bsc 2085 lesson 12
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
endocrine system
communicates by means of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood
Nervous system
utilizes neurons to send messages from cell to cell by electrical and chemical means
Steps of neuron communication
receives stimuli from external environment and transmits messages to central nervous system
the CNS processes the information and determines the response
CNS issues commands to muscle and/or gland cells to carry out the response
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerves and ganglia
Nerve
a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) wrapped in fibrous connective tissue
Ganglion
knot-like swelling in a nerve where neuron cell bodies of the PNS are concentrated
Sensory (afferent) division
carries signals from receptors (sense organs) to CNS
Somatic sensory division
carries signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bones, and joints
outside the body sensory
Visceral sensory division
carries signals from the viscera (heart, lungs, stomach, and urinary bladder)
inside the body sensory
Motor (efferent) division
carries signals from CNS to the effectors (glands and muscles that carry out the body’s response)
Somatic motor division
carries signals to skeletal muscles; causes voluntary muscle contraction and automatic reflexes
Visceral motor division (autonomic nervous system, ANS)
carries signals to glands, cardiac, and smooth muscle; no voluntary control; responses called visceral reflexes
Sympathetic division of ANS
stimulates and prepares the body for action (fight or flight)
Parasympathetic division of ANS
has a calming effect on the body
Enteric plexus (enteric nervous system) of ANS
within digestive tract wall, enables coordination and communication within the digestive tract
Tract
a bundle of axons in the CNS
Nerve
a bundle of axons in the PNS
Nucleus
a cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS
Ganglion
a cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS
excitability
ability to respond to stimuli
conductivity
produce electrical signals that are conducted to other cells
secretion
when signal reaches end of the neuron’s axon, the neuron secretes a neurotransmitter that signals the next cell
Interneurons
receive signals from other neurons, process this information, and make resulting decisions; entirely within CNS
Sensory (afferent) neurons
detect stimuli and transmit information about the stimuli toward the CNS
Motor (efferent) neurons
send signals out to muscles and gland cells (the effectors)
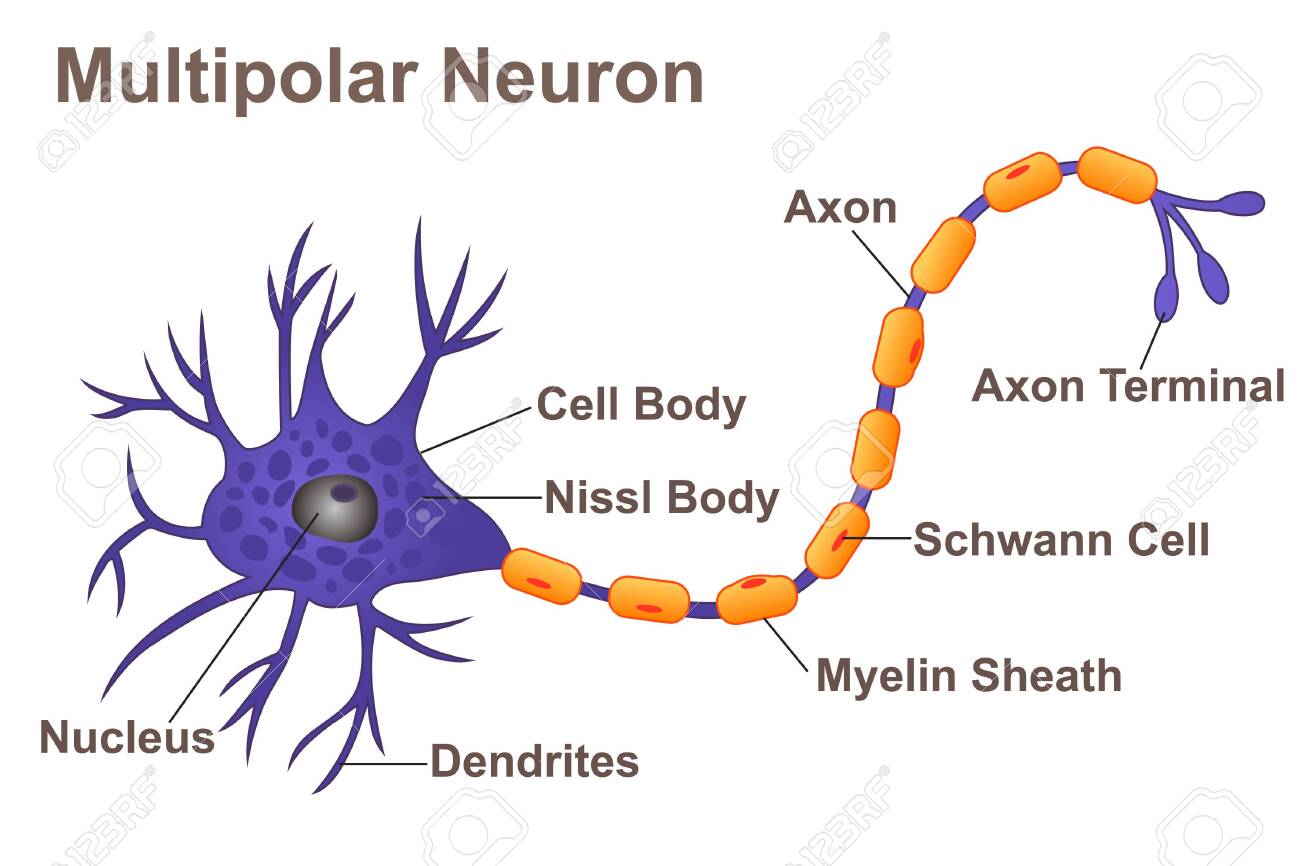
Dendrites
most numerous neurites, resemble branching of a tree; primary sites for receiving signals from other neurons
axon (nerve fiber)
long extension, relatively unbranched but give off axon collaterals, specialized for rapid conduction of nerve signals
Axon hillock
where axon originates, mound on one side of cell body
axoplasm
cytoplasm
axolemma
axon membrane
terminal arborization
where axon branches profusely at its end
Axon terminal (terminal bouton)
bulbous end of each brand of arborization, forms a synapse with next cell
Multipolar neuron
one axon and multiple dendrites, most common in body, most neurons in CNS
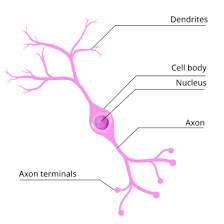
Bipolar neuron
one axon and one dendrite, most uncommon
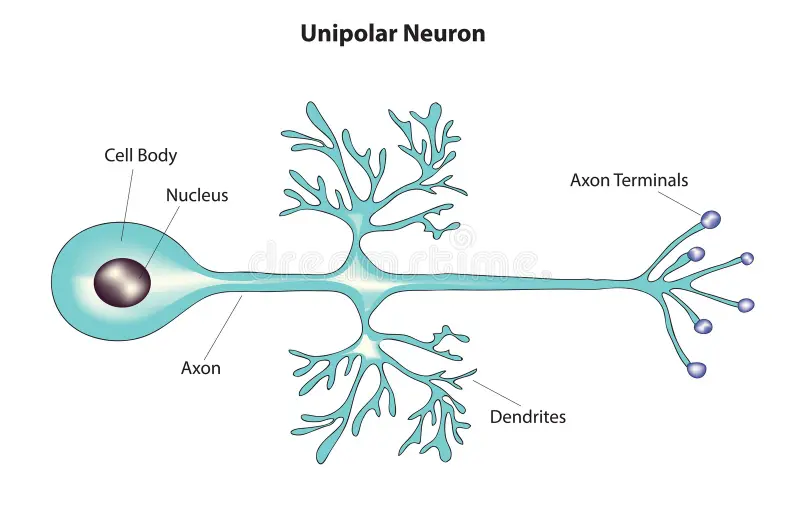
unipolar neuron
single process leading away from cell body, splits into peripheral process and central process
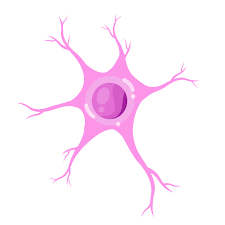
anaxonic neuron
many dendrites but no axon
Axonal transport
two-way passage of materials along an axon
Anterograde transport
movement away from cell body, down the axon
driven by motor protein kinesin
Retrograde transport
movement up the axon toward the cell body
driven by motor protein dynein
Why can’t neurons undergo mitosis?
they are stuck in G0
Neuroglia (Glial cells)
binds neurons together, prevents neurons from touching each other by maintaining synaptic cleft
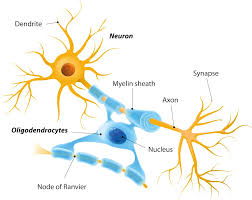
Oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheaths in CNS
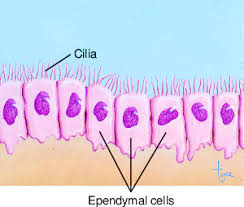
Ependymal cells
secrete and circulates cerebrospinal fluid
line internal cavities of brain
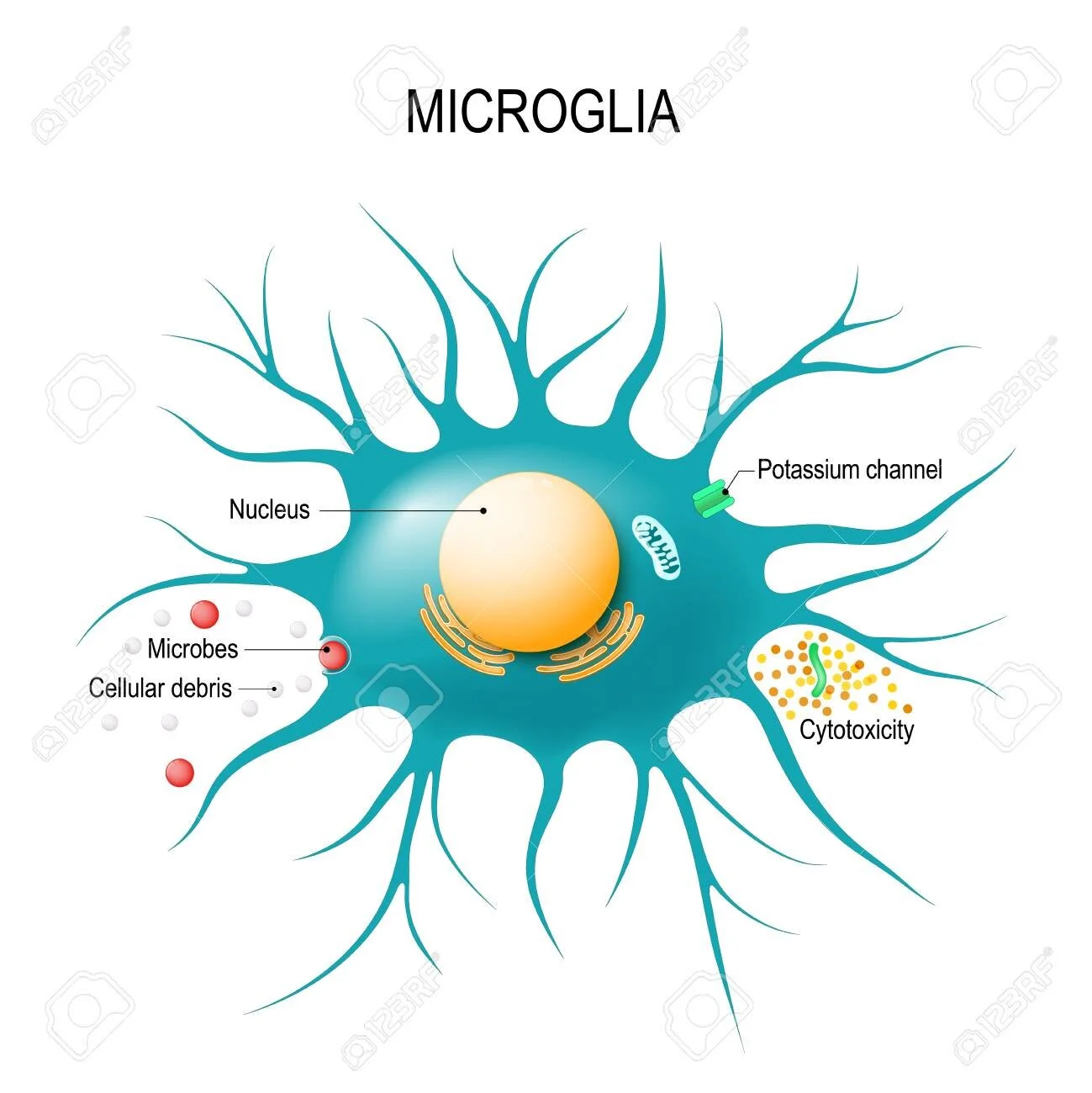
Microglia
macrophages
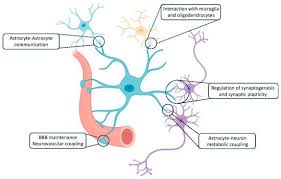
Astrocytes
most abundant type; variety of functions
Schwann cells
envelop axons of PNS, form myelin sheath, and assist in regeneration of damaged fibers
Satellite cells
surround nerve cells bodies in ganglia of PNS, provide insulation around cell body
Gliomas
tumors of glial cells
Myelin sheath
spiral layers of insulation around an axon
Schwann cells in PNS
Oligodendrocytes in CNS
Neurilemma
thick outermost coil of myelin
Myelination in CNS
each oligodendrocyte extends several processes that wrap around small portions of many axons in immediate vicinity
Myelin sheath gap (node of Ranvier)
gap between segments
Internodal segments
myelin-covered segments
Initial segment
bare section of axon between the axon hillock and first glial cell
Trigger zone
axon hillock and initial segment of axon
important role in initiating nerve signal (action potential)
Multiple sclerosis
Oligodendrocytes and myelin sheaths in CNS deteriorate
myelin replaced by hardened scar tissue
Tay-sachs disease
Abnormal accumulation of glycolipid called GM2 in the myelin sheath
normally decomposed by lysosomal enzyme
enzyme missing in individuals homozygous for Tay-Sachs allele
Unmyelinated axons
In PNS, schwann cells hold small unmyelinated axons in surface grooves
Regeneration of damaged PNS axon can only occur if
nerve cell bodies are intact and at least some neurilemma remains
Regeneration of PNS axon step 1
Axon distal to injury degenerates, macrophages clean up tissue debris
Regeneration of PNS axon step 2
Cell body swells, ER breaks up, and nucleus moves off center
Regeneration of PNS axon step 3
Axon stump sprouts multiple growth processes
Regeneration of PNS axon step 4
Schwann cell neurolemma, endoneurium, and basal lamina form regeneration tube
Regeneration of PNS axon step 5
Regeneration tube guides the growing axonal sprout back to original target cells to re-establish their synapses
Regeneration of PNS axon step 6
Once contact is re-established with original target, the neurosoma shrinks and returns to its original appearance
Can damaged CNS axons regenerate?
no because astrocytes with produce scar tissue that physically interferes with regrowth of axons