Lecture 12: Brain Development
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What happens to the brain by 9th month of development?
The cortex is wrinkled, recognizable as human and structures under the cortex are in working order
What is the process where the brain gets rid of extra or unused connections?
Synaptic pruning
What is neuronal maturation after birth?
Neurons begin to extend their axons and connect to other neurons
What are the principals on brain development?
Specialization is evident early in development
Specialization takes on two forms
Different brain systems specialize at different rates
Successful specialization requires stimulation from the environment
The immature brain’s lack of specialization has plasticity (a benefit)
What are the memory regions that continue to develop throughout childhood?
The medial temporal lobe that contains the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex
At what age is there a slight decrease in hippocampus volume seen?
Middle age
What happens when the hippocampus is developing during adolescences? What does it indicate?
Complex memories are encoded indicating the development of the hippocampus and connection with the prefrontal cortex
Which brain lobes are associated with language?
Frontal and temporal
What are the two specific areas associated with language? Where are they?
Broca’s area → inferior frontal gyrus
Wernicke’s area → superior temporal gyrus
In childhood, what is there a rapid increase of in language related areas?
Synaptic growth
In adolescence, what is there an increase of that supports complex language processing?
Connectivity between Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area
A decrease of what tissue in the brain in older age may impact language processing speed?
Gray matter
When is the peak development of the prefrontal cortex?
Young adulthood
What decreases in older adulthood in the prefrontal cortex?
Connectivity and volume
What develops first: limbic system or prefrontal region?
Limbic system
What is the limbic system responsible for?
Seeks pleasure, motivation, rewards and risky behaviour
What is the prefrontal region responsible for in terms of the limbic system?
Executive functions and behavioural self-control
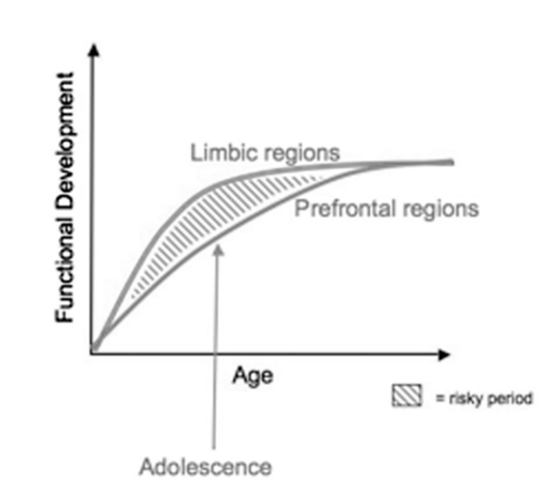
Use this graph to explain how it relates to behaviour
The limbic system, which is the pleasure-seeking and reward center, is fully active. But the prefrontal regions, which is the self-control, is not fully developed. Therefore, risky (rewarding) behaviours will occur even if there are consequences because of the limited self-control
Connections between which regions occur in adolescences that often result in heightened emotions?
Amygdala and prefrontal cortex
The cortical maturation continues until at least what age?
30 years old
Which cortical area matures first?
Primary cortical regions
Areas responsible for spatial and language skills mature when?
Puberty
Which cortical area matures last?
Tertiary cortical areas
Cognitive developmental has several types of intellectual abilities. What is the term to describe that?
Multidimensional
Intelligence can improve or decline during adulthood. What is the term to describe that?
Multidirectional
What is fluid intelligence?
Involves flexible, adaptive thinking, ability to reason and solve novel problems
What is crystallized intelligence?
Involves the knowledge, facts and skills we know through experience
Which type of intelligences declines throughout adulthood?
Fluid intelligence
Which type of intelligences improves over time?
Crystallized intelligence
What is important for recognizing faces, voices and movement in infancy (development of memory)?
Sensory and motor memory
How do infants communicate in infancy?
Through gestures, sounds and expressions
In the cross-sectional data study, what are the cognitive declines and when do they start?
Declines are seen in all domains except for verbal and numeric ability. Starts before age of 55
In the longitudinal data study, what are the cognitive declines and when do they start?
Declines are only seen in processing speed before age of 55 and all other domains after 55
Cross-sectional results of cognitive performance may be influenced by what?
Cohort effects
What are cumulative abilities that built over time?
Crystallized abilities
What are abilities that require flexibility of cognitive processing at time of test?
Fluid abilities
What are examples of fluid abilities?
Processing speed, attention, task-switching
What are examples of crystallized abilities?
General knowledge, vocabulary
In older adults, which type of attention is preserved?
Sustained attention
In older adults, which type of attention declines?
Divided attention and selective attention
Which types of memories are most preserved?
Short term memory (and most of long term semantic memory)
Which types of memories declines the most?
Long term episodic memory (most decline) and working memory
What remains stable for language development?
Vocabulary and semantic memory
What declines for language development?
Visual confrontation naming and verbal fluency
Which type of abilities (intelligence) remains stable over time?
Crystallized abilities
Which type of abilities (intelligence) declines with age?
Fluid abilities
When does the total cerebrum volume peak at?
Just before the onset of puberty
When does gray matter volume peak at?
Around 6 years old
When does subcortical gray matter volume peak at?
Mid-puberty
When does white matter volume peak at?
Young adulthood
When was the rate of growth of GMV, WMV and sGMV at its max?
Infancy and early childhood