Functional Movement Screen (FMS): Tests, Scoring, and Injury Prediction
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is the purpose of the Functional Movement Screen (FMS)?
To assess functional movement patterns, establish a baseline, identify poor movement patterns, and predict injury.
Who developed the Functional Movement Screen?
Gray Cook and Lee Burton in 1995.
How many tests are included in the FMS?
Seven tests.
What are the seven tests of the FMS?
1. Deep Squat, 2. Hurdle Step, 3. Inline Lunge, 4. Shoulder Mobility, 5. Active Straight Leg Raise, 6. Trunk Stability Pushup, 7. Rotary Stability.
What does neuromuscular control refer to?
The nervous system's control over muscle activation and factors influencing task performance.
Define proprioception.
Afferent signal information received from proprioceptors located in body segments and joints, contributing to posture control and joint stability.
What is functional training?
Progressive multi-joint, multi-planar weight-bearing activities that integrate and coordinate the nervous system and muscles for movement and joint stability.
What were the results of the functional training program for firefighters?
Lost time injuries reduced by 62% and total injuries reduced by 44%.
What is the significance of proprioception in functional training?
It is essential for controlling muscle activation and ensuring efficient movement patterns.
What is the highest score attainable on the FMS?
21.
How is scoring conducted in the FMS?
Each test is scored from 1 to 3, with pain resulting in a score of 0. The lowest score is recorded for bilateral assessments.
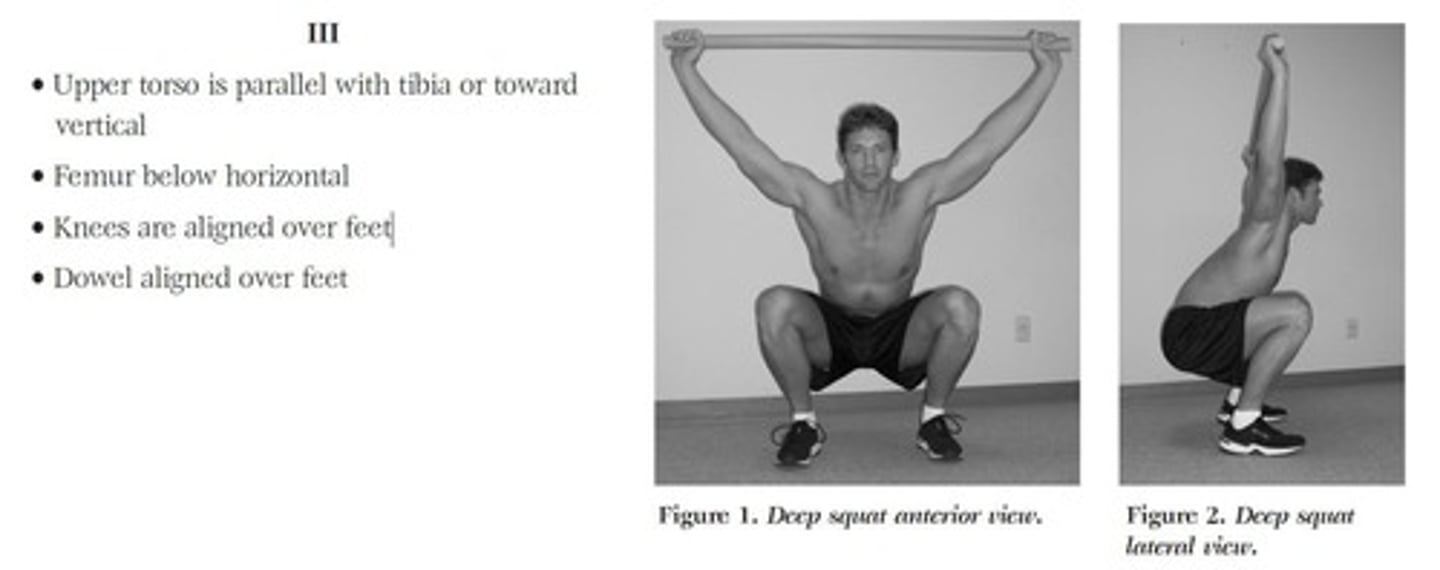
What are the clinical implications of a poor deep squat?
Indicates poor dorsiflexion, knee or hip flexion, thoracic spine extension, shoulder flexion, and core stability.
What does a score of III indicate in the FMS?
The individual successfully completed the test with proper form.
What is the role of dynamic restraints in neuromuscular control?
They prepare for and respond to joint motion and loading to maintain joint function and stability.
What is the role of the FMS in injury prevention?
It identifies compensatory movement patterns that could lead to injuries.
What is assessed during the Hurdle Step test?
Proper stride mechanics and coordination between hips and upper body.

What is the significance of the pre-testing measurements in the FMS?
They provide necessary data for assessing movement capabilities, such as the distance from the floor to the tibial tuberosity.
What does a score of 0 indicate in the FMS?
Pain was present during the test.
What is the importance of the Deep Squat test?
It serves as the starting position for most athletic skills and assesses lower extremity mobility.
What is the relationship between functional training and injury reoccurrence?
Both proprioception and neuromuscular training interventions are effective for preventing injury reoccurrence.
What is the assessment focus of the Inline Lunge test?
It evaluates balance and stability during a lunge movement.
What is the purpose of the Shoulder Mobility test?
To assess the range of motion and stability of the shoulder joint.
What does the Active Straight Leg Raise test assess?
It evaluates hamstring flexibility and pelvic stability.
What does the Trunk Stability Pushup test measure?
It assesses core stability and upper body strength.

What does the Rotary Stability test evaluate?
It assesses the ability to maintain balance and control during rotational movements.
What is the purpose of the Hurdle Step test?
To assess function and stability of the hip, knee, and ankles.
What is the starting position for the Hurdle Step test?
Feet together, toes touching the base of the hurdle, with the hurdle height adjusted to the patient's tibial tuberosity.
What does the patient do during the Hurdle Step test?
The patient steps over the hurdle, touching heel to floor with knee extended, then returns the leg to the starting position.
What are the clinical implications of poor performance in the Hurdle Step test?
Indicates poor stability of the stance leg, poor mobility of the step leg, or anterior pelvic tilt.
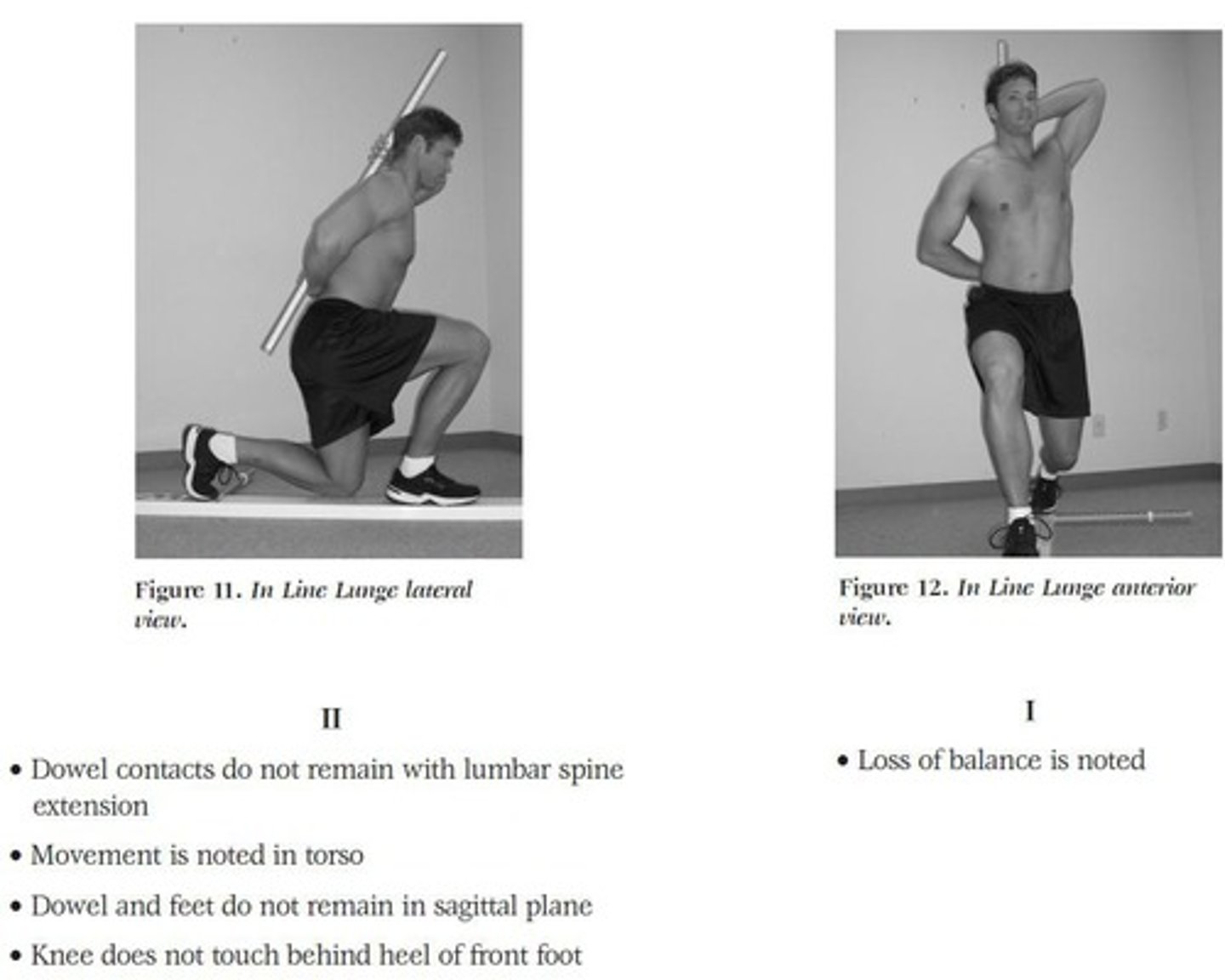
What is assessed in the In-Line Lunge test?
Hip and ankle range of motion (ROM), stability of the knee, and quadriceps flexibility.
What is the starting position for the In-Line Lunge test?
Patient holds a dowel against the spine with one arm externally rotated and the other internally rotated, measuring tibia length from floor to tibial tuberosity.
What indicates a low score in the In-Line Lunge test?
Loss of balance or failure to maintain dowel contact with the spine, head, and sacrum.
What are the clinical implications of issues found during the In-Line Lunge test?
Indicates hip mobility issues, stability issues at hip, knee, or ankle, and muscular imbalances.
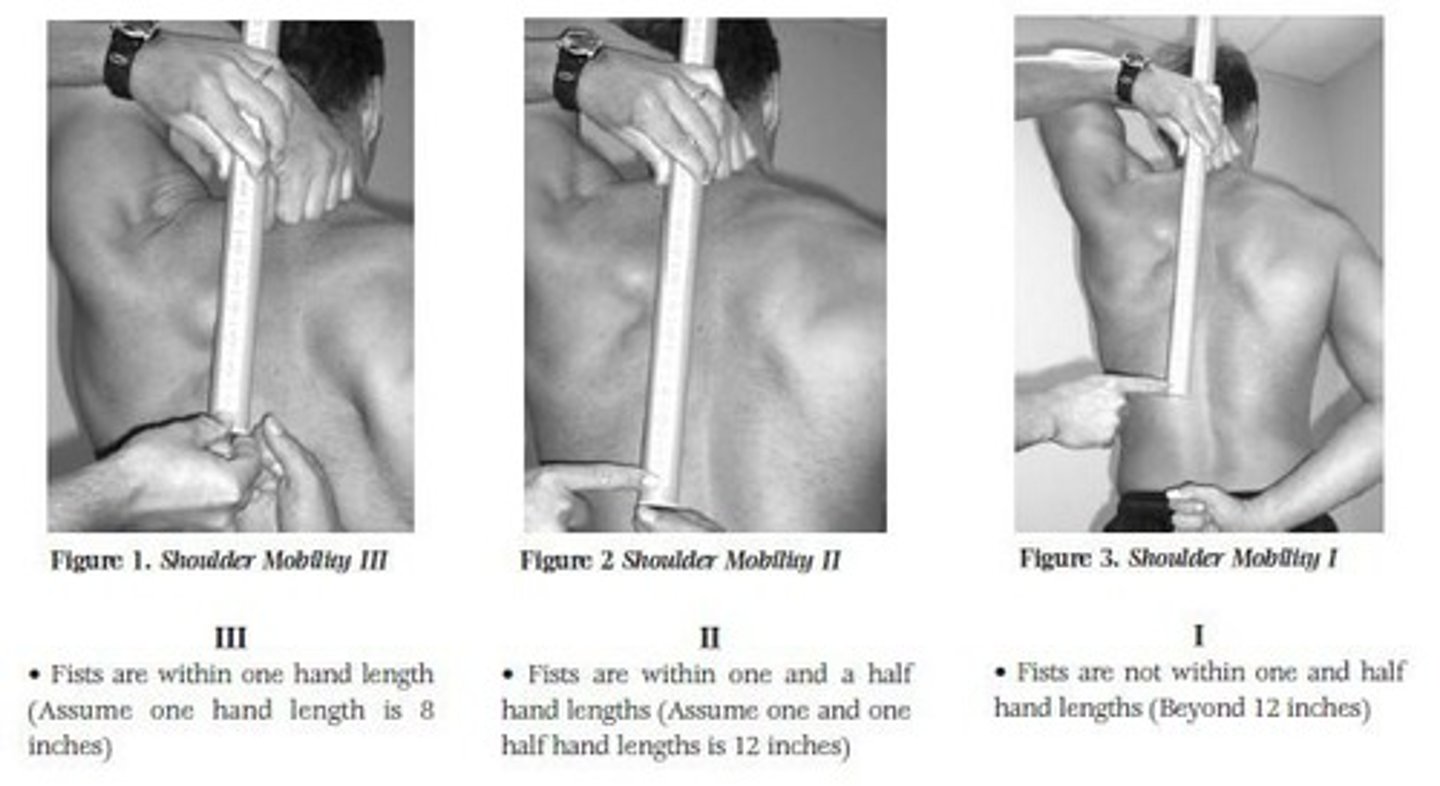
What is the starting position for the Shoulder Mobility test?
Patient makes fists and simultaneously externally rotates and abducts one arm while internally rotating and adducting the other arm behind the head.
What does the clearing test in the Shoulder Mobility test assess?
Shoulder impingement syndrome as a cause of decreased shoulder range of motion.
What are the clinical implications of poor results in the Shoulder Mobility test?
Indicates glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD), overdevelopment of pectorals and latissimus dorsi, and scapulothoracic dyskinesis.
What is the purpose of the Active Straight Leg Raise test?
To assess the patient's ability to controllably move the lower extremity while maintaining trunk stability.
What is the starting position for the Active Straight Leg Raise test?
Patient lies supine with extremities flat on the ground, and a dowel held perpendicular to the ground between the ASIS and patella.
What indicates poor performance in the Active Straight Leg Raise test?
Poor hamstring flexibility, poor abdominal stability, or poor mobility of the opposite hip.
What is the purpose of the Trunk Stability Push-up test?
To assess the ability to stabilize the spine during movement.
What is the starting position for the Trunk Stability Push-up test?
Patient lies prone with hands shoulder-width apart and knees extended.
What indicates a successful completion of the Trunk Stability Push-up test?
The body lifts through the push-up as one unit, maintaining core stability.
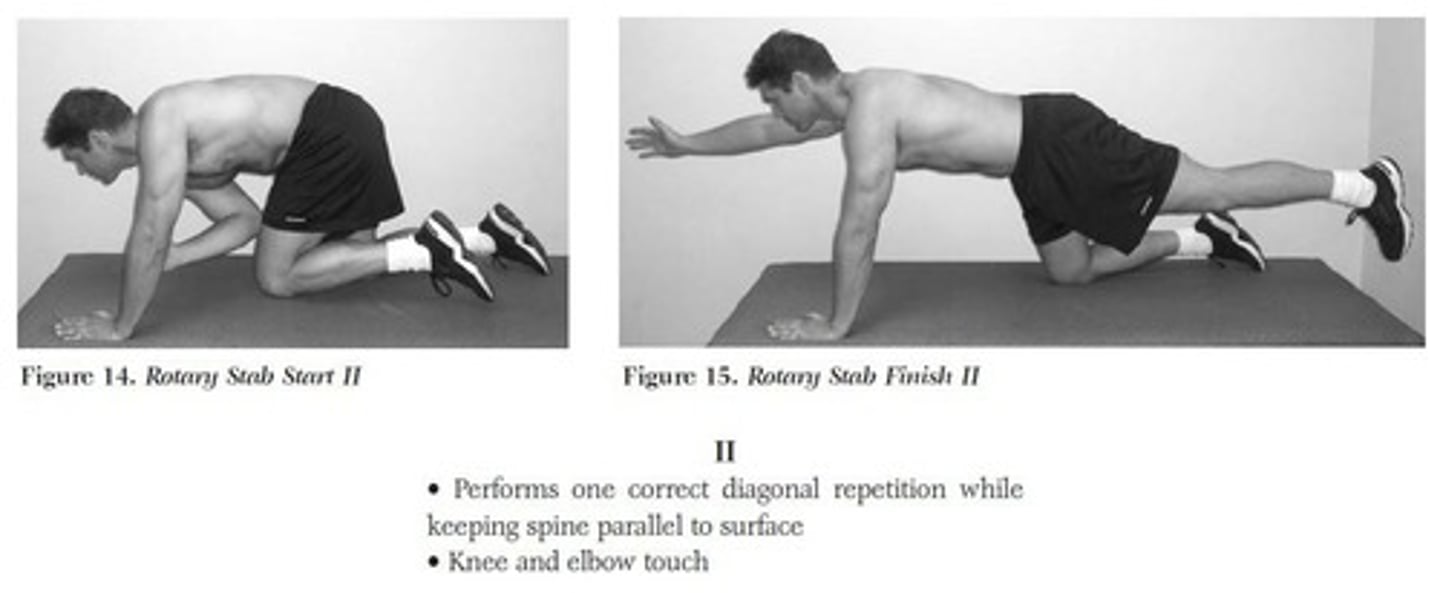
What is the purpose of the Rotary Stability test?
To assess the patient's ability to perform complex movements requiring neuromuscular control.
What is the starting position for Test 7: Rotary Stability?
Patient begins on hands and knees with shoulders, hips, and knees flexed at 90 degrees, and ankles dorsiflexed.
What does the patient do during Test 7: Rotary Stability?
The patient flexes the shoulder and extends the hip and knee on the same side to 6 inches off the floor, then brings elbow and knee together before returning to the flexed and extended positions.
What is assessed in Test 7: Rotary Stability?
Symmetrical trunk stability in the sagittal and transverse planes.
What happens if a patient cannot complete Test 7 with the same side?
The test is attempted with the opposite arm and leg, but this will affect the score.
What significant finding did Kiesel and Plisky's research reveal about FMS scores?
A score of 14 or less on the FMS can predict serious injury with a specificity of 0.91 and sensitivity of 0.54.
What was the overall conclusion of Dorrel et al.'s systematic review on FMS?
Findings do not support the predictive validity of the FMS for injury prediction.
What are the diagnostic parameters for FMS to predict injury?
Specificity: 85.7%, Sensitivity: 24.7%, Positive Predictive Value: 42.8%, Negative Predictive Value: 72.5%.
What does the Area Under the Curve (AUC) indicate in FMS research?
The AUC of 0.587 indicates the predictive accuracy of the FMS for injury.
What is the significance of the likelihood ratios in FMS research?
Likelihood Ratio Positive (LR+): 1.7, Likelihood Ratio Negative (LR-): 0.87.
What is the importance of blinding and dropout rates in FMS studies?
Future research should include and report these aspects to strengthen conclusions about FMS predictive validity.
What is the definition of Sensitivity in clinical tests?
Sensitivity = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives).
What is the definition of Specificity in clinical tests?
Specificity = True Negatives / (True Negatives + False Positives).
What does Positive Predictive Value indicate?
The chance that a positive test result will be correct.
What does Negative Predictive Value indicate?
The chance that a negative test result will be correct.
What is the ROC curve analysis used for?
To evaluate the diagnostic ability of a test.
What does the Confidence Interval (CI) represent in FMS studies?
It indicates the range within which the true parameter is expected to lie with a certain level of confidence.
What is the significance of the effect size in FMS research?
It quantifies the magnitude of the difference between groups in terms of injury prediction.
What is the role of proprioception in functional joint stability?
Proprioception is crucial for motor control and maintaining functional joint stability.
What is the main focus of the Functional Movement Screen?
To assess fundamental movements as an indicator of function and injury risk.
What did the systematic review identify about the quality of previous FMS literature?
Overall, the quality was poor with inconsistent reference standards and lack of methodological reporting.
What is the purpose of the FMS?
To identify movement dysfunctions that may lead to injury.
What is the significance of the study by O'Connor in FMS literature?
It serves as a reference standard for evaluating the predictive validity of the FMS.
What are the implications of a systematic review on FMS for active adult populations?
It evaluates the effectiveness of FMS as an injury prediction tool.
What does a score of 14 or less on the FMS indicate?
It is associated with a higher risk of serious injury.
What is the relationship between FMS scores and injury risk according to Kiesel and Plisky?
There is a significant difference in mean scores between injured and uninjured individuals.
What is the main objective of the FMS?
To screen individuals for movement patterns that may predispose them to injury.