Business complete flashcards
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
360-degree feedback
When an employee receives feedback from all of the people around them
360-degree marketing
A marketing campaign that reaches customers at all possible points of contact.
above the line promotion
Promotion aimed at mass audiences, generally not targeted.
absorption costing
Used to allocate indirect costs. Divides indirect costs among products/ departments/ regions based on a predetermined criteria such as output/ sales revenue/ nr of employees etc.
acid test (quick) ratio
A liquidity ratio that measures the value of current assets without stock included, shows business’s ability to pay its short-term debts (cover current liabilities)
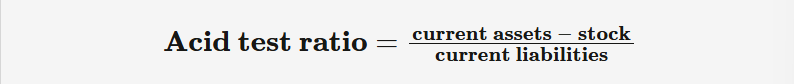
McClelland’s acquired needs theory
Motivation theory, humans have 3 dominant needs that drive motivation:
achievement
power
affiliation
acquisition
external growth where one company purchases another one, usually friendly
adverse variance
when actual income and expenditure is worse that expected
agent
person who acts on behalf of another person or group
antitrust laws
Laws that limit the market power of individual companies, encourage competition and lower prices
appraisal
assessment of an employee’s performance
arbitration
method for conflict resolution, management and employees present arguments to a third party who resolves the conflict
artificial neural networks
The connections of computing systems and nodes that are like the neurons of a human brain.
autocratic leadership
leadership style, leader controls all decision making, does not delegate to lower levels
average rate of return (ARR)
investment appraisal technique, expresses the annual predicted returns as a percentage of the initial capital cost
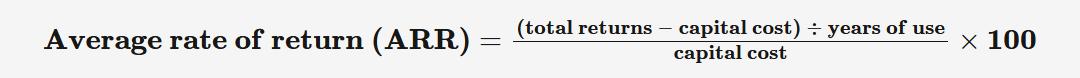
B2C
Direct business to consumer selling
Balance sheet
A statement that records a business's assets, liabilities and equity
Batch production
a production method that involves producing similar items in groups
below the line promotion (BTL)
Promotion aimed at specific segments and do not rely on mass market techniques.
benchmarking
The process of a business comparing itself with industry leaders on certain criteria, to learn from other’s techniques.
biomimicry
The process of mimicking nature’s forms, processes and systems to solve human problems.
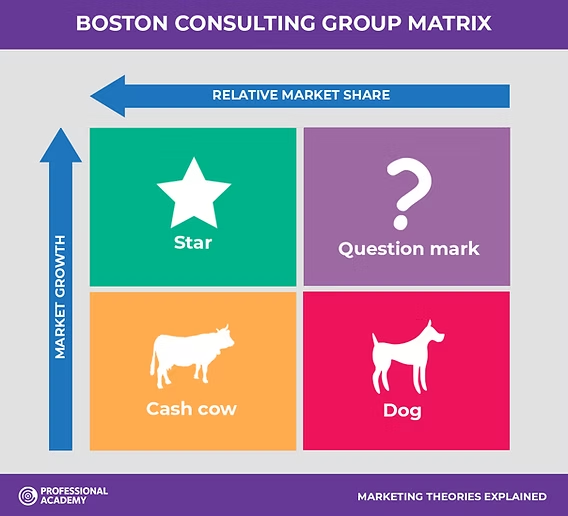
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix
A matrix that classifies the products of a business into high and low market share and market growth categories.
brand
A name, symbol or design that is used to identify a product or company.
brand development
Building brand awareness by cultivating the business's values and consumer perceptions of the product.
brand value
How much the brand itself is an asset (form of goodwill)
break-even
The output when total revenue equals total cost.
broker
An intermediary in the process of selling and buying a product.
business cycle
A cycle of economic growth and recession.
C2C
consumers selling to consumers
capacity utilisation
The extent to which a business is using its productive capacity, expressed as a percent.
capital employed
The value of all sources of internal and external finance for a business, calculated from the sum of non‐current liabilities and equity.

capital expenditure
Spending on the non-current (fixed) assets of a business.
capital gains
The increase in the value of an asset.
capital intensive
Production process with more physical capital than human labour.
capital productivity
How efficiently a business uses its capital. Total output/ capital input
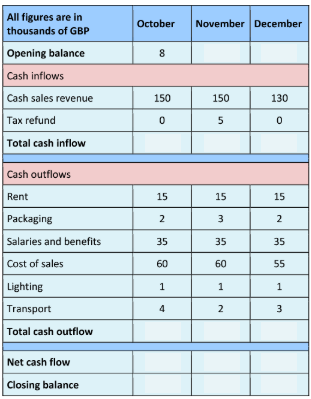
Cash flow forecast
predicts future cash flow
Causal model
represents real-world business dynamics
Centralisation
when only one person or a small group makes all the decisions
Circular business model
when output becomes the input, minimal waste
cloud computing
data storage, computer networking, allow information to be stored and accessed anywhere in the world
clustering
when similar businesses are located near each other
collective bargaining
when employees and management negotiate together
competitive pricing
when a company sets the same prices as its its competitors
conciliation
method for conflict resolution when the management and employees present their arguments to a third party who resolves the conflict
contingency planning
an action plan to follow in case a crisis occurs
continuous improvement (kaizen)
when employees are encouraged to always seek and implement improvements.
contribution per unit
price of the product - variable costs per unit
contribution costing
cost accounting method that considers the direct cost of the product/ department and their resulting contribution to covering the businesses overall indirect costs.
conversions
getting customers to respond to the “call to action” of a business
cooperative
a business that is owned and operated by its members who share all profits
copyright
legal protection that gives the creator the exclusive right to reproduce the work for a period of time
corporate social responsibility
business seeking ways to improve the society and environment
cost focus strategy
when a business is the low-cost option in a niche market
cost leadership strategy
when a business is the low-cost option in the whole industry
cost-plus (markup) pricing
a markup is added to the direct and indirect costs of the product
creditor days
the average number of days it takes a business to pay its debts.
(creditors / cost of sales) x 365
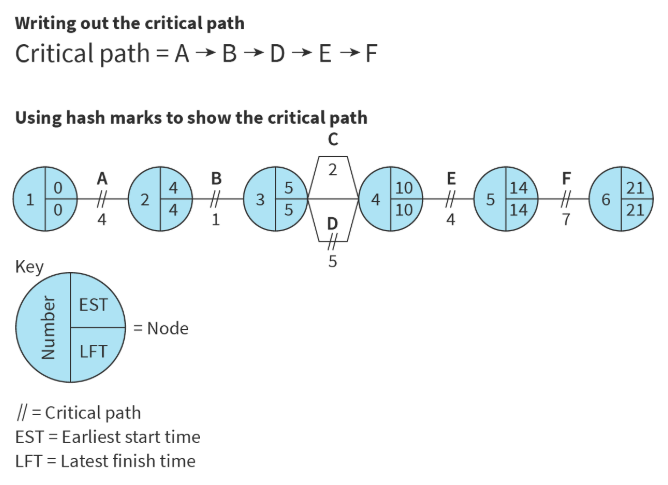
critical path analysis (CPA)
shows the minimum time period that a project needs to be completed
current assets
assets that the business plans to convert into cash in less than 1 year
current liabilities
payables that are due within one year
current ratio
measures the value of current assets relative to current liabilities.
current assets / current liabilities
cyclical variations
variations in data due to economic cycles
data centers
buildings that contain servers/ other computer stuff
data mining
process of searching for patterns and trends in data
debt finance
money that is borrowed
debtor
a person or business that has bought something from another business but has not paid for it yet
debtor days
measures the average number of days it takes a business to collect its debts.
(debtors / sales revenue) x 365
decentralisation
when the decision-making powers are passed down to lower levels
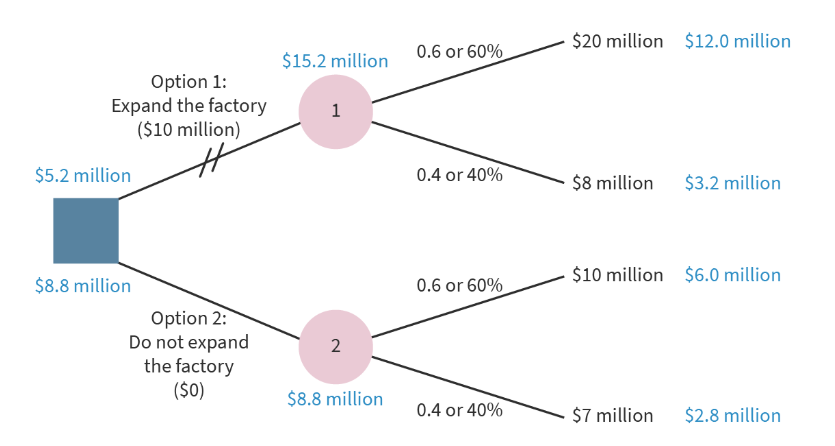
decision tree
decision making tool, each branch represents a choice, its cost, probability and result
deflation
a decrease in the general price level
democratic leadership
when the leader actively seeks employee participation in decision-making.
demographic segmentation
dividing consumers into target groups according to characteristics like age, gender, occupation
dependent variable
variable that is being measured
depreciation (2 definitions)
the loss of value of an asset over time
in a financial statement shows the cost of a long-term asset over its lifetime
differentiation
highlighting differences between a product and its rivals
digital Taylorism
uses digital technology to monitor employee performance
direct cost
can be precisely traced to a specific product/ department
direct distribution
when the producer deals directly with the customers
direct investment
when a company opens operations in another company
direct marketing
communicates directly with the target audience, measures their response
discount rate
rate of return that the business could earn on another comparable investment, reflects today’s value of future cash flow
dismissal
“getting fired” when a business releases an employee, usually because of bad performance
distribution channel
network used to move the product from the manufacturer to the end user
disruptive business
a business that optimises value for multiple stakeholders rather than maximising profits for shareholders
diversification
selling new products in new markets
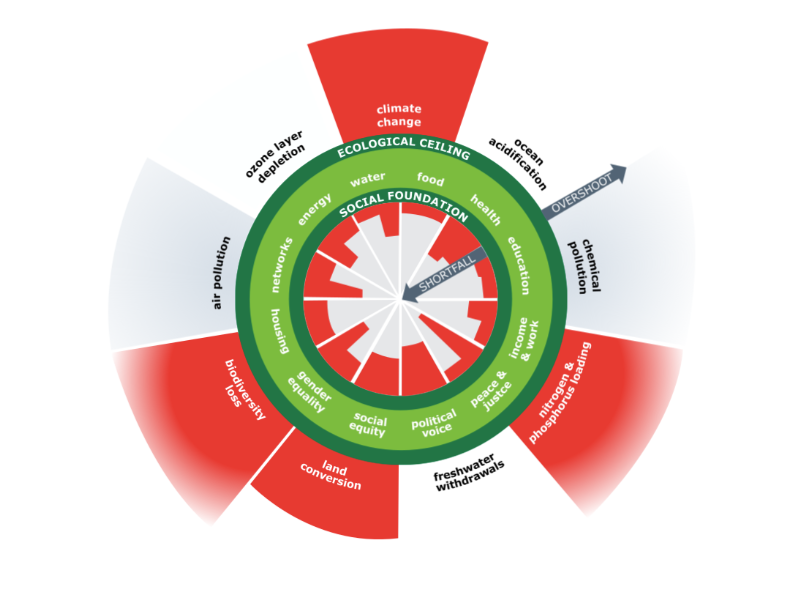
Doughnut economics model
outlines the social needs and ecological ceiling that economic activity needs to respect to find a “safe and just space for humanity”
dynamic pricing
changing the price of a good according to demand
efficiency ratio
how well a business transforms input into output
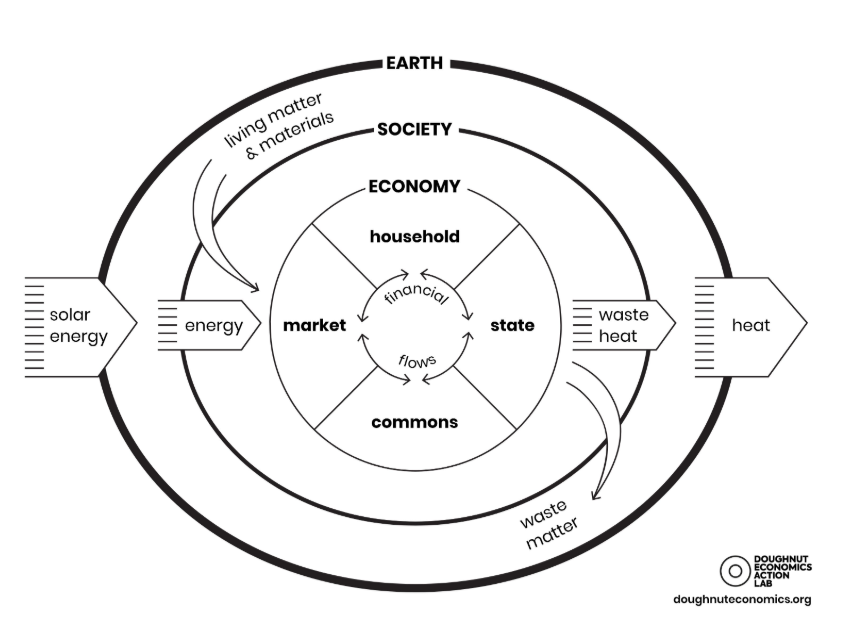
embedded economy model
shows the economy embedded in nature, inputs of energy and outputs of waste, distributions from markets, households, the state, and the commons.
employee participation
when employees are actively involved in decision-making
employee share ownership schemes
when employees are allowed to buy shares in the business at below market price
equity
the value of shares issued by a company
equity finance
funding through selling shares (ownership)
equity stake
ownership of a company as a shareholder
equity theory
motivation theory, claims employee satisfaction comes from fairness in the workplace
expectancy theory
motivation theory, employees are motivated if they think their performance will be recognized
extension strategy
extends the product’s “maturity” stage in its lifecycle
extrinsic motivation
when a person does something purely for the reward
favourable variance
when actual income and expenditure figures are better than expected
fixed asset
an item/ property that has value and the business plans on holding for longer than 1 year
fixed costs
costs that do not vary with output