crystalline & amorphous solids
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
crystalline properties
well defined faces & edges
amorphous
powder
curved surfaces, globular
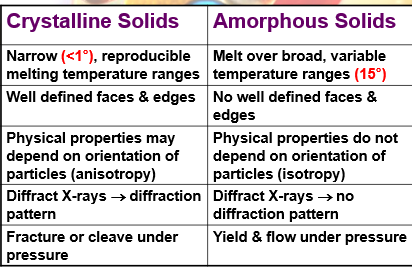
differences between crystalline solids and amorphous solids (3)
why are amorphous materials less thermodynamically stable than crystalline forms
they have very high viscosities
what are pharmaceutical uses of amorphous solids (2)
used as active ingredient as its more soluble
additives
what is crystallisation?
production of a single component crystalline phase
crystallisation process
supersaturation
formation of crystal nuclei
crystal growth around the nuclei
what is supersaturation
formation of a solution containing more dissolved solute than would be present in a saturated solution at max solubility
how can supersaturated solutions be obtained
cooling of a saturated soluton
evaporation —————-
chemical reaction