Membrane Proteins and Transport Mechanisms in Cells
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Enzyme Protein
A type of membrane protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions.
Signal Protein
A type of membrane protein that transmits signals across the membrane.
Transport Protein
A type of membrane protein that facilitates the movement of substances across the membrane.
Attachment/Recognition Protein
A type of membrane protein that helps cells recognize each other and attach.
Passive Transport
Movement of a substance across the membrane without using energy.
Diffusion
The process that drives passive transport, where molecules/ions move from high to low concentrations.
Simple Diffusion
Movement of small/non-polar substances across the membrane without using energy.
Facilitated Diffusion
Use of proteins to help move substances across the membrane.
Channel Protein
A hydrophilic pathway through the membrane used to transport certain ions.
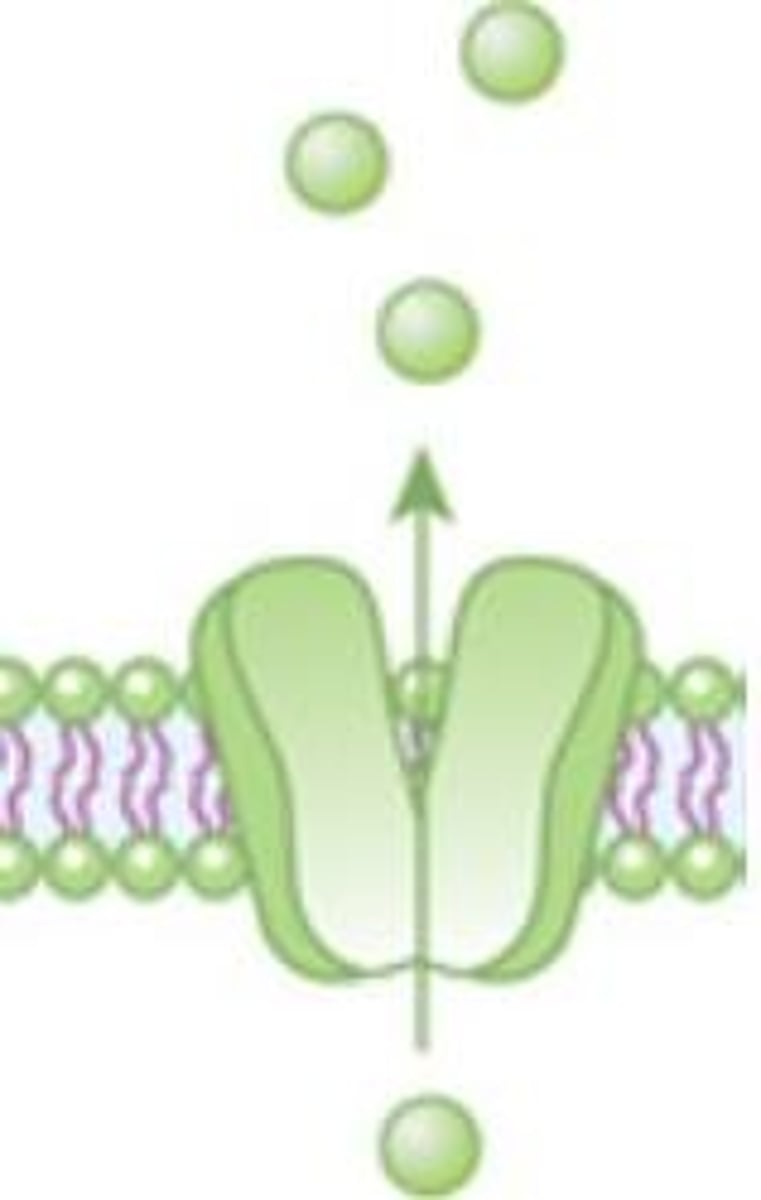
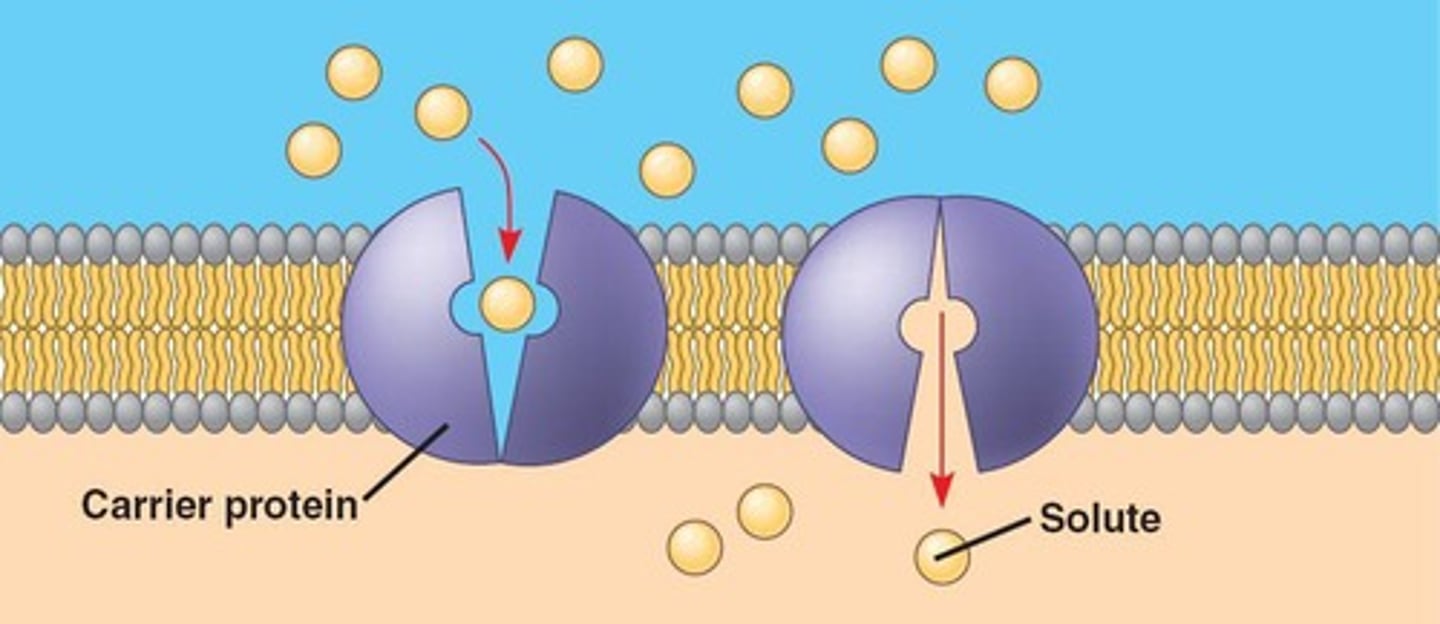
Carrier Protein
A protein that physically binds to molecules to aid in transportation.
Osmosis
The passive diffusion of water across a membrane.
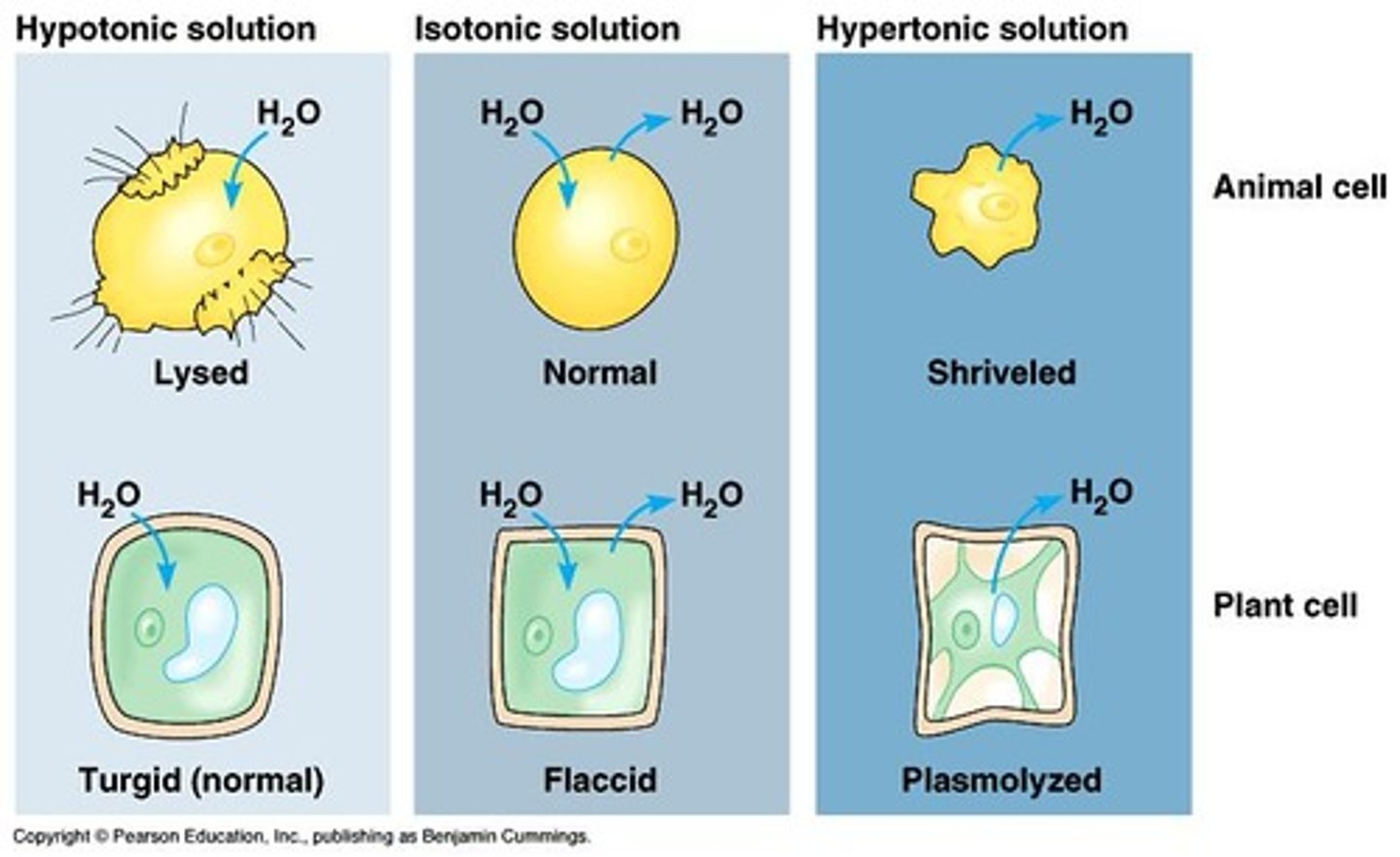
Hypotonic Solution
A solution with a high concentration of solutes inside the cell, causing water to rush into the cell.
Isotonic Solution
A solution with equal concentration of solutes inside and outside of the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
Hypertonic Solution
A solution with a high concentration of solutes outside the cell, causing water to rush out of the cell.
Active Transport
The movement of substances across the membrane using energy.
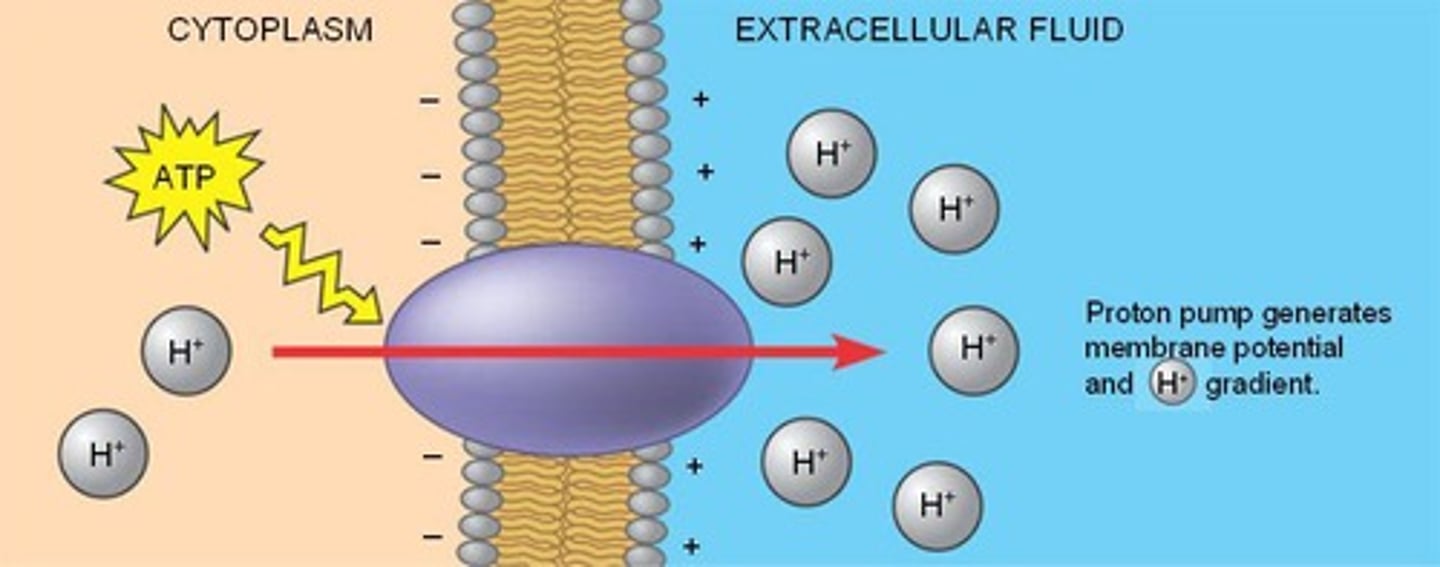
Primary Active Transport
Movement of positively charged ions across membranes, generally relying upon ATP.
Secondary Active Transport
Uses energy from the concentration gradient built up by primary active transport to transport substances.
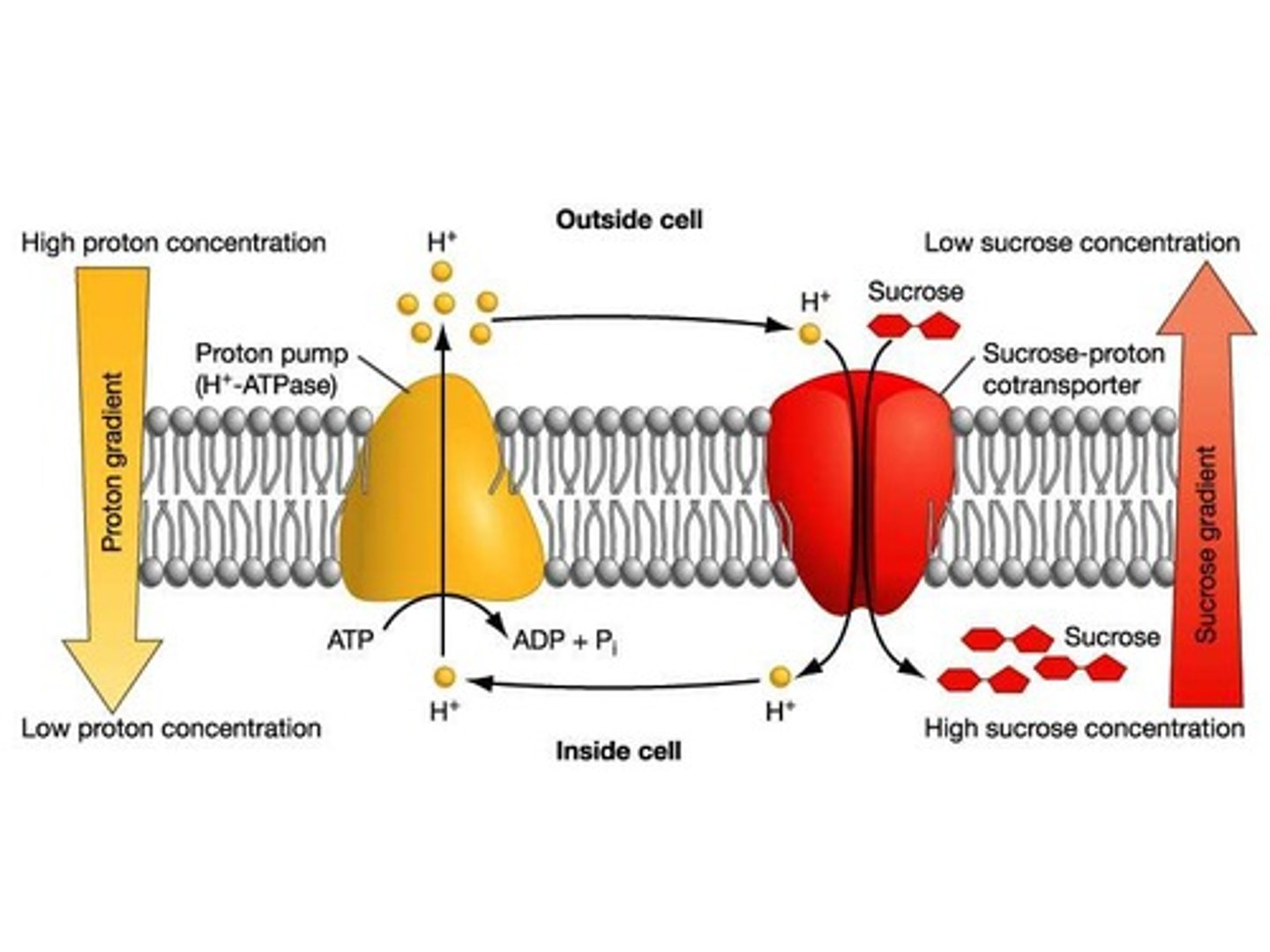
Symport
Transported substances move in the same direction as ions.
Antiport
Transported substances move in the opposite direction as ions.
Exocytosis
Transport of substances from inside the cell to outside of the cell using vesicles.
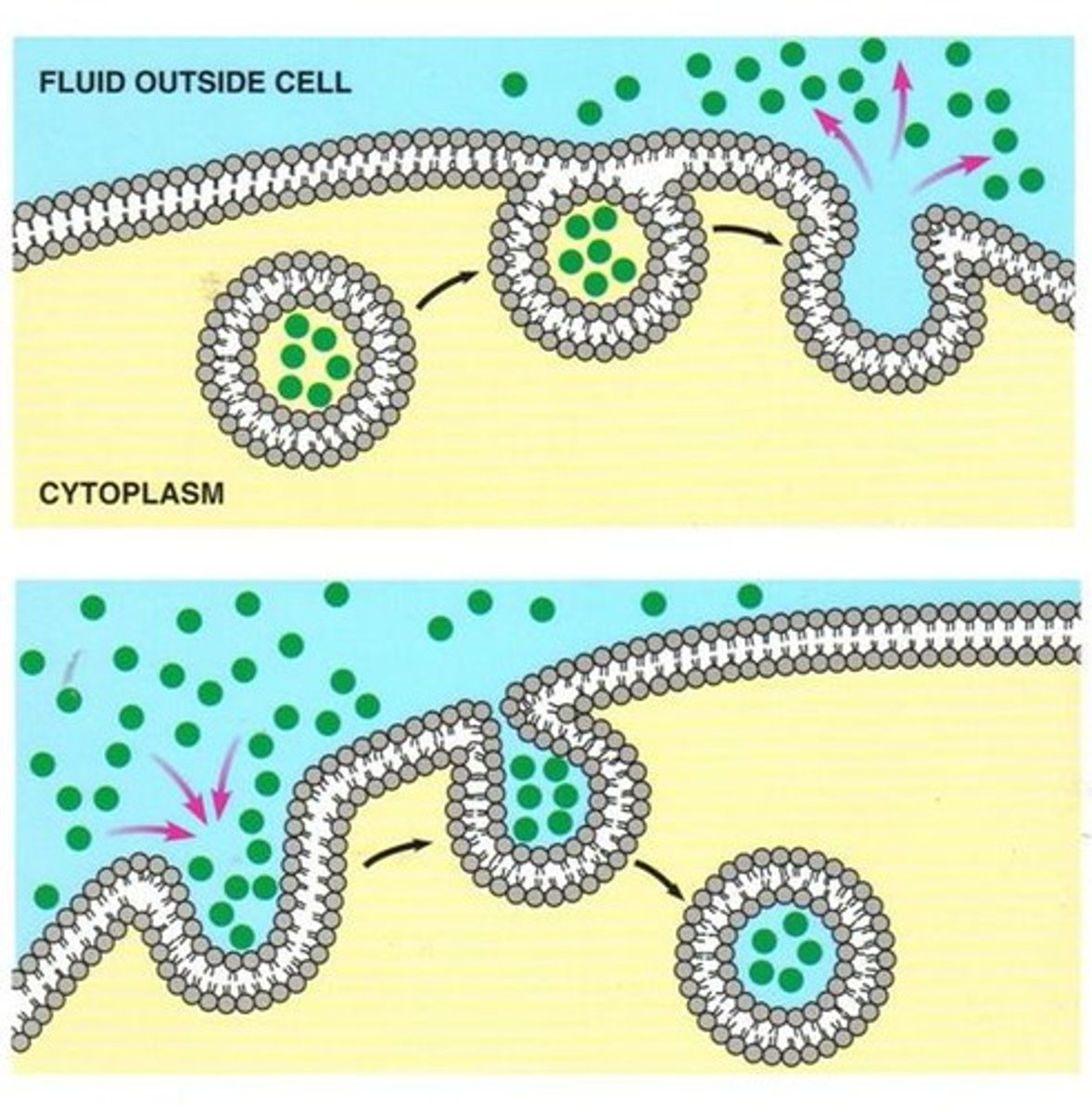
Endocytosis
Transport of substances from outside the cell to inside the cell using vesicles.