BAN Quiz 2
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
opsonization, kill (MAC), recruit phagocytes, inflammation, remove dead/dying cells
functions of complement
ESR
systemic inflammation marker that rises and falls SLOWLY, increased by plasma protein (esp. FIBRINOGEN)
obesity, infection, cancer, autoimmune diseases
potential causes of elevated CRP (that cause inflammation)
kidney disease, pregnancy, chronic bacterial infection, RA
potential causes of elevated ESR (that cause inflammation)
alveolar osteitis (dry socket)
moderate to severe pain near extraction site raises concern for what condition?
irrigation and ZOE
how would you treat alveeolar osteitis
chronic gingivitis, periodontal disease, poor wound healing
result of primary (genetic) phagocyte deficiency
caries, periodontitis, pulpitis, oral ulcerations
pts with RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS are at a higher risk of developing what dental/oral health issues
injectable corticosteroid
recommended treatment for acute GOUT FLARE
risk of periodontitis, DDIs (drug-drug interactions)
dental consideration of pts with gout
oral NSAIDs (flares), topical pain relievers (specific joints)
treatments for OSTEOARTHRITIS
diclofenac gel
topical NSAID used for OSTEOARTHRITIS
celecoxib and proton pump inhibitor
NSAID prescribed for osteoarthritis pts with GI ulcer or reflux history
paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome/ severe pemphigus
should be referred to oncologistic ASAP if there are signs of this
paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome (PAMS)
severe pemphigus-like lesions that can occur in patients with cancer, leading to a range of autoimmune symptoms.
hardness, fixation, persistence, enlargement, unilateral
what conditions of lymph nodes might indicate malignancy
>1cm
size of lymphnode considered abnormal
ventrolateral tongue
#1 site for oral cancer
torus palatinus (normal)
bony growth on the hard palate
ventral tongue
#2 site of oral cancer
lips, tongue, floor of mouth, mucosa, palates, oropharynx
components of intraoral examination
asymmerty, borders, color, diameter, evolution
skin/scalp evaluation criteria
acute iritis, narrow angle glaucoma, uncontrolled asthma
under what circumstances should sialagogues not be used
CRP
rises and falls rapidly, first to show change in acute inflammation
1:80
threshold for positive ANA titer
patient 2
Which patient has more autoantibodies in serum?
Patient 1: ANA positive at 1:80
Patient 2: ANA positive at 1:160
rash on upper trunk (more common than butterfly rash)
most common rash associated with SLE
heart failure, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension
serious concerns associated with progressive systemic sclerosis
Anti-SCL70
diagnostic test for systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)
NO (non-specific)
does an ANA test mean a person has SLE
Type I Hypersensitivity (angioadema)
What is the most likely cause of acute onset
lip swelling?
eosinophils
WBC type elevated in allergic reaction
autoimmunity
what occurs if regulatory T cells don’t work properly
ANCA-associated vasculitis
COMPLEMENT-mediated disease that causes “strawberry gums”
C1, C2, C4 deficiency
potential cause of systematic lupus erythematous and infection risk
hereditary hemolytic-uremic syndrome, C3 glomerulonephritis
caused by deficiency of complement regulatory factors H, I, CD46
ANCA-associated vasculitis
abnormal C5a-mediated activation of neutrophils, symptoms include tongue ulcerations and strawberry gums
hemolytic uremic syndromes and ANCA-associated vasculitis
complement mediated diseases
macrophage
tissue-resident, eat and kill pathogens, promote inflammation and tissue repair
neutrophil
in blood, first responder, major phagocyte that KILLS pathogens, promotes inflammation
dendritic cells
in tissue/lymphatics, presents antigens, activates naive T cells
leukocyte adhesion deficiency, chronic granulomatous disease, acquired neutropenia
examples of primary genetic phagocyte deficiency
B cells
A type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune response by producing antibodies and presenting antigens to T cells.
T cells
A type of white blood cell that is essential for cell-mediated immunity, helping to regulate immune responses and directly attacking infected or cancerous cells.
innate immunity
The body's first line of defense against pathogens, involving physical barriers and immune cells that respond quickly to infections.
adaptive immunity
A specialized immune response that develops over time, involving B and T cells that provide long-lasting protection against specific pathogens.
calor, dolar, tomor, rubor
signs of acute inflammatory response
type 1 hypersensitivity
IgE/mast cell mediated
allergic rhinitis
example of type 1 hypersensitivity
type 2 hypersensitivity
antibody (IgG/IgM) mediated
mucous membrane pemphigoid
example of type 2 hypersensitivity
Type 3 hypersensitivity
immune complex mediated
systematic lupus erythematosus
example of type 3 hypersensitivity
type 4 hypersensitivity
T cell mediated ex: delayed hypersensitivity, allo-immunity, autoimmunity, allergy
rheumatoid arthritis
example of autoimmune type 4 hypersensitivity
recurrent bacterial sinopulmonary infections and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
b cell/immunoglobulin deficiencies
sinitus, otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia
examples of recurrent bacterial sinopulmonary infections (B cell/Ig deficiencies)
oral lichen planus
radiating white lines in bilateral mucosa, “band-like” infiltration of T cells, made worse by acids and spicy food
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) AND Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) biopsies
Definitive diagnosis of oral pemphigus vulgaris or mucous membrane pemphigoid requires?
systemic lupus erythematosus
fatigue, joint pain, “butterfly” rash
systemic lupus erythematosus
what is indicated by positive ANA with antibodies to both anti-Smith AND anti-dsDNA
MALT lymphoma
Sjogrens disease increases risk for what hematologic condition?
osteoarthritis
type of arthritis that is common in older patients
disc displacement
cause of popping/clicking of TMJ
cone beam CT (CBCT)
What is the best imaging study to determine the
severity of TMJ?
osteoarthritis
worse after activity, hard bony joints, mostly affects pts over 50 years old
rheumatoid arthritis
worse in the morning or inactivity, soft warm tender joints, onset ages 30-50
Folate
what nutrient supplement is prescribed with methotrexate to prevent side effects.
leucovorin
given as a rescue to pts experiencing methotrexate related side effects
behavioral/lifestyle changes, NSAIDs, Occlusal guard
TMD treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis
giant cell arteritis
jaw pain, jaw fatigue, headache, can often be confused with TMD
blindness, transient ischemic attack, stroke
major risk of patients with giant cell arteritis
systemic corticosteroids (prednisone)
how is giant cell arteritis treated
pemphigus vulgaris
Suprabasilar splitting w/ “row of tombstones”
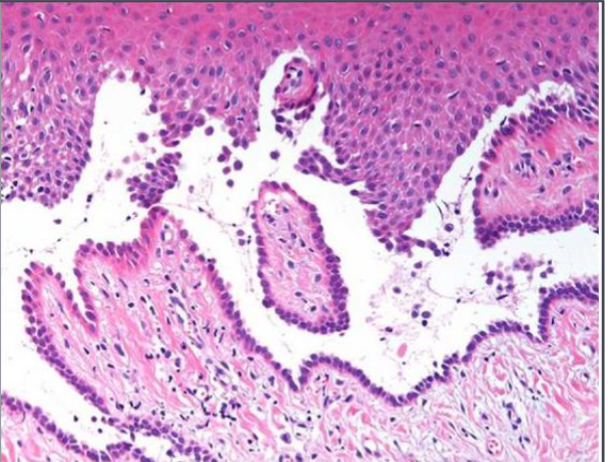
pemphigus vulgaris
“fishnet” / “chicken wire” appearance
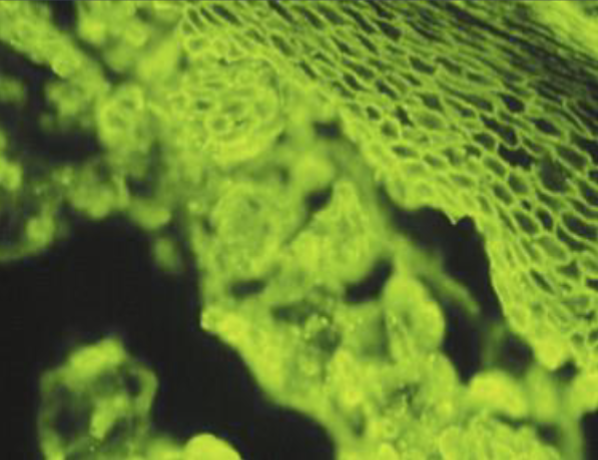
desmosomes
what does pemphigus vulgaris attack
prednisone, rituximab
treatment of pemphigus vulgaris
elevated glucose, immunosuppression, adrenal suppression, osteoporosis
side effects associated with systemic corticosteroids
mucous membrane pemphigoid (mucosal blisters MMP ONLY)
mucosal blisters, oral ulcerations, desquamative gingivitis
oral lichen planus
T cell mediated autoimmune disease, characteerized by lacy white lines and thinning of tissues
mucous membrane pemphigoid
Sub-basilar splitting
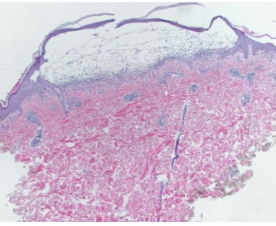
mucous membrane pemphigoid
Uniform line along basement membrane
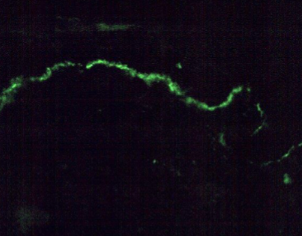
dry mouth, dry eyes, fatigue, brain fog, dysphagia, joint pain
symptoms of sjogrens
dental caries, oral candidiasis, mucosal irritation/burning, swollen salivary glands
majors risks of sjogrens disease
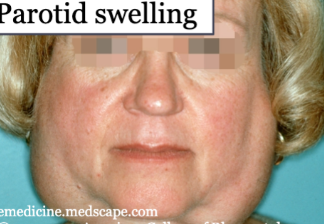
sjogrens
which disease is associated with parotid swelling
anti SSA, labial salivary gland biopsy
best diagnostic tests for sjogrens (3 points each) (≥4 points diagnostic)
pilocarpine (salagen), cevimeline (evoxac)
sialagogue medications approved to treat sjorgens
Calcinosis cutis, Raynaud phenomenon, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, and Telangiectasia
what does CREST stand for?
non-specific
limitation of ANA test
oral cancer
major risk of OLP
C-reaective protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
non-specific biological markers of systemic inflammation
acute inflammation
causes elvated C-reactive protein
chronic inflammation
characterized by simultaneous destruction and partial healing of tissue
innate response without resolution
leads to chronic inflammation
rheumatoid arthritis
attack of synovial membrane (joint lining) by self-reactive T and B cells that drive chronic inflammation.
osteoarthritis
degenerative joint disease that results from the breakdown of cartilage and underlying bone, causing pain and stiffness
bouchard’s and heberden’s node
signs of osteoarthritis seen in hands
infectious arthritis
inflammation of a joint caused by an infection, often due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
infectious arthritis
symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, and rashes. Could be caused by LYME disease.
reactive arthritis
associated with GI/GU pathogens, STDs/STIs (reiter’s syndrome)and drug reactions, causes conjunctivitis, urethritis, and arthritis