Cell membrane structure
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are the roles of phospholipids in a membrane?
- Form bilayers
- Allow lipid-soluble molecules across but not water-soluble molecules
- Make the membrane flexible + self-sealing
What are the 2 ways that proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer?
- Extrinsic proteins: on either surface of the bilayer, provide mechanical support and act as cell receptors
- Intrinsic proteins: extend across both layers of bilayer, some are channel proteins, some are carrier proteins
Define channel proteins
- Form pores that, when open, allow specific solutes (e.g. ions such as Na+ or Cl-) to pass through the membrane.
- Occurs faster than in carrier proteins
Define carrier proteins.
- Bind specific solute molecules (e.g. glucose, amino acids) and undergo a conformational change to transfer the bound molecule from one side of the membrane to the other.
What other molecules are found in the membrane?
Cholesterol, glycoproteins, glycolipids
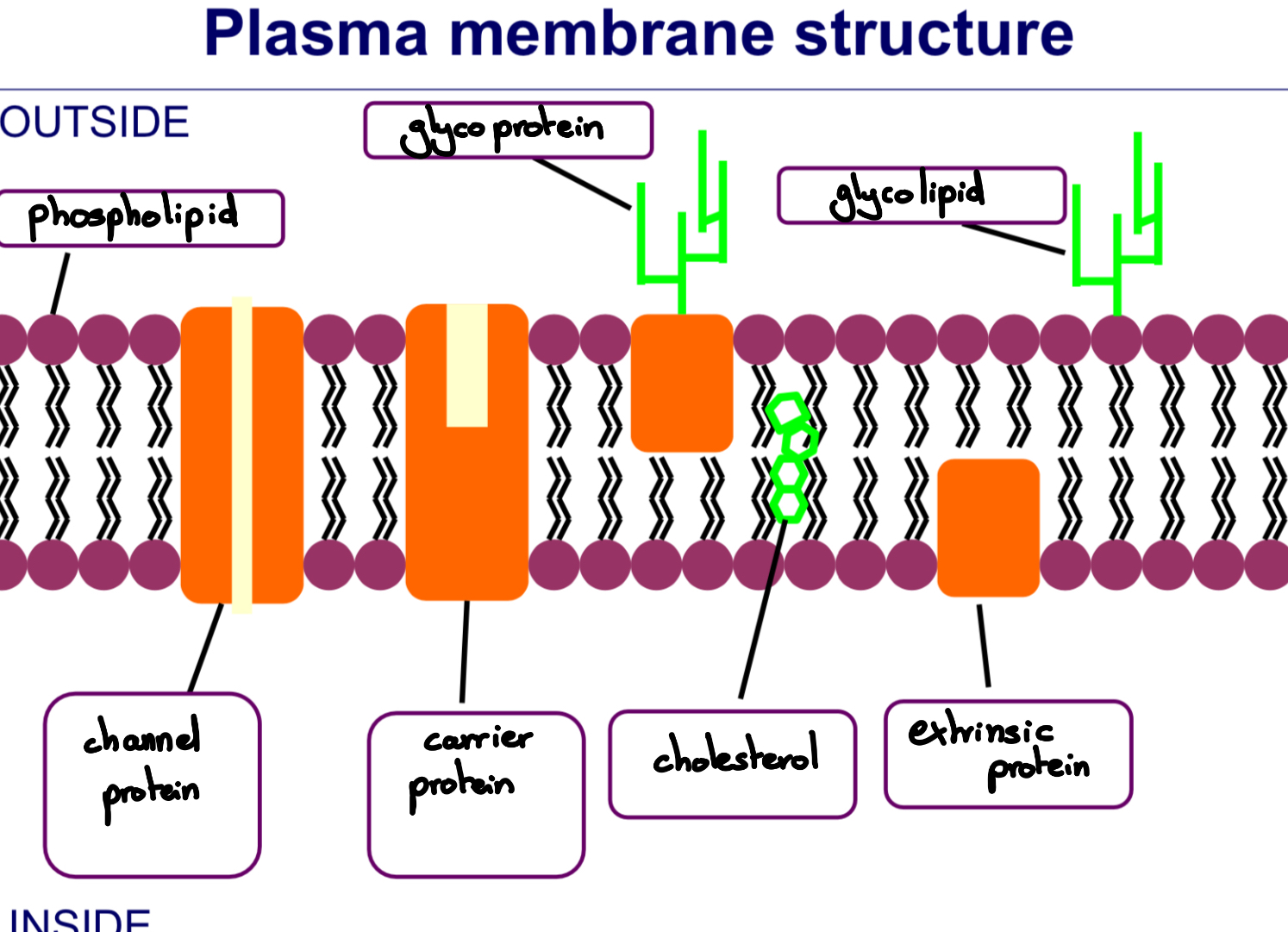
What does cholesterol do in the membrane?
- Found in between phospholipids
- Make the membrane stronger and more rigid
- Very hydrophobic: important role in preventing loss of water and dissolved ions from cell.
What do glycoproteins do in membranes?
- Act as cell surface receptors
- Help cells attach to one another to form tissues
- Allow cells to recognise each other
What do glycolipids do in the membrane?
- Carbohydrate portion extends from the phospholipid bilayer into the watery environment outside the cell
- Acts as a cell-surface receptor for specific chemicals
- Help maintain stability of membrane + help cells attach to one another to form tissues
What is allowed and prevented when crossing the phospholipid bilayer?
- Allows lipid-soluble (non-polar) substances to pass through (and small molecules e.g. H2O)
- Prevents most water-soluble (polar) substances passing through
Why is the structure of a membrane described as fluid-mosaic?
- Fluid since the phospholipids are able to move around
- Mosaic since the formation of proteins and phospholipids of different shales and sizes make a mosaic-like pattern