Excretion- bio 20
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:40 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
How does the excretory system regulate the composition of body fluids
By removing wastes: ammonia, urea and uric acid, excess ions, other metabolites
2
New cards
How does the excret. System regulate the volume of water
By excreting extra water or reabsorbing water as needed. Humans lose two litres of water a day
3
New cards
how does the excret. System balance pH
By removing excess hydrogen ions via the kidneys
4
New cards
Role of lungs
Remove CO2 from the blood and remove other gases and water vapour
5
New cards
The role of skin
Excretes water, salts and urea in perspiration
6
New cards
Role of the digestive system
Excretes water, salts, lipids and other cellular chemicals. Note that feces is not a product of excretion
7
New cards
Where do nitrogenous compounds come from
Through the breakdown of amino acids and nucelic acids (DNA RNA)
8
New cards
What’s deamination
The removal of an amino group from a molecule
9
New cards
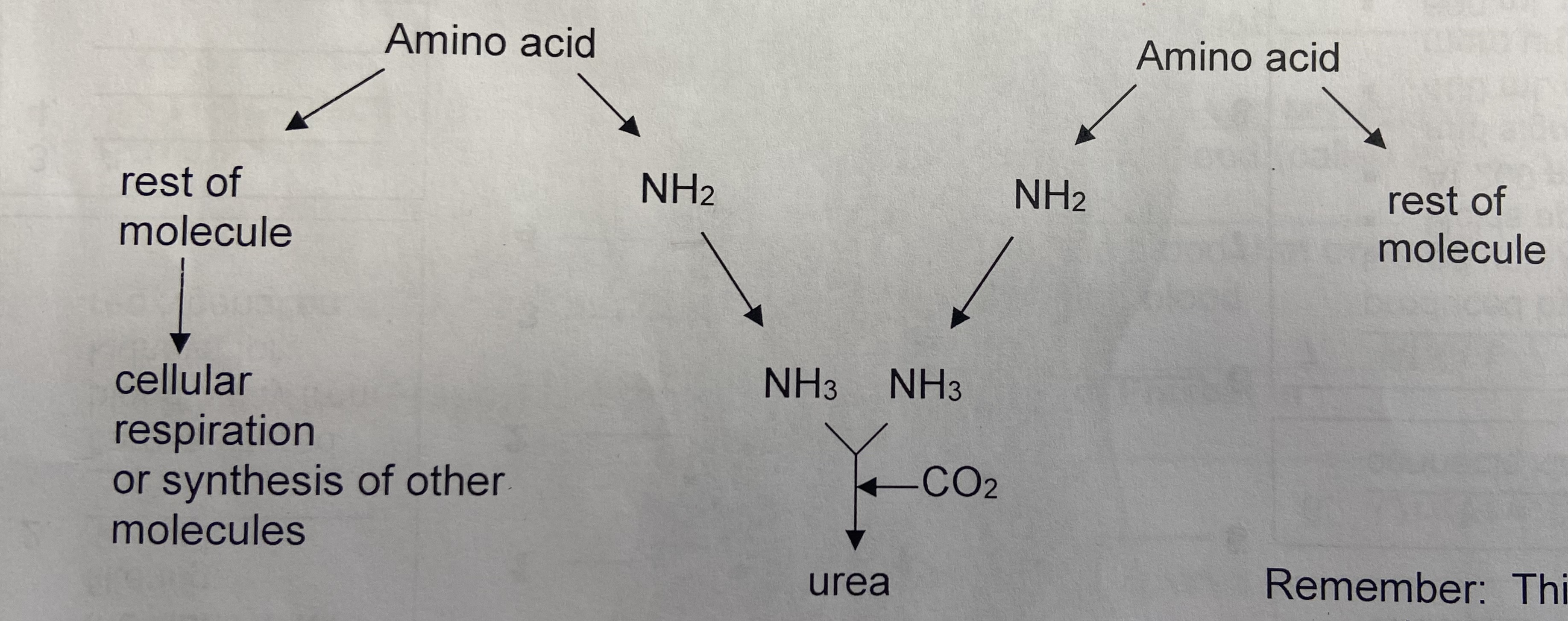
What is ammonia converted into to make it less toxic
Into urea in the liver
10
New cards
Renal artery/ vein
Renal artery: carries blood to the kidneys for filtration
Renal vein: carries filtered blood away from kidneys for reoxygenation
Renal vein: carries filtered blood away from kidneys for reoxygenation
11
New cards
Kidney
Organ where waste is removed from the blood. Blood is filtered by nephrons
12
New cards
Ureter
Tune that connects the kidney to the bladder
13
New cards
Bladder
Where urine is temporarily stored until it is voided from the body
14
New cards
Urethra
Tube through which urine exits the bladder and body
15
New cards
Renal cortex
Outer layer of kidneys. Most of filtration occurs here
16
New cards
Renal medulla
The inner structures of the kidney. Most of reabsorption occurs here
17
New cards
Renal pelvis
Where urine collects before it’s moved to the urethra
18
New cards
Glomerulus
A network of capillaries which filters the blood components according to size.
Small components: move through capillary cells
Large components: remain
Small components: move through capillary cells
Large components: remain
19
New cards
Proximal tubule
Reabsorption of nutrients, ions and water back into the blood begins, both by active and passive transport
20
New cards
Loop of Henle
Mostly water and ions are reabsorbed into the blood again by active and passive transport
21
New cards
Distal tubule
Continued reabsorption of water and ions as well as secretion of H+, K+ and other substances like drugs by active transport
22
New cards
Bowman’s capsule
Collects filtrate from the glomerulus. Not only has wastes but also substances needed by the body
23
New cards
Collecting duct
Connects the nephron to the renal pelvis. Reabsorption of water by osmosis occurs as urine moves along the collecting duct
24
New cards
Difference between active and passive transport
Passive does not require energy while active require atp. A concentration gradient is an example of passive transport.
25
New cards
Where does filtration occur
Thé glomerulus
26
New cards
The blood capillaries in the glomerulus is…
Semi permeable and allow water and small substances to move out of the blood and into the bowman’s capsule
27
New cards
What allows the filtrate to be pushed out of the blood
The pressure of the blood that enters the glomerulus
28
New cards
Substances present in filtrate
Water, ions, glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, ammonia
29
New cards
Substances not present in filtrate
RBCs and plasma proteins
30
New cards
What is the goal of reabsorption
To return water and required substances back to the blood
31
New cards
Where does reabsorption occur
Proximal and distal tubule, loop of Henle and the collecting duct
32
New cards
Where is most of filtrate reabsorbed
In the proximal tubule (65%)
33
New cards
substances reabsorbed through active transport
Nutrients and positively charged ions
34
New cards
Substances reabsorbed through passive transport
Negatively charged ions (by following positively charged ions)
35
New cards
Substances reabsorbed through osmosis
Water
36
New cards
The main substances reabsorbed in the loop of Henle
Water and ions
37
New cards
Reabsorption in the distal tubule involves…
The active transport of sodium ions, passive transport of negative charged ions along with the sodium ions and the reabsorption of water through osmosis
38
New cards
How can the distal tubule be changed
Depending on the body’s hydration, blood ions concentration and blood pressure. Controlled by hormones
39
New cards
Reabsorption in the collecting duct
There is still a lot of water that needs to be reabsorbed. As the collecting duct passes through the renal medulla, water is reabsorbed into the blood
40
New cards
Secretion
Occurs in the kidney to rid the blood of unwanted materials. Occurs by the active transport of substances from the blood into the nephron
41
New cards
Substances secreted into the nephron
Hydrogen ions, potassium ions, ammonia
42
New cards
Osmoreceptors and hypothalamus
A part of the brain that measures the osmotic pressure of the blood
43
New cards
What happens when the level of water in plasma decreases
Signals are sent to the pituitary gland to increase the secretion of a hormone called ADH
44
New cards
How does ADH decrease the volume of urine
By increasing the permeability of the distal tubules and the collecting ducts to water
45
New cards
When the concentration of water in the blood plasma increases…
The volume of urine decreases
46
New cards
Diabetes insipidus
Disease where a person does not make ADH
47
New cards
Aldosterone
Another hormone produced to regulate reabsorption. Increases permeability of the collecting ducts to sodium ions and the reabsorption of water
48
New cards
\