AP World 1.6 Developments in Europe, AP World 1.5
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Middle Ages
Also known as the medieval period, the time between the collapse of the Roman Empire and the High Middle Ages during which trade and intellectual life declined.
Feudalism (European)
A system of exchanges of land for loyalty: A monarch granted fiefs to lords and the lords became the king's vassal. Lords gave the land to knights, who pledged to fight for the lords. The lords also gave land to peasants, who were then obligated to farm the lord's land, provide them with crops, and obey their orders.
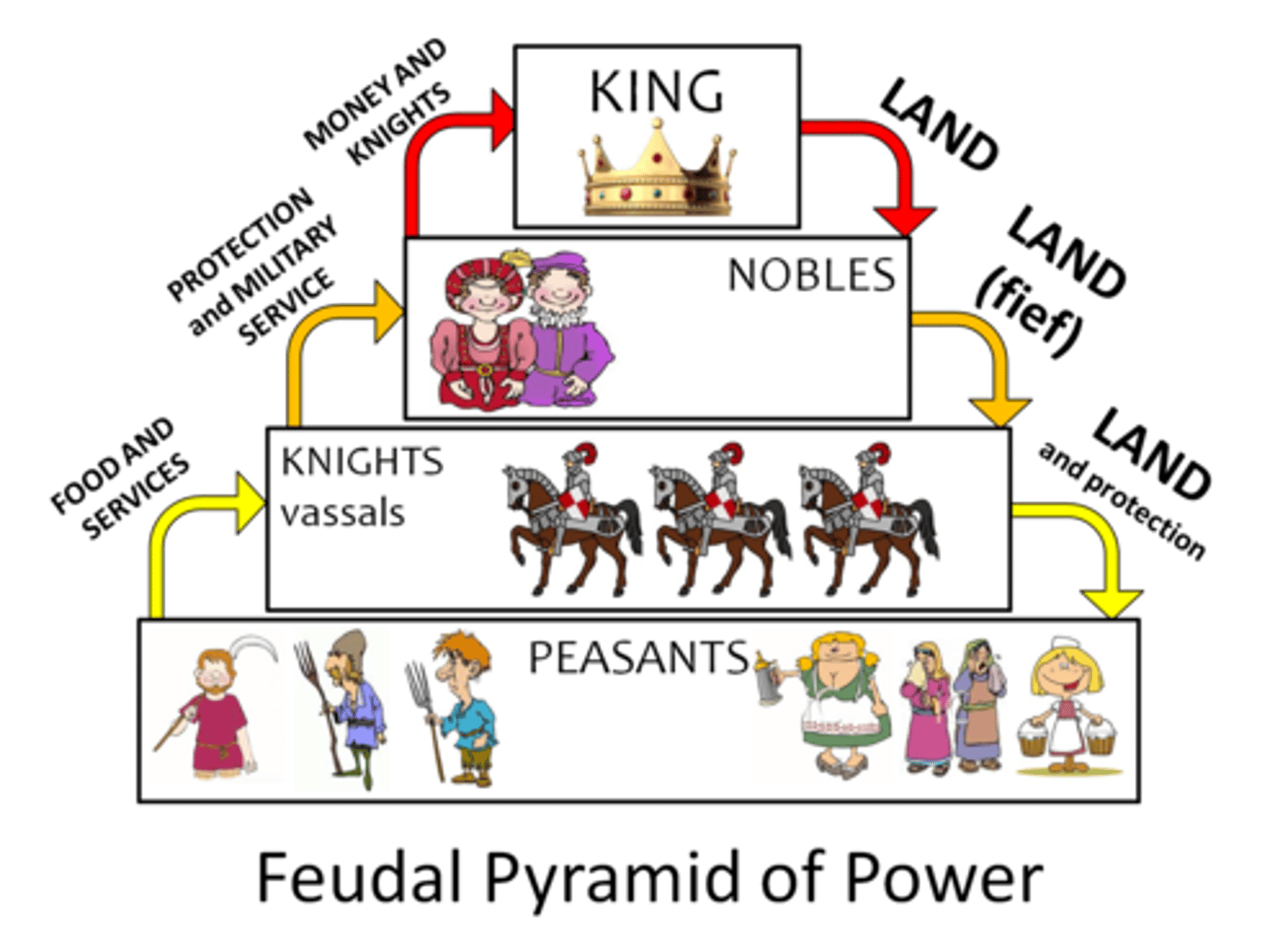
Fiefs
Tracts of land given to lords by monarchs.
Vassal
A person who owed service to another person of higher status.
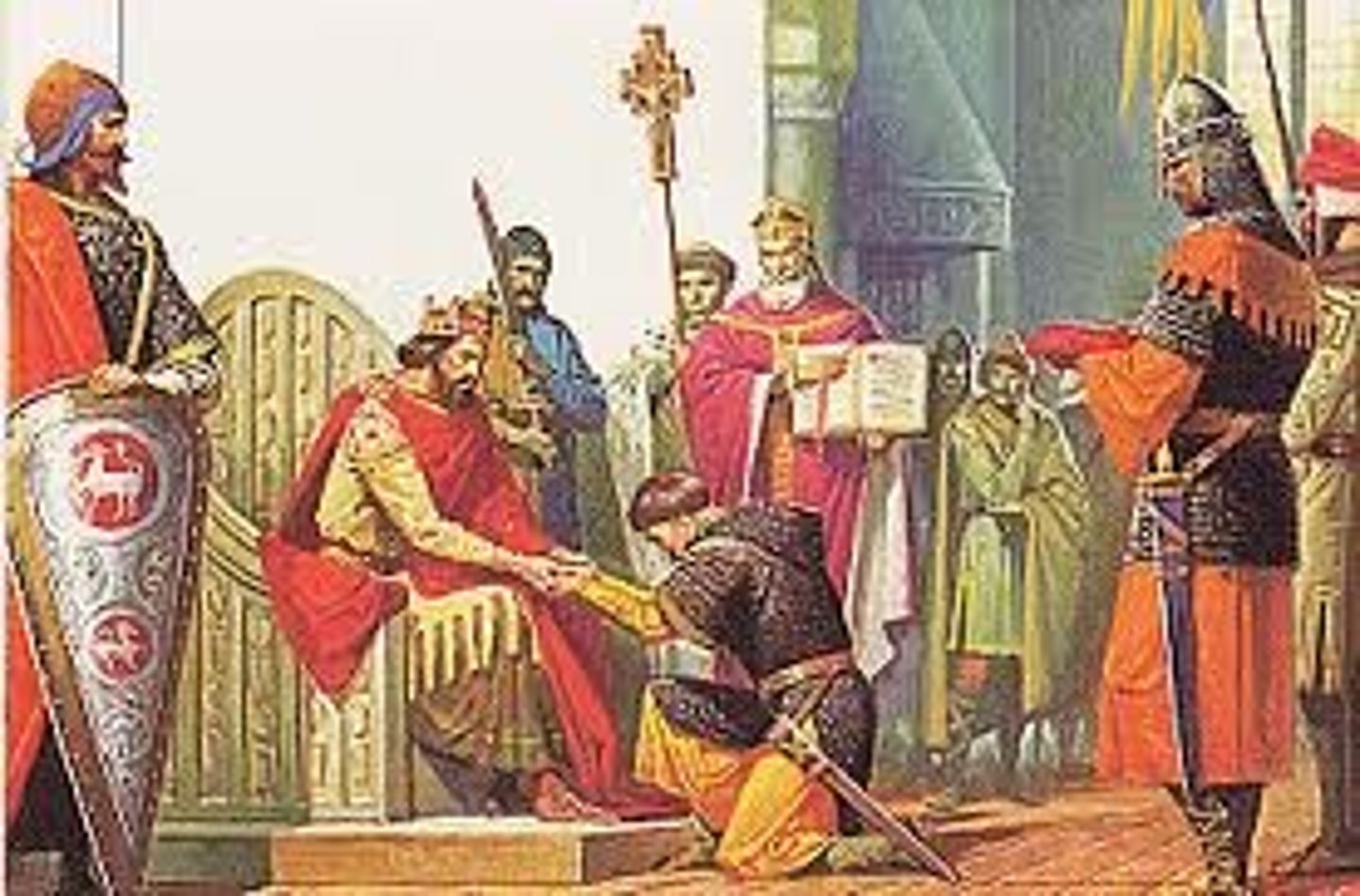

What did European feudalism provide?
Security for peasants, equipment for warriors, and land to those who served a lord.
Code of Chivalry in European Feudalism
An unwritten set of rules for conduct focusing on honor, courtesy, and bravery.
Manors
Large fiefs or estates. They were small villages that might have a church, a blacksmith shop, a mill, and a wine press.
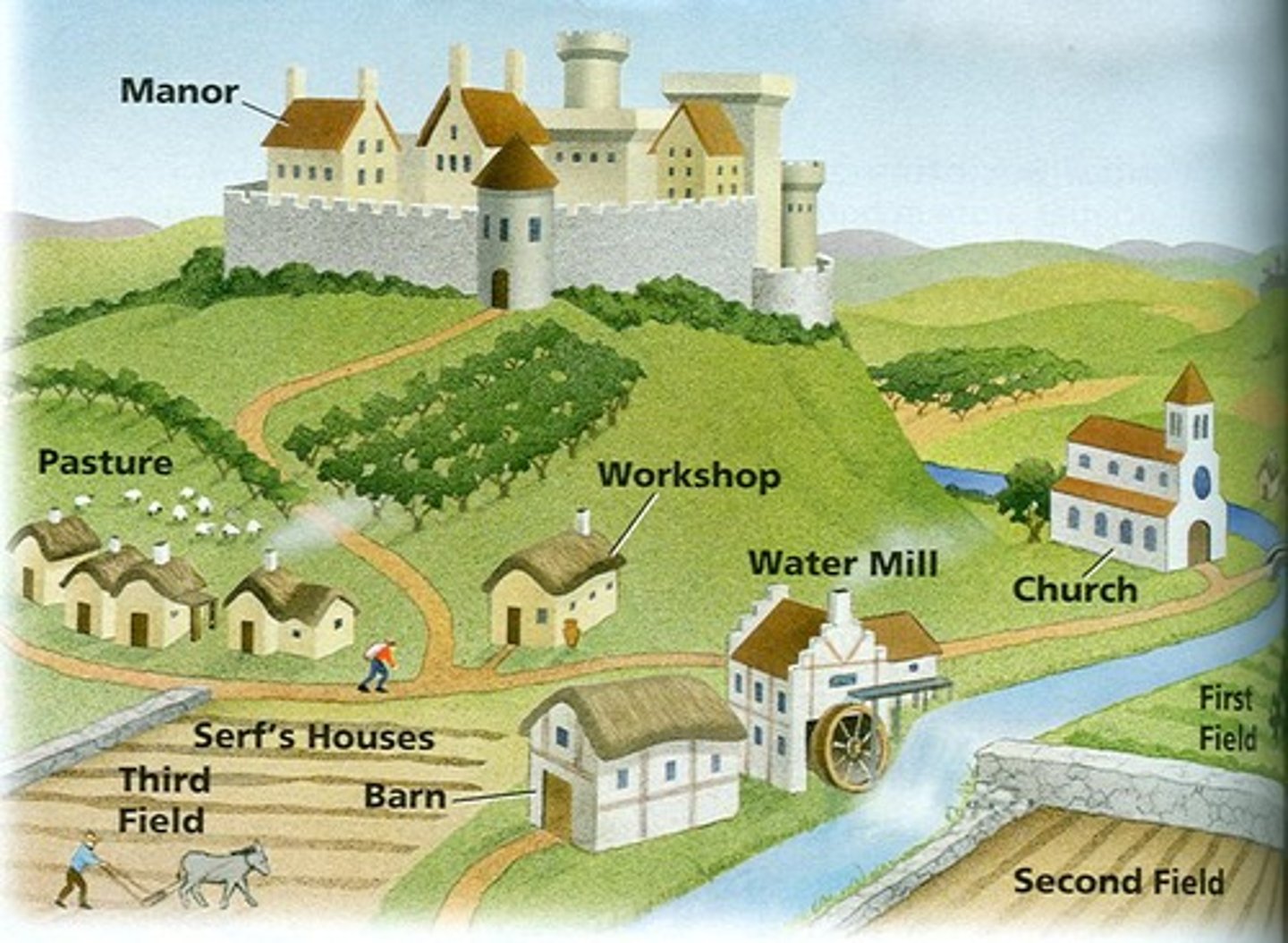
Manorial System
A system that provided economic self-sufficiency and defense by producing everything that the people living on it required, limiting the need for trade.
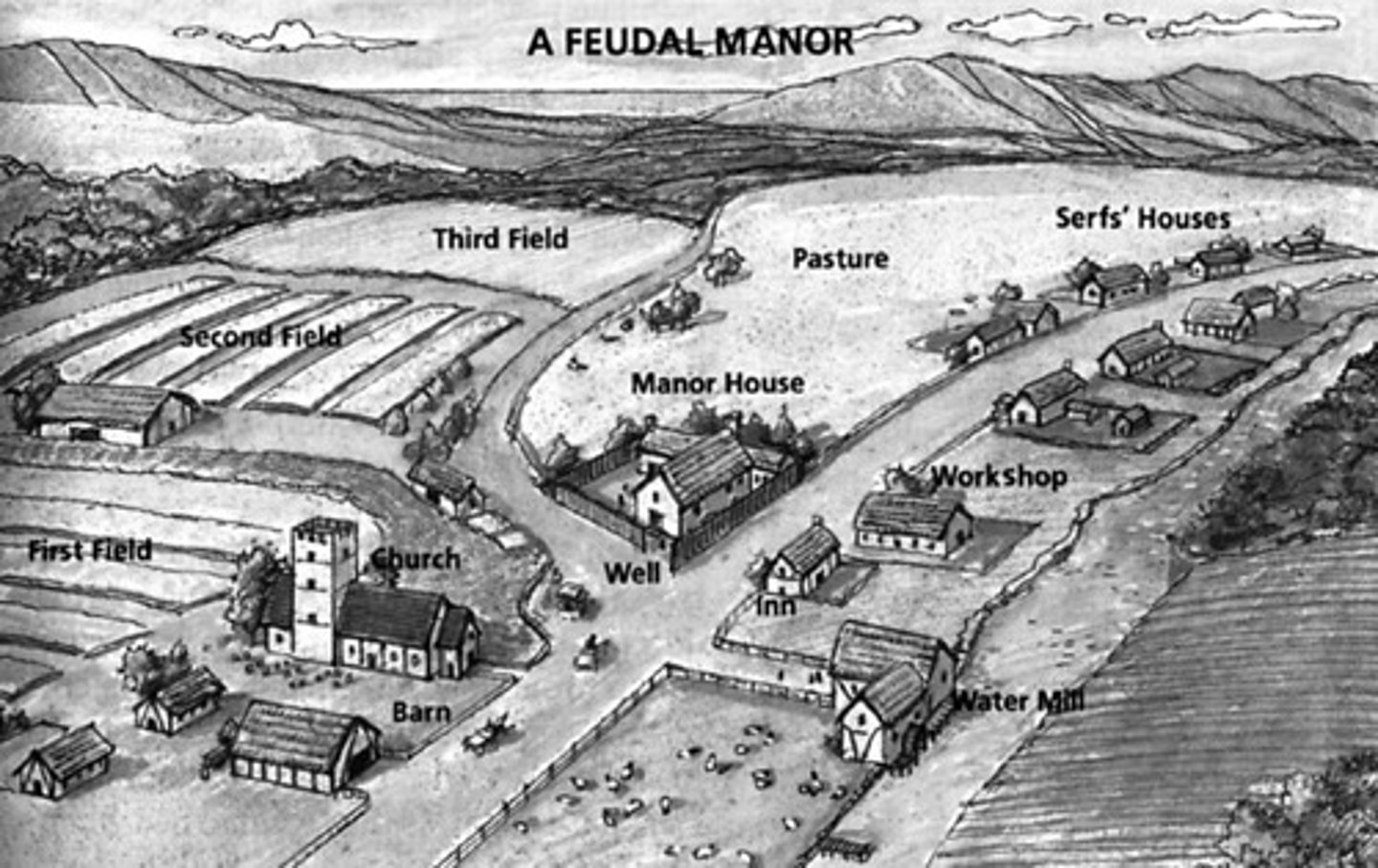
Serfs
Peasants who were bound to their lord's land and paid tribute to their lord in the form of crops, labor, or coins.
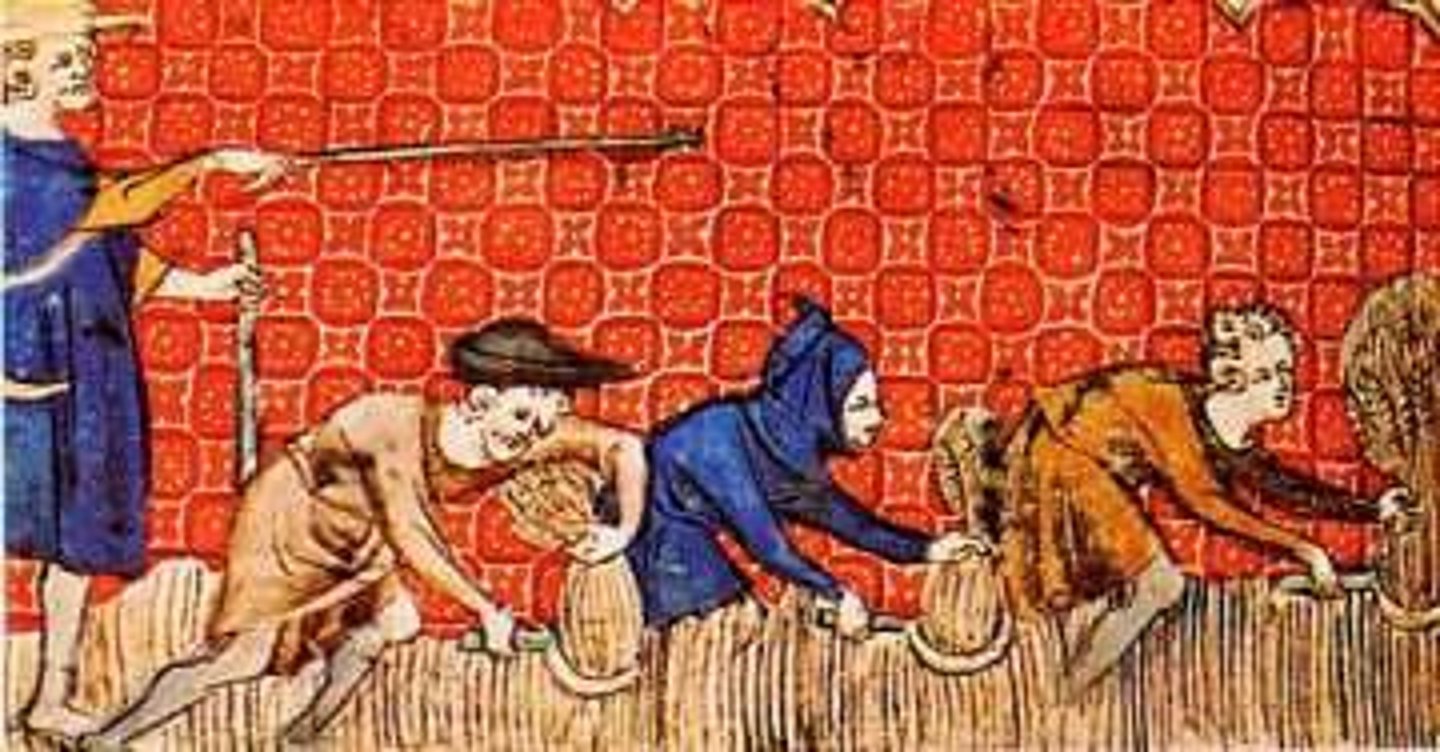

Three-Field System
A system of farming in which one field was used to grow crops that provided food, a second field was planted with peas, lentils, or beans that provided nitrogen to the soil, and the third field was unused each year.
How did agriculture become more efficient near the end of the Middle Ages?
The three-field system, windmills, and new types of plows (heavy/light depending on location) led to agricultural productivity and population growth.
Why did monarchies grow more powerful near the end of the Middle Ages?
Monarchies employed their own bureaucracy and military and the employees worked directly for the king or queen.
King Philip II
1180-1223; the first French monarch to develop a real bureaucracy.
Estates-General
A body to advise the king that included representatives from each of the three legal classes: the clergy, nobility, and commoners. It had little power because the kings did not exact regular taxes on the two upper classes, so they did not feel responsible to protect a government they were not funding.
Otto I
The first emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Lay Investiture Controversy
A dispute over whether a secular leader, rather than the Pope, could invest bishops with the symbols of office. It was resolved at the Concordat of Worms in 1122.
When and why did the Holy Roman Empire end?
It was destroyed during the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648) and came to a formal end when Bonaparte invaded Europe in 1806.
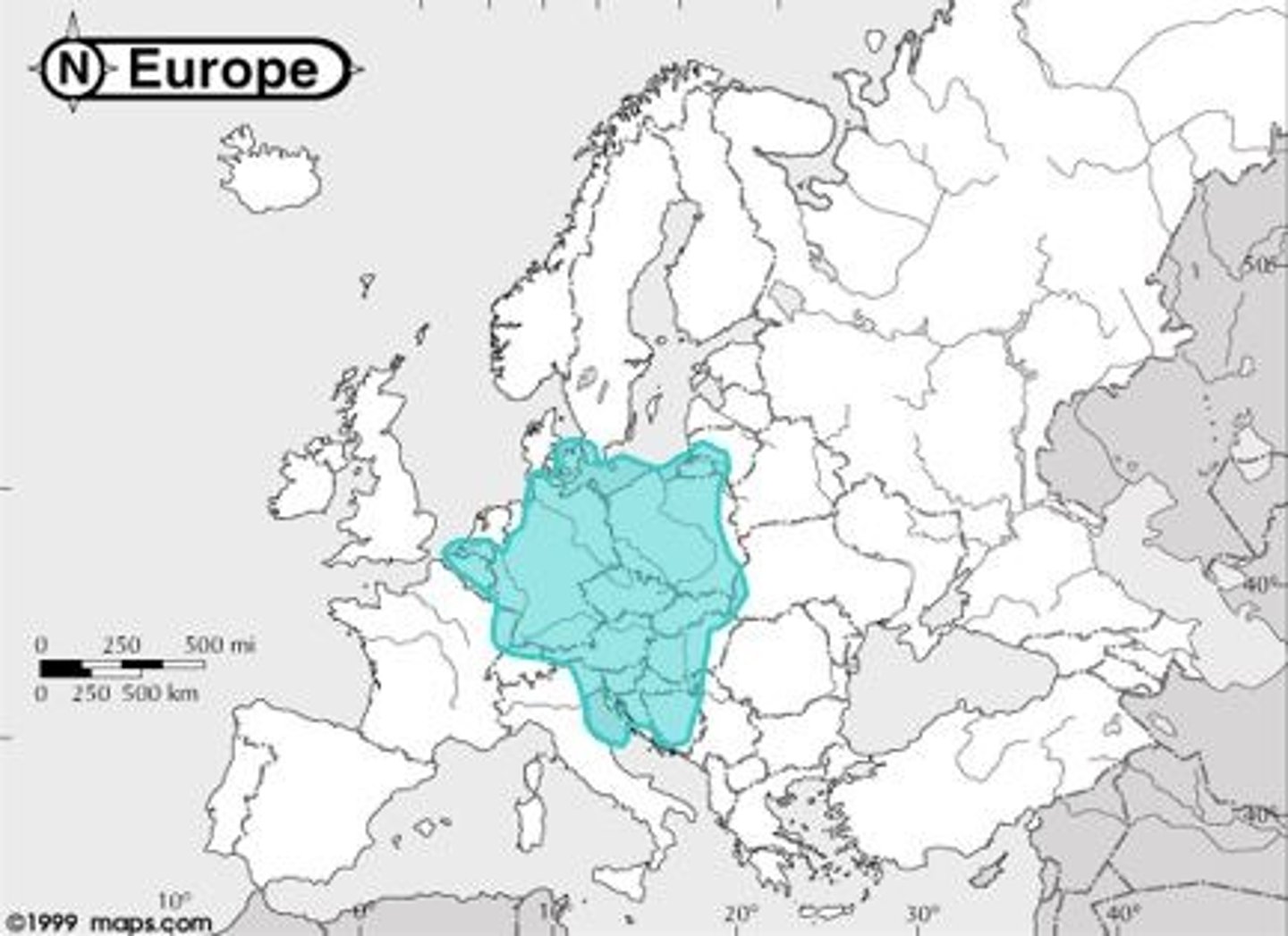
How and when did the Normans arrive in England?
In 1066, William the Conqueror invaded England and organized a feudal system.
Magna Carta
A document that required the King of England to respect certain rights, like the right to a jury trial before a noble could be sentenced to prison.
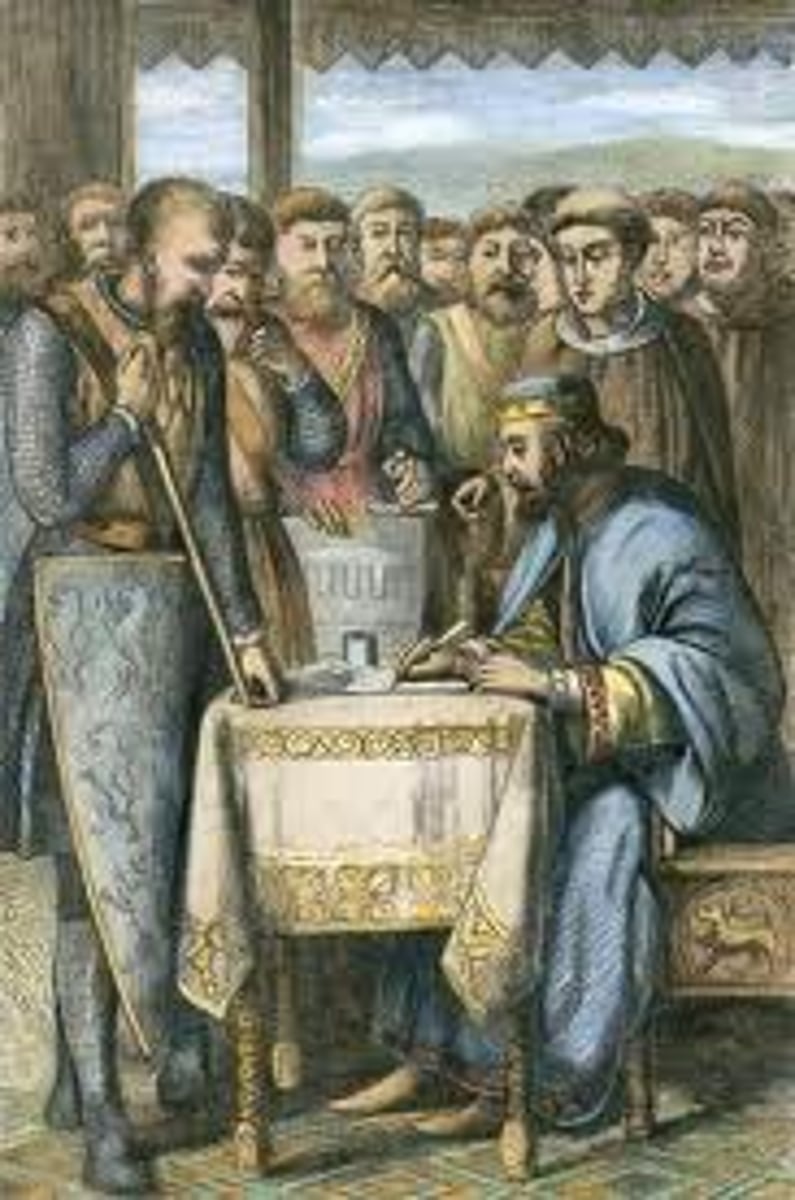

English Parliament
The English legislature that consisted of the House of Lords (nobles and Church) and the House of Commons (wealthy townspeople). It first met in 1265.
Hundred Years' War
1337-1453; a series of battles between England and France. English archers with longbows won early victories, but later only had control over Calais in France.
What were the two important results of the Hundred Years' War?
Serving under one monarch made people identify as "English" or "French", and the war demonstrated the use of gunpowder weapons.
Reconquista
Christian campaigns to retake Spain from the Muslims, which they finally did in 1492.
Great Schism
1054; The division of the Christian Church in Europe into the Roman Catholic Church and the Orthodox Church.
What kind of education and art was present in the Roman Catholic Church during the Middle Ages?
The church established the first universities and all artists worked for the church and made religious artwork to help illiterate serfs understand the Bible.
How did the Roman Catholic Church influence the feudal system?
If a lord displeased the church, it could pressure the lord. Bishops selected and supervised local priests.
Bishops
Regional religious leaders in the Roman Catholic Church.
Monasteries
Communities of monks that had the same functions of agriculture and protection as the manors.
Why did reformers like Martin Luther feel the need to reform the Roman Catholic Church in the 16th century?
Wealth and political power in the clergy led to corruption, and theological disagreements.
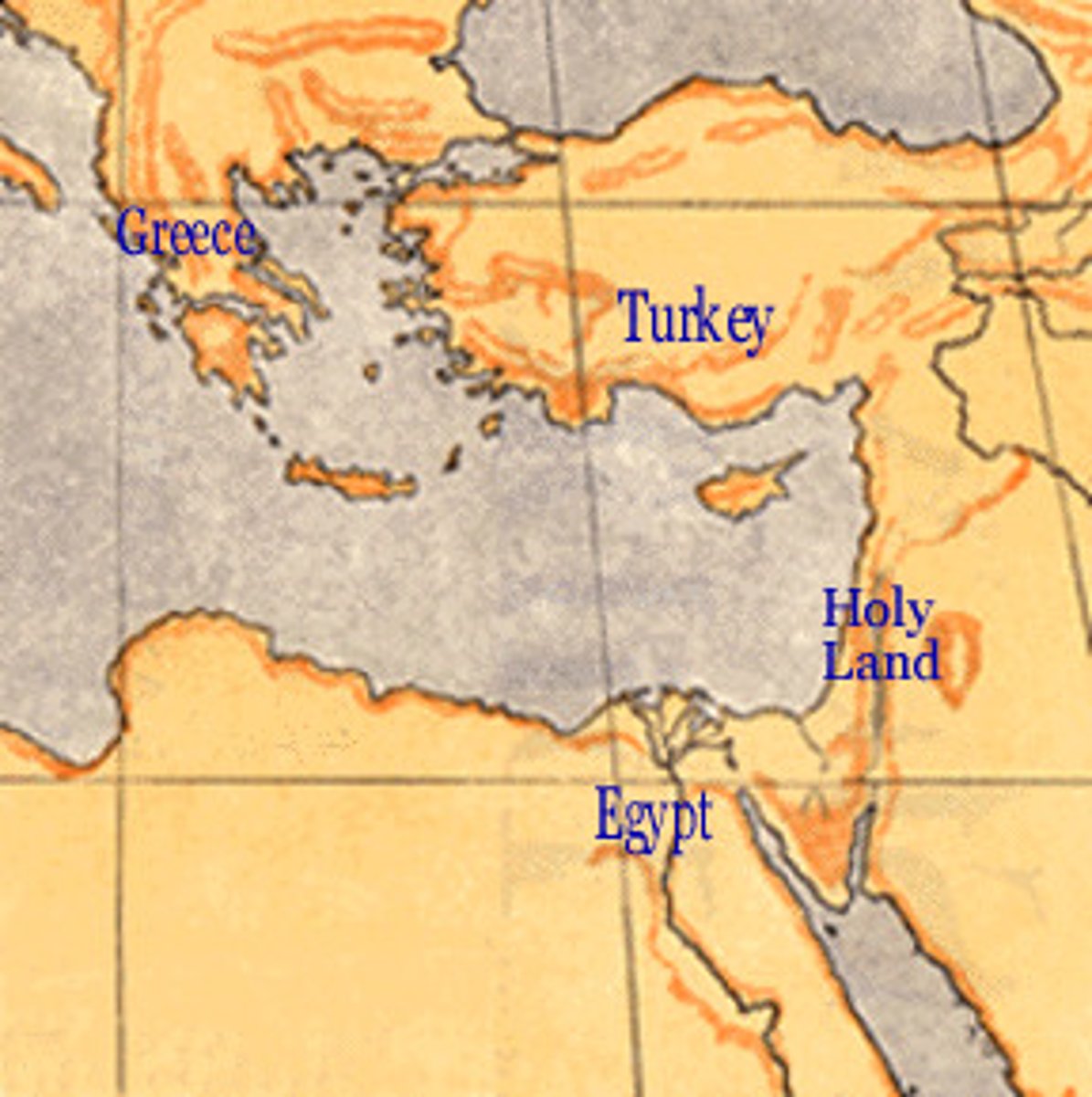
Holy Land
The region of Palestine in the Middle East that contains sites of spiritual significance to Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
Primogeniture
A system of inheritance in which the eldest son inherited the family estate and left a generation of younger sons with little access to wealth and land.
Why did the Europeans decide to start crusades?
Primogeniture, diverting the ambitions of restless nobles and unemployed peasants, and opening up trade routes in the Middle East.
Crusades
A series of military campaigns in the Middle East between 1095 and 1200.
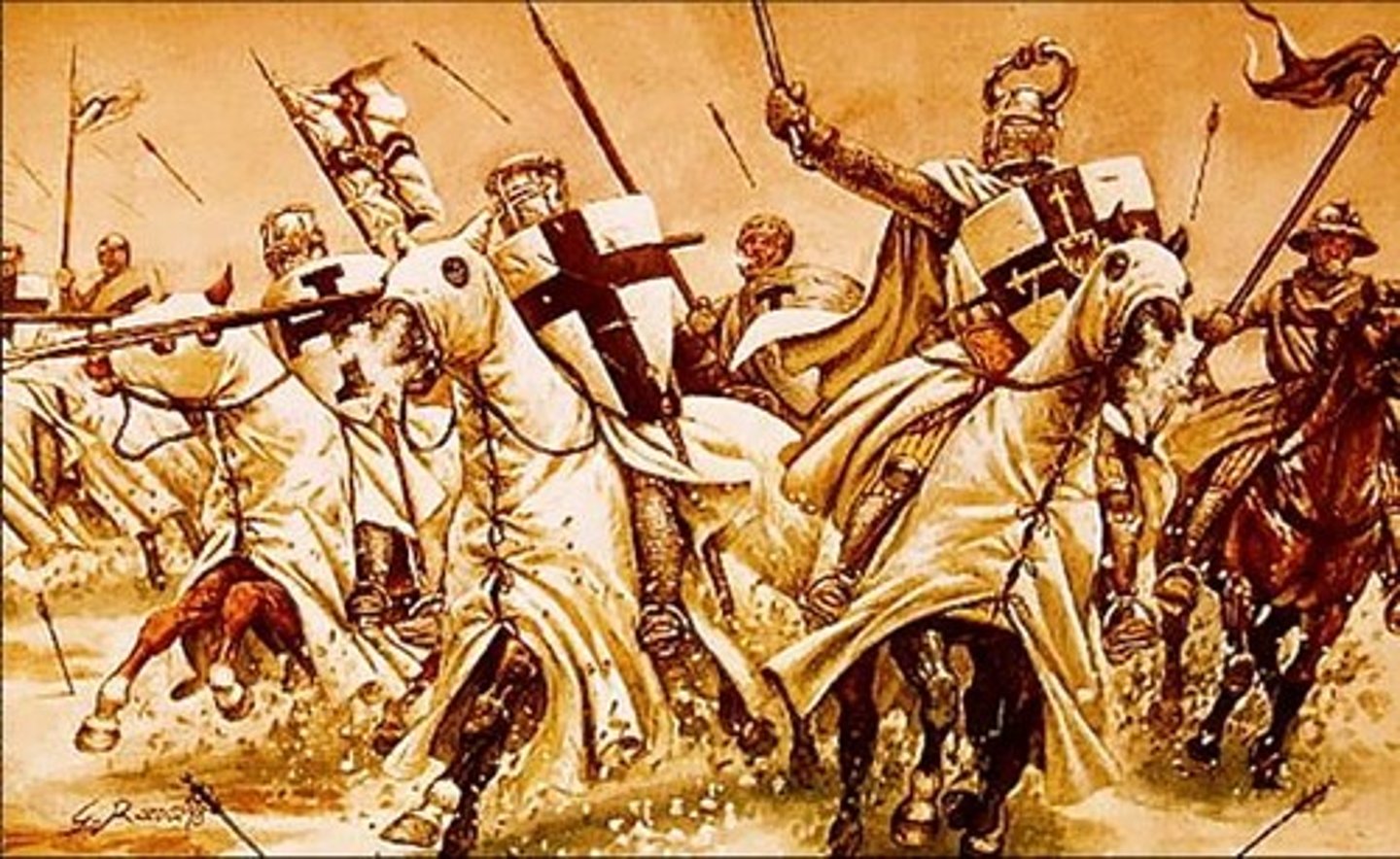

How did the Europeans recruit people for crusades?
The Roman Catholic Church granted people relief from acts of atonement and told people they would reach heaven sooner if they joined a crusade and the Orthodox patriarch was alarmed that the Seljuk Turks were persecuting Christians.
First Crusade
The crusade during which the Christians conquered Jerusalem in 1099.
Fourth Crusade
1202-1204; it was diverted into a battle for Constantinople and failed to recapture Jerusalem.
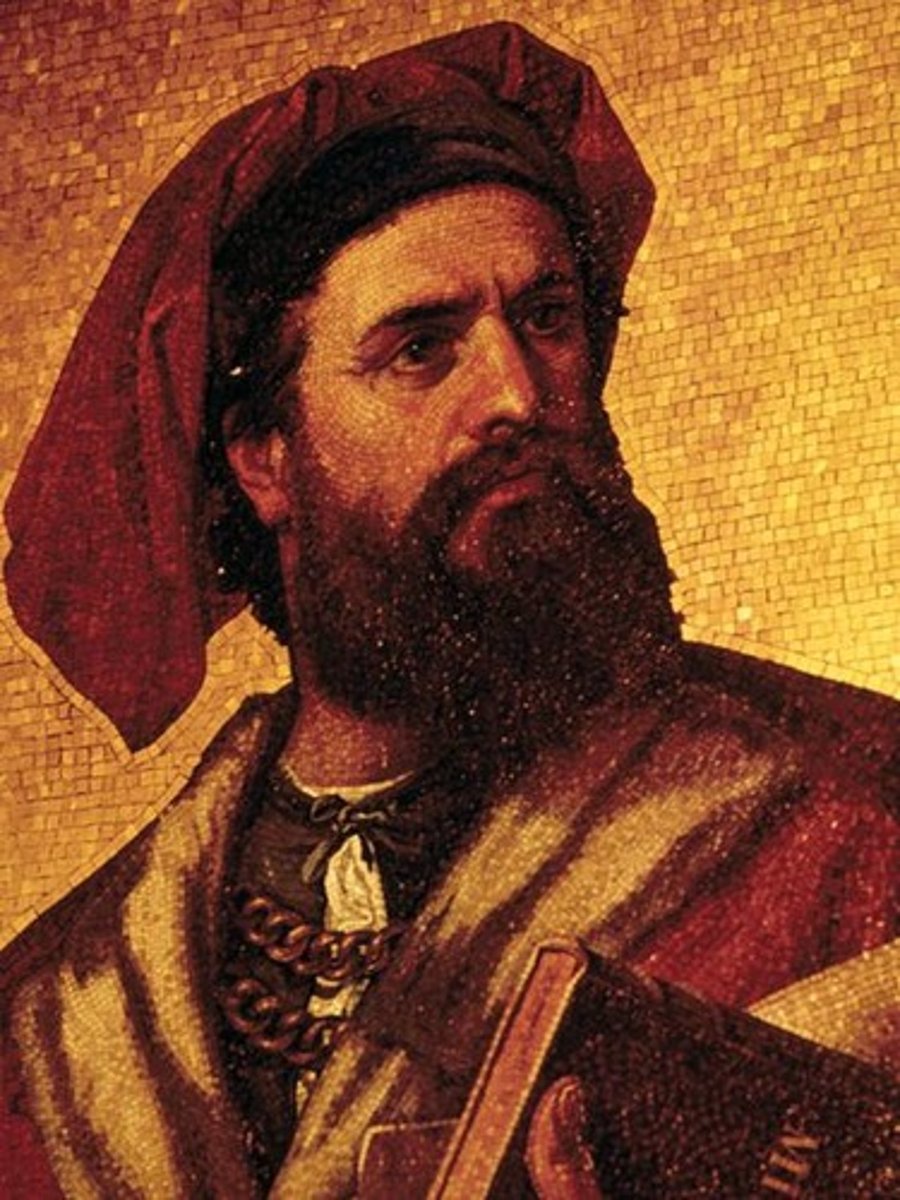
Marco Polo
An Italian explorer who visited Kublai Khan and reported his discoveries to Europeans, stimulating interest in Asia and mapmaking.

Bourgeoise (Burghers)
The middle class between the nobles and peasants that included shopkeepers, merchants, etc.
What were the results of the Black Death in Europe?
1/3 of the European population died, serfs gained more bargaining power with lords because of the lack of people.
Little Ice Age
A five-century cooling of the climate that reduced agricultural productivity , increasing disease and unemployment and creating social unrest.
How did the population of Jews in Europe change and influence Europe during the Middle Ages?
The Jewish population increased and Jews who could moved to North Europe where many became moneylenders, increasing economic growth. Some political leaders welcomed them but others were anti-Semitic because they believed Jews were untrustworthy. Jews were expelled from England, France, Spain, and Portugal.
How did the population of Muslims in Europe change and influence Europe during the Middle Ages?
Many Muslims moved to southeastern Europe due to persecution in Spain. Countries in the Muslim Ottoman Empire developed large Muslim populations. Contacts with traders in Muslim caliphates allowed more trade and ideas to flow.
What were the gender roles in Europe in the Middle Ages?
Women did not receive education but sometimes managed manor accounts. Women sometimes became artisans and members of guilds (associations of merchants and craftspeople).
How were Scandinavians connected to the Mediterranean and Central Asia?
They were connected through trade of furs, fish, and grain.
Kievan Rus
A city-state that was a trading center that maintained close cultural relationships with Byzantium.
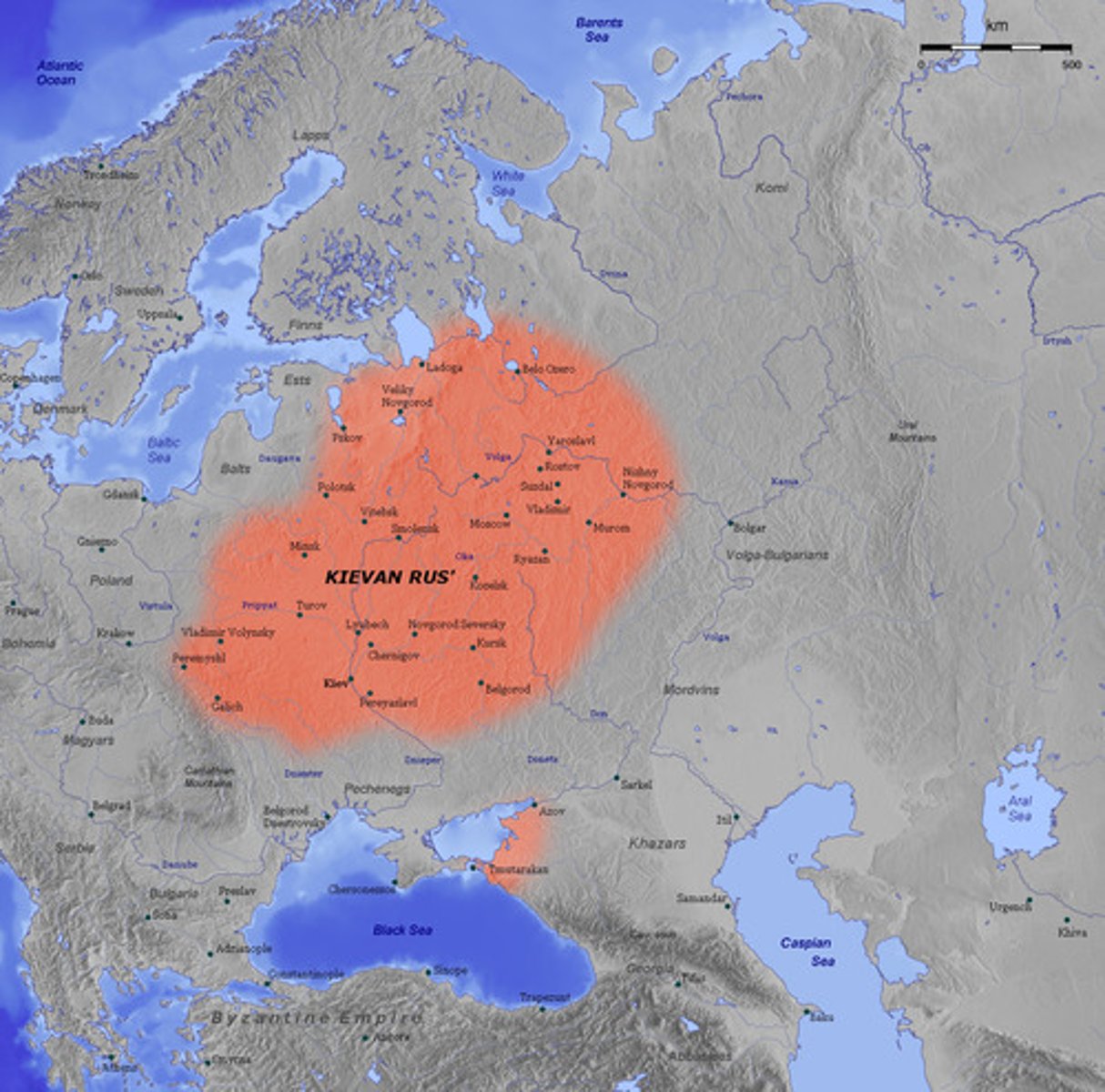
Ivan the Great
A Moscow-based ruler who resisted Mongol rule in Kievan Rus, which helped the region become independent of the Mongols and become the state of Russia.
Renaissance
A period characterized by a revival of interest in classical Greek and Roman art, literature, culture, and civic virtue. It developed because the expansion of trade, an agricultural surplus, and a growing middle class sparked creativity in Europe.
What was the significance of the printing press?
It allowed manuscripts to be mass-produced at affordable costs, fostering a growth in literacy and the rapid spread of ideas.

Humanism
The focus on individuals rather than God. Humanists sought education and reform, and wrote secular literature.
What were the results of cultural changes in the Renaissance?
Powerful monarchies, centralization of governments, and nationalism.
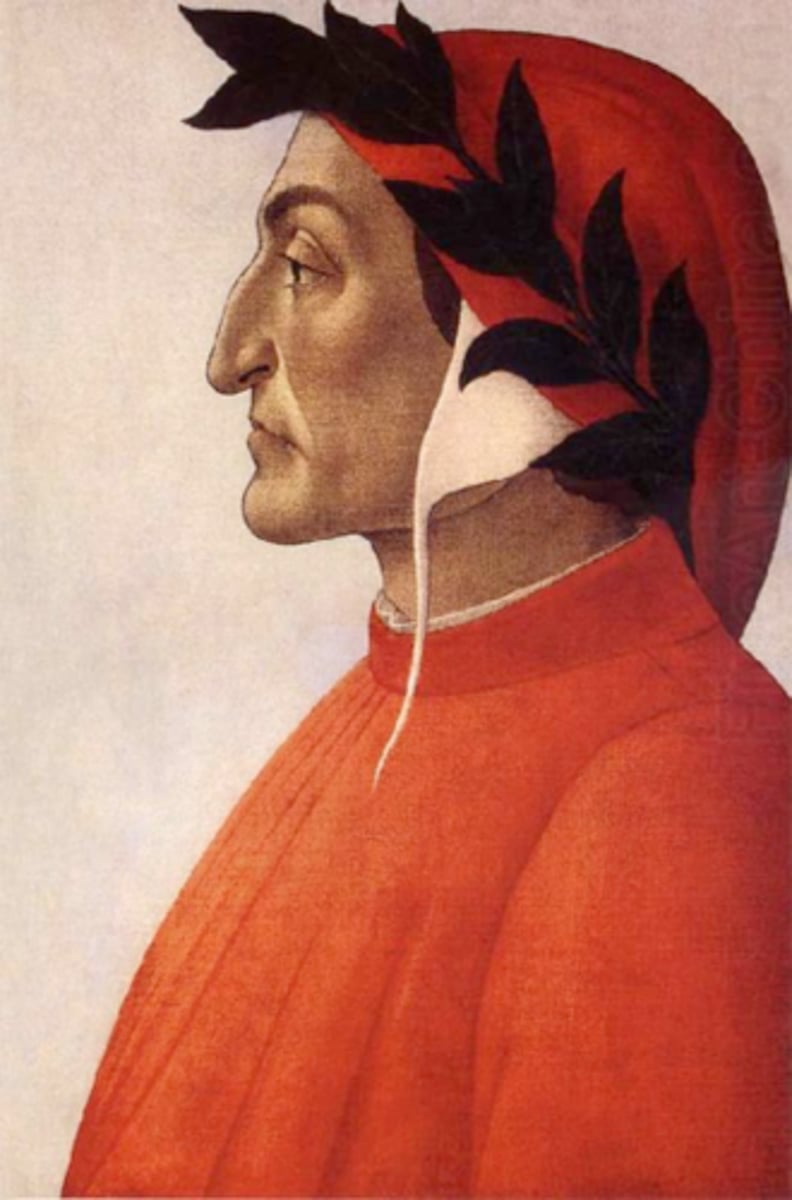
Dante Alighieri
The Italian poet who wrote The Divine Comedy, which criticized corrupt officials and used Italian vernacular instead of Latin.

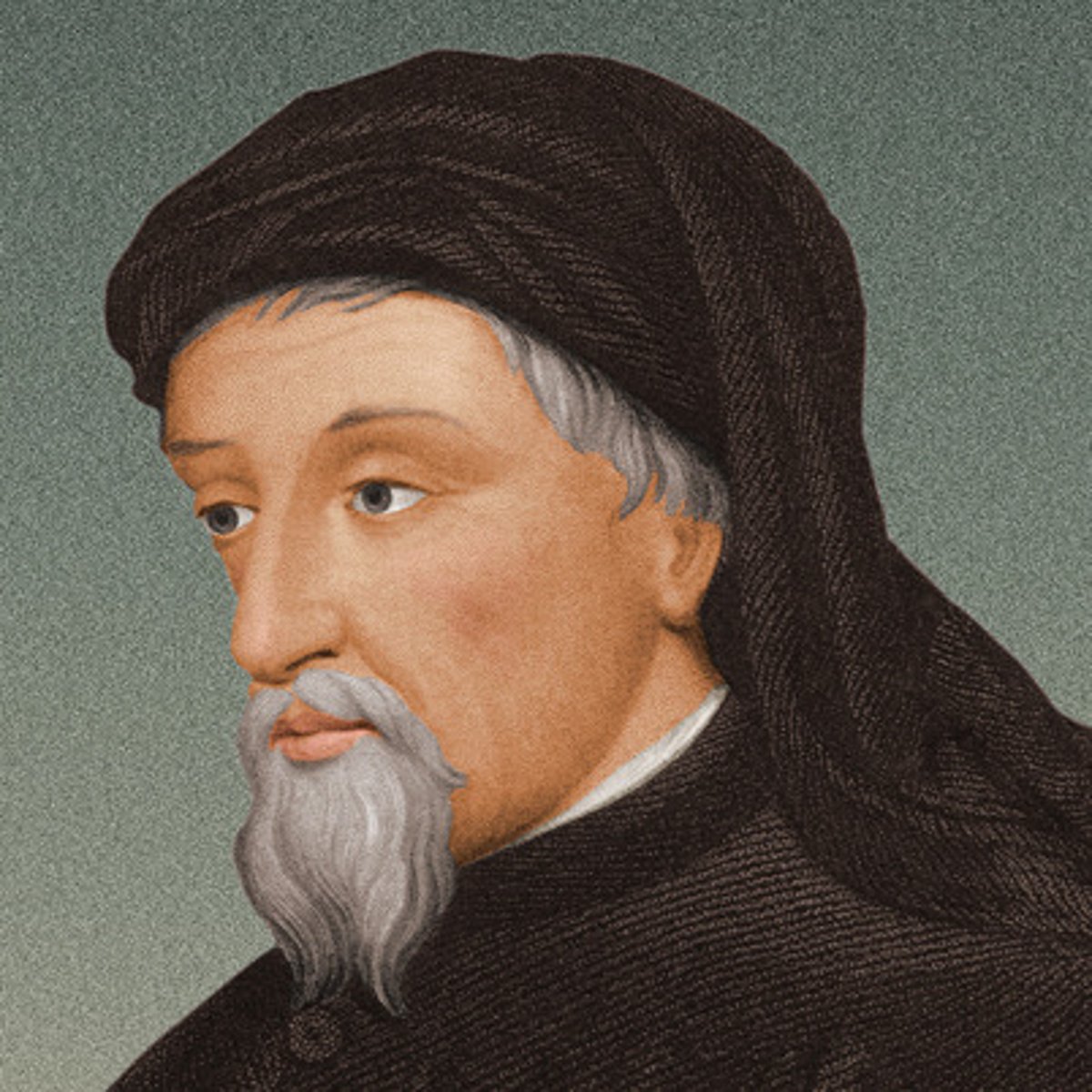
Geoffery Chaucer
The author of the Canterbury Tales, a satirical novel written in Middle English (a vernacular).

Vernacular
Everyday language of people in a certain place.
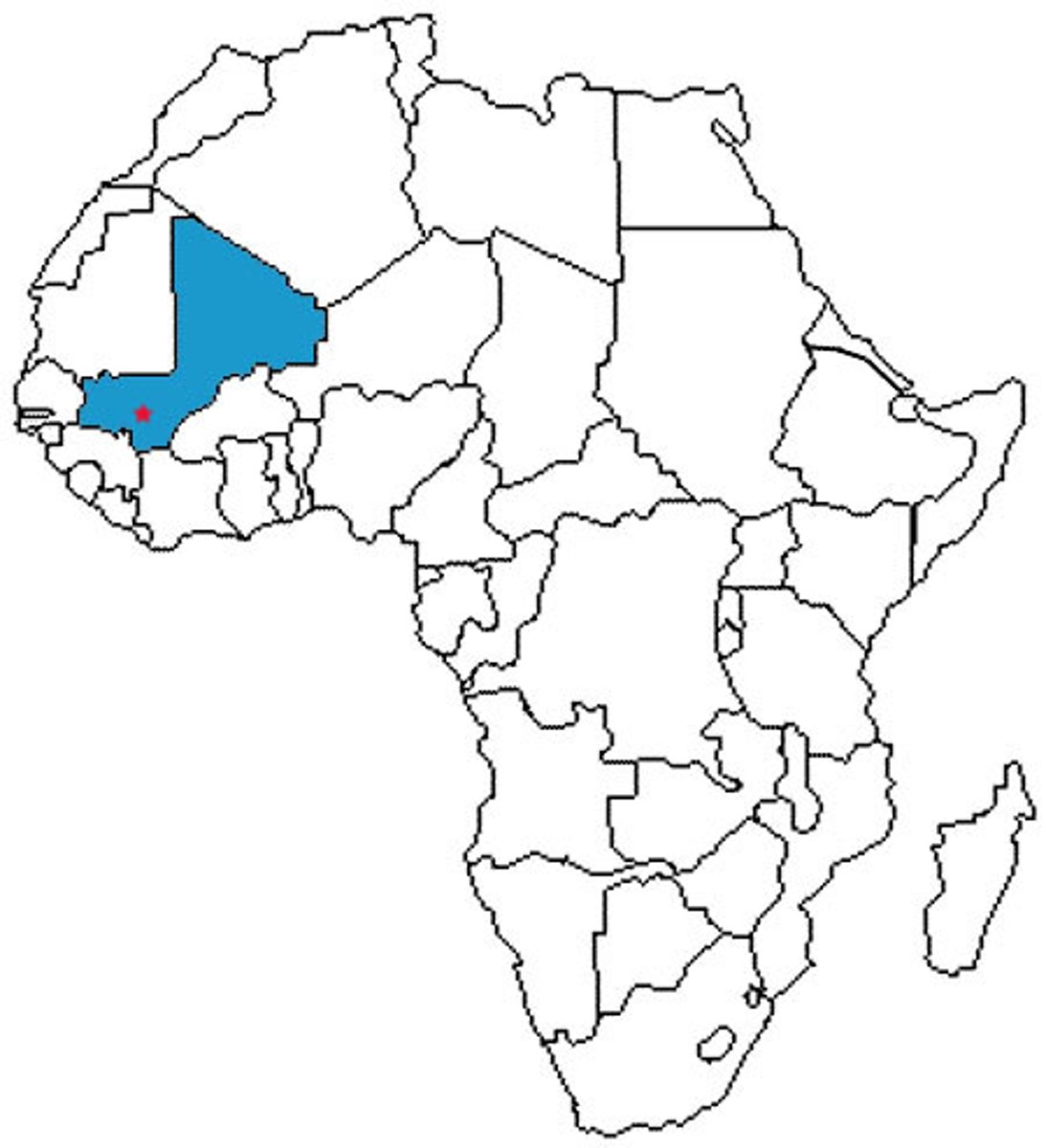
Mali
The kingdom in West Africa that followed the Kingdom of Ghana; its wealth is also based on trans-Saharan trade; this kingdom encouraged the spread of Islam.
Sub Saharan Africa
Portion of the African continent lying south of the Sahara.
Versed
(adj.) Highly experienced, practiced, or skilled; very knowledgeable; learned: He is a well-versed scholar on the subject of biblical literature.

Shariah
Islamic code of law that outlines behavioral requirements for daily life

Travelogue
Written or spoken description of travel

Labryinth
A complicated network of winding passages; a maze

Bantu
The people who spread throughout Africa spreading agriculture, language, and iron.

Sedentary
Requiring a lot of sitting
Districts
The geographical areas represented by members of a legislature.
Prominence
Importance

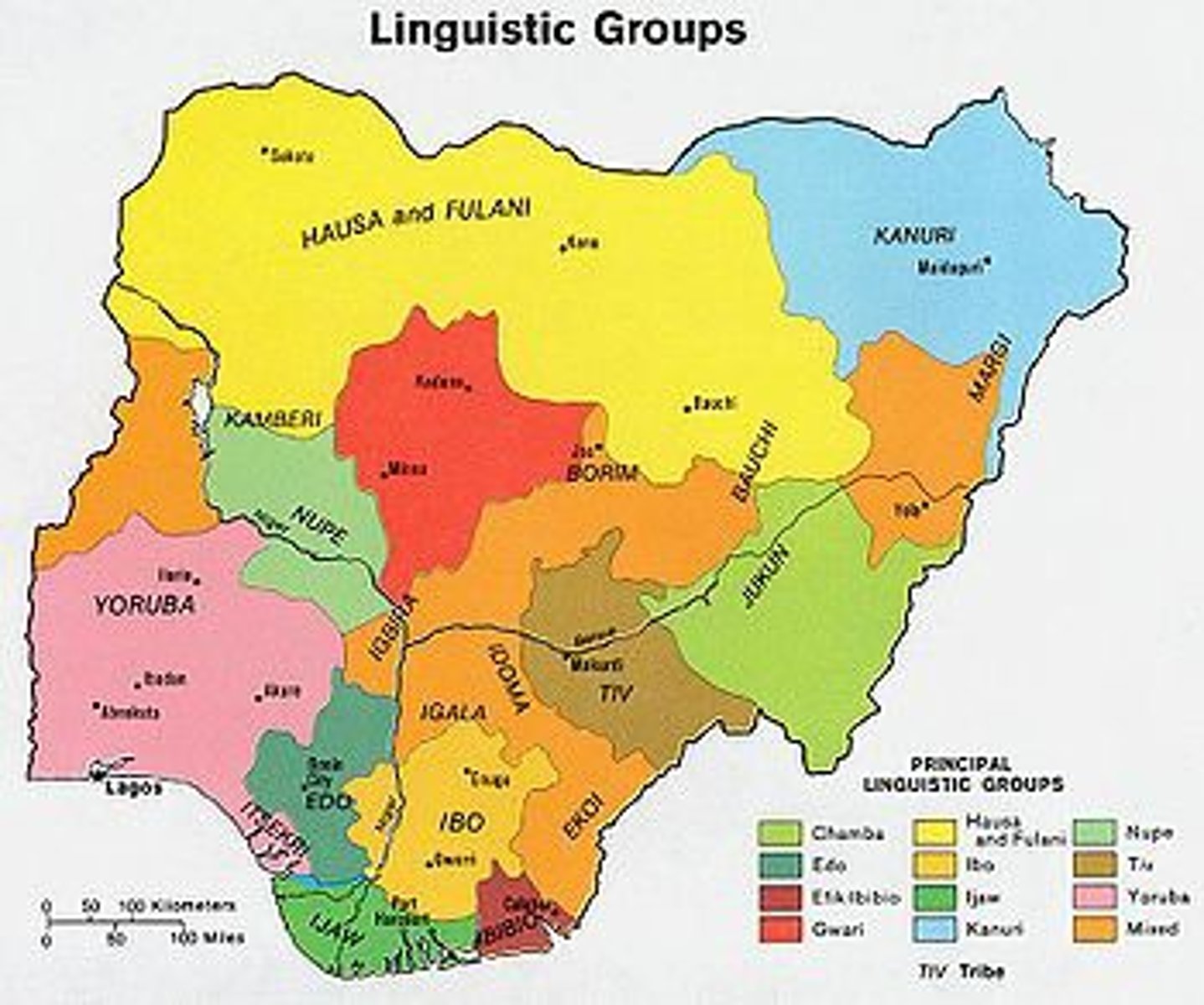
Hausa
Peoples of northern Nigeria; formed states following the demise of Songhay Empire that combined Muslim and pagan traditions

Missionaries
A person sent on a religious mission, especially one sent to promote Christianity in a foreign country.

Decentralized Politics
An organized political structure that distributes some or all of the governmental power to different points throughout a state. The purpose of a decentralized political system is to make citizens more active in the decision-making process in their government, therefore allowing individual people to exercise more power over their own lives.
Animism
Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life.

Dwellings
The places in which people live

Grazing
Eating the whole plant (above ground parts), the eating of plants by livestock which are out to pasture

Ports
A town or city with a harbor where ships load or unload, especially one where customs officers are stationed.
Places on the outside of the computer that connect to the motherboard and allows hardware to work

Mortar
1. a mixture of sand, water, lime, and cement used in building for holding bricks and stones together
2. a heavy gun that fires bombs and shells high into the air; the bombs that are fired by this gun

Bustling
Busy, full of energetic and noisy activity

Orthodox
Adhering to the traditional and established, especially in religion, in agreement with established or generally accepted beliefs or ways of doing things

Veneration
Great respect; reverence, and regard

Clan
group of families related by blood, marriage, or a common ancestor

Tanner
A person who treats and turns animal skins into leather

Blacksmiths
A person who can shoe horses create and forge tools, farm implements, wagon parts, and other iron products in fire and through a refining process.

Centuries
100 years

Griots/Griottes
Oral Storytellers and keepers of history in Africa. They possessed vast knowledge of family history as well as the deeds of great leaders. They were both feared and respected. Adept at music, they also sang their stories too, passing history from one generation to another

Kinship
A social bond based on common ancestry, marriage, or adoption
Great Zimbabwe
A powerful state in the African interior that apparently emerged from the growing trade in gold to the East African coast; flourished between 1250 and 1350 C.E.
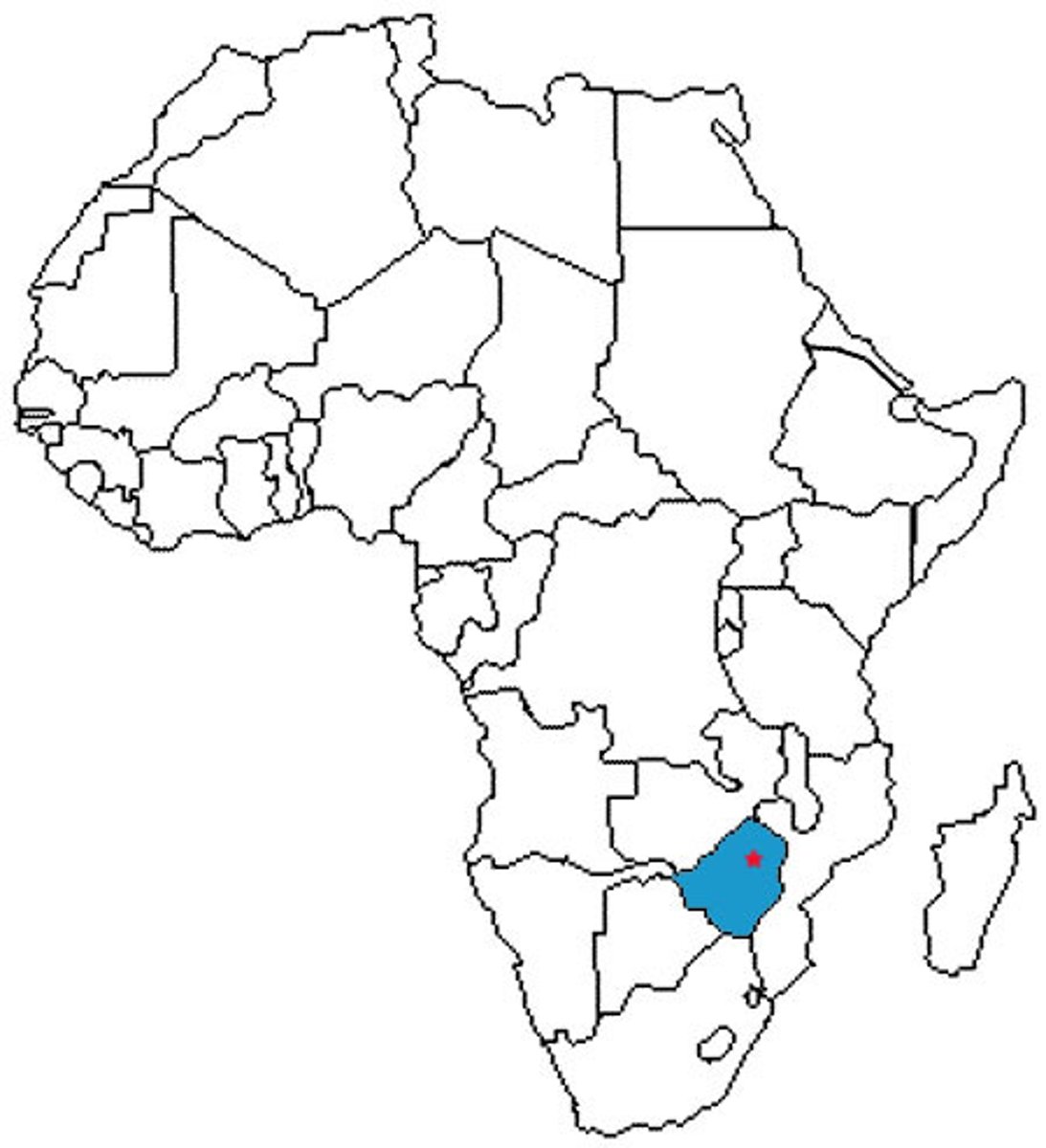
Ethiopia
East African highland nation lying east of the Nile River. A Christian kingdom that developed in the highlands of eastern Africa under the dynasty of King Lalibela; retained Christianity in the face of Muslim expansion elsewhere in Africa
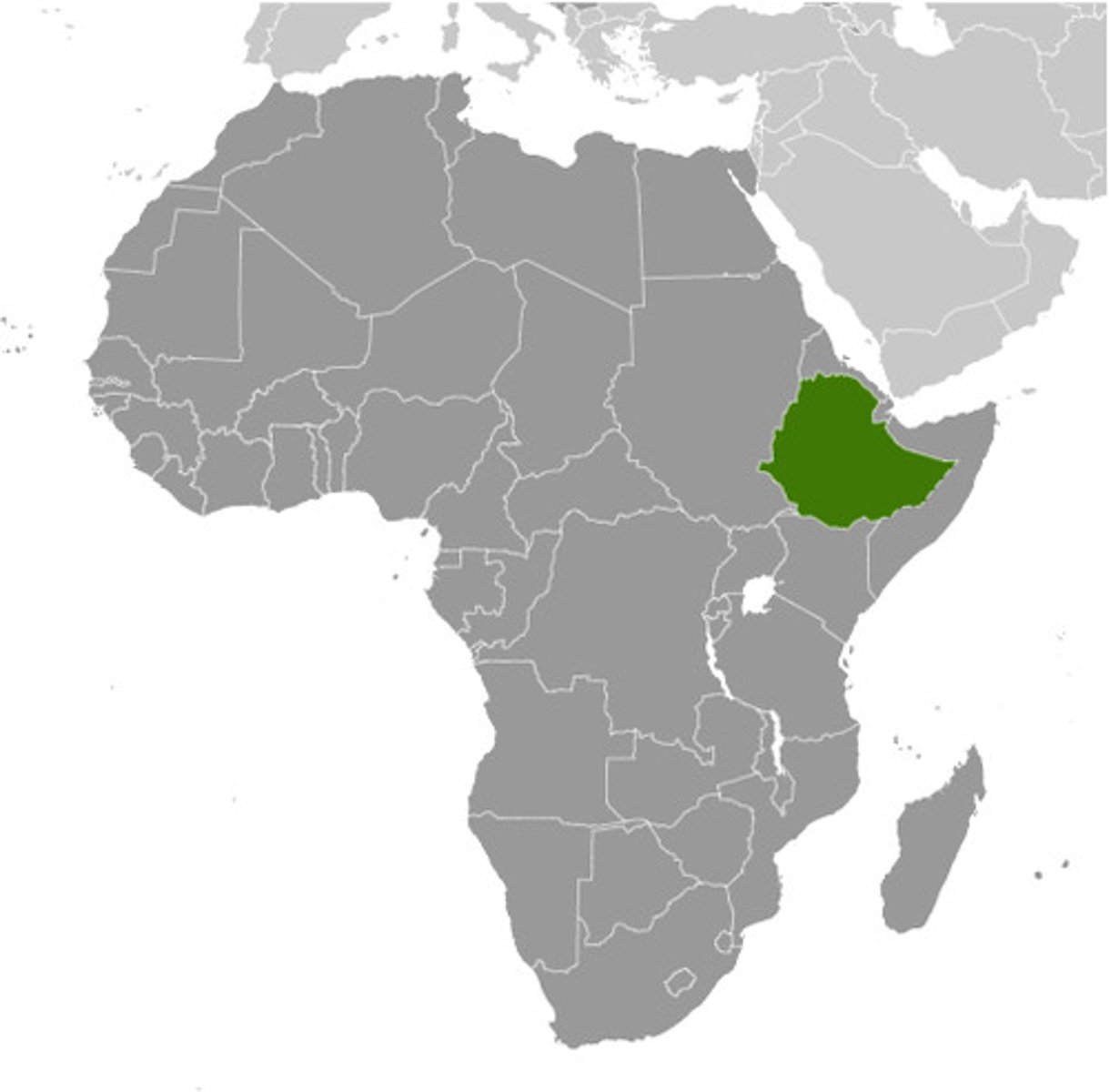
Hausa Kingdoms
1 kingdom divided into 7 states that were connected through kinship, blood, or ethnic ties; had no main central authority but rather ruled each state separate from one another; mainly benefited economically from the trans-Saharan trade network