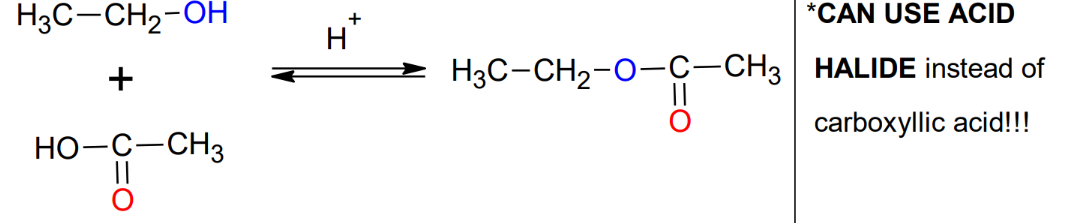Organic Chemistry 1: All Reaction Mechanisms
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All mechanisms, starting from chapter 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
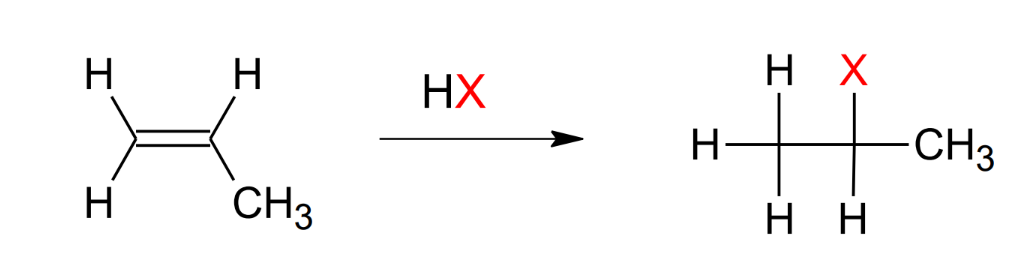
Addition of HX
Follows Mark
Mechanism:
protonation of the double bond
add Br to the carbocation
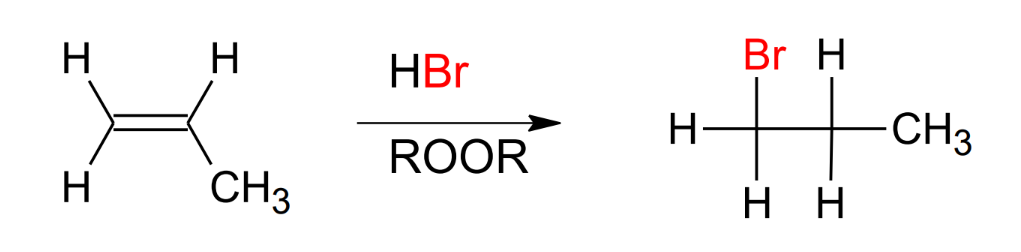
Addition of HBr on ROOR
Anti-Mark
same mechanism as addition of HX, except Br adds to the least substituted
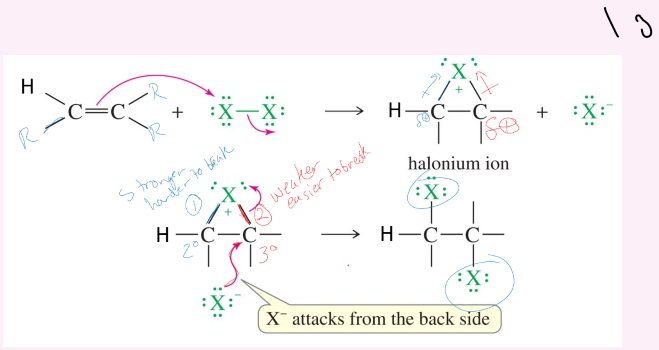
Halide Addition X2
Solvent can be CH2Cl2 or CCl4 (NO WATER)
Anti-Stereochemistry.
Mehanism:
1. double bond breaks and has one X attach to both of the carbons in the double bond (triangle)
Second X attacks and it forms a bond with one of the Cs.
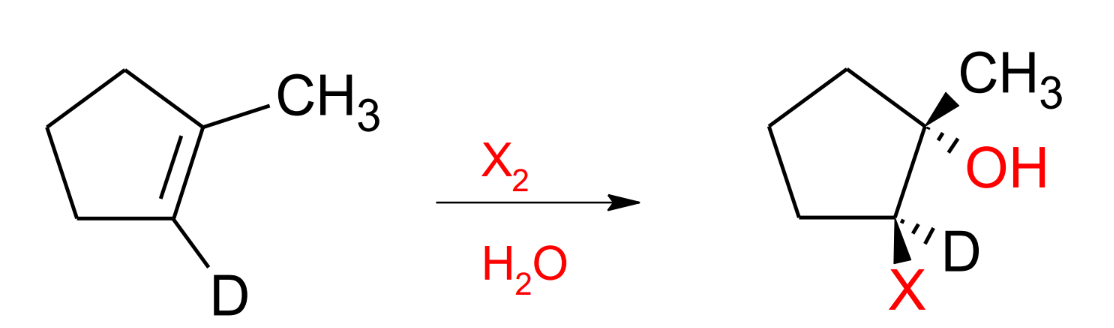
Halohydrin Reaction X2 + H2O
Mark
Anti-stereochemistry
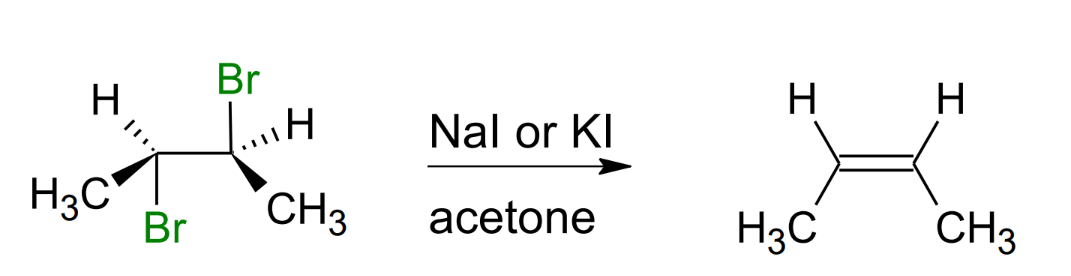
Forming alkene from vicinal dihalide
(wanting to create a double bond when u have 2 halogens attached to vicinal carbons)
Need to have a NaI of KI under an acetone solvent
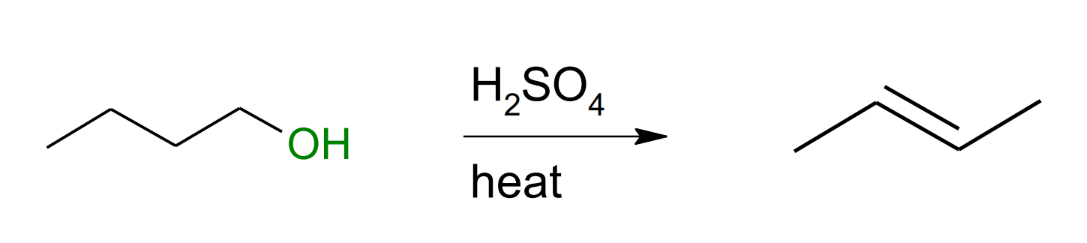
Dehydration to alkene With H2SO4
Only gives a middle alkene
add a hydrogen to the OH
the H2O leaves
give one of the electrons of one of the H to create a doube bond and take the H with the water.
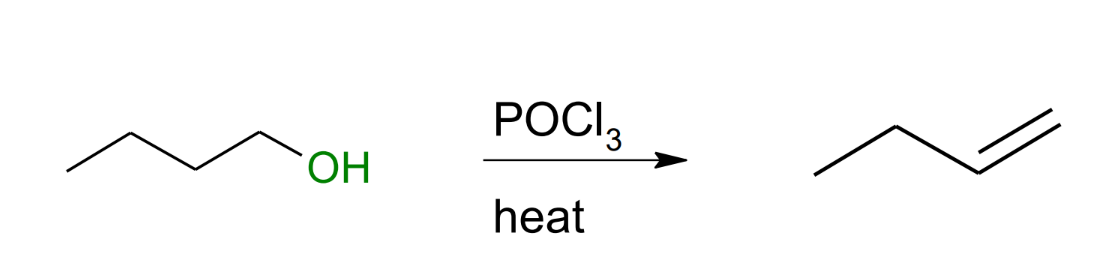
Dehydrogenation of alkene with POCl3
Only gives a terminal alkene
Addition of OH
racemic mixture
mark
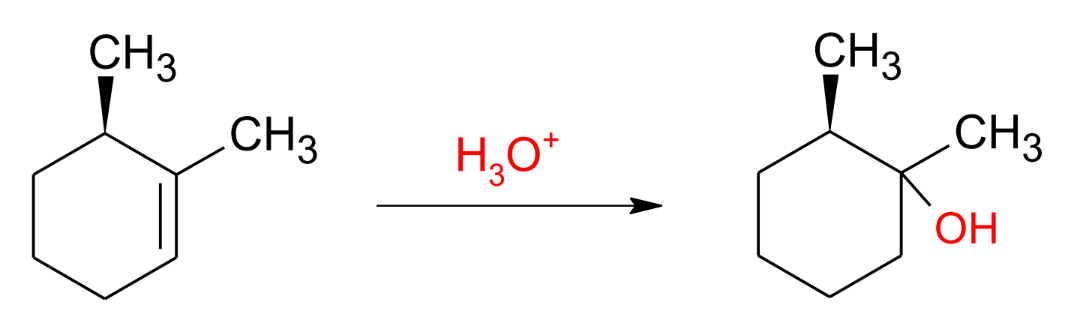
Oxymercuration/ demercuration (only water)
mark, antistereochemistry (see other to check mechanism (too long))
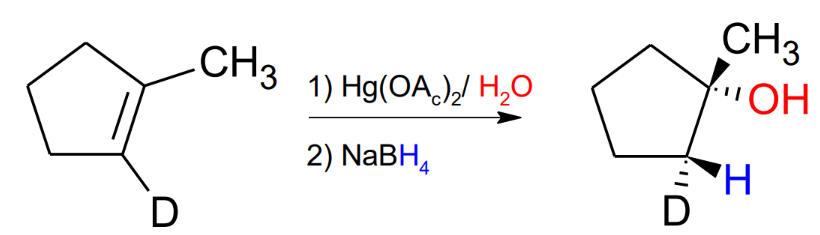
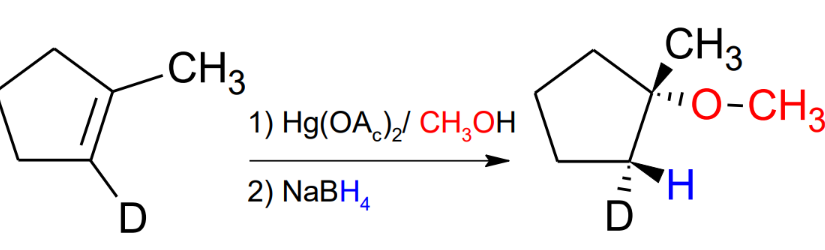
Oxymercuration / Demercuration with CH3OH
mark and anti-stereochemistry
Adds a CH3 to the Oxygen, compared to just the alcohol in the reaction with ony water.
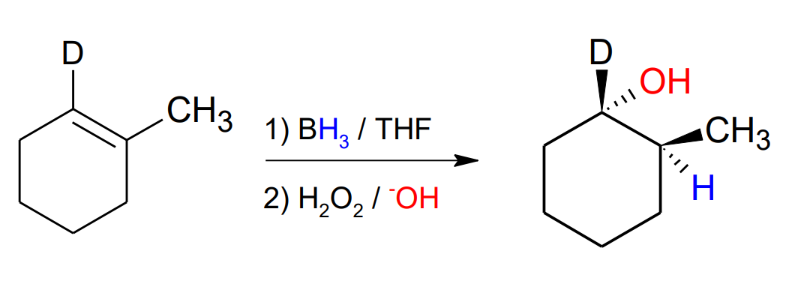
Hydroboration
BH3 / THF
2) H2O2 / -OH
anti mark, same stereochemistry.
Mechanism:
1. BH3 adds to the double bond on a single step
Then gets replaced by a OH
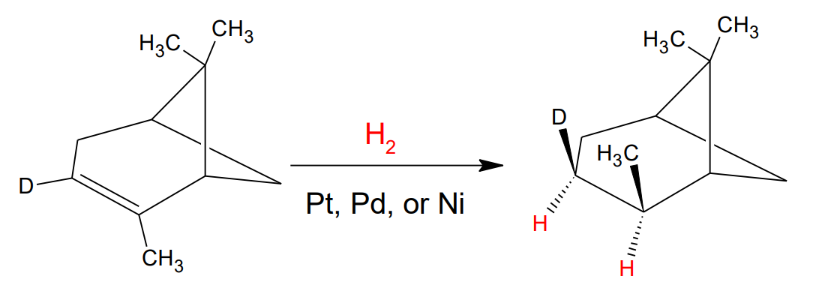
Catalytic Hydrogenation, Pt, Pd, or Ni
same stereochemistry, adds 2 Hydrogens to where the double bond was
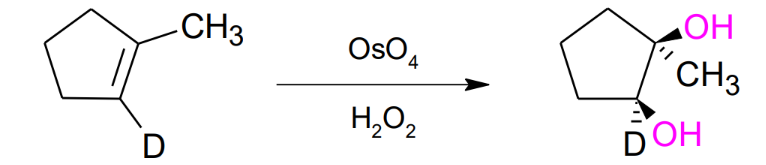
Hydroxylation of Alkenes by OsO4 / on H2O2
Syn formation of 2 alcohols (OH)
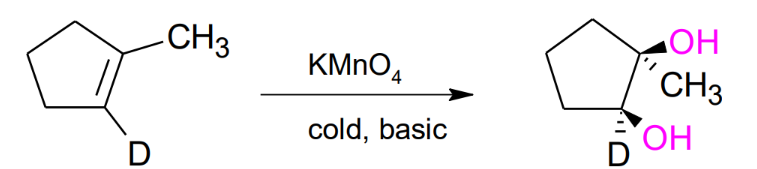
Hydroxylation of Alkenes by KMnO4 (cold / basic) / on H2O2
Cold - Basic reaction conditions needed
Syn formation of 2 alcohols
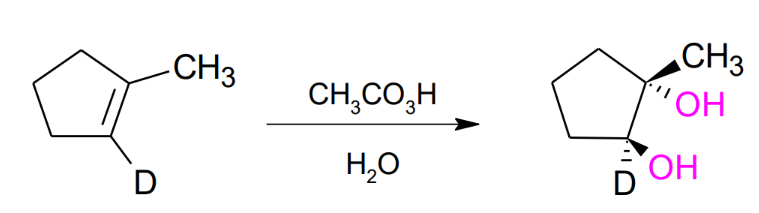
Hydroxylation of Alkenes by CH3CO3H / on H2O
ANTI STEREOCHEMISTRY
Epoxidation
An alkene reacts with peroxide acit to produce an epoxide

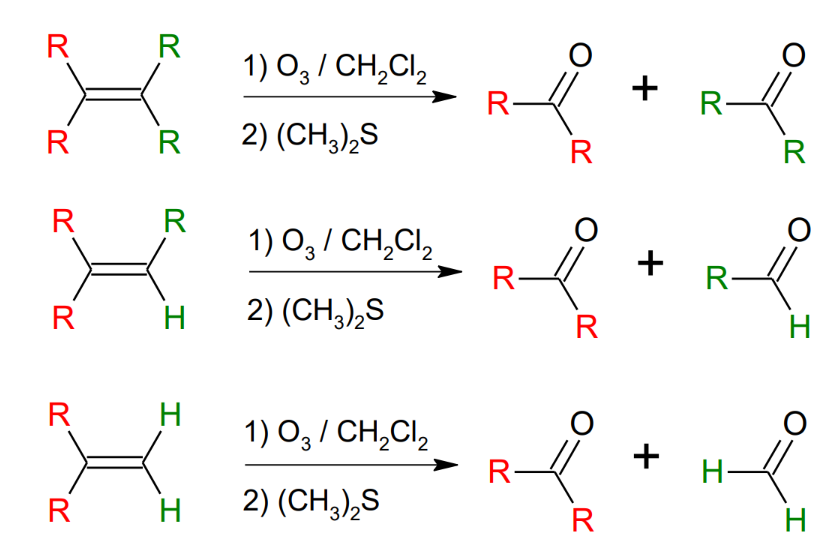
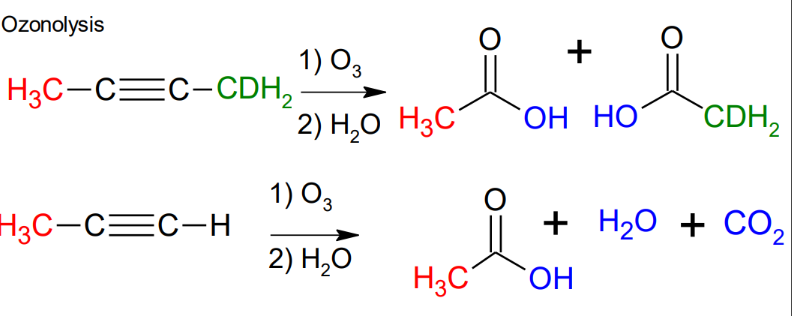
Oxidation of alkenes: Ozonolysis
Ozone breaks the double bond to produce aldehydes and ketones.
Breaks through the middle.
*Can use Zn/acetic acid instead of (CH3)2S
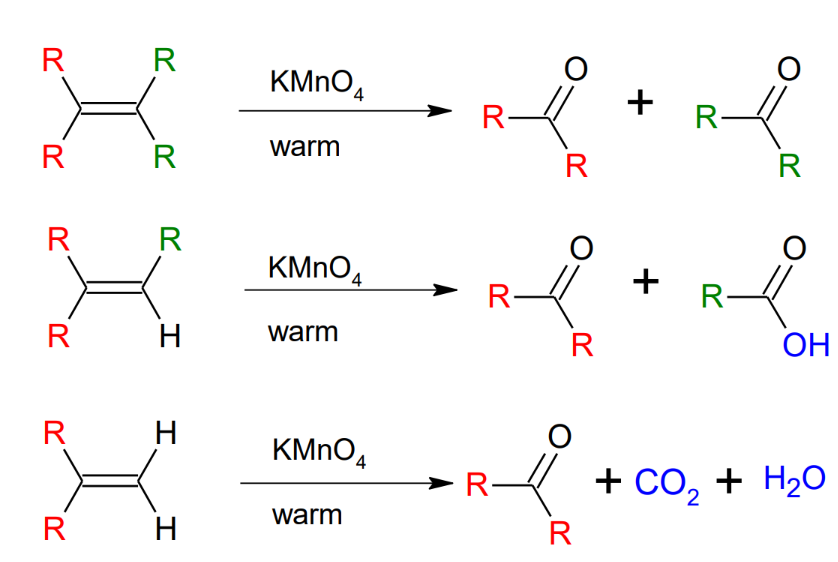
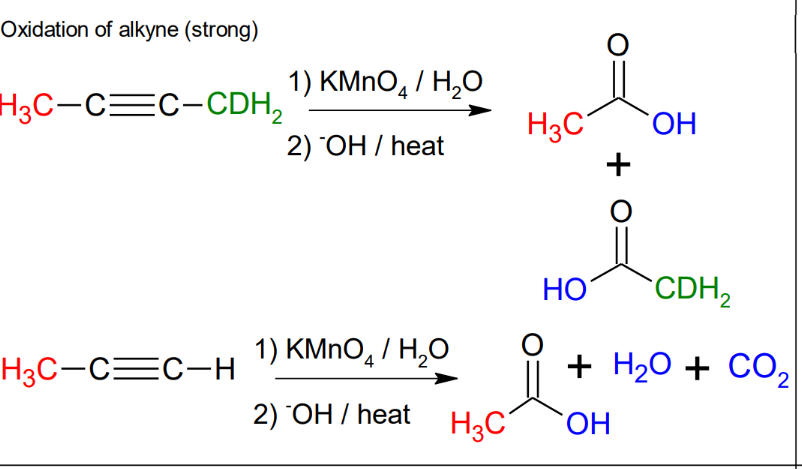
Oxidation of Alkenes: Warm KMnO4 Cleavage
*further oxidizes to form carboxylic acids
*cannot isolate the formaldehyde (the H2C=O)
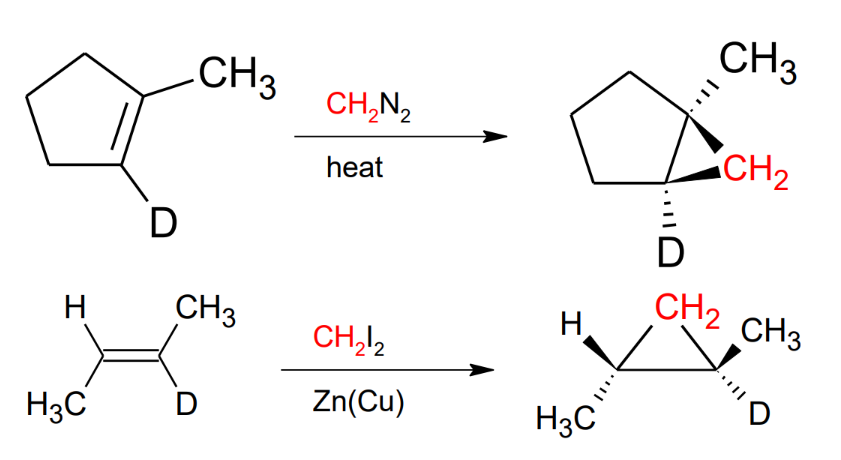
Addition of Carbenes (R2C:)
Either uses CH2N2 + heat or uses CH2I2 + Zn(Cu)
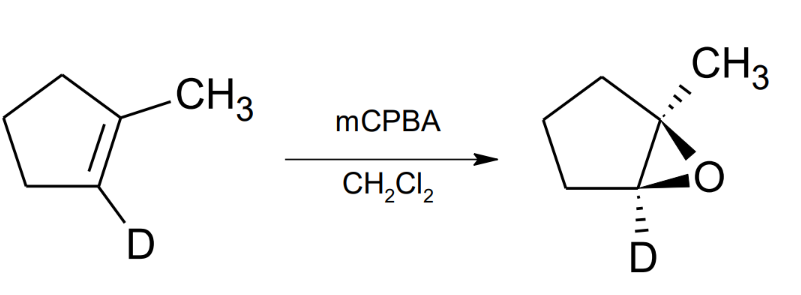
Oxidation of Alkenes: oxirane synthesis mCPBA
to form an oxygen bonded to two carbons mCPBA
Basic E2 Reaction
E2 is anti periplanar ( H and X have to be opposite from eachother)
requires a strong base (anything that involves Na works, if you see Na it is probably E2)
Take down a hydrogen and the halogen to create a double bond. take the hydrogen from the least substitued side
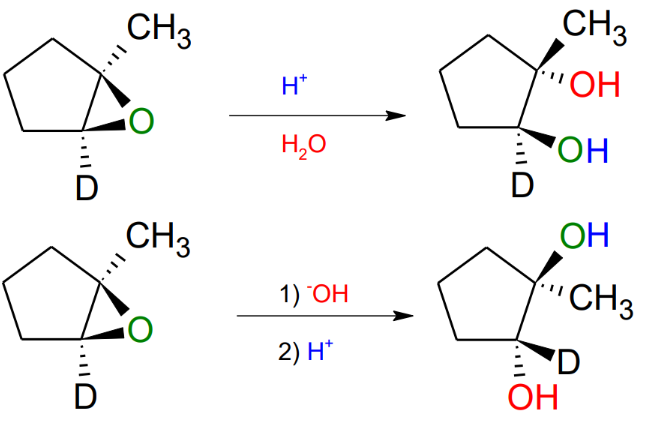
Opening of Epoxides
So you can open epoxides and add hydroxiles to both sides, you can do it with just water of hydroxyle, both leave it with an anti-stereochemistry.
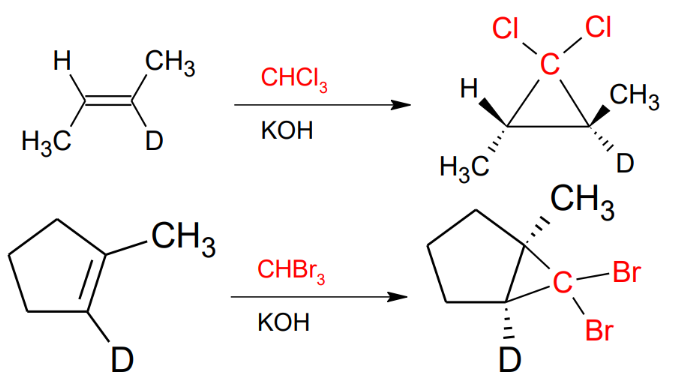
Formation of Dibromocarbenes and Dichlorocarbenes
In order do form a diXcarbene you need to take the electrons of the double bond and connect them with the C that needs electrons that is already connected to 2 X.
KOH as a solvent, CHX3
Formation of the acetylide anion
in handy when connecting with other moecules. Basically removes an extreme H that was adjacent to a triple bond.
NaNH2
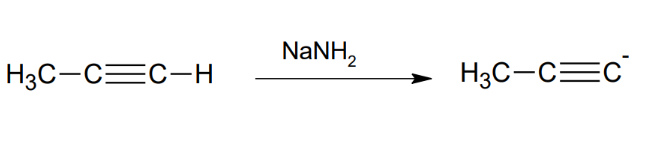
Uses of the acetylide anion with methyl or primary halides
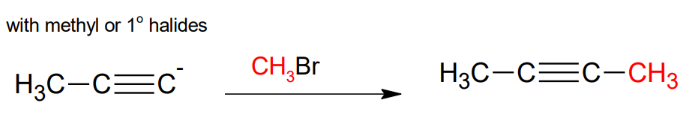
Uses of the acetylide anion
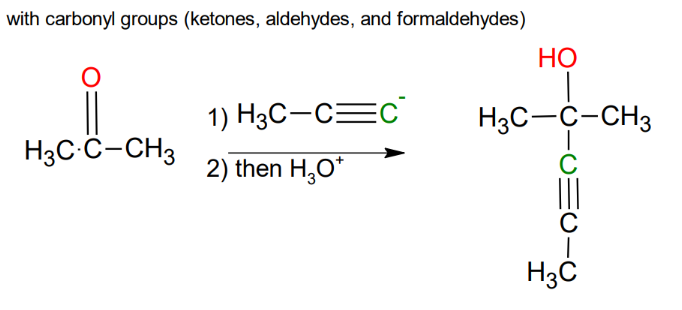
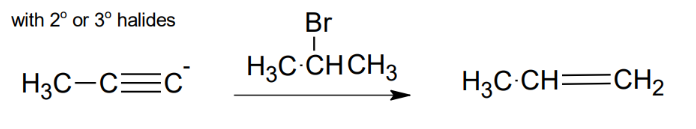
Uses of the acetylide anion with secondary or tertiary halides
E2 reaction,
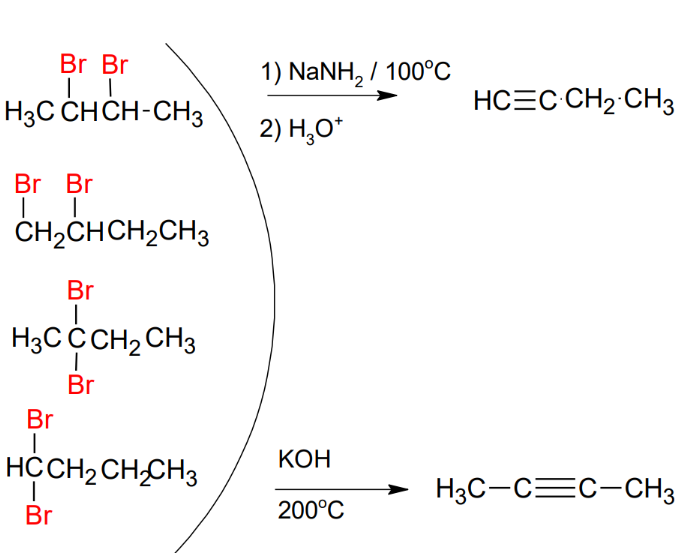
Synthesis of Alkynes
*Need either geminal or
vicinal dihalides
*Look up mechanism
*NaNH2
FAVORS
terminal
*KOH FAVORS internal
Halogenation of Alkynes - X2 and Alkyne
Stereochemistry cannot be controlled, so you get a racemic mixture. If you do the step again you will break the double bond and add other 2 Br.
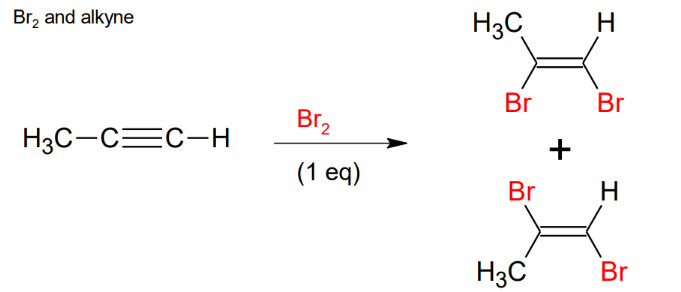
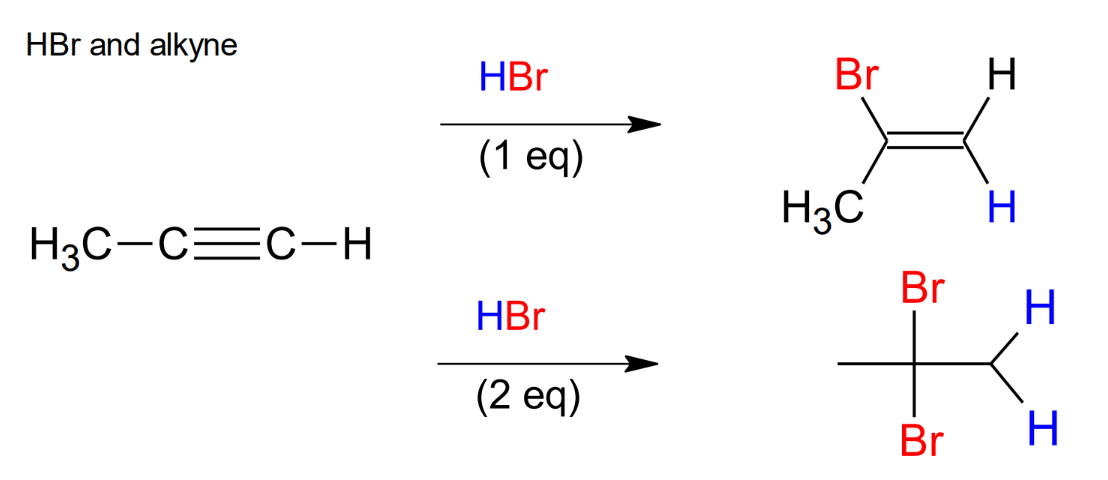
Halogenation of Alkynes HX
Mark (Hs add to the side that has the most H (less sub)) , same stereochemistry
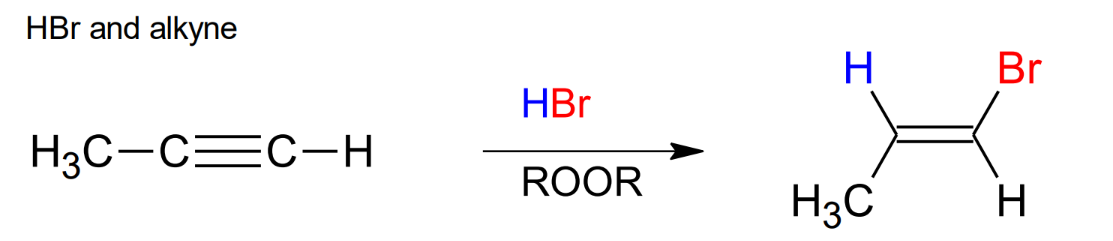
Halogenation of Alkynes, HBr and ROOR
anti mark, same stereochemistry
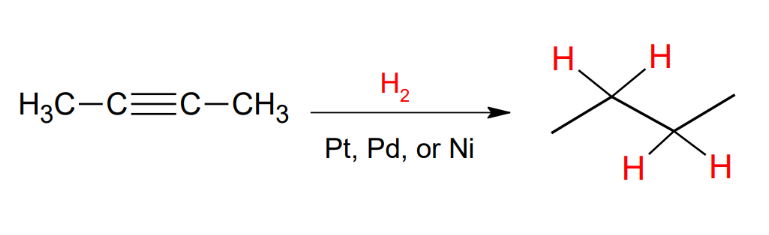
Catalytic reduction with reactive catalyst of a triple bond
takes it all the way back to the alkane, too reactive to yield a double bond.
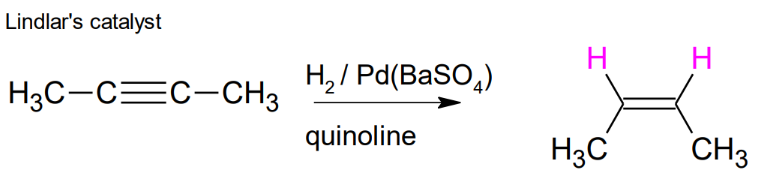
Alkyne to Alkene:
TRIPLE to DOUBLE Lindlar's catalyst
quinoline, H2 / Pd(BaSO4) , syn addition
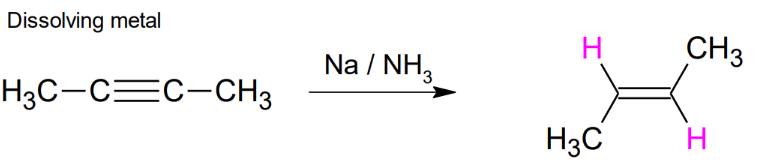
Alkyne to Alkene:
TRIPLE to DOUBLE Dissolving a metal
Na / NH3, anti addition
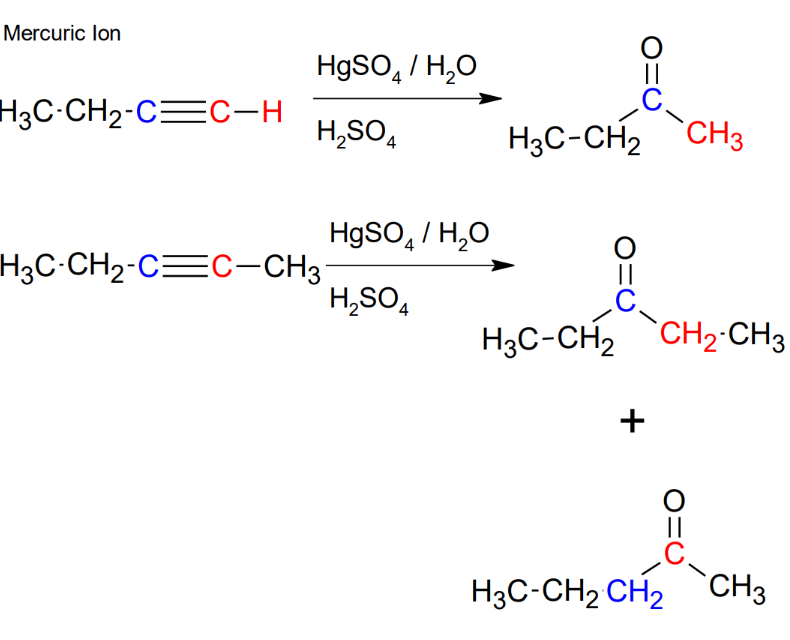
Addition of H-OH to alkynes - mercuric ion
*Mark addition
*If not terminal, you will
get a mixture.
*Formation of ketone
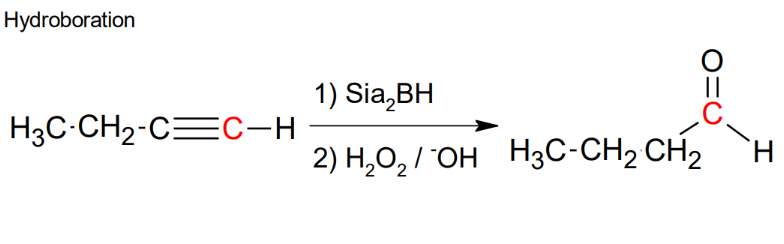
Addition of H-OH to alkynes - hydroboration
*Antimark addition
*will get a mixture if not
terminal
*Formation of aldehyde
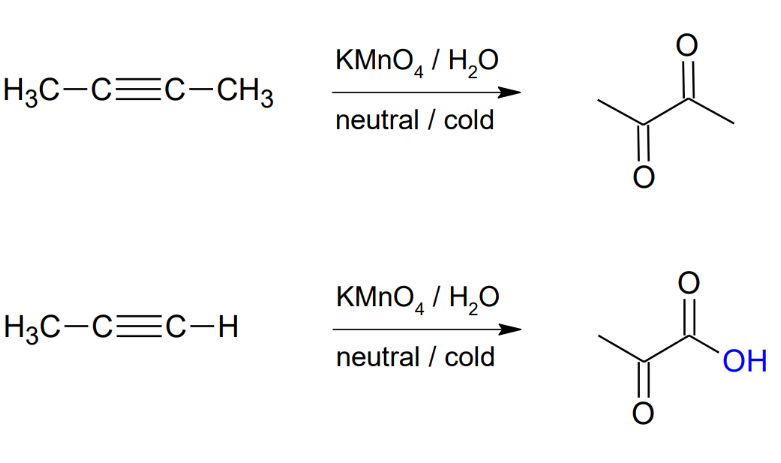
Oxidation of alkynes (mild conditions)
*Forms vicinal
carbonyls
*further oxidizes terminal
alkynes to form
carboxylic acid.
Oxidation of alkyne (strong)
cleavages of alkynes
ozonolysis
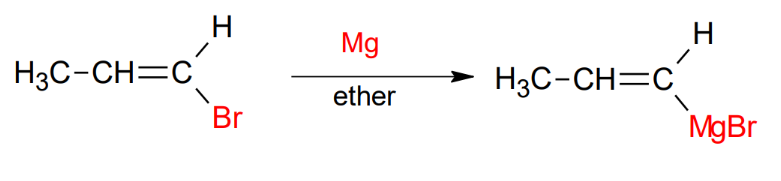
The Grinard Reagent Mg
The organolithium reagent
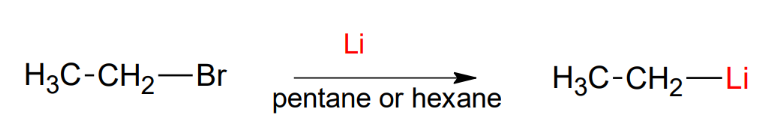
Formation of alcohols
from Grignard
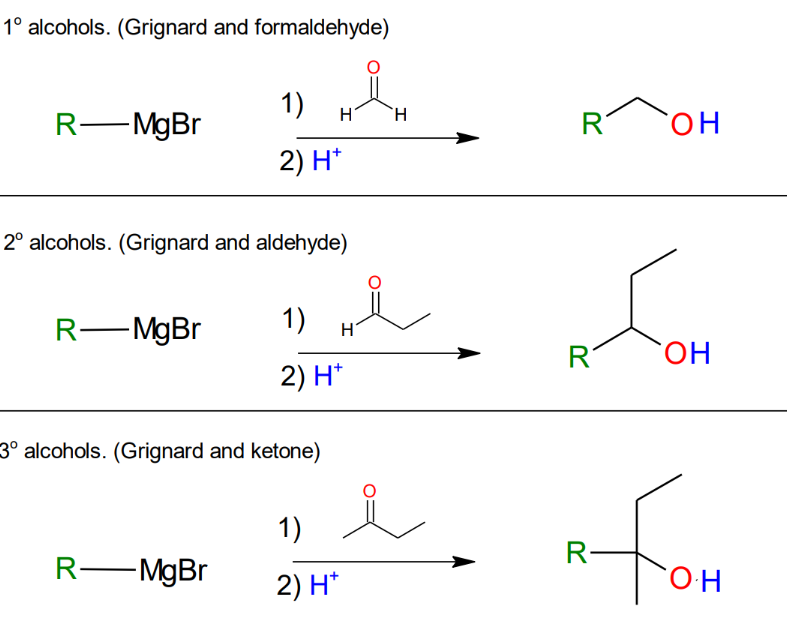
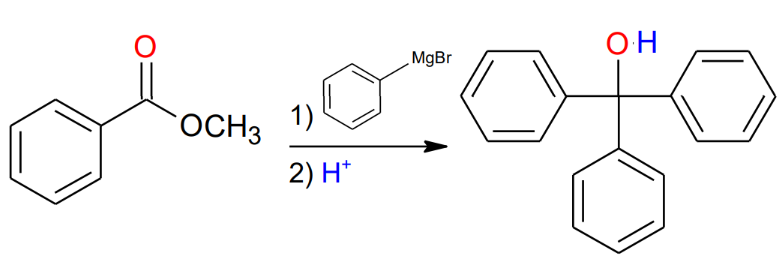
Grignard and esters
or acid halides
Grignard and Epoxides
(opening of epoxides)
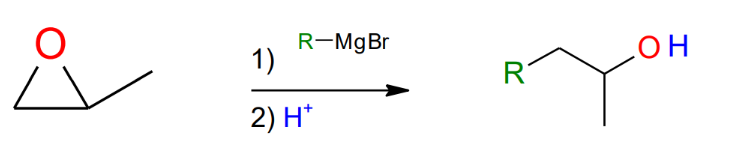
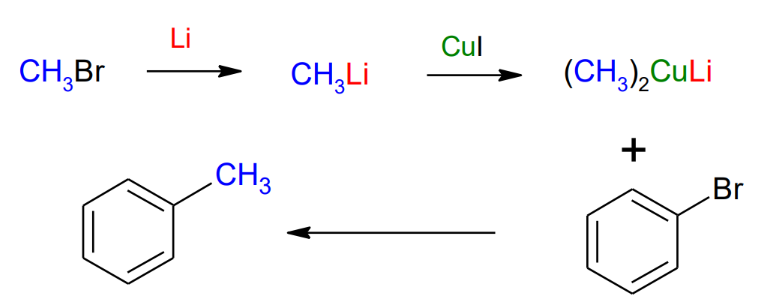
Corey-House Reaction
Hydride reduction of carbonyls - mild conditions (NaBH4
as reagent)
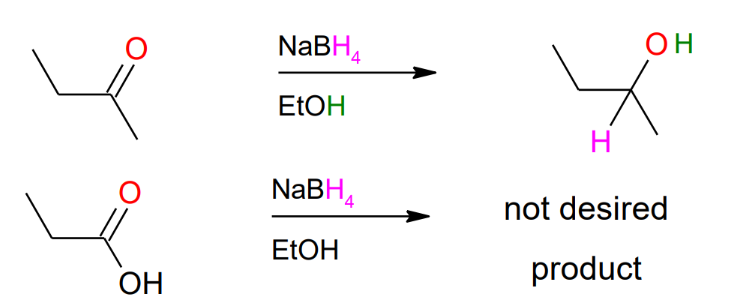
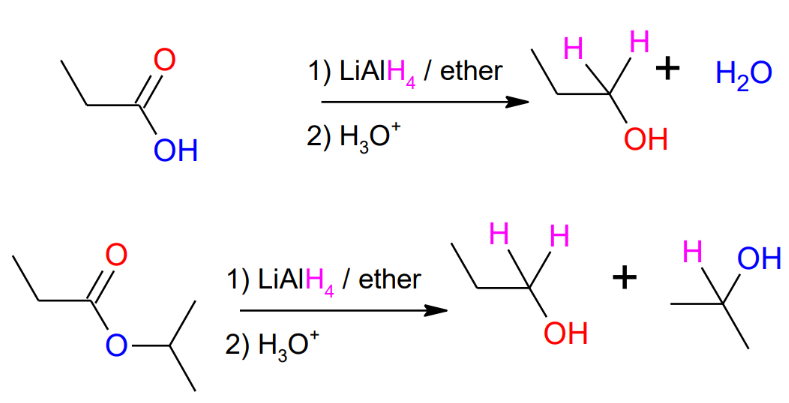
Hydride reduction of carbonyls - strong conditions (LiAlH4
as reagent)
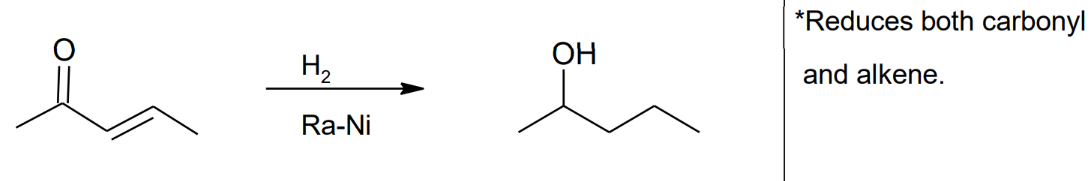
Rayney Nickel
Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols
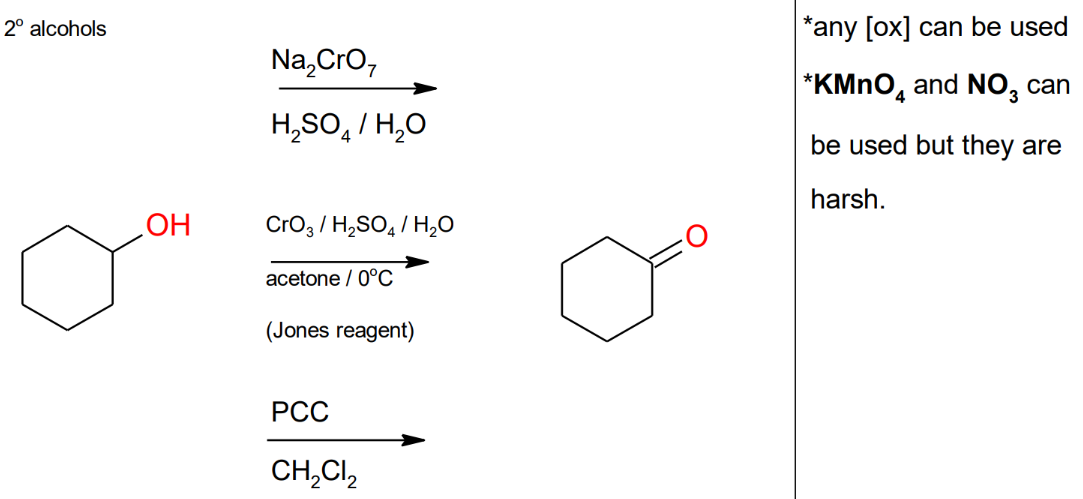
Oxidation of primary Acohols
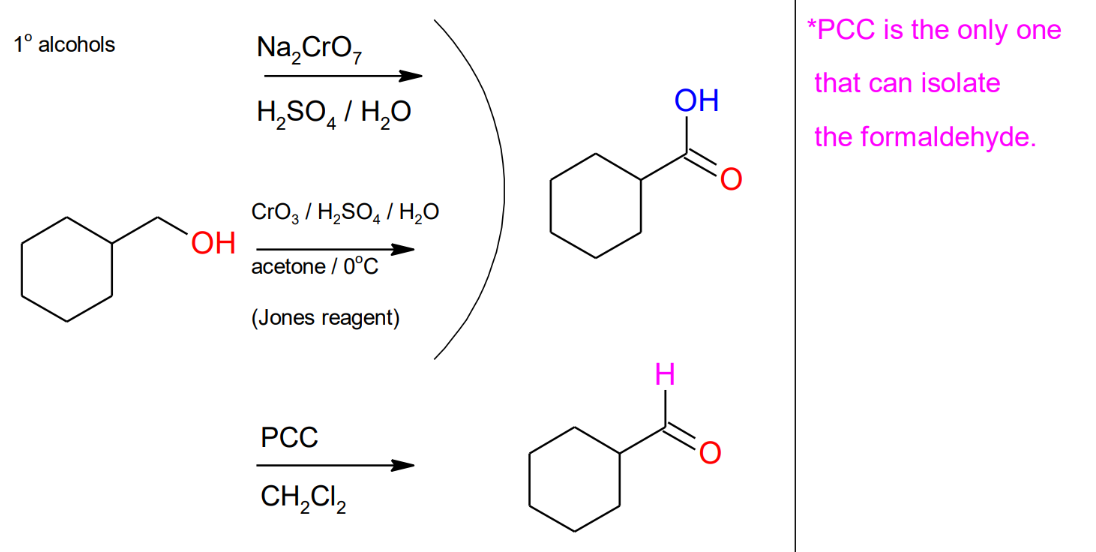
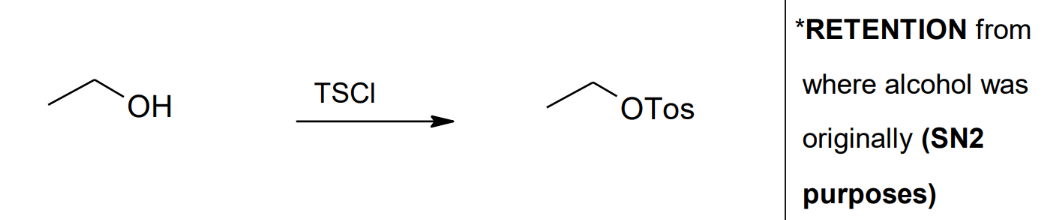
Formation of the
Tosylate Ester
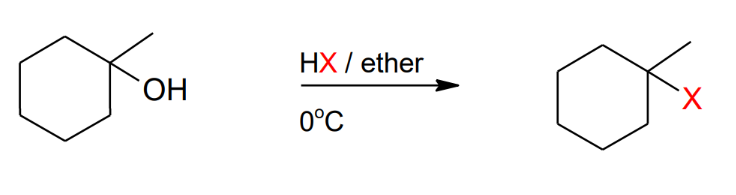
Formation of alkyl halide
from 3ary alcohols
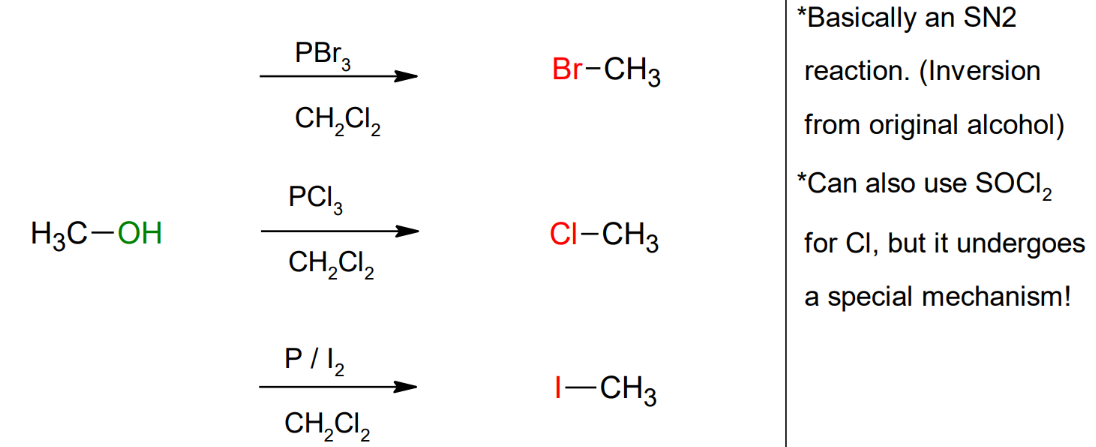
Formation of 1o
/2o
alkyl halides from 1o
/2o
alcohols
Unique cleavage with
HIO4
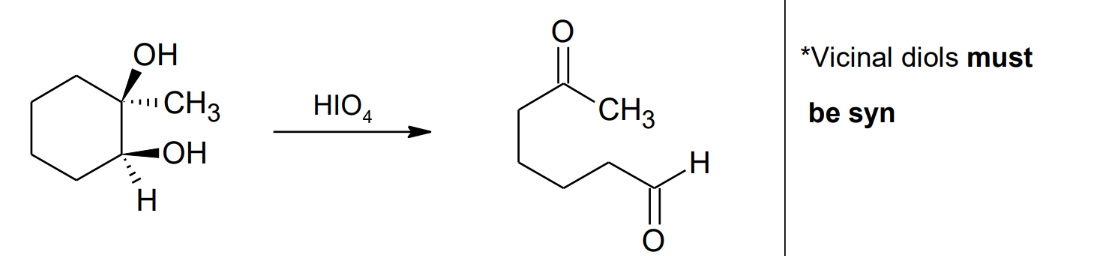
Formation of Alkoxide Anion
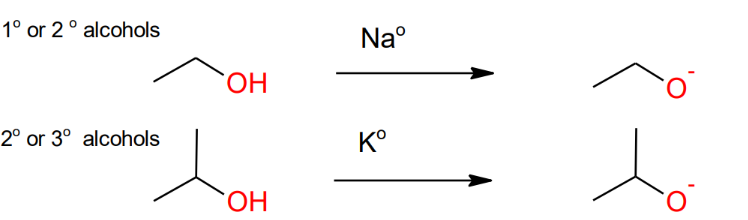
Williamson ether
synthesis
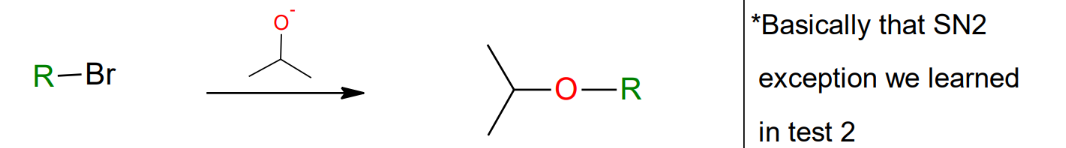
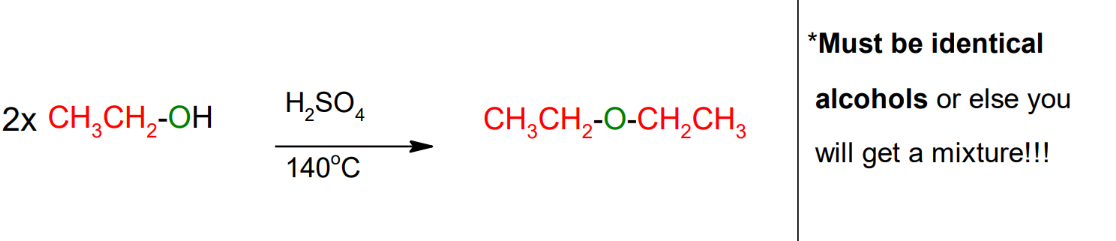
Ethers from intermolecular
dehydration
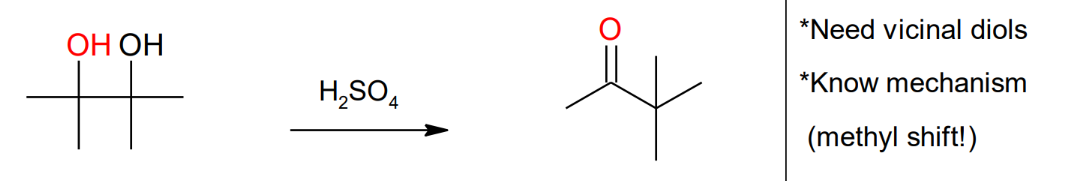
Pinacol - Pinacolone
Rearrangement
Fischer Estherification