PD- Khan
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What disease results from the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra?
Parkinson’s disease
The D1 receptor is the ___________ pathway and ____________ movement.
a. direct, inhibits
b. indirect, inhibits
c. direct, enables
d. indirect, enables
c.
The D2 receptor is the ___________ pathway and ____________ movement.
a. direct, inhibits
b. indirect, inhibits
c. direct, enables
d. indirect, enables
b.
Which of the following receptors is inhibited in PD?
a. D1
b. D2
a.
The majority of Parkinson’s cases are ______________.
a. genetic
b. idiopathic
c. caused by drugs
d. caused by environmental toxins
b.
What are some causes linked to parkinson’s?
Infectious diseases (viral encephalitis)
Drugs (antipsychotics, antiemetics)
Environmental toxins
genetics
What are the symptoms of PD?
bradykinesia
muscle rigidity
tremor
postural instability
What are the 2 proposed MOAs of Amantadine?
1. Promotes release of DA from remaining striatal dopaminergic terminals
2. Antagonism of NMDA receptor of Glutamate
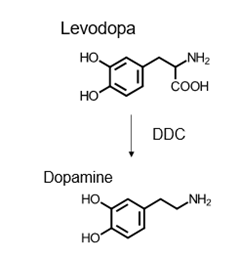
What is the MOA of Levodopa? Carbidopa?
levo: dopamine precursor, converted to dopamine in the brain and Increases dopamine synthesis in the striatum
carb: Inhibit dopa decarboxylase (DCC) in the periphery and makes levodopa more available to the CNS
What is the MOA of COMT inhibitors?
does it work centrally or peripherally?
what does it do to DA?
Inhibits COMT in the periphery —> Increases DA and levodopa levels in the brain
What is the MOA of MAO-B inhibitors? What conversion does it prevent?
Selective inhibitor of MAO-B —> MAO-B converts DA to DOPAC
What is the MOA of anticholinergic agents used in PD?
Prevents activation of cholinergic receptors in CNS
Side effects of Amantadine?
Somnolence (drowsy)
Psychosis
Dizziness
Orthostatic hypotension
Side effects of Carbidopa/Levodopa?
n/v
dyskinesia
CV effects (postural hypotension)
Psychiatric effects (hallucinations, psychosis)
Positive Coomb’s test (d/c the drug)
Dark discoloration of urine, sweat, saliva
priapism
Side effects of COMT inhibitors?
Diarrhea
Confusion
hallucination
Side effects of MAO-B Inhibitors?
C/I with hepatic impairment
Visual changes
Side effects of Dopamine agonists?
n
Hallucinations
Confusion
Sudden sleep attacks
Orthostatic hypotension
Side effects of anticholinergic agents?
Intense anticholinergic SEs (dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, tachycardia, confusion)
98% of the oral dose of levodopa is converted to dopamine in the peripheries. What’s the consequence of this?
less levodopa gets to brain, DA SEs in the periphery
Does levodopa have a long or short t ½ ?
What enzyme inactivates levodopa in the peripheries?
short t ½
COMT enzyme
Carbidopa/levodopa is contraindicated in what condition?
glaucoma
What are the drug interactions with carbidopa/levodopa?
nonselective MAO inhibitors
antipsychotic drugs
pyridoxine
Before initiating carbidopa/levodopa what drug should be discontinued at least 2 weeks prior due to hypertension?
nonselective MAO inhibitors
Why does levodopa interact with pyridoxine?
pyridoxine stimulates decarboxylase activity= decrease levodopa therapeutic effects
In some pts. what develops near the end of the dosing interval with carbidopa/levodopa?
gradual loss or “wearing off”
What is the on-off phenomenon seen in pts. taking carbidopa/levodopa?
randomly occurring event
off times can be minutes—> hours
off times increase in frequency/intensity as disease progresses
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the carbidopa/levodopa combination?
Advantages
Daily requirement of Levodopa may be reduced
Decrease GI and cardiac SEs
More rapid onset
Improved control
Enhanced efficacy
Disadvantages
Dyskinesia and psych disturbances may be more intense and occur sooner
Be able to recognize the structures of dopamine AND levodopa
Apomorphine must be given concomitantly with what and why?
with antiemetic (ex: trimethobenzamide) bc apomorphine is a POTENT emetic (stimulates CTZ-vomiting center)
Apomorphine is what dosage form?
a. IV
b. SQ
c. oral
d. patch
b.
When is apomorphine C/I?
with 5HT3 antagonists (severe hypotension, loss of consciousness)
What enzyme converts levodopa to dopamine?
l-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase also called DDC-dopa decarboxylase
What conversions are catalyzed by COMT?
Dopamine—> 3-methoxytyramine
DOPAC—> HVA
Levodopa—> 3-O-methyldopa
What drug interactions are associated with MAOIs?
combining a SSRI/SNRI with MAOI (results in serotonin syndrome)
do not take with other MAOIs or opioids
An SSRI should be discontinued ___ weeks before starting MAOIs?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b.
MAOIs should be avoided with what food?
tyrosine containing foods (sausage, sauerkraut, cheese, airdried meat)
Anticholinergics are contraindicated in what 3 conditions? why?
narrow-angle glaucoma—> mydriasis, increase IOP, retinal damage
GI obstruction—> further decrease in GI tone/secretion
BPH—> aggravation of urinary hesitancy, dribbling
What drugs can cause Parkinson’s symptoms?
1st and 2nd gen antipsychotics
Antiemetics: metoclopramide, promethazine
What drugs can be used to treat Parkinson’s symptoms caused by drugs?
preferred: QUETIAPINE
pimavanserin
What are the ADRs of quetiapine?
metabolic comp. (increase blood sugar and cholesterol)
What drug is used to treat “off” condition? class?
safinamide—> MAO-B inhibitor
ADRs of Selegiline?
insomnia, jitters