2.5 Membrane Transport, 2.6 Facilitated Diffusion
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Concentration gradient
when the concentration of one side of the membrane is greater than the other side
the selective permeability of the cell membranes regulates what enters and exits due to the hydrophobic interior(tails) preventing polar/charged molecules from passing through
this creates and maintains concentration gradient of solutes across the membrane
Passive transport
transport of a molecule that does not require energy from the cell because a solute is moving with its concentration or electrochemical gradient
no energy required
high concentration → low concentration
involved in the import of materials and export of waste
examples are diffusion,osmosis, and facilitated diffusion
Diffusion
spontaneous process resulting from the constant motion of molecules
substances move from a high to low concentration
move DOWN the concentration gradient
molecules diffuse directly across the membrane
different rates of diffusion for different molecules
even with diffusion, membrane is still selectively permeable
affected by SA, being non polar, being small
Osmosis
the diffusion of water down its concentration gradient across a selectively permeable membrane
can also be thought of as the diffusion of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration (hypotonic→hypertonic)
can use aquaporins in facilitated diffusion, which are specialized channel proteins for water
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion of molecules through the membrane via channel or carrier proteins
does not require energy because molecules are still moving down their concentration gradient
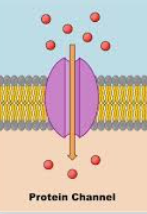
Channel proteins
form an open pore/channel in the membrane
move charged ions (like Na+ and K+)
most are not permanently open
“gates” can open/close in response to stimuli (ex signaling molecules, changes in electric potential across membrane, too much sugar, etc.)
ion channels are highly selective
direction of flow is determined by the electrochemical gradient(concentration and charge)
movement of ions can polarize the membrane(affect the charge across the membrane) meaning one side is more positive/negative than the other side
aquaporins are specialized channel proteins for water
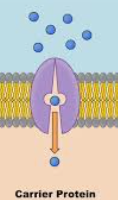
Carrier proteins
alternate between 2 conformations
carry large polar molecules(like glucose/sugars, amino acids, nucleosides)