Alkaloids
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
True about alkaloids except:
a. Bitter
b. They contain nitrogen usually in heterocyclic ring
c. Most of them are physiologically active even in small amounts
d. Almost all are poisonous
e. All alkaloids are basic
f. None
e. All alkaloids are basic
NOT ALL alkaloids are basic.
Non-basic alkaloids:
a. Colchicine
b. Piperine
c. Caffeine
d. a and b
e. All
d. a and b
Colchicine
Piperine
To convert an alkaloid salt into a free base, which of the following should be added?
a. NaCl
b. NaOH
c. Na2CO3
d. NaHCO3
c. Na2CO3 - Sodium carbonate
Alkaloids are mostly solids. The following are the liquid alkaloids except:
a. Coniine
b. Arecoline
c. Nicotine
d. Sparteine
e. None
e. None
Coniium maculatum
Poison hemlock
a. Coniine
b. Arecoline
c. Nicotine
d. Sparteine
a. Coniine
Scotch broom
Cystisus scoparius
a. Coniine
b. Arecoline
c. Nicotine
d. Sparteine
d. Sparteine
Soluble in ether and chloroform
a. Free alkaloids
b. Alkaloidal salts
a. Free alkaloids
Highly insoluble precipitates in heavy metals.
a. Free alkaloids
b. Alkaloidal salts
b. Alkaloidal salts
Alkaloidal salt + ______ = Free base
a. Alkali
b. Acid
a. Alkali
Free base + ___________ = Alkaloidal salt
a. Alkali
b. Acid
b. Acid
Polar form of alkaloids.
a. Free
b. Alkaloidal salts
b. Alkaloidal salts
Non polar form of alkaloids.
a. Free
b. Alkaloidal salts
a. Free
Derived from amino acids and have heterocyclic ring with nitrogen.
a. True alkaloids
b. Protoalkaloids
c. Pseudoalkaloids
a. True alkaloids
Derived from amino acids but do not have heterocyclic ring with nitrogen.
a. True alkaloids
b. Protoalkaloids
c. Pseudoalkaloids
b. Protoalkaloids
Not derived from amino acids but have heterocyclic ring with nitrogen.
a. True alkaloids
b. Protoalkaloids
c. Pseudoalkaloids
c. Pseudoalkaloids
Types of alkaloids.
Pyridine-piperidine
Tropane
Quinoline
Isoquinoline
Indole
Imidazole
Steroid
Terpenoid
Alkaloidal amine
Purine
a. True
b. False
a. True
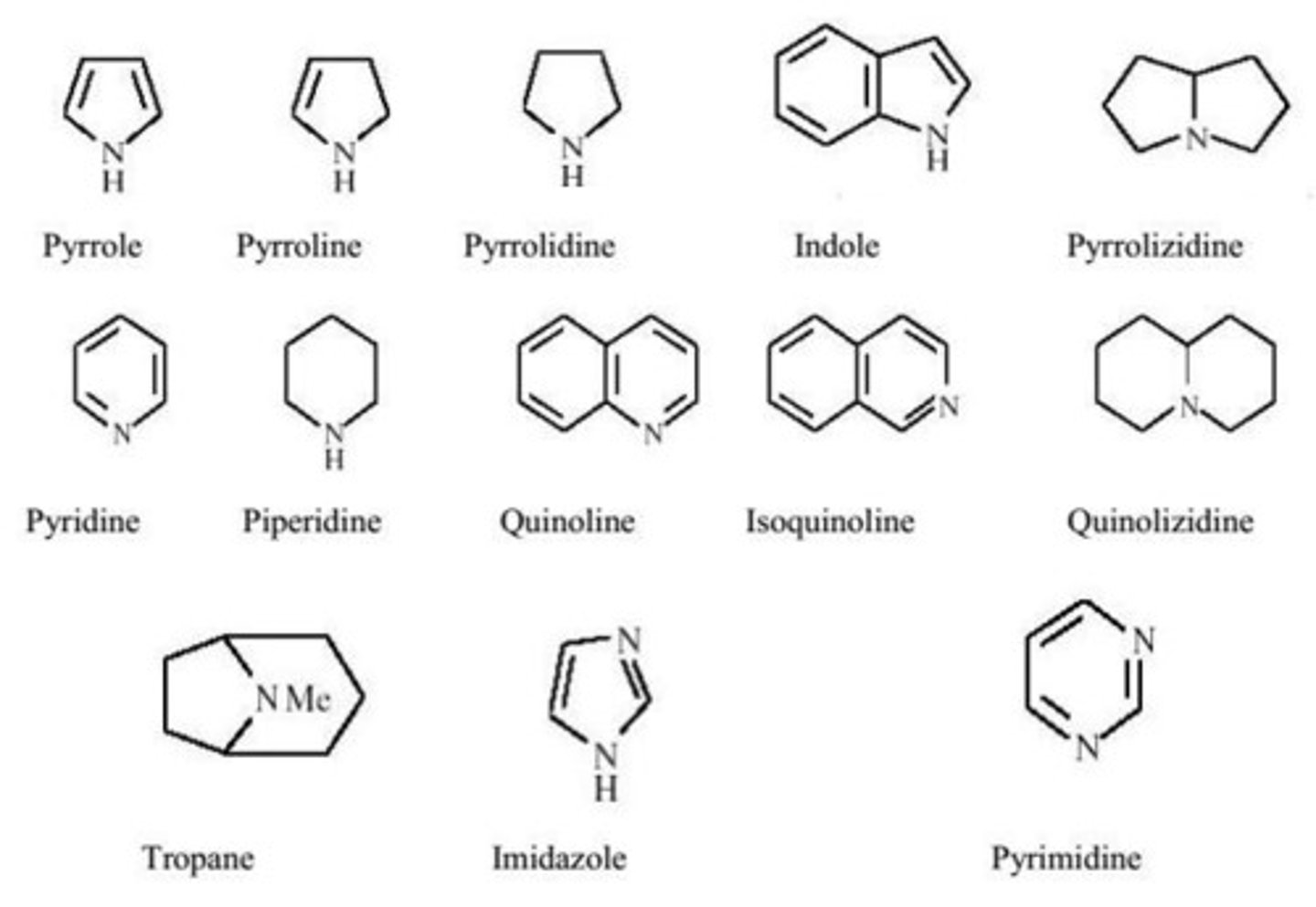
Alkaloidal precipitants can be all of the following except:
a. Reagents that form double salts
b. Reagents containing halogens
c. Organic acids
d. Oxygenated high molecular weight acids
e. None
e. None
Alkaloidal reagents that form double salts except:
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
f. None
e. Wagner's reagent - This is IODINE CONTAINING alkaloidal reagent.
Mercuric Potassium Iodide
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent -
Ma-MeKI
Potassium Bismuth Iodide
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
a. Dragendorff's reagent
KI and HgI
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
d. Valser's reagent
Halogen containing but do not form double salt.
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
Iodine in Potassium Iodide
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Gold chloride
d. Valser's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
Most sensitive alkaloidal reagent composed of Iodine in KI.
a. Dragendorff's reagent
b. Mayer's reagent
c. Bouchdart's reagent
d. Valser's reagent
e. Wagner's reagent
c. Bouchdart's reagent
K Cd Iodine
a. Marme's reagent
b. Bouchdart's reagent
c. Hager's reagent
d. Sonnenschein's reagent
e. Scheibler's reagent
a, Marme's reagent
Picric acid which is an organic acid alkaloidal reagent
a. Marme's reagent
b. Bouchdart's reagent
c. Hager's reagent
d. Sonnenschein's reagent
e. Scheibler's reagent
c. Hager's reagent
Organics acids that can be used as alkaloidal reagent.
a. Tannic acid
b. Picric acid
c. Tartaric acid
d. a and b
e. All
d. a and b
Tannic acid
Picric acid
Alkaloidal reagents that are oxygenated HMW acids.
a. Sonnenschein's reagent
b. Scheibler's reagent
c. Silicotungestic acid
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Phosphomolybdic acid
a. Marme's reagent
b. Bouchdart's reagent
c. Hager's reagent
d. Sonnenschein's reagent
e. Scheibler's reagent
d. Sonnenschein's reagent
Phosphotungstic acid
a. Marme's reagent
b. Bouchdart's reagent
c. Hager's reagent
d. Sonnenschein's reagent
e. Scheibler's reagent
e. Scheibler's reagent
Chemical tests for alkaloids.
Dragendorff's Test
Mayer's Test
Wagner's Test
Hager's Test
Tannic Acid Test
Ammonia Reineckate Test
a. True
b. False
a. True
Positive result: formation of orangish red color
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
a. Dragendorff's test
Positive result: formation of creamy-white precipitate
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
b. Mayer's test
Positive result: formation of reddish-brown precipitate
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
c. Wagner's test
Positive result: formation of crystalline yellow precipitate
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
d. Hager's test
Positive result: formation of buff colored precipitate
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
Positive result: formation of pink flocculent precipitate
a. Dragendorff's Test
b. Mayer's Test
c. Wagner's Test
d. Hager's Test
e. Tannic Acid Test
f. Ammonia Reineckate test
f. Ammonia Reineckate test
PYRIDINE-PIPERIDINE ALKALOIDS
I. Nicotine
II. Arecoline
III. Lobeline
a. I, II, III
b. I, II
c. I, III
d. III, IV
a. I, II, III
Leaves of Nicotiana tabacum
CNS stimulant, smoking deterrent
Gum (Nicoret); Patch (Nicoderm)
a. Nicotine
b. Arecoline
c. Lobeline
a. Nicotine
Used as temporary aid for the cessation of cigarette smoking and is available as transdermal patches.
a. Nicotine
b. Arecoline
c. Lobeline
a. Nicotine
PYRIDINE-PIPERIDINE ALKALOIDS except:
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
e. None
e. None
Areca/Areca Nut/Betel nut
Areca catechu
CNS stimulant
Anthelmintic
Tannin content causes esophageal cancer or oral cancer
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
a. Arecoline
Alkaloid present in betel nut which ca cause esophageal cancer.
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
a. Arecoline
Lobelia/Indian Tobacco
Lobelia inflata
CNS stimulant
Smoking deterrent
Respiratory stimulant, used in asthma preparation
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
b. Lobeline
Alkaloid smoking deterrent found in Indian tobacco.
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
b. Lobeline
Pepper
Piper nigrum
Treatment gonorrhea/chronic bronchitis
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
c. Piperine
Antispasmodic, sedative, anodyne alkaloid found in poison hemlock.
a. Arecoline
b. Lobeline
c. Piperine
d. Coniine
d. Coniine
TROPANE ALKALOIDS except:
a. Scopolamine
b. Cocaine
c. Atropine
d. Mandragorine
e. None
e. None
TROPANE ALKALOIDS sources:
Henbane
Belladona
Stramonium
Duboisa
Withania
Mandragora
a. True
b. False
a. True
Commercial source of atropine except:
a. Hyoscyamus niger
b. Hyoscyamus muticus
c. Duboisia myoporoides
d. Withania somnifera
e. None
e. None
Duboisia myoporoides and Withania somnifera are major commercial source.
Main commercial source of atropine.
a. Hyoscyamus niger
b. Hyoscyamus muticus
c. Duboisia myoporoides
d. Withania somnifera
c. Duboisia myoporoides
True about tropane alkaloids:
a. From Solanaceae family except cocaine
b. Tropane ring is from arginine and ornitine
c. Tropic acid is from phenylalanine
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Tropane alkaloids that is not from Solanaceae family but from Erythroxylaceae instead.
a. Scopolamine
b. Cocaine
c. Atropine
d. Mandragorine
b. Cocaine
First transdermal made.
a. Nicotine
b. Lobeline
c. Scopolamine
d. Hyoscine
c. Scopolamine
Atropa belladonna
Contains atropine
• Parasympathetic
• Adjunct in treatment of peptic ulcer
• Spasmolytic agent
• Antidote for physostigmine and organophosphate insecticides
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
b. Belladona
Hyoscyamus niger
Hog + Bean
• Toxic to swine
• Anticholinergic
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
a. Henbane
Jimson Weed, Jamestown Weed, Talumpunay, Thorn apple
Datura stramonium, Datura metel
Contain scopolamine aka hyoscine
• Treatment of asthma (vapor)
• Treatment of motion sickness
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
c. Stramonium
Brompton's cocktail is a preparation used for terminal cancer containing:
a. Morphine/Heroin
b. Cocaine
c. High% alcohol
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Duboisia myoporoides
• Treatment of motion sickness, stomach disorders
• Treatment of side effects of cancer therapy
• Antispasmodic, analgesic
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
d. Duboisa
Indian ginseng, Winter cherry
Withania somnifera
• Sedative
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
e. Withania
“Satan’s apple”, European mandrake
Mandragora officinarum
Contains mandragorine:
• Emetic
• Most popular anesthetic during the middle ages
• In the Elizabethan age it was still being used as a narcotic
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
f. Mandragora
Satan's apple
a. Henbane
b. Belladona
c. Stramonium
d. Duboisa
e. Withania
f. Mandragora
f. Mandragora
Cocaine:
a. Pyschoactive
b. Psychomotor stimulant with a strong abuse potential
c. Vasoconstrictor and local anesthetic
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Huanoco, Bolinian Cocaine
Erythroxylum coca - more pleasant preferred effect
a. Erythroxylum coca
b. Erythroxylum truxillense
a. Erythroxylum coca
Truxillo, Peruvian Cocaine
a. Erythroxylum coca
b. Erythroxylum truxillense
b. Erythroxylum truxillense
Alkaloid used to reduce rigidity and tremors for those suffering from Parkinson's disease.
a. Scopolamine
b. Cocaine
c. Atropine
d. Mandragorine
a. Scopolamine
Racemized hyoscyamine during extraction.
a. Scopolamine
b. Cocaine
c. Atropine
d. Mandragorine
c. Atropine
Principal cinchona alkaloid employed therapeutically as anti-protozoal drug.
a. Scopolamine
b. Cocaine
c. Atropine
d. Mandragorine
e. Quinine
e. Quinine
Reaction is used to identify quinine.
a. Thealleioquin
b. Borntrager
c. Valser
d. Frasch
a. Thalleioquin
Overdose of Peruvian bark results in temporary loss of hearing and impaired sight commonly known as:
a. Alcoholism
b. Cinchonism
c. Solecism
d. Cinchonism
QUINOLINE ALKALOIDS sources:
a. Cinchona
b. Peruvian bark
c. Quina
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Cinchona succirubra
a. Yellow cinchona
b. Red cinchona
b. Red cinchona
Cinchona calisaya
a. Yellow cinchona
b. Red cinchona
a. Yellow cinchona
Cinchonism:
a. Tinnitus
b. Headache
c. Confusion
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Commercial source of quinidine.
a. Remijia purdieana
b. Erythroxylum truxillense
c. Duboisa myoporoides
d. Datura metel
a. Remijia purdieana - Cuprea
Antimalarial
a. Quinine
b. Quinidine
c. Cinchotannic acid
d. All
a. Quinine
Anti arrhythmic
a. Quinine
b. Quinidine
c. Cinchotannic acid
d. All
b. Quinidine
Condensed tannin.
a. Quinine
b. Quinidine
c. Cinchotannic acid
d. All
c. Cinchotannic acid
Thalleioquin reaction include Br2 TS + NH3 TS which will result to:
a. Yellow green
b. Emerald green
c. Dark green
d. Blue green
b. Emerald green
Template for synthetic anti-malarials such as quinacrine, chloroquine and mefloquine.
a. Quinine
b. Quinidine
c. Cinchotannic acid
a. Quinine
An isomer of quinine used to treat type I-cardiac arrhythmias.
a. Quinine
b. Quinidine
c. Cinchotannic acid
b. Quinidine
ISOQUINOLINE ALKALOIDS except:
a. Emetine
b. Saguinarine
c. Tubocurarine
d. Opium
e. Hydrastine/Berberine
f. None
f. None
ISOQUINOLINE ALKALOIDS sources except:
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium
e. Golden seal
f. None
f. None
Precursor of isoquinoline.
a. Tryptophan
b. Tyrosine
c. Isoleucine
d. Lysine
b. Tyrosine
Cephaelis ipecacuanha
Contain emetine or methylcephaeline
• Emetic
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium
a. Ipecac
Ipecac syrup is used for the treatment of drug overdose and in certain poisoning and it has the active isoquinoline alkaloid known as.
a. Emetine
b. Methylcephaeline
c. Sanguinarine
d. Tubocurarine
e. Opium
a. Emetine
Ipecac that is 14 times stronger than the liquid syrup form.
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
a. Fluid extract
Camphorated opium tincture.
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
c. Paregoric
Ipecac + opium
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
b. Dover's powder
Diaphoretic
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
b. Dover's powder
Deodorized opium tincture
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
d. Laudanum
Opium tincture 10%
More potent than paregoric
a. Fluid extract
b. Dover's powder
c. Paregoric
d. Laudanum
d. Laudanum
Sanguinaria canadensis
Contain saguinarine
• Stimulating expectorant and emetic
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium poppy
b. Bloodroot
South American arrow poison
Strychnos castelnae
Contain tubocurarine
• Skeletal muscle relaxant
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium
e. Hydrastis
c. Curare
Standardization include head drop assay in rabbits wherein there is determined least amount of drug capable of producing muscle relaxation so that head of animal drops in a characteristic manner.
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium
e. Hydrastis
c. Curare
Official test animal used to assay curare alkaloids by the "head drop" cross-over method wherein animals and control group are used in alternate base.
a. Mice and rabbits
b. Pigs
c. Cats
d. Lizards
a. Mice and rabbits
Strychnos castelnaei
a. Pot
b. Calabash
c. Tube
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Pot
Calabash
Chondrodendron tomentosum
a. Pot
b. Calabash
c. Tube
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
c. Tube
Papaver somniferum
a. Ipecac
b. Bloodroot
c. Curare
d. Opium
e. Hydrastis
d. Opium
Opium Alkaloids
Morphine
Codeine
Heroin
Papaverine
Hydromorphine
Apomorphine
Narcotine/Noscapine
a. True
b. False
a. True