Ch. 18: Income Taxes
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards focuses on key terms and concepts related to income taxes, deferred tax assets and liabilities, and the accounting standards governing them.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Deferred Tax Liability (DTL)
Asset GAAP Basis > Asset Tax Basis
Transactions that generate deferred tax liabilities → FUTURE TAX OBLIGATIONS
Asset GAAP basis - Asset tax basis = taxable temporary difference (after one year)
Increases future taxable income (when difference is reversed in future years)
Taxable income is lower now than financial accounting income BUT taxable income will be greater later (higher future tax)
DTL= taxable temporary difference X tax rate → comes into effect in year of reversal
Asset GAAP Basis > Asset Tax Basis
DTL
What does it mean by taxable temporary difference “comes into effect in year of reversal”?
represents additional tax you’ll need to pay when DTL is reversed
Deferred Tax Asset (DTA)
Liability GAAP Basis > Liability Tax Basis or Asset GAAP Basis < Asset Tax Basis
Transactions that generate deferred tax assets.
Liability GAAP basis - Liability tax basis = deductible temporary difference
Decreases future taxable income (when difference is reversed in future years)
Taxable income is higher NOW (than financial accounting income) but taxable income will be lower later
Lower future taxable income = Lower future tax
DTA = deductible temporary difference X tax rate → comes into effect in year of reversal
Liability GAAP Basis > Liability Tax Basis
DTA: liab. is when you have recorded a larger liability in GAAP that is recognized for tax purposes
Example→ warranty liability of $10k in GAAP books but $0 for tax until claims are paid; creates a future deductible amount because you’ll get a tax deduction later
Asset GAAP Basis < Asset Tax Basis
DTA: asset is when your tax basis for an asset is higher than what’s recorded in GAAP
Example→ accounts receivable with $10k GAAP basis but $12k tax basis due to a larger allowance for bad debts in GAAP; creates a future deductible amount because the higher tax basis will provide larger deductions when utilized
What does it mean by deductible temporary difference “comes into effect in year of reversal”?
the benefit of the DTA will be realized when the temporary difference reverses in the future
Reversal of DTL → revenue cases
when you collect cash from installment sales or realize gains on investments that were already recorded in GAAP
Reversal of DTL → expense cases
when your accelerated tax depreciation becomes less than GAAP depreciation in later years
Reversal of DTA → revenue cases
when you collect advance payments that were taxed upfront but recognized as revenue in GAAP over time
Reversal of DTA → expense cases
when you actually pay for expenses that were already recorded in GAAP (like warranty costs or restructuring costs)
When is the accounting basis under GAAP higher than the tax basis?
Installment sale receivable
Investment account under FV-NI: gain
Equity method investment
Prepaid expense
Fixed assets
Intangible
These are all examples of temporary differences that create deferred tax liabilities because the GAAP income is more than the taxable income (DTL)
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of installment sale receivable (asset) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
sale recorded on an accrual basis for GAAP, but are taxable when cash is collected
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of investment account under FV-NI (asset) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
unrealized holding GAIN or investment (FV-NI) recognized for GAAP, but gain is taxable if realized upon sale
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of equity method investment account (asset) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
revenue recognized for proportionate share of investee’s net income for GAAP, but for tax, revenue is taxable when dividends are received.
proportionate share of income > dividends received
Expenses are deducted on tax return BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of prepaid expense (asset) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
prepaid expenses are expensed over period of usage for GAAP, but are taxable when paid
Expenses are deducted on tax return BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of fixed assets (assets) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
fixed assets are generally depreciated under the straight-line method for GAAP, but are depreciated under accelerated methods for tax
Expenses are deducted on tax return BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of purchased intangible (asset) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
amortization method for GAAP purposes may differ from amortization method for tax purposes. Here we assume a more accelerated method for tax
JE to record income tax expense: DTL
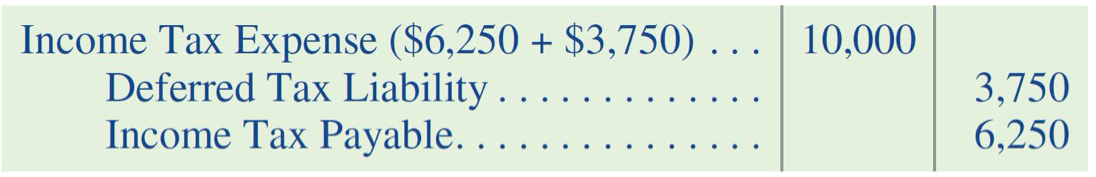
JE to reverse income tax expense: DTL

When is the accounting basis under GAAP lower than the tax basis?
Deferred revenue (liab)
Deferred rent revenue (liab)
Deferred contract revenue (liab)
Warranty liab (liab)
Investment account under FV-NI (asset): loss
Account receivable
These are all examples of temporary differences that create deferred tax assets (DTA)
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of deferred revenue (liab) is…
… higher for GAAP than for tax
customer advances are deferred for GAAP, but are taxable when cash is collected
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of deferred rent revenue (liab) is…
… higher for GAAP than for tax
advance rental receipts are deferred for GAAP, but are taxable when cash is collected
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes BEFORE GAAP Income: Basis of deferred contract revenue account (liab) is…
…higher for GAAP than for tax
prepaid contracts received are deferred for GAAP, but are taxable when cash is collected
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of warranty liability (liab) is…
… higher for GAAP than for tax
warrant expense is accrued for GAAP, but are deductible when cash is paid
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of investment account under FV-NI (asset) is…
…lower for GAAP than for tax
unrealized holding LOSS on investment (FV-NI) recognized for GAAP, but is only deductible if realized upon sale
Revenue is recognized for tax purposes AFTER GAAP Income: Basis of accounts receivable is…
…lower for GAAP than for tax
bad debt expense recognized for GAAP, but only accounts written off are deductible for tax
JE to record income tax expense: DTA
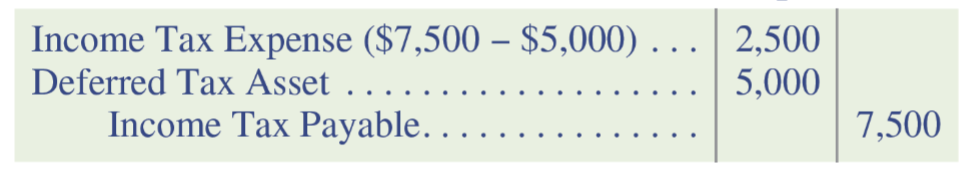
JE to record reverse income tax expense: DTA

Tax Basis
The value assigned to an asset or liability for tax purposes, which may differ from its GAAP basis.
Permanent Differences
Differences that do not reverse and do not result in deferred tax assets or liabilities
If a company only has permanent differences, income tax expense for financial reporting equals income tax on the tax return for the pd
Examples of permanent differences: GAAP revenue
interest revenue on tax-exempt munis
proceeds from life insurance policy
Examples of permanent differences: GAAP expenses
fines and expenses related to legal violations
premiums paid on life insurance policy
To realize a deferred tax asset, a company must have what?
a future taxable income against which the future deductible amounts can be applied
Valuation Allowance
A contra asset account that reduces the carrying amount of a deferred tax asset.
It is recorded for the portion of the def4erred tax asset that more likely than not (>50%) will not be realized
YOU MUST consider all available evidence, both negative and positive, when determining whether the DTA will be realized
Positive evidence: strong earnings history, existing revenue contracts
Negative evidence: historical operating losses, expected losses
DTA positive evidence for valuation
strong earnings history, existing revenue contracts
DTA negative evidence for valuation
historical operating losses, expected losses
JE for establishing DTA valuation allowance

Income Tax Payable
The amount of income tax a company owes to tax authorities.
Rate Reconciliation
companies disclose a reconciliation between the US statutory rate and the effective tax rate
this means that rate reconciliation is a breakdown that explains why a company’s actual tax rate differs from the standard tax rate
Effective Tax Rate
( Income tax expense / Pretax GAAP income )
permanent differences impact the effective tax rate
ex: a nontaxable revenue recognized under GAAP does not impact income tax expense, but it does adjust GAAP income
** the actual percentage of income a company pays after all adjustments
Statutory rate:
legally imposed rate (federal tax rate)
Other items affecting rate reconciliation
permanent differences
state income tax
increases effective tax rate beyond the US federal state rate (statutory rate)
tax credits
reduces taxes owed through a credit
change in valuation allowance
adjusts income tax expense but does not impact taxes owed currently
Changes in Tax Rate
adjustments to the statutory tax rate that impact tax calculations
ex: tc&ja reduced the statutory tax rate form 35% to 21%
recognize adjustments in NI in the pd that the new tax rate is enacted into law
apply new tax rates to DTA and DTL in the year(s) of reversal
What if a tax rate decreases?
DTA:
balance decreases
bc future tax benefits will be at a lower rate
income tax expense decreases
bc you record the adjustment as a tax benefit
DTL:
balance decreases
bc future tax pmts will be at a lower rate
income tax expense decreases
bc the reduction in future tax obligation is recorded as a tax benefit
What are the uncertainties in income tax decisions?
company can take position that is subject to a different interpretation by taxing authorities
differences are resolved through negotiation or through negotiation or through litigation (less often)
company may be liable for additional taxes if the position is not accepted upon a dispute with taxing authorities
so a company should accrue a liability now for the tax that would be due if the taxing authorities disagree with the position taken and require more tax payments
this accrual is determined through a two-step process
The two-step process for determining the value of the accrual is:
recognition threshold
a. if it does not meet threshold→ record no tax benefit
b. if it meets threshold…
measurement of tax benefit
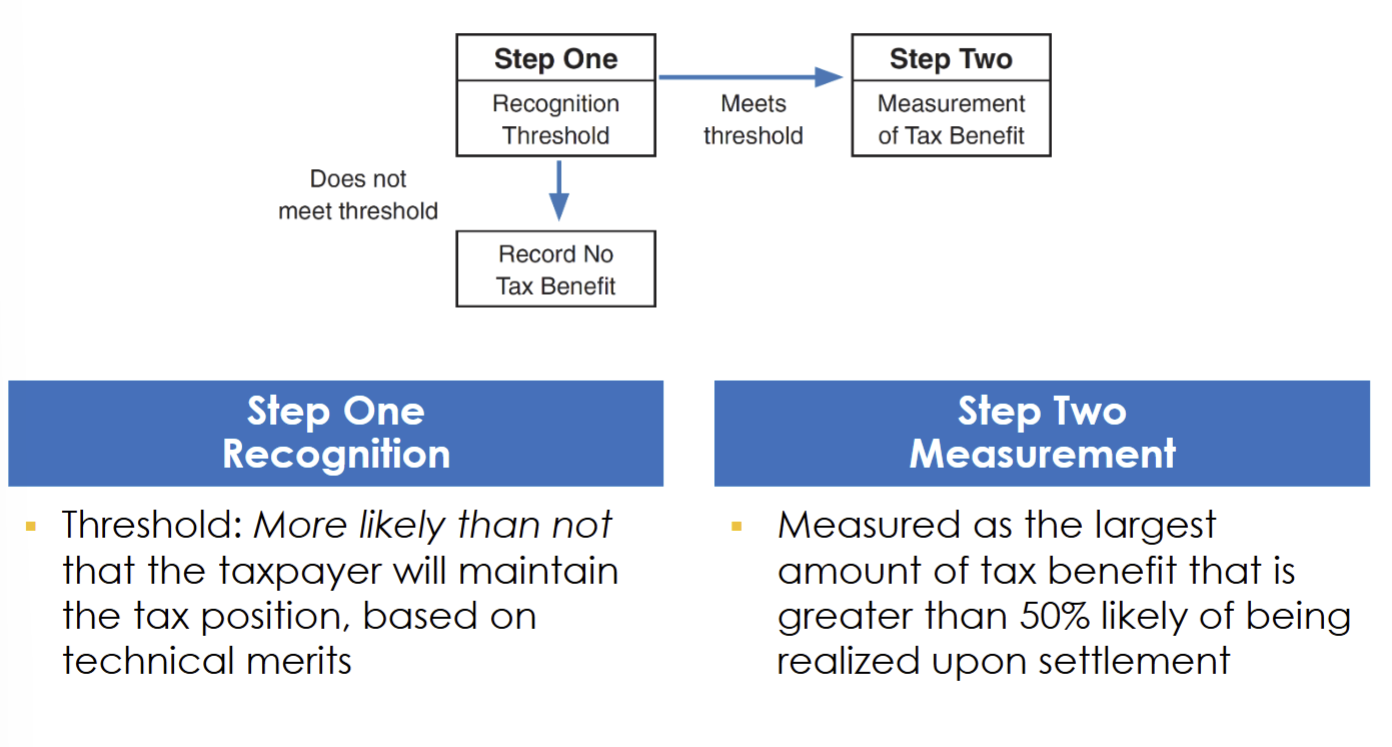
Step One: Recognition
threshold: more likely than not that the taxpayer will maintain the tax position based on technical merits
Step Two: Measurement
measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon settlement
Net Operating Loss (NOL)
negative taxable income for the pd
company has no tax obligation for the pd
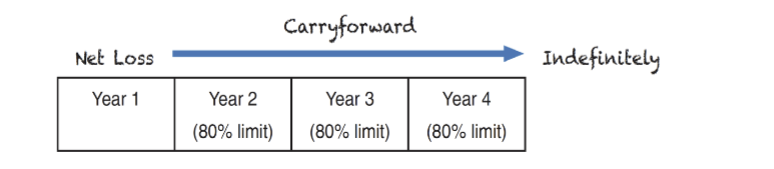
Net Operating Loss Carryforward (Generating DTA)
generally, current tax law allows NOLs to be carried forward indefinitely to future years to offset future taxable income (and thus reduce taxes in future years)
with few exceptions, NOL carryforwards can only offset a max of 80% of taxable income in each of the future years
results in the recording of a deferred tax asset
assessment for a valuation allowance is required
Balance Sheet Recognition: Current vs Noncurrent Assets & Liabilities
Current Liab: Income tax payable
Noncurrent: (merged into either noncurrent assets or noncurrent liab)
deferred tax assets
valuation allowances
deferred tax liabilities
Disclosures for Income Tax
total of all deferred tax liabilities and assets
total adjustments to and net change in the valuation allowance
approximate tax effect of each major source of temporary difference and carryforward that gives rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and liabilities
reconciliation between the effective tax rate and the US statutory rate
Disclosures for Income Tax Pt. II
current and deferred portion of income tax expense or benefit
tax credits
government grants to the extent they are used as reduction of income tax expense
adjustments of deferred tax assets or liab as a result of enacted tax law or rate changes or changes in tax status
Accrual Basis
An accounting method where revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not when cash is exchanged.
IRS Regulations
Rules and guidelines issued by the Internal Revenue Service pertaining to taxation.
Tax Credits
Amounts that reduce the tax liability dollar for dollar.