ISM - Lesson 5 - Entry Modes-Karteikarten | Quizlet
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Internationalization - Definition
The process of a firm expanding its attention outside its home market (domestic market) to serve new customers in a new country
Why do companies want to internationalize?
1. Market seeking (Netflix)
2. Efficiency seeking (Tesla)
3. Resource seeking (Glencore)
4. Strategic asset seeking (Luxury goods)
Why may companies not want to internationalize?
1. Unknown markets present unknown risks and challenges of control
2. Dilution of focus on current market
3. Resources needed
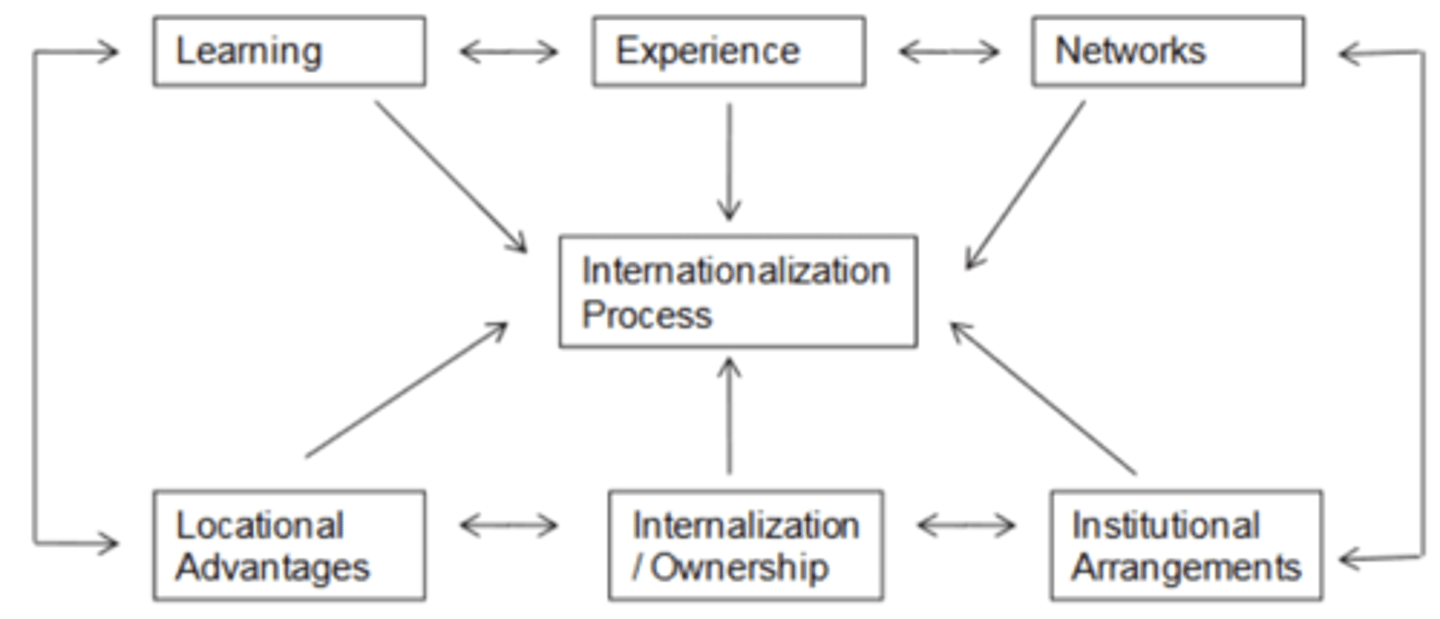
Factors influencing a firm's Internationalization Process
1. Learning
2. Experience
3. Networks
4. Locational Advantages
5. Internationalization/Ownership
6. Institutional Arrangements
Entry Mode - Definition
An institutional arrangement for the entry of a company's products and services into a new foreign market
Entry Mode Types
1. Without significant partners
2. With significant partners
Direct Export - Overview
1. No intermediary
2. Direct contact with foreign customers
Direct Export - Advantages
1. Greater profits (no intermediaries)
2. High degree of control
3. Direct business relation with customers & direct customer feedback
4. Showing full commitment
5. Good protection of patents, etc.
Direct Export - Disadvantages
1. High cost & time-consuming
2. Direct responsibilty for failures/problems
3. Competitive disadvantages (local competitors: market knowledge, response time)
4. Necessity to handle complex logistics issues
Indirect Exports - Overview
1. International business through intermediary
2. No direct contact with foreign customers
Indirect Exports - Advantages
1. Low risk & minimal involvement in the export process
2. Possibility to concentrate on the home market
3. Limited responsibility for problems/failures
4. No or limited involvement in logistic issues
5. Local knowledge of local agent
Indirect Exports - Disadvantages
1. Lower profits
2. Low degree of control over the foreign business
3. No direct contact with customers & no direct customer feedback
4. Risk of creating a future competitor
Own Subsidiary - Overview
1. Owned by the parent company
2. Greenfield investment or acquisition
Own Subsidiary - Advantages
1. High degree of control over the foreign business
2. Low risk of losing IP to competitors
3. Cost synergies between parent company and subsidiary (e.g. joint marketing campaigns)
4. Rather direct contact with customers
Own Subsidiary - Disadvantages
1. High cost & large capital investment
2. Middle- or long-term commitment
3. Difficult to develop relationships with foreign customers & suppliers
4. No/limited local knowledge
Indirect vs. Direct Exports
Indirect:
1. Export Consortia
2. Freight Forwarders
3. Selling to an Exporter Client
Direct:
1. Middleman
2. Direct contact with retailers
3. Direct sales
Owned Subsidiary
1. Partly Owned:
1.1. Owns 50% or more but less than 100%
1.2. Parent company does not get full control
2. Wholly Owned:
2.1. Owns 100% of shares & controls subsidiary fully
2.2. Not a merger
Licensing - Overview
Licensor sells the right to use technologies/processes/patents/brands etc. to a licensing company
Licensing - Advantages
1. Low financial risk & low cost of market access
2. Avoiding tariffs & restrictions on foreign investments
3. Not necessary to acquire detailed market knowledge
4. Quick expansion without large investment
Licensing - Disadvantages
1. Limited market opportunities
2. Dependence on licensee, potential conflicts
3. Risk of creating a competitor
4. Incompetent licensees can produce image problems
Franchising - Overview
Franchisor sells the right to run the business under the franchisor's name to a franchisee in a foreign country
Franchisee - Advantages
1. Low financial risk & low cost of market access
2. Avoiding tariffs & restrictions on foreign investments
3. Not necessary to acquire detailed market knowledge
4. More control than in the case of licensing
Franchisee - Disdvantages
1. Limited market opportunities
2. Dependence on franchisee, potential conflicts
3. Risk of creating a competitor
4. Rather low degree of control over the foreign business
5. Incompetent licensees can produce image problems
Joint Venture - Overview
1. Cooperation between two/more local and foreign companies (equal contribution to the new entity, shared revenues/expenses/control)
2. Creation of a (third) new company
Joint Venture - Advantages
1. Benefit from local partner's knowledge
2. Shared costs/risks
3. Reduced political risk
Joint Venture - Disadvantages
1. Losing control over technologies to the partner
2. Risk of conflicts due to the necessity to cooperate
How to choose a mode of entry?
1. Naive rule
2. Pragmatic rule
3. Strategy rules
Naive rule
1. The decision-maker uses the same entry mode for all foreign markets
2. Ignores the heterogeneity of the individual foreign markets
Pragmatic rule
The decision-maker uses a workable entry mode for each foreign market
Strategy rule
This approach requires that all alternative entry modes are systematically compared and evaluated before any choice is made
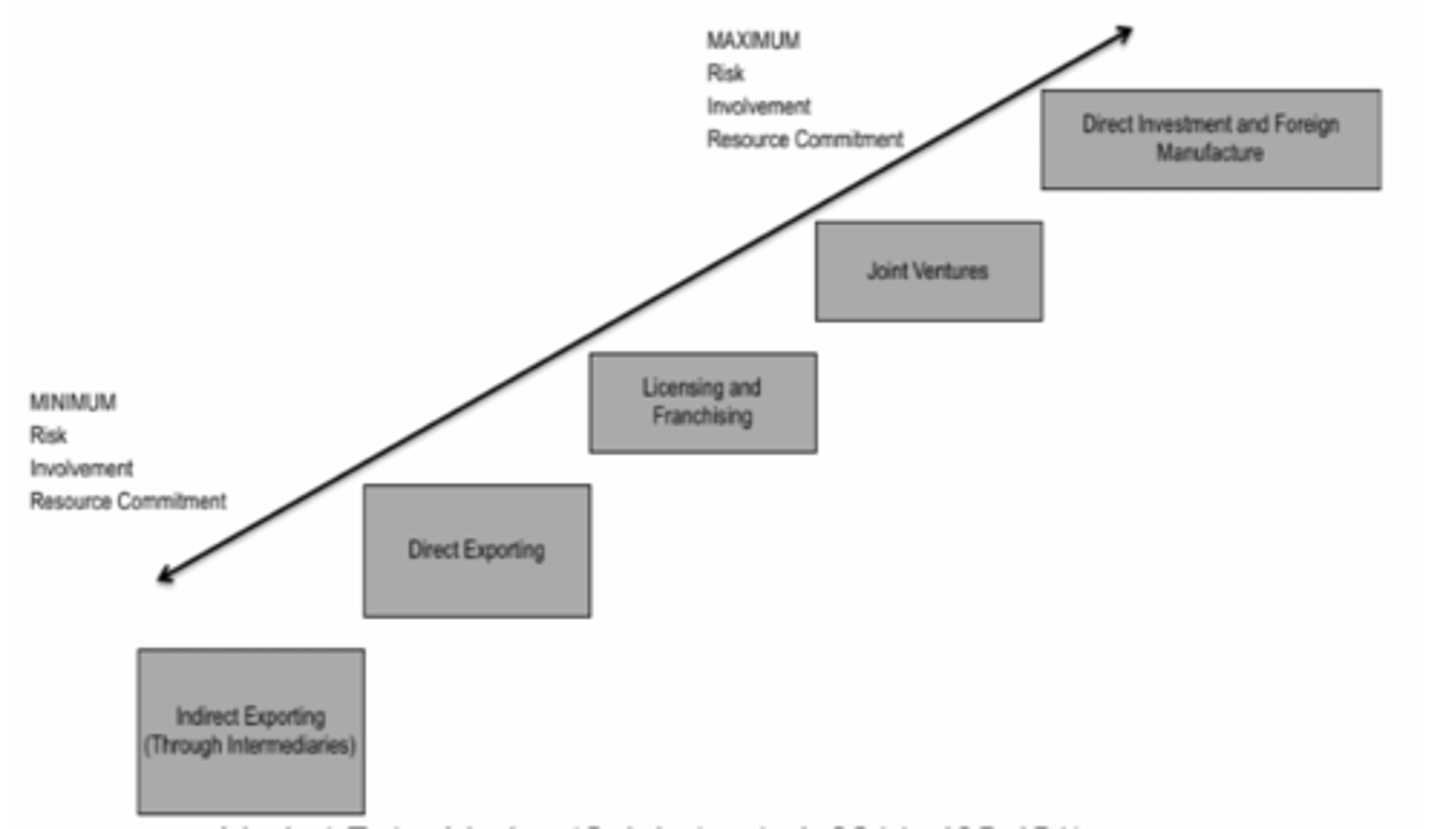
Comparison of entry modes
From minimum to maximum risk, involvement & resource commitment:
1. Indirect Exporting (Intermediaries)
2. Direct Exporting
3. Licensing & Franchising
4. JV
5. Direct Investment & Foreign Manufacture
Factors influencing the choice of entry mode
1. Internal factors
2. Desired mode characteristics
3. Transaction-specific factors
4. External factors
5. Product
Internationalization - Stage Model (Uppsala Model)
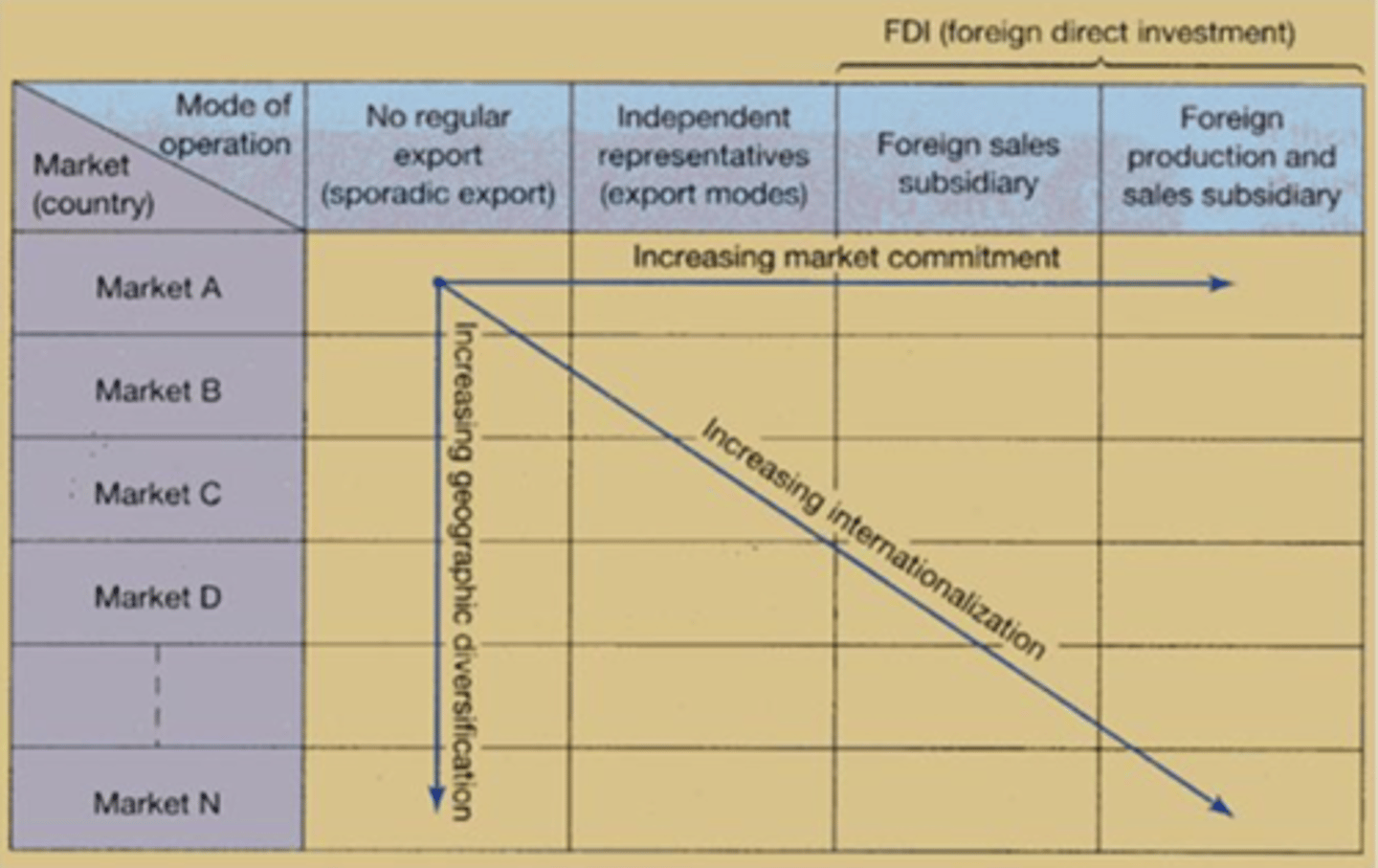
Stage Model Theory - Key takeaway
Companies first gain experience from the domestic market before they foray into international market
Stage Model - Internationalization as sum of target country patterns
1. Prioritization of markets: based on market attractiveness, psychic distance & degree of difficulty
2. Constraints: Resources available, level of commitment needed, longer term firm objectives
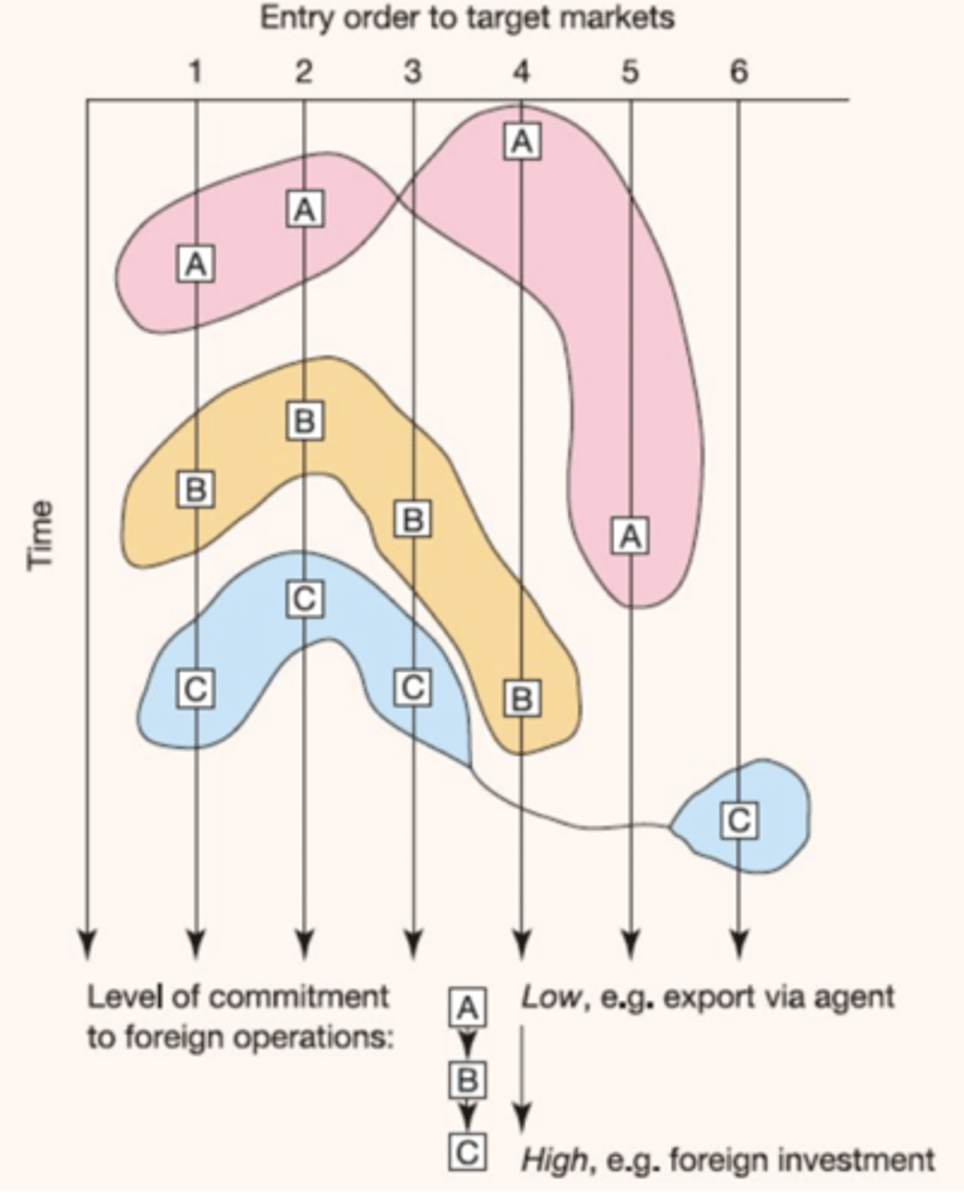
2 paths to Internationalization
1. Slow & Steady
2. Quick & Ready (Born Global)
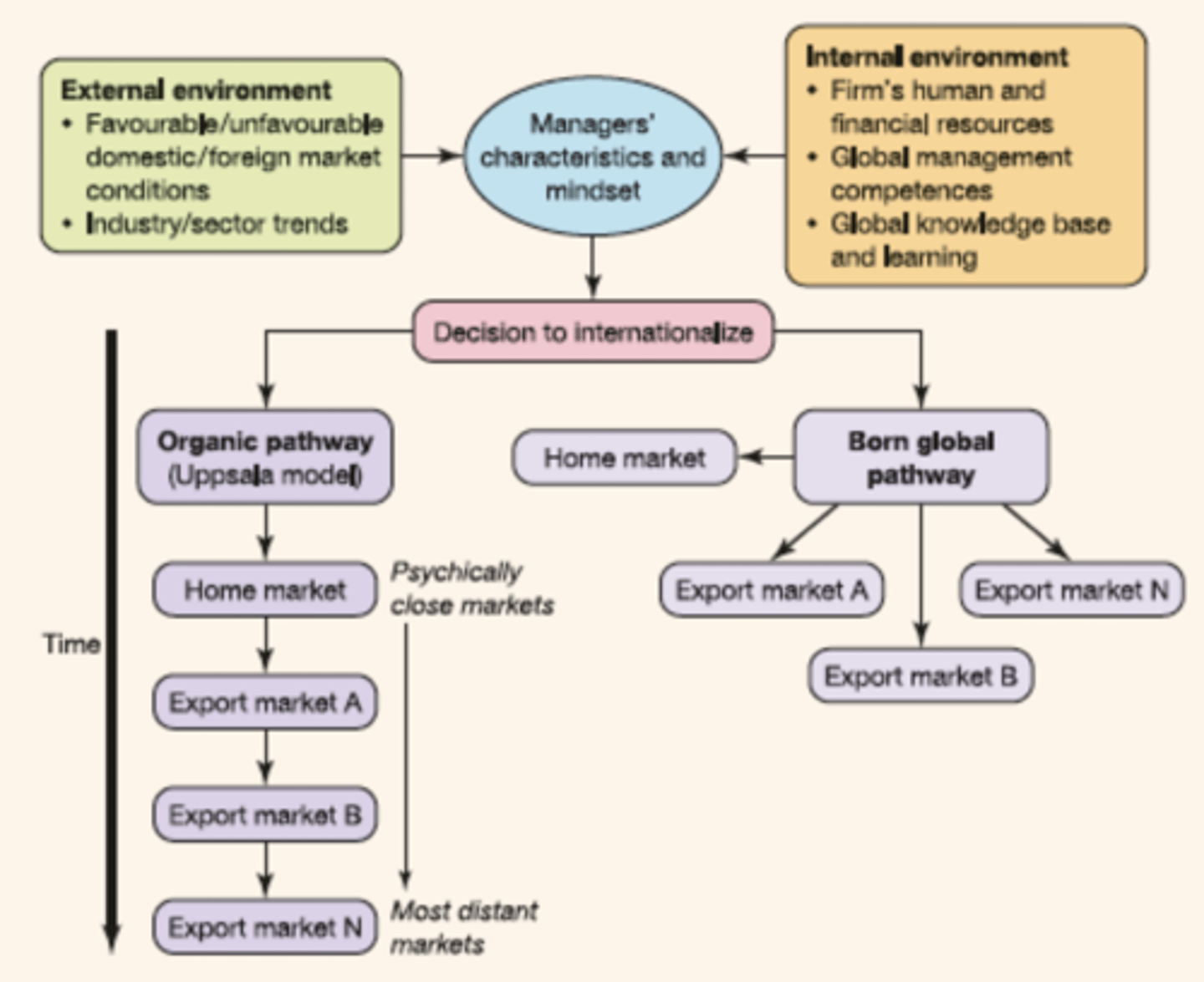
2 paths to Internationalization - Slow & Steady
1. Develop expertise through learning curve of business & industry
2. Consolidate domestic market first
3. Build networks that have future international relevance
4. Expand in a staged and prioritized manner
2 paths to Internationalization - Quick & Ready
1. Useful in a highly internationalized environment
2. Low differentiation in offerings across markets
3. Based on a foundation of global sourcing model -> rapid dissemination of innovation
Mode of Entry - Internal Factors
1. Costs/risks
2. Speed
3. Long-term objectives
4. Company size/flexibility
5. International experience
6. Control/managerial reasons
7. Product complexity & differentiation
8. Relationships
Mode of Entry - External Factors
1. Socio-cultural distance
2. Country risk & demand uncertainty
3. Market size & growth
4. Direct & Indirect trade barriers
5. Competitive environment
6. Small number of relevant intermediaries available
7. Laws & regulations
8. Geographical distance