Introduction to Human Geography: Food, Agriculture, and Political Boundaries
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
What is the focus of geography in agriculture?
The study of the relationship between people and land.
What is agrarian life?
A way of life deeply embedded in the demands of agricultural production.
What is agriculture?
The science of cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance and profit.
What major changes have occurred in agriculture over the last five decades?
Agricultural systems are facing an uncertain future, influenced by climate change.
What is subsistence agriculture?
A system where agriculturalists consume all they produce.
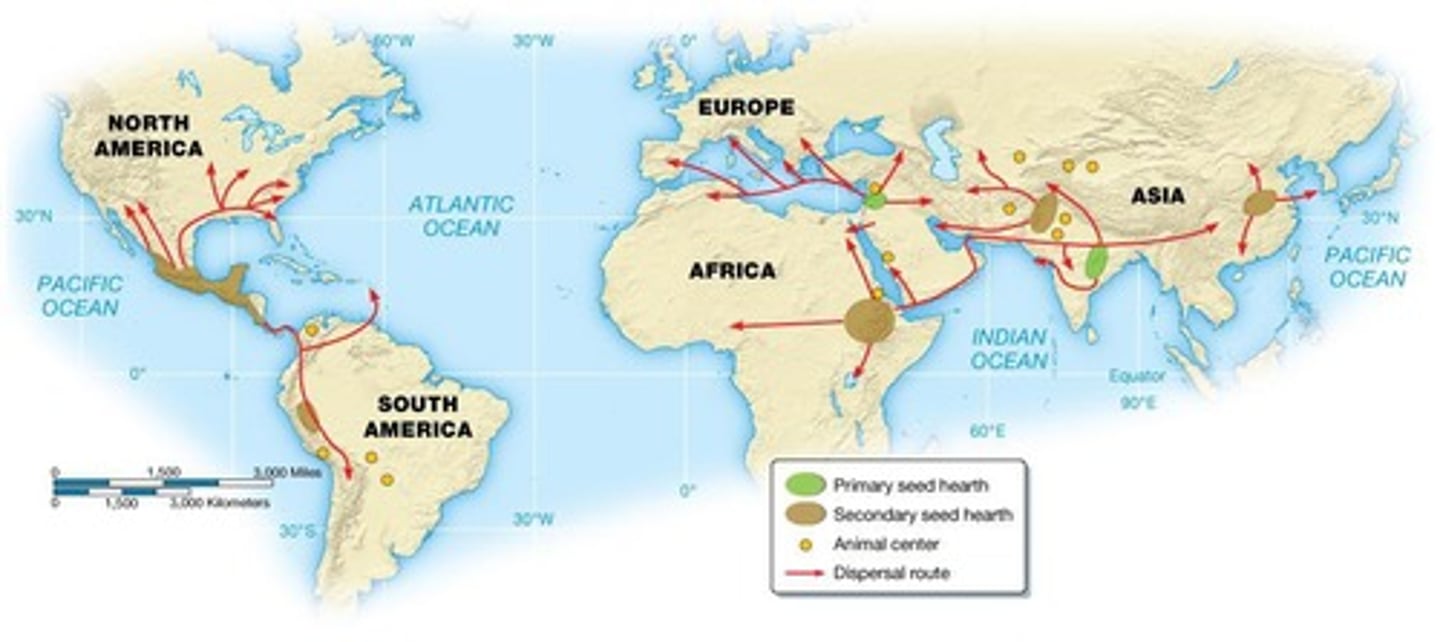
What are primary seed hearths?
Locations believed to be the first places of plant and animal domestication.
What distinguishes commercial agriculture from subsistence agriculture?
Commercial agriculture is primarily for sale, while subsistence agriculture is for personal consumption.
What is shifting cultivation?
A form of agriculture found in tropical forests that aims to preserve soil fertility by rotating fields.
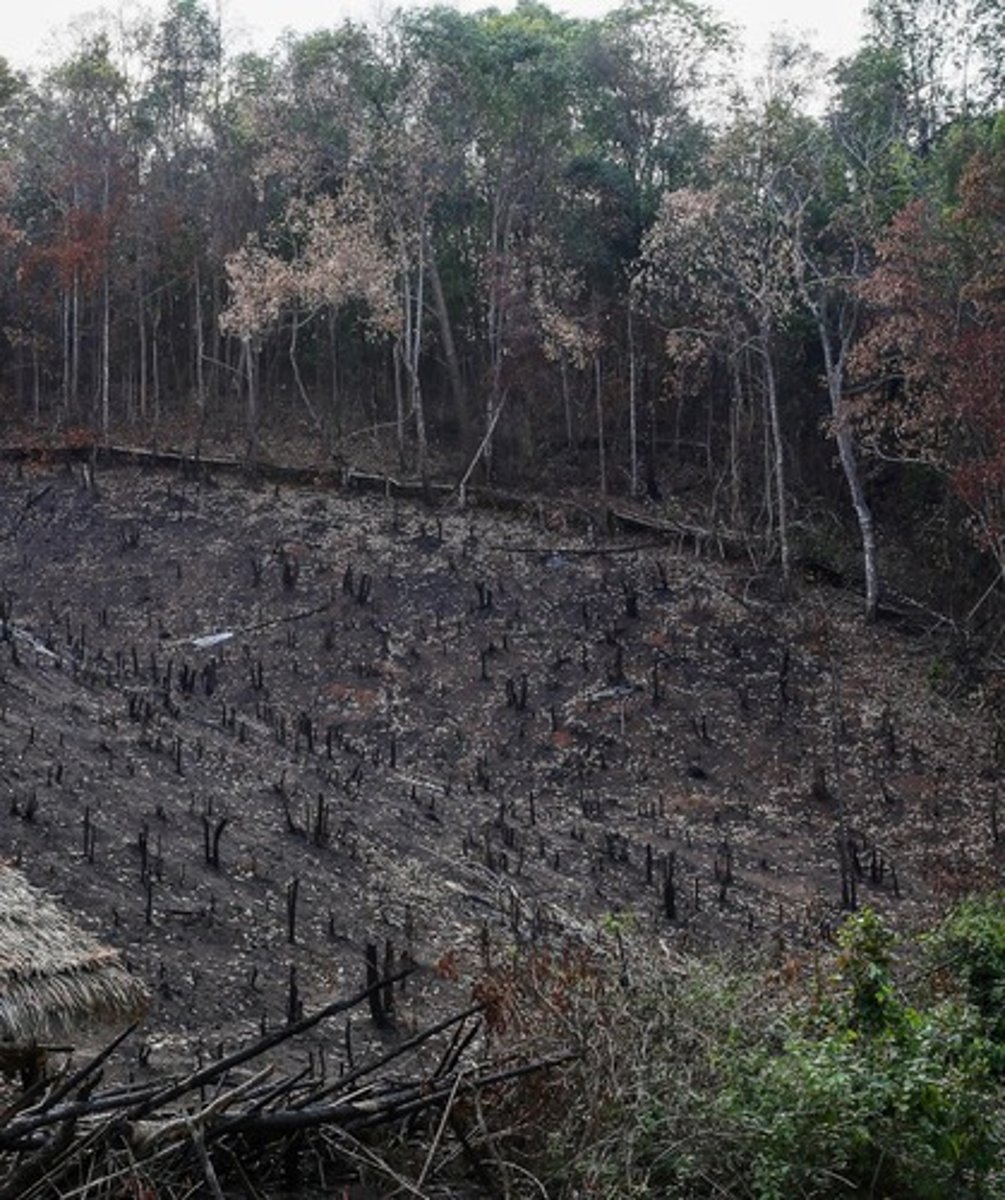

What technique is used in shifting cultivation to prepare land?
Slash and burn techniques.
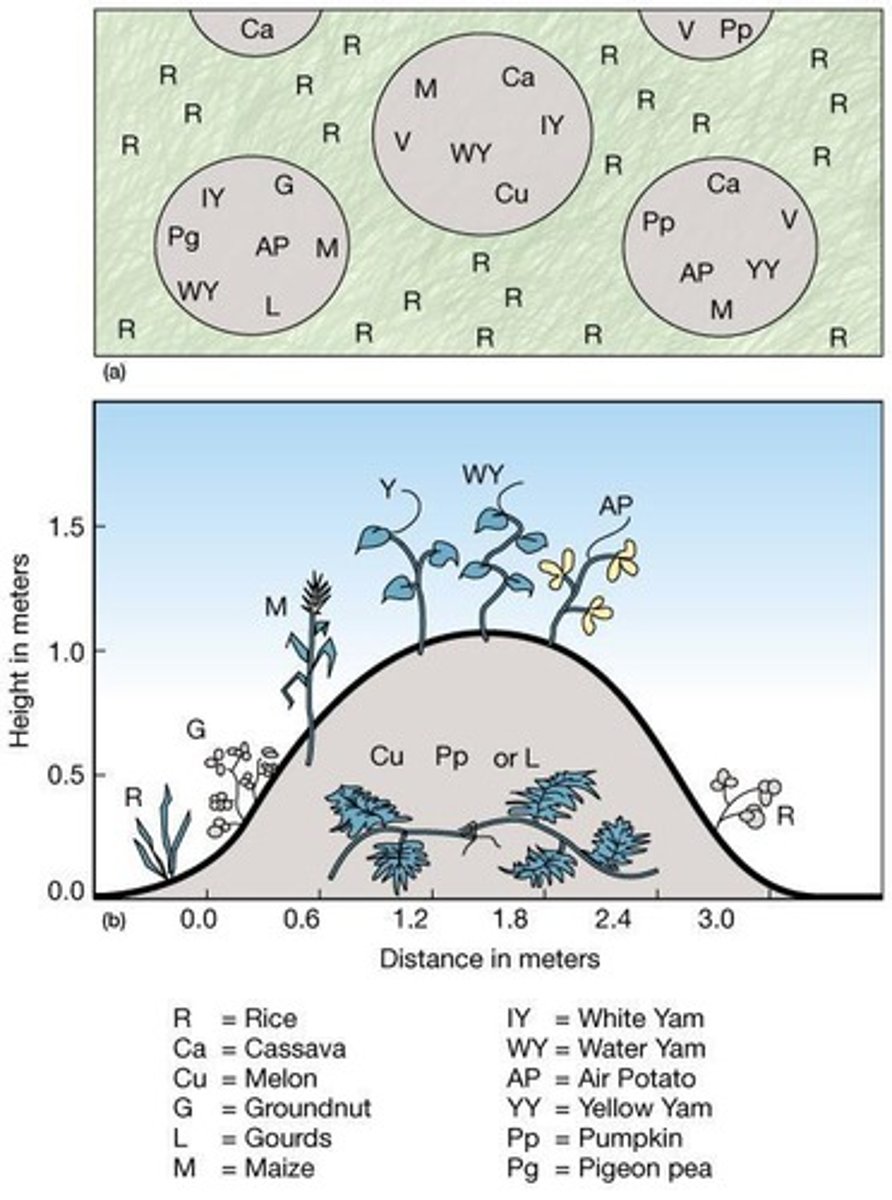
What is intertillage?
The practice of mixing crops in a field to reduce the risk of crop failure and allow for staggered harvesting.
What is intensive subsistence agriculture?
The effective use of a small parcel of land to maximize crop yields, often requiring extensive labor.
How does intensive subsistence agriculture support large populations?
By maximizing limited available land through innovative farming techniques.
What is pastoralism?
The breeding and herding of animals to satisfy human needs for food, shelter, and clothing.
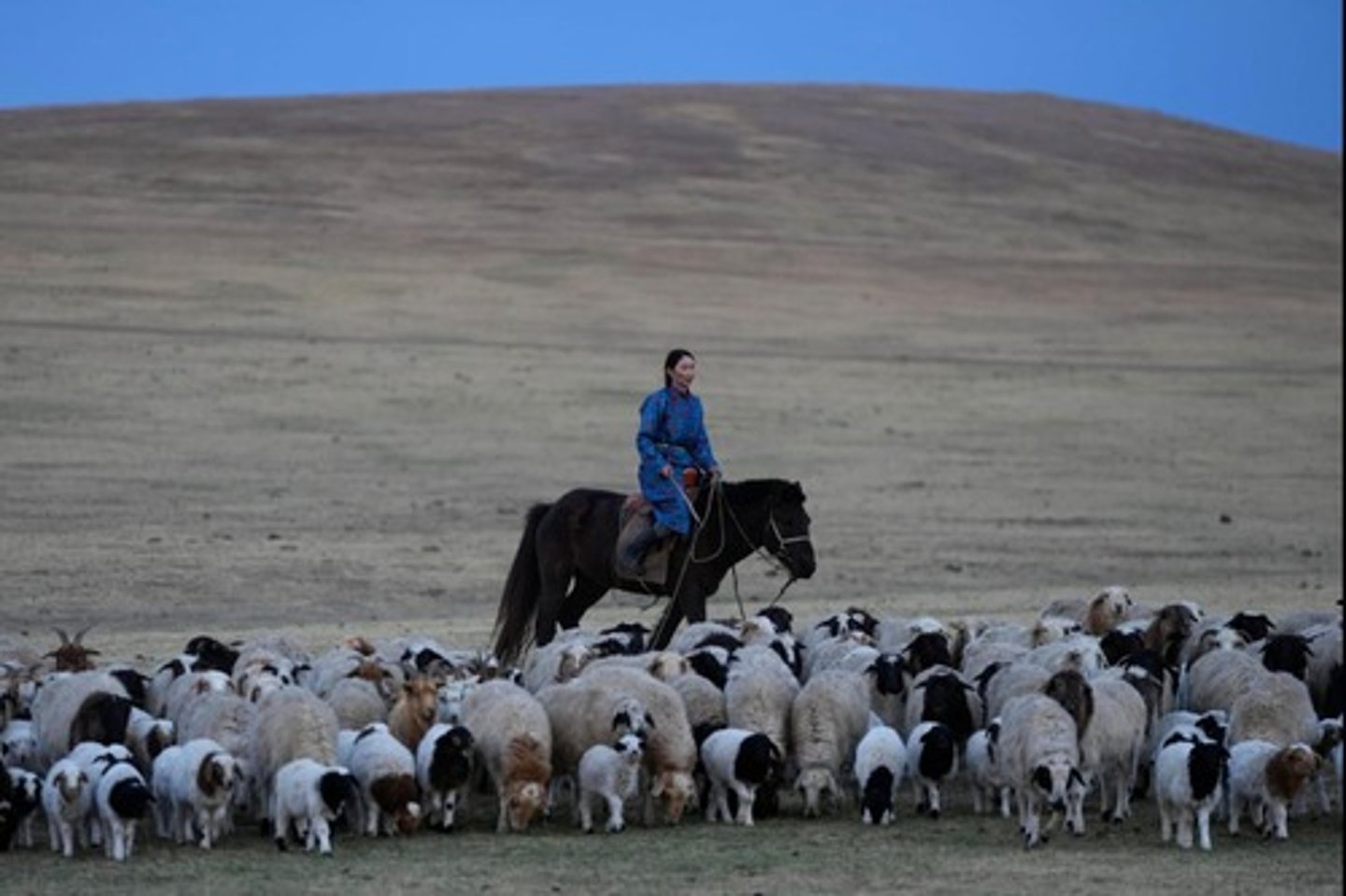

What is nomadism in agriculture?
The continuous movement of groups of herders and families in search of forage.
What is transhumance?
The seasonal movement of livestock between grazing grounds, typically from lowlands in winter to highlands in summer.
What role does climate change play in agriculture?
It affects crop forecasts and agricultural productivity, with varying impacts on different regions.
What are the three dominant forms of agriculture in the periphery?
Shifting cultivation, intensive subsistence agriculture, and pastoralism.
What is the significance of fertilizers in intensive subsistence agriculture?
They allow fields to be planted every year and support high yield crops.
How does land inheritance affect agricultural practices?
Land is often passed down from father to son, resulting in smaller parcel sizes over generations.
What is the ecological impact of shifting cultivation?
It can be ecologically destructive, especially in areas with endangered species or competing land interests.
What is the main goal of intertillage?
To balance diet and reduce the risk of crop failure.
What is the relationship between agriculture and human systems?
Agriculture is influenced by both physical and human systems, shaping how food is produced and consumed.
What is the historical significance of domestication in agriculture?
Domestication allowed humans to settle in one area and transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture.
What is the global distribution of agriculture?
Agricultural practices vary widely across the globe, with distinctions between core and periphery regions.
What is the effect of climate on shifting cultivation?
It is globally distributed in tropics where climate, rainfall, and vegetation produce nutrient-poor soils.
What is the impact of commercial agriculture in core countries?
It became the dominant agricultural system during the 20th century.
What is the primary activity of nomadic life in the North of Iran?
Grazing cattle, sheep, goats, and camels.
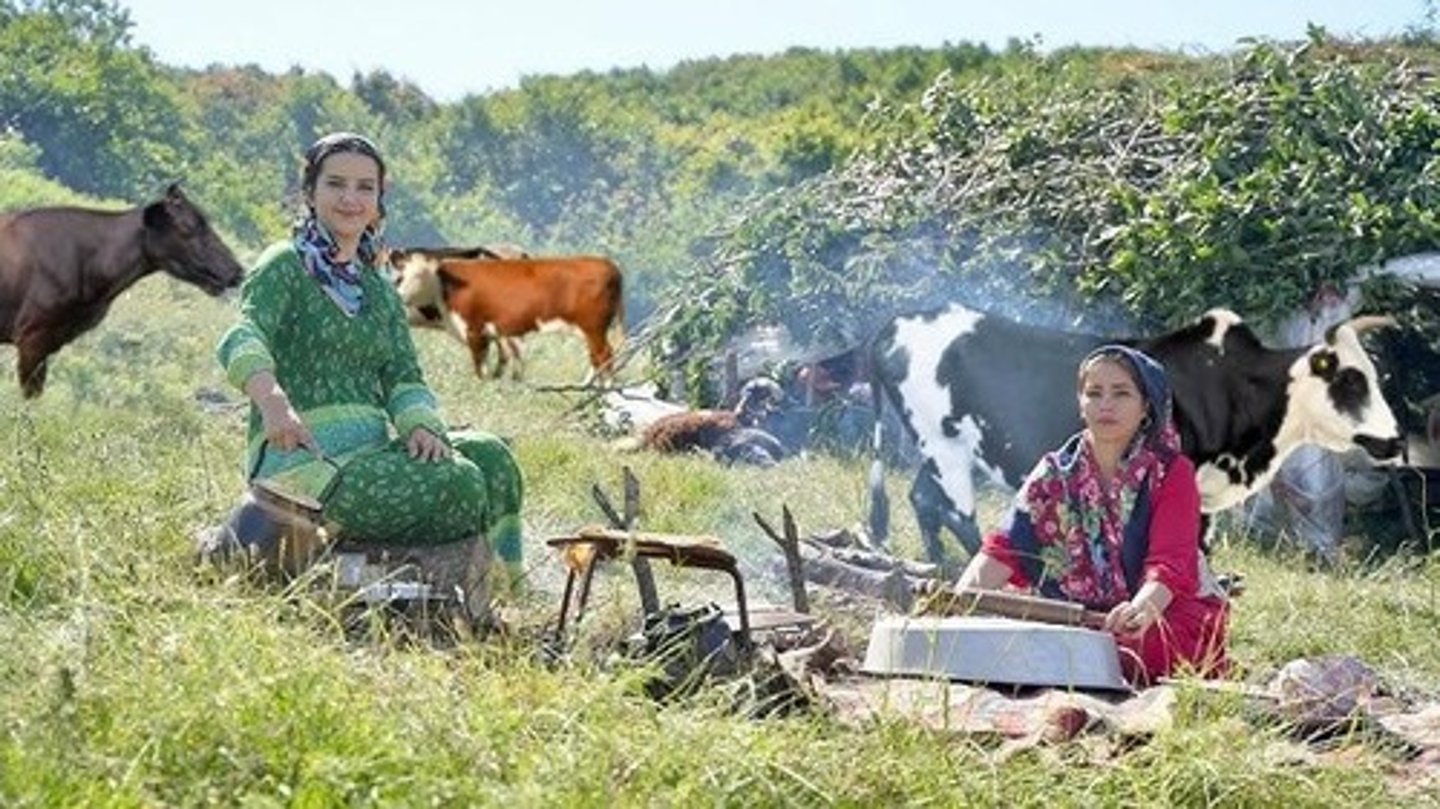

What governance structure is typically found in nomadic societies?
Governance by a chieftain or leader.
What significant shift occurred during the Agricultural Revolution?
The transition from subsistence to capital-intensive agricultural practices.
How is the history of agriculture divided?
Into three distinctive periods.
What characterized the First Agricultural Revolution?
Development of seed agriculture and the use of the plow and draft animals.
What crops were domesticated during the First Agricultural Revolution?
Rice, wheat, sheep, and goats.
What was the timing and impact of the Second Agricultural Revolution?
Historians debate its timing; it coincided with the Industrial Revolution and led to food surpluses.
What innovations were introduced during the Second Agricultural Revolution?
Crop rotation, fertilizers, and the use of oxen and horses.
What defines the Third Agricultural Revolution?
The shift to contract farming and the use of advanced agricultural technologies.
What are the three phases of the Third Agricultural Revolution?
Mechanization, chemical and synthetic fertilizers, and global food manufacturing.
What is agricultural industrialization?
The process by which farms become components in a larger agricultural process.
What is the bio-revolution?
Genetic engineering of plants and animals to enhance productivity.
What are GMOs?
Genetically modified organisms created by altering DNA in a lab.
What are some benefits of biotechnology in agriculture?
Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and aids in soil depletion.
What are food deserts?
Geographic areas with limited access to affordable, healthy whole foods.
What is the food chain?
A commodity chain consisting of inputs, production, processing, distribution, and consumption.
What are the external mediating forces for food chains?
State, international trade, physical environment, and credit & finance.
What is the role of farm subsidies?
To keep agricultural products profitable and ensure affordability for consumers.
What are alternative food movements?
Movements promoting organic farming and local food systems.
What is the locavore movement?
A movement focused on consuming food grown within 100 miles.
What challenges do organic farming movements face?
They are often seen as exclusionary, as poorer individuals may not afford higher costs.
What is the significance of fast food in modern agriculture?
It reflects changes in food production and consumption patterns.
What is a key feature of food regimes?
Links among food production, consumption, capital investment, and accumulation opportunities.
How did colonialism affect food production?
Efficient food production in colonies forced industrialization in Europe.
What is the impact of globalization on agriculture?
It has led to a decline in some forms of agriculture, such as shifting cultivation and family farms.
What is political geography?
A subfield of geography that examines the complex relationships between politics and geography, both human and physical.
What does geopolitics refer to?
A state's power to control space or territory and shape its foreign policy and international relations.
Who was Friedrich Ratzel?
A German geopolitical theorist who portrayed the state as behaving like a biological organism.
What is Lebensraum?
A policy of Nazi Germany involving the expansion of territories to provide land and resources for the German people.
What are Ratzel's laws of state growth?
Seven laws describing how states grow, including territorial growth following development and the absorption of smaller units.
What does the term 'territory' mean in political geography?
A delimited area over which a state exercises control, recognized by other states.
What is the difference between boundaries and frontiers?
Boundaries are defined and enforced territorial limits, while frontiers are areas where boundaries are weakly developed.
How do formal boundaries typically form?
They tend to follow natural barriers like rivers and mountains, or are established along straight lines where no natural features exist.
What are de jure territories?
Legally recognized territories delimited by formal boundaries, such as national states and municipalities.
What is the significance of the U.S.-Mexico border?
It is heavily patrolled and serves as an example of exclusionary borders that manage conflict and competition.
How have the boundaries of European states changed over time?
They have changed significantly since World War I, reflecting the instability of international politics.
What is the role of boundaries in territoriality?
Boundaries enable territoriality to be defined and enforced, allowing for management of conflict and competition.
What characterizes frontier regions?
They are areas where boundaries are weakly developed and are distinctive for marginality rather than belonging.
What happens to boundaries when no natural features exist?
Formal boundaries are fixed along the easiest and most practical cartographic device, often a straight line.
What is the nested hierarchy of de jure territories?
A system where different spatial scales of administrative and governmental territories fit within a larger framework.
What is the impact of the Crimean Peninsula's seizure by Russia?
It illustrates geopolitical tensions, with the U.N. and U.S. refusing to recognize Russia's claim.
What is the importance of ocean access for states?
Ocean access is crucial for trade and transportation, allowing states to send and receive goods.
What is the relationship between population growth and state expansion according to Ratzel?
The space of the state grows with the expansion of the population sharing the same culture.
What does it mean for a state to absorb politically valuable territory?
It refers to the state's growth strategy of acquiring areas that enhance its political or economic power.
What does the term 'contagious growth' refer to in political geography?
The idea that the trend toward territorial growth spreads and increases through interaction among states.
What is a state?
An independent political unit with recognized boundaries.
What is a nation?
A group of people sharing elements of culture such as religion, language, history, or political identity.
Why are pure nation-states rare?
Nations are often created from diverse populations, leading to a lack of entirely pure nation-states.
What is nationalism?
A feeling of belonging to a nation and the belief that a nation has the right to determine its own affairs.
How does the history of the former Soviet Union illustrate tensions between state, nations, and nationalism?
It shows the complexities and conflicts that arise when national identities and state authority intersect.
What is imperialism?
The extension of state authority over the political and economic life of other territories.
What is colonialism?
The formal establishment and maintenance of rule by a sovereign power over a foreign population through settlements.
What is orientalism?
The idea that the West is culturally superior to the East, viewing Eastern cultures as inferior.
What is decolonization?
The reacquisition of control over territory by colonized peoples, often achieved through armed conflict.
What does the East/West divide refer to?
The gulf between communist and non-communist countries, particularly during the Cold War.
What is the domino theory?
The idea that if one country falls to communism, neighboring countries will also fall to communism.
What was the significance of NATO?
Formed in 1949 to safeguard the West against Soviet expansion during the Cold War.
What is the 'new world order' proclaimed by President H.W. Bush?
The assertion that the United States became the sole superpower after the Cold War.
What is globalization in relation to security?
It has led to increased issues with security, including foreign and domestic terrorism.
What is international terrorism?
Terrorism by individuals or groups inspired by or associated with foreign terrorist organizations.
What is domestic terrorism?
Terrorism inspired by U.S.-based movements that espouse extremist ideologies.
What are state-based attacks?
Attacks carried out by or against a state, such as the Chechen separatist movement in Russia.
What is a supranational organization?
A collection of individual states with a common goal that may reduce the independence of those states.
What is the aim of the European Union (EU)?
To increase economic integration and cooperation among member states.
What is self-determination?
The right of a group with a distinctive identity to determine its own destiny through control of its territory.
What is sectionalism?
An extreme devotion to local interests and customs, often leading to conflict.
What is reapportionment?
The process of allocating electoral seats to geographical areas.
What is redistricting?
The defining and redefining of territorial district boundaries.
What is gerrymandering?
Redistricting for partisan purposes to advantage a particular political party or candidate.