4.1.8.9 - Government Intervention in markets
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Types of Market Failures
- Negative externalities
- Positive externalities
- Merit goods
- Demerit goods
- Public Goods
- Lack of property rights
- Imperfect info / info failure
- Factor Immobility
- Monopoly Power
Reasons for Government Intervention
- Reduce Market Failure
- Reduce Inequalities in the Distribution of Income & Wealth
- Achieve Macroeconomic Objectives (PUBE)
Evaluating Policies (IDO's)
- Effectiveness (factors like elasticity of good)
- Cost (cost to introduce & enforce)
- Choice (does it retain choice for consumers?)
- Time (how long to work & will it last)
- Popularity
- Evidence
- Equity (will certain groups suffer more)
Indirect Taxation
A tax levied on the sale of goods and services
- Acts as a CoP (shifts supply curve left)
What Market Failures does Indirect Taxation Solve?
Overconsumption:
- Demerit goods
- Negative externalities in consumption
- Negative externalities in production
Indirect Tax Diagram
- Tax per Unit?
- Tax Revenue for Gov?
- Consumer Price?
- Producer Price?
- Consumer burden?
- Producer burden?
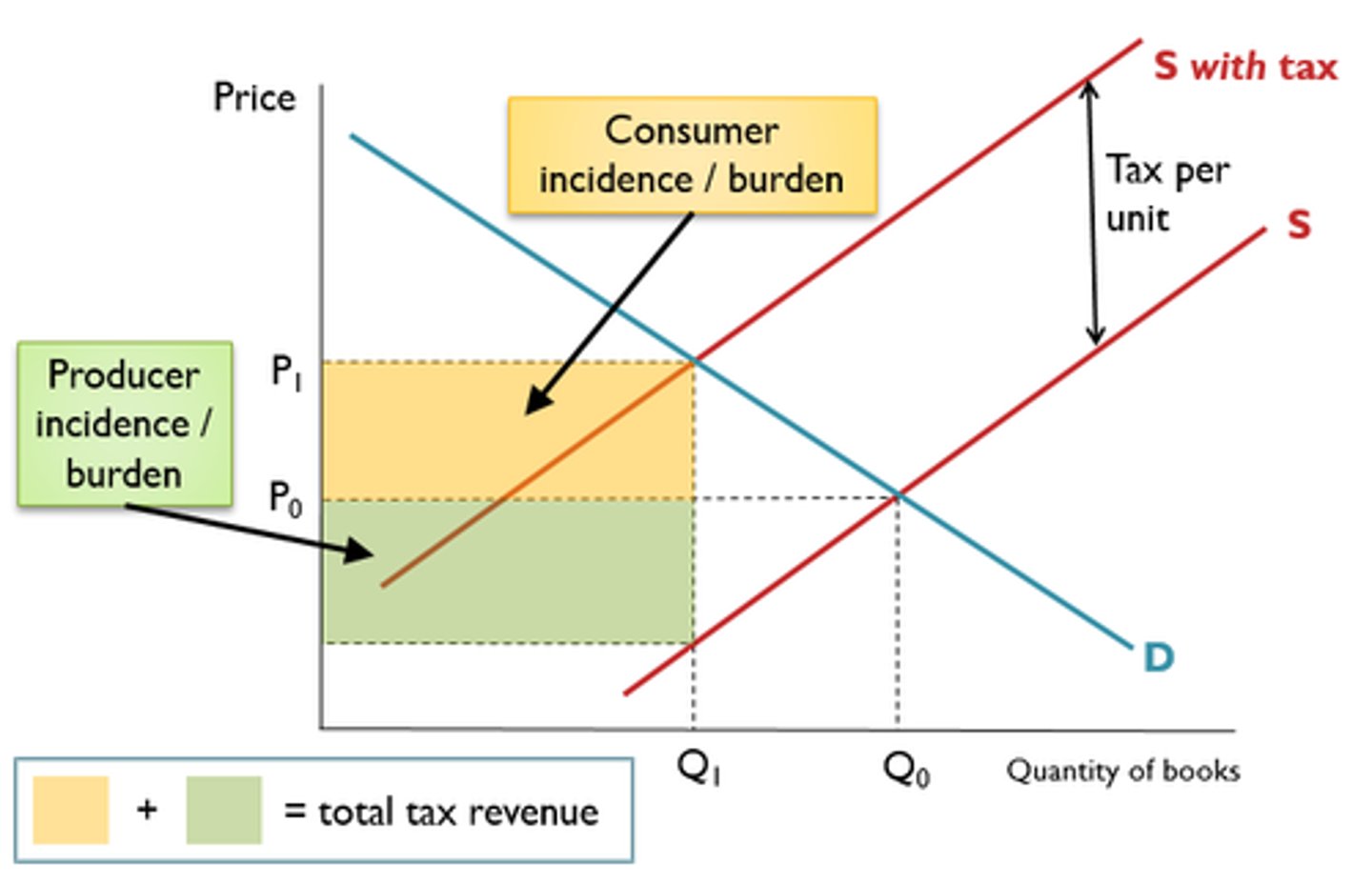
Indirect Taxation Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
Indirect tax can solve the market failure of overconsumption due to the good being a demerit good/has negative externalities
Indirect taxation increases the costs of production for firms
This means producers are less willing and able to supply at any given price so supply decreases and causes the supply curve to shift left (S1 to S1+tax or MPC to MPC+tax)
This results in equilibrium price increasing from Pm to Ps so there is a contraction of demand and equilibrium quantity falls from Qm to Qs.
The equilibrium quantity is now at the socially optimal point which solves the overconsumption of the good
Now fewer scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the overallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so indirect taxation has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Indirect Tax (eval)
Internalises the Externality - Makes the producer and consumer pay more for the goods, reducing impact to third parties
Tax Revenue for Government - Tax can be hypothecated to help fund other solutions to the mkt failure or solve other mkt failures, or to achieve PUBE objectives
Acts on price mechanism - to dissuade consumption through substitution & income effect
Choice isn't Eliminated - Doesn't ban consumption
Little cost to government - compared to reg, easier to enforce
Time Effective - Has fairly immediate impact on consumption
Flexible - Can be constantly adjusted over longer-term to adapt to market changes
Disadvantages of Indirect Tax (eval)
Depends on PED - Less effective at reducing consumption of price inelastic goods
Difficult to Estimate Size - Difficult to estimate correct level of tax as size of mkt failure needs value judgement
Unintended Consequences - Tax may encourage consumers to seek cheaper & more harmful alternatives, worsening social welfare --> gov failure
Equity Issues - May have regressive impact where higher prices affect lower income consumers more
Less Internationally Price Competitive - Higher prices
Subsidy
A payment from government to producers/firms to reduce their costs of production and encourage production of certain goods
What Market Failures does Subsidies Solve?
Underconsumption:
- Merit goods
- Positive production externality
- Positive consumption externality
- Public Goods
Subsidy Diagram
- Subsidy per Unit?
- Total Subsidy paid by Gov?
- Consumer Price?
- Producer Price?
- Consumer benefit?
- Producer benefit?
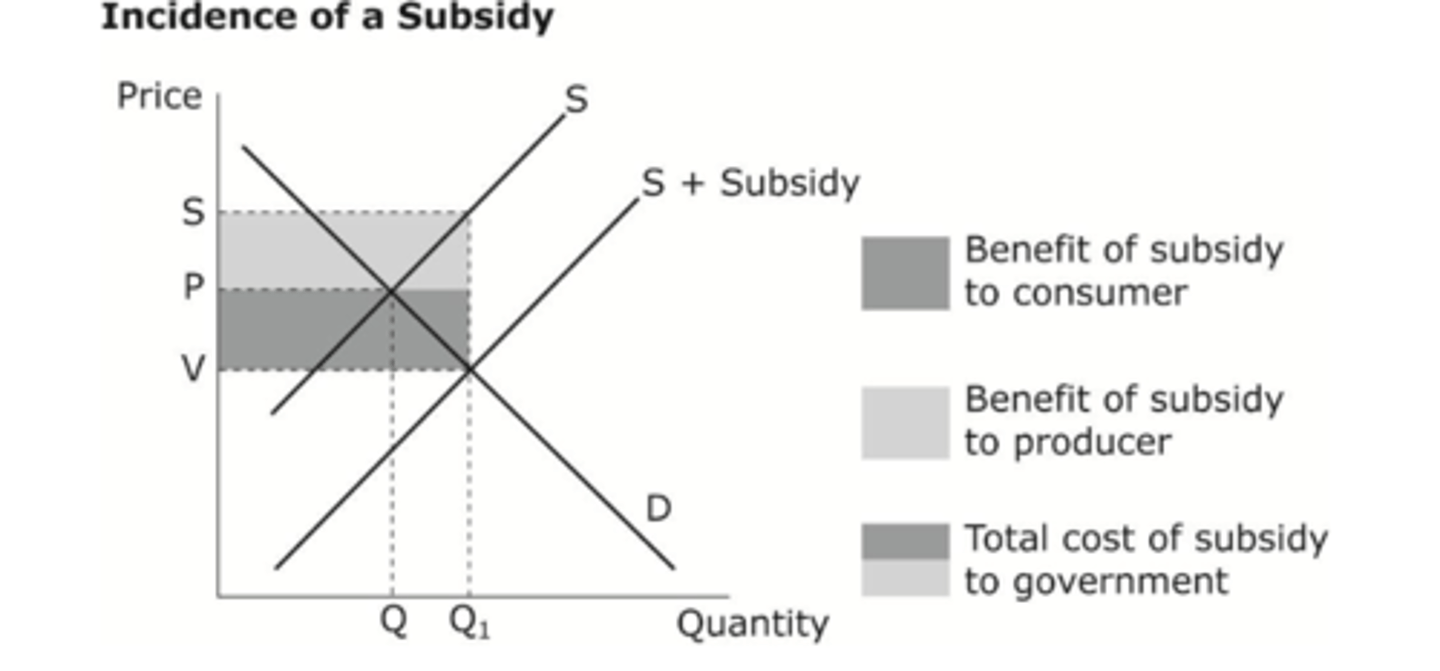
Subsidy Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
Subsidies can solve the market failure of underconsumption due to the good being a merit good/has positive externalities
Subsidies are a payment from the government to producers
So subsidies lower the costs of production for firms
This means producers are more willing and able to supply at any given price so supply increases and causes the supply curve to shift right (S1 to S1+subsidy or MPC to MPC+subsidy)
This results in equilibrium price decreasing from Pm to Ps so there is an extension of demand and equilibrium quantity rises from Qm to Qs.
The equilibrium quantity is now at the socially optimal point which solves the underconsumption of the good
Now more scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the underallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so subsidies has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Subsidies (eval)
Equitable Policy - Lower income households benefit from lower prices from subsidies
Time Effective - Has a fairly immediate impact on consumption
Promotes Innovation & Investment - Reduces barrier of costs & financial burden so encourages innovation and investment
Disadvantages of Subsidies (eval)
Depends on PED - Less effective at increasing consumption of price inelastic goods
Difficult to Estimate Size - Difficult to estimate correct level of subsidy as size of mkt failure needs value judgement
Opportunity Cost - Subsidies cost governments which could have been spent elsewhere (e.g. on healthcare)
Producer may not Pass On the Subsidy - Producers may not reduce prices but instead add to their profits by keeping subsidy
Unfair - Can't subsidise everything
Subsidies Application
In 2023, the UK gov allocatted £450 million in grants to homeowners for installing energy-efficient heat pumps, aiming to reduce carbon emissions
Maximum Prices (price ceiling)
A legal limit that prevents firms from charging prices above this price ceiling
- Must be set below market equilibrium
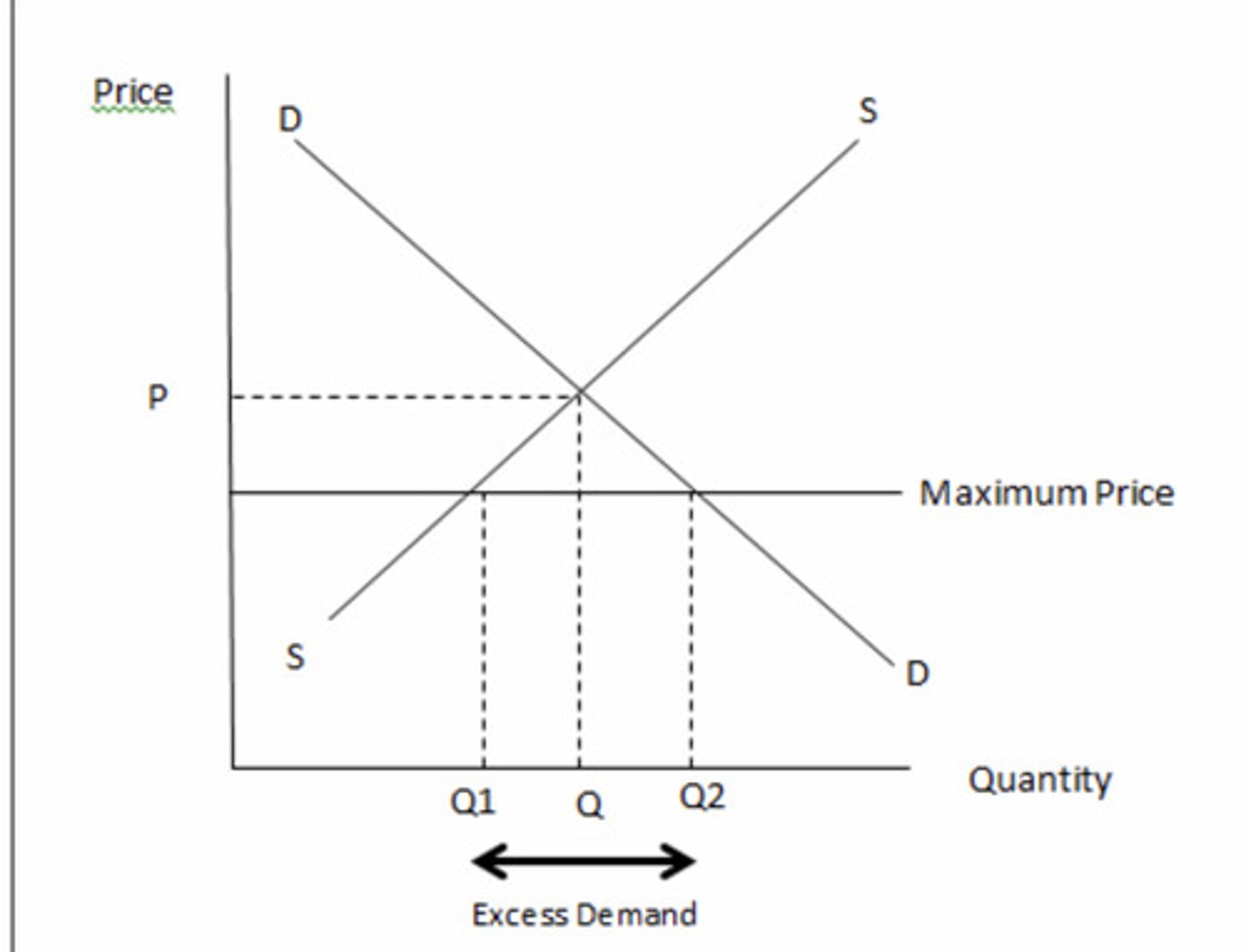
What Market Failures does Maximum Prices Solve?
Underconsumption:
- Merit goods
Maximum Price Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
Initially, the free market equilibrium is at Pm,Qm
Government imposes a maximum price of Pmax below the equilibrium price
This causes a contraction of supply to Qs and extension of demand to Qd, resulting in a disequilibrium
There is now excess demand of Qd-Qs
At this maximum price, demand is now at the socially optimal quantity of Qd
Therefore, the underconsumption of the good due to it being a merit good/positive externalities is now solved.
Now more scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the underallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so the maximum price has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Maximum Prices (eval)
Effective in the Short-Term - During emergencies when affordability of essential goods/necessities is an issue
Disadvantages of Maximum Prices (eval)
Shortage/Excess Demand - Firms less w&a to supply at this lower price --> long waiting lists for goods
Informal/Black Markets - Shortages/excess demand could lead to selling in informal markets where prices are higher so mkt failure still occurs
Maximum Price Application
Over 1 million apartments in NYC have a maximum price imposed
Minimum Prices (price ceiling)
A legal limit that prevents firms from charging prices below this price floor
- Must be set above market equilibrium
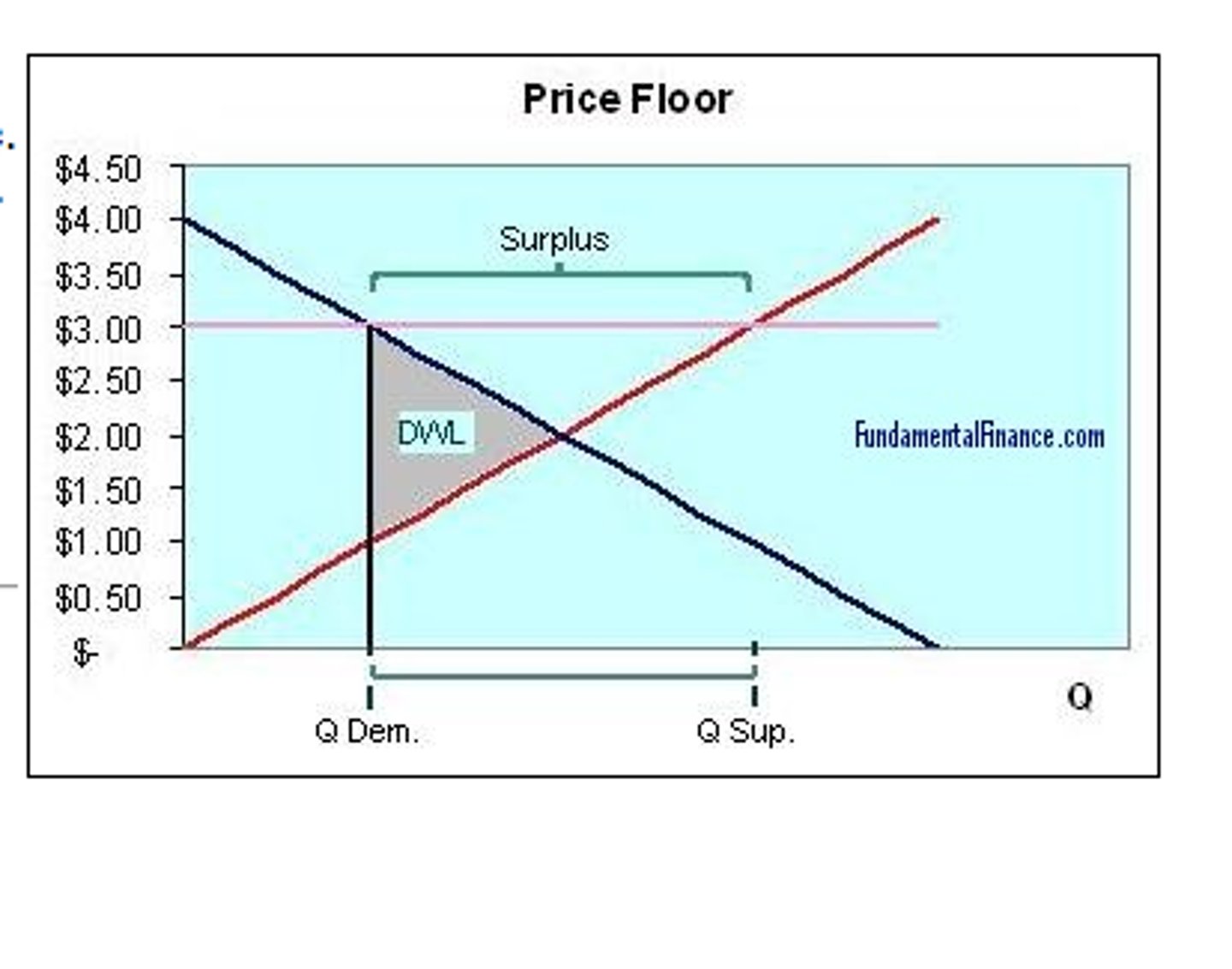
What Market Failures does Minimum Prices Solve?
Overconsumption:
- Demerit goods
Minimum Price Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
Initially, the free market equilibrium is at Pm,Qm
Government imposes a minimum price of Pmin above the equilibrium price
This causes a extension of supply to Qs and contraction of demand (income & substitution effect) to Qd, resulting in a disequilibrium
There is now excess supply of Qs-Qd
At this minimum price, demand is now at the socially optimal quantity of Qd
Therefore, the overconsumption of the good due to it being a demerit good/negative externalities is now solved.
Now less scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the overallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so the minimum price has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Minimum Prices (eval)
Higher prices dissuades consumption due to income & substitution effect
More production of merit goods is encouraged
Disadvantages of Minimum Prices (eval)
Excess Supply - Encourages firms to oversupply and thus waste scarce resources
Depends on PED - Less effective at reducing consumption of price inelastic goods
Difficult to Estimate Level - Difficult to estimate correct level to set min price as size of mkt failure needs value judgement
Unintended Consequences - Higher prices may encourage consumers to seek cheaper & more harmful alternatives, worsening social welfare --> gov failure
Equity Issues - May have regressive impact where higher prices affect lower income consumers more
Less Internationally Price Competitive - Higher prices
Minimum Price Application
Scotland has a minimum price on alcohol of 65p per unit
State (Direct) Provision
When the state provides the good/service
State Provision Diagram
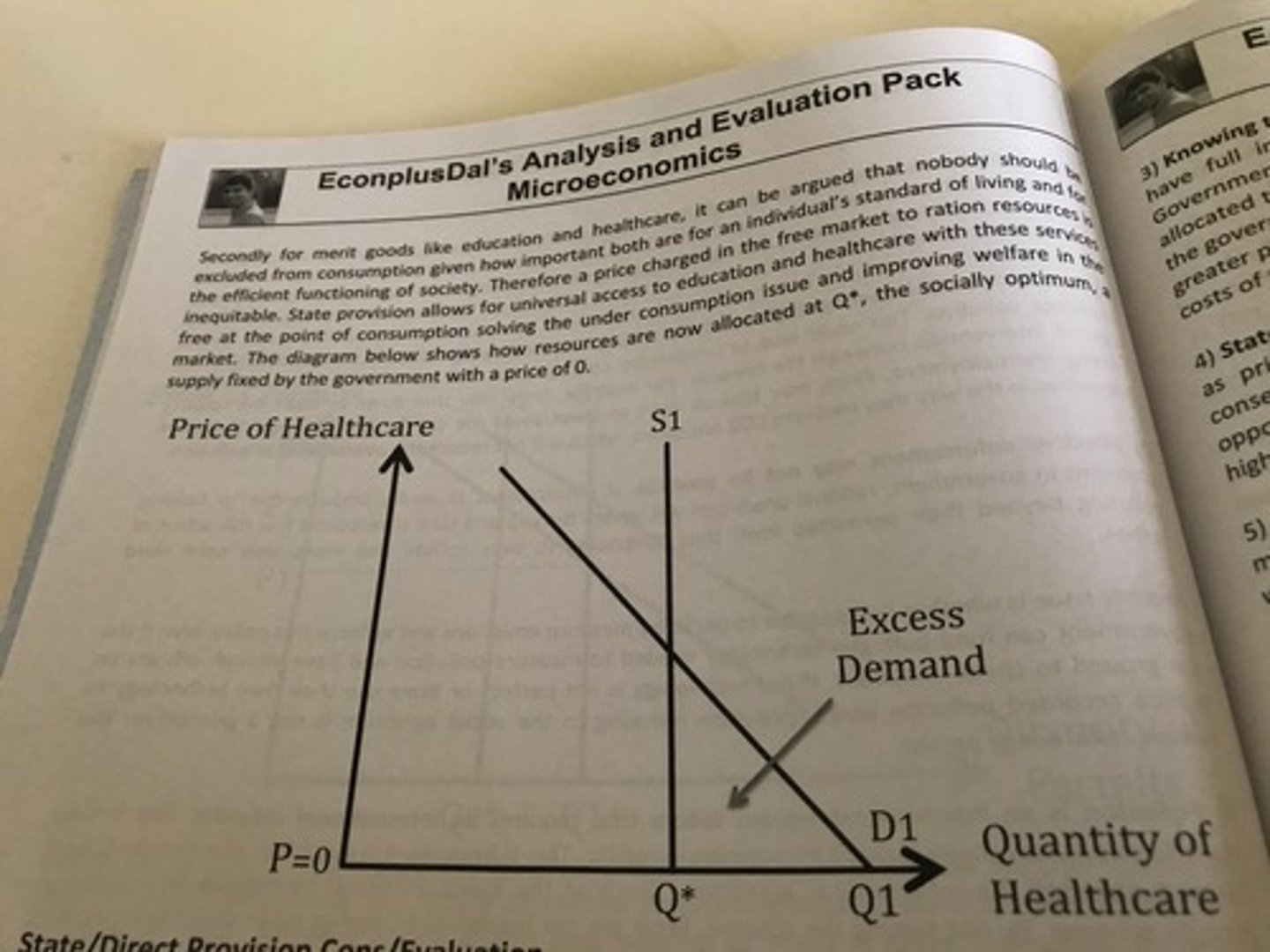
What Market Failures does State Provision Solve?
Underconsumption:
- Public Goods
- Merit goods
- Positive production externalities
- Positive consumption externalities
State Provision Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
State provides the good/service
Increased supply of the good in the market
Government sets a price to achieve optimal level of consumption
Lower prices for consumers or sometimes made free at the point of use
Lower prices means consumers are more willing and able to demand the good so encourages more consumption
Demand is now at the socially optimal quantity of Q*
Therefore, the underconsuption of the good due to it being a public/merit good/positive externalities is now solved.
Now more scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the underallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so the state provision has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of State Provision (eval)
Solves failure directly for public goods - gov has direct control
Can ensure correct standards - Gov in control can ensure correct standards, fair distribution and consistency as not driven by profits and competition
Equitable - Low prices/free at point of use means more people can access the service
Disadvantages of State Provision (eval)
Cost - Expensive policy, opportunity cost
Lead to excess demand - Low price/free means too much demand compared to quantity supplied - long waiting lists
Inefficient Providers - Lack of profit incentive means state providers may be inefficient compared to private sector
Often needs to be backed up by regulation to encourage consumption if Information Based market failure
Overconsumption - Might result in overconsumption
Regulation
The imposition of laws, rules or controls that forces a change in consumption or production
Types of Regulation to Solve Market Failures
Act as an additional cost (solving overconsumption)
Force more consumption (solving underconsumption)
(e.g. compulsory education)
Force less consumption (solving overconsumption)
(e.g. gun BANS, drug bans, legal drinking age)
Force firms to provide adequate information (solving information failure - demerit goods)
(e.g. nutritional information, facts & photos on cigarette packaging)
Force firms to produce in a different way (solving overproduction - negative production externalities)
(e.g. limit on pesticides, nail varnish exposure)
Reduce monopoly power
(e.g. blocking mergers, fines for collusion)
Regulation Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
[DIFFERENT DEPENDING ON QUESTION & REGULATION IMPOSED]
Government imposes regulation: e.g. bans, compulsory education, cigarette packaging
As regulation has the weight of the law behind it, the threat of prosecution acts as a deterrent and forces consumers/producers to obey to (less consumption/less production)
Demand/supply falls to optimum (shown by D+reg or S+reg)
......
mkt failure solved
Advantages of Regulation (eval)
Backed up by the weight of the law - So threat of prosecution acts as deterrent so more likely to change behaviour
Effective for inelastic PED goods - Directly influences quantity consumed unlike policies that rely on price mechanism
Only effective policy for severe negative externalities / demerit goods that must be BANNED
Can be backed up by fines - can generate additional gov revenue to help fund other policing
Disadvantages of Regulation (eval)
Difficult to Estimate Level - Difficult to estimate correct level of regulation as size of mkt failure needs value judgement
Expensive & Difficult - Policing & enforcement expensive
Informal/Black Markets - Could lead to selling in informal markets (unregulated) so mkt failure still occurs
If regulations are extreme like bans, any benefits of the product will be lost as a whole
Regulation/Ban Application
On October 1 2023, the UK gov banned certain single-use plastics
Information Provision
When information about the benefits or consequences of consuming a good is provided to consumers
What Market Failures does Information Provision Solve?
Information Failure:
- Merit goods
- Demerit goods
Information Provision for DEMERIT GOODS Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
In the free market, consumers have imperfect information about the private costs of consuming this good such as [APPLICATION]
So consumers underestimate these costs, therefore demand is at D (partial) and equilibrium is at Pm,Qm
The government can use information provision policies like ad campaigns, risks on packaging, to make people more aware of the true private costs of this good such as [APPLICATION]
This allows consumers to make more informed decisions on consuming this good
So demand will decrease causing the demand curve to shift left to D (full)
Quantity has decreased to the social optimum of Qs.
Therefore, the overconsumption of the good due to it being a demerit good is now solved.
Now fewer scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the overallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so the information provision has reduced the partial market failure
Information Provision for MERIT GOODS Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
In the free market, consumers have imperfect information about the private benefits of consuming this good such as [APPLICATION]
So consumers underestimate these benefits, therefore demand is at D (partial) and equilibrium is at Pm,Qm
The government can use information provision policies like ad campaigns, to make people more aware of the true private benefits of this good such as [APPLICATION]
This allows consumers to make more informed decisions on consuming this good
So demand will increase causing the demand curve to shift right to D (full)
Quantity has increased to the social optimum of Qs.
Therefore, the underconsumption of the good due to it being a merit good is now solved.
Now more scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the underallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so the information provision has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Information Provision (eval)
Choice isn't Eliminated - Doesn't ban consumption
Can lead to Long-lasting Behavioural Changes - Can permanently solve mkt failure in long-term
Disadvantages of Information Provision (eval)
Difficult to target the right audience
Expensive - to research info and provide it to everyone (opp cost)
Does not always change behaviour - People may willingfully ignore information, not believe information, or good may be addictive of nature so struggle to stop consumption
Information Provision Application
UK government implemented the traffic light labelling system for food to indicate how healthy its ingredients are
Tradeable Pollution Permits
The right to pollute a certain amount that can be bought and sold in a market
What Market Failure does Tradeable Pollution Permits Solve?
Negative production externalities
Tradeable Pollution Permits Diagram
NEEDS 2 DIAGRAMS
1) Market for Pollution Permits
2) Market for Pollution Producing Good (normal p,c,b diagram mpc --> mpc+permit left)
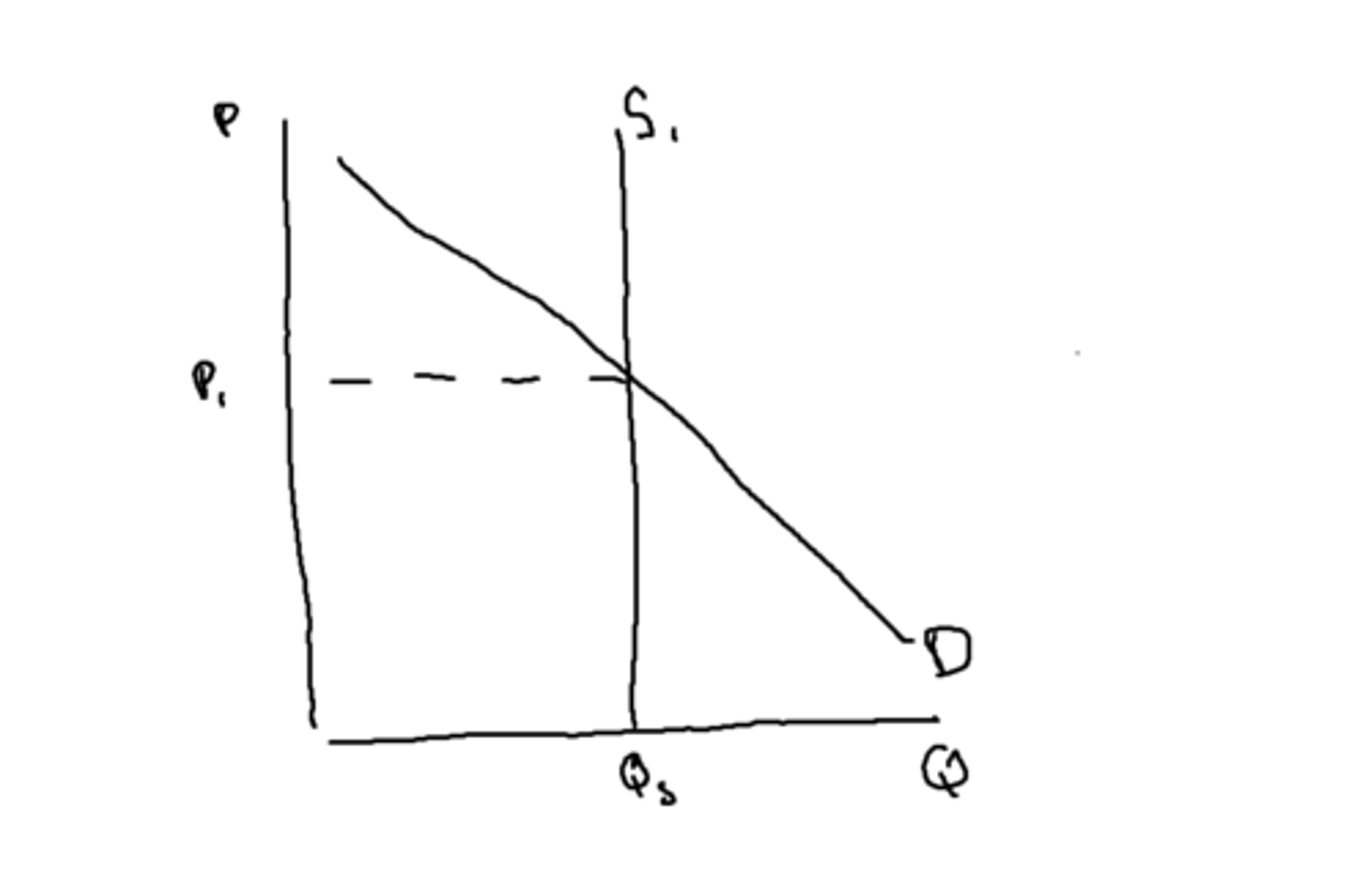
Tradeable Pollution Permits Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
There is market failure of an overproduction of cars which leads to negative externalities in production of environmental costs in the form of pollution
The government sets an overall level of desired pollution and issues permits to firms based on this overall level (e.g. EU Emissions trading scheme [app])
There is a set quantity of permits at Q*1 which can be traded.
Tradeable permits increase the costs of production for firms that pollute as firms either have to buy permits or invest in greener technology
This means producers are less willing & able to supply at any given price so shifts supply to the left from MPC to MPC+permit
This results in equilibrium price increasing from Pm to Ps so there is a contraction of demand and equilibrium quantity falls from Qm to Qs.
The equilibrium quantity is now at the socially optimal point which solves the overconsumption of the good
Now fewer scarce resources are allocated to this market meaning the overallocation of scarce resources has been solved/reduced.
This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so tradeable pollution permits has reduced the partial market failure
Advantages of Tradeable Pollution Permits (eval)
Internalises the Externality - Makes the polluter pay so reduces external cost to third parties
Encourages Investment into Greener Technology
Pollution limit set by gov
Disadvantages of Tradeable Pollution Permits (eval)
Costs of policing/enforcing - Hard to measure whether firms are complying with limits
Needs to be applied globally - If one country doesn't enforce the permits, firms will just move their production there instead
Price is set by market which may fall too low and not create incentive to invest in green tech
Extending Property Rights
To transfer previously common resources over to private ownership.
What Market Failures does Extending Property Rights Solve?
- Negative externalities of over-use and pollution of a common resource (public goods)
Extending Property Rights Chain of Analysis (to solve mkt failure)
- A negative externalitiy occurs if there is over-use or pollution of a shared common resource (e.g. oceans, forests, grazing land) due to the tragedy of the commons.
- Extending property rights by transferring this common scarce resource over to private ownership can solve the market failure of over-use and/or pollution.
- The private owner has a strong incentive to manage the resource and take care of it for future use.
- It allows owners to have exclusive authority to determine how a resource is used and to prosecute those who exploit the resource.
- As a result, any external costs are internalised.
- The private owners now bear any externalities, so the private costs to the polluter increases shown by shift left from MPC to MPC + increased costs
- This reduces the over-use of the scarce resources
- This means the market is now more allocatively efficient and social welfare has improved, so extension of property rights has reduced the market failure
Extending Property Rights Diagram
Externalities Diagram. Shift MPC left to MPC + Increased Costs
Advantages of Extending Property Rights (eval)
Uses the market mechanism to ensure an efficient use of resources
Internalises the externality - directly transfers resources from polluters to those who suffer, bringing the third party into the market mechanism
Government doesn't have to assess the value of property as it is assumed the owners will have a better knowledge of its value
Disadvantages of Extending Property Rights (eval)
Government may not have ability to extend property rights over international boundaries
Legal costs involved in prosecuting a polluter could be high
May be difficult to clearly prove the link between the polution and the source
Gov Intervention for Positive Consumption Externalities
Subsidies
State Provision
Regulation (force ↑consumption)
Gov Intervention for Negative Consumption Externalities
Indirect Tax
Minimum Price
Regulation
Extending Property Rights
Gov Intervention for Positive Production Externalities
Subsidies
State Provision
Regulation
Gov Intervention for Negative Production Externalities
Indirect Tax
Minimum Price
Tradeable Pollution Permits
Regulation