine Prioplasms?
Fever, lethargy, edema, pale mucous membranes, anemia, and thrombocytopenia
True or False: Prevention of Equine Prioplasm is different depending on endemic and non-endemic regions.
True
How do you prevent Equine Prioplasm in the US and Canada?
Import and export surveillance, thorough examination of ticks, and reduce contact of horses with ticks in areas bordering endemic nations
What do you do with a horse that is positive for Equine Prioplasm?
Quarantine until complete clearance
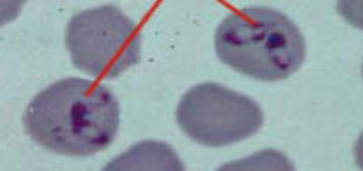
What is this?
Babesia caballi
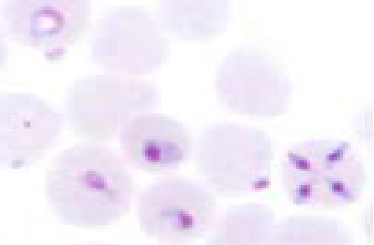
What is this?
Theileria equi
True or False: About 80% of entomology and acarology species are arthropods.
True
What does mechanical vector mean?
Pathogens are transmitted by arthropods via contaminated appendages (usually mouthparts) or regurgitation of an infectious blood meal
What does biological vector mean?
Pathogens undergo development or reproduction in the arthropod host
What are the three body regions of insects?
Head, thorax, and abdomen
What is included in the head region of an insect?
Eyes, antennae, and mouthparts
What is included in the thorax region of an insect?
Legs (jointed appendages) ± wings
Up to how many segments are in the abdomen region of an insect?
Up to 11 segments
True or False: The exoskeleton of an insect is impermeable to water.
True
True or False: Insects undergo molting to accommodate growth.
True
What is the stage between two molts called?
Instar
What are the three main fly groups?
Nematocera, Brachycera, and Cyclorrhapha
What type of antennae do Nematocera flies have?
Multisegmented antennae
What type of antennae do Brachycera flies have?
Stylate antennae
What type of antennae do Cyclorrhapha flies have?
Aristate antennae

What type of antennae are these?
Multisegmented antennae
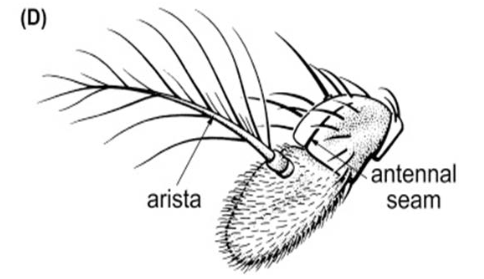
What type of antennae is this?
Aristate antennae
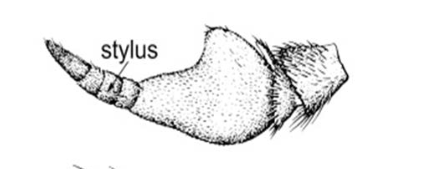
What type of antennae is this?
Stylate antennae
What species are in the fly group Nematocera?
Mosquitoes, black flies, sand flies, and biting midges
What species are in the fly group Brachycera?
Horse flies and deer flies
What species are in the fly group Cyclorrhapha?
House flies, blow flies, and bot flies
What diseases do mosquitoes cause in intermediate hosts?
Dirofilaria immitis in dogs and cats, and Seteria in horses, cattle, and deer
What diseases do mosquitoes cause in definitive hosts?
Malaria, EEE, WEE, SLE, Yellow Fever, West Nile, Dengue, Chikungunya, etc.
What is the causative agent of Malaria?
Plasmodium spp.
Personal protection against mosquitoes includes what?
Window screens, synthetic pyrethroid impregnated bed nets, chemical repellents such as DEET applied to skin or clothing
Organized control programs/surveillance against mosquitoes includes what?
Surveillance for mosquito-borne disease pathogens, mosquito distribution, abundance and activity - implement abatement programs
Habitat modifications against mosquitoes includes what?
Rendering adult mosquito resting places unsuitable, reducing sources to prevent oviposition, hatching, and larval development
Biological control against mosquitoes for fish includes what?
Prevent feeding on mosquito larvae and remove aquatic vegetation that supports mosquito larvae
Genetic control of mosquitoes includes what?
Releasing sterile males and replacement of natural populations with strain that are poor vectors
Chemical control of mosquitoes includes what?
Larvicides and adulticides
What is the genus of black flies?
Simulium
Where are black flies found?
Northern US and Canada
Black flies are active when and breed where?
Active in late spring to early summer, breed on swiftly flowing waters
True or False: Black fly bites are painful and the mouthparts lacerate tissues creating a pool of blood that they imbibe.
True
Where are black fly eggs laid?
Eggs are laid on vegetation at surface of flowing water
What are biological vectors of Simulium?
Onchocerca of horses, cattle, and sheep. Dirofilaria ursi of bears. Leucocytozoon (protozoa of birds)
How can you prevent Simulium?
Smoke screens, personal protection, shelters for livestock and poultry, and petroleum jelly to inner surface of pinna
What are the two different genera of sand flies?
Phlebotomus and Lutzomiya (US)
True or False: Sand flies have short and broad wings. They are weak flyers; have short hops; are easily blown away by air currents, and are nocturnal.
True
Where do adult sand flies lay eggs?
Adult sand flies lay eggs in cracks and crevices, under stones with moderate temps, darkness, and 100% humidity
What disease do sandflies cause?
Leishmaniasis
What are 3 ways to prevent Leishmaniasis from sand flies?
Insect repellents, deltamethrin impregnated collars, permethrin and imidacloprid spot-on formation
What is the genera of biting midges?
Culicoides
What are two other names for biting midges?
Punkies and no-see-ums
True or False: Biting midges are very painful biters.
True
Where do female biting midges lay their eggs?
In moist soil, mud, or decaying matter
True or False: Biting midges are found in the Southern US.
True
What do biting midges cause in sheep and cattle?
Bluetongue virus
What do biting midges cause in ruminants and deer?
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus
What do biting midges cause in horses?
Allergic dermatitis
True or False: Biting midges breeding sites are hard to locate, and biting midges can pass through mosquito screens.
True
Repellents containing what are effective against biting midges?
DEET
Besides repellent, what are two ways to control biting midges?
Avoid outdoor activities during fly active periods and treatments of resting sites with residual insecticides
Horse flies and deer flies are known as what?
Brachycera
True or False: Brachycera flies have a blade-like mouth with a sponging labella. They are strong fliers, hard to repel, painful biters, and consume 4x their body weight.
True
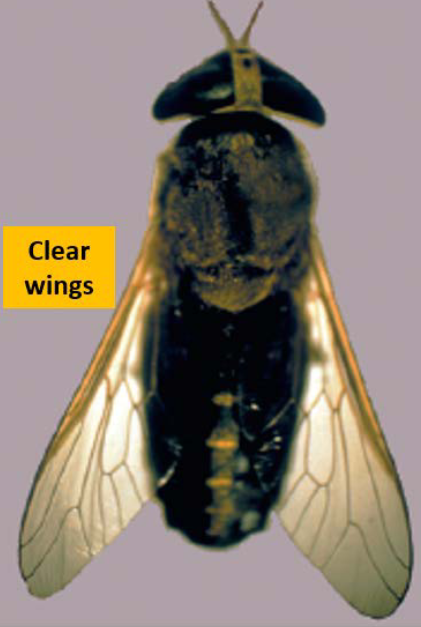

What Brachycera fly is this?
Horse fly
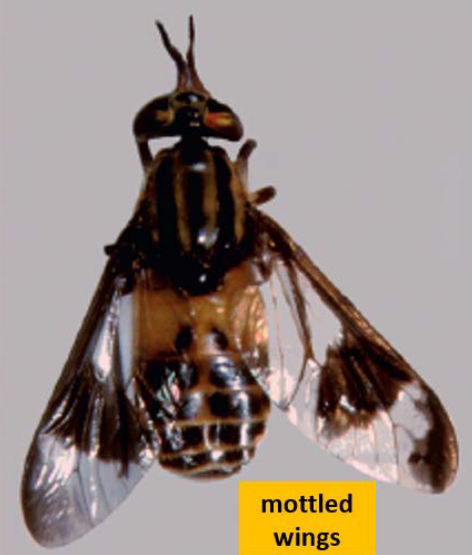

What Brachycera fly is this?
Deer fly
Where do Brachycera flies bite cattle, deer, and horses?
Shoulders, back, and sides
True or False: Brachycera fly bites bleed for many minutes attracting opportunists such as Musca spp. These bites can cause production loss and behavior changes.
True
What do mechanical vectors of disease transmission with Brachycera flies cause?
Equine infectious anemia, anaplasmosis, and anthrax
What do biological vectors of disease transmission with Brachycera flies cause?
Trypanosoma theileri of cattle and Elaeophora schneideri of deer, elk, and sheep
What are ways to control Brachycera flies?
Put livestock in stables during fly activity periods and use fly repellent
True or False: Brachycera flies are easy to control.
False - they are hard to control
House flies, blow flies, and bot flies are known as what?
Cyclorrhapha
What are the characteristics of Cyclorrhapha pupa?
Cylindrical, hardened cuticle
What are the characteristics of Cyclorrhapha larvae?
Posterior respiratory spiracles
What are the two non-biting muscid flies?
Musca domestica and Musca autumnalis
What are the two biting muscid flies?
Stomoxys calcitrans and Haematobia irritans
What is the difference between Musca domestica and Musca autumnalis?
Musca domestica has a pointed abdomen and the Musca autumnalis has a rounded abdomen
What is the difference between Stomoxys calcitrans and Haematobia irritans?
Stomoxys calcitrans has a checkerboard abdomen and the Haematobia irritans is smaller in size

What fly is this?
Musca domestica

What fly is this?
Musca autumnalis

What fly is this?
Stomoxys calcitrans

What fly is this?
Haematobia irritans
What is the common name of Musca domestica?
House fly
What is the common name of Musca autumnalis?
Face fly
What is the common name of Stomoxys calcitrans?
Stable fly
What is the common name of Haematobia irritans?
Horn fly of cattle
What is this breeding site for Musca domestica? Musca autumnalis?
Musca domestica: Manure or decaying material
Musca autumnalis: Fresh cow feces
What is the breeding site for Stomoxys calcitrans and Haematobia irritans?
Stomoxys calcitrans: Old manure (horse and cow)/decaying vegetation
Haematobia irritans: Fresh cow manure
What are the characteristics of adult Musca domestica, Musca autumnalis, and Stomoxys calcitrans?
Musca domestica: 6-9mm with 4 dark stripes; sponging mouthparts
Musca autumnalis: Same as domestica but larger
Stomoxys calcitrans: Same ss domestica but with bayonet mp
What are the characteristics of Haematobia irritans?
1/2 the size of Musca domestica; mouth parts similar to Stomoxys calcitrans but smaller
What does Musca domestica transmit?
Draschia megastomum, Habronema muscae, and poultry tapeworms
What does Musca autunmnalis transmit?
Pinkeye and Thelazia
What does Stomoxys calcitrans transmit?
T. evansi, possibly Habronema
What does Haematobia irritans transmit?
Stephanofilaria
What are the 4 ways to control muscid flies?
Prevetion of breeding, ridding of adult flies, exclusion of adult flies, and a combination of all three
How do you prevent breeding of muscid flies?
Sanitation, adulticides, larvicides, waste disposal, and compost piles
How do you get rid of adult muscid flies?
Traps and baits, chemical fogs or mists