Main Body: Head and Neck
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
mental line
angle of mandible-mastoid process-superior nuchal line that distinguishes the head from the neck
jugular notch
line from the clavicle-acromion-horizontal line around C7, distinguishes the neck from the thorax
maxillary, nasal, zygomatic, palatine, lacrimal, inferior nasal conchae
fascial bones
frontal, parietal, occipital, and sphenoid
bones of the neurocranium
supra-orbital foramen
small hole above the orbit where the opthalamic branch of the trigeminal nerve (V1) exits the skull
infra-orbital foramen
small hole below the orbit where the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve exits the skull
mental foramen
small hole on the on either side of the mandible underneath alveloar part where the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve exits (V3) the skull
superior and inferior orbital fissures
holes in the back of the orbit various nerves exit to innervate the eye
hyoid bone
small U shaped bone that serves as a strong bony anchor for several muscles and soft tissue structures in the head and neck (suprahyoid, infrahyoid, pharyngeal, extrinsic muscles of the tongue)
CN VII
innervates all the muscles of facial expression, has zygomatic, buccal, cervical, and marginal mandibular branches, as well as temporal and posterior auricular, emerges from the stylomastoid foramen
muscles of facial expression
thin and flat, insert on skin, some may arise from bone or skin or fascia, vasculature comes from the facial artery and vein, and are named by their actions
bells palsy
only the facial nerve is affected, occurs due to excessive autoimmine response such as recent viral infection, see drooping of the right side of mouth, loss of orbicularis oculi tone causing inability to lubricate the right eye
muscles of mastication
include the massater, lateral and medial pterygoids, temporalis, responsible for chewing movement of the mandible at the temporomandibular joint, innervated by CN V (trigeminal)
stylomastoid foramen
where the facial nerve exits the skull, then goes on to innervates all the muscles of fascial expression
temporal fossa
where the temporalis and masseter originate from
infratemporal fossa
where the lateral and medial pterygoids originate from
temporalis
O: temporal fossa
I: coronoid process of mandible
Inn: mandibular division of CN V (V3)
A: 1) closes mandible (elevation) 2) retracts mandible (retrusion) 3) lateral movement (grinding)
masseter
O: zygomatic arch
I: ramus of mandible
Inn: mandibular division of CN V (V3)
A: 1) closes mandible (elevation), 2) protracts mandible 3) deep fibers retract mandible and grind/chew
lateral pterygoid
O: lateral pterygoid plate (on sphenoid bone)
I: neck of mandible and TMJ capsule
Inn: mandibular branch of CV V (V3)
A: 1) opens mandible 2) bilateral= protrusion of mandible 3) ipsalateral contraction= contralateral deviation
medial pterygoid
O: medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate
I: ramus of mandible, inner surface
Inn: mandibular division of CN V (V3)
A: closes mandible, protrusion, contralateral deviation
trigeminal nerve
CN V, has 3 divisions- opthalmic division, maxillary division, and mandibular division, innervates glands, sensory, and motor
temporomandibular joints
allow opening and closing of the mouth and complex chewing of side to side movement of the lower jaw, synovial joint, formed between the head of the mandible and the articular fossa and articular tubercle of the temporal bone
lower part of TMJ
allows for mainly hinge like depression and elevation of the mandible
upper part of TMJ
allows the head of the mandible to protrude onto the articular tubercle and retract into the mandibular fossa
facial layers of the neck
superficial, deep investing, carotid sheath, prevertebral, pretracheal
compartmental layers of neck
visceral, vascular, vertebral
frontalis
attaches from the front of the skull to the aponeurosis of the skull, wrinkles the skin of the forehead
orbicularis oculi
surrounds the orbit and eye, responsible for blinking and squinting
zygomaticus major
attaches from corner of the mouth and attaches on the zygomatic bone (high on the cheekbone), minor is found just medially and superior to it, activates in wide smiling
levator anguli oris
reaches up from the corned of the mouth to the midway between the mouth and eye, raises the corner of the mouth into a snarl
orbicularis oris
surrounds the mouth, responsible for making an o with the lips
depressor anguli oris
attaches from the corner of the mouth and inferior to the mandible, responsible for bringing the corner of the mouth down into a pout
depressor labii inferioris
attaches to either side of the bottom of the mouth medial to depressor anguli oris and bringing the lower lip inferior
mentalis
attaches from the chin undernear depressor labii inferioris, wrinkles the chin
platysma
thin and superficial muscle over either side of the neck, “duck muscle”
risorius
attaches from the corner of the mouth to the side of the cheek, responsible for pulling mouth laterally
buccinator
muscle deeper in the cheek, assists in tightening the cheek when making an o with mouth
levator labii superioris
attaches from top of mouth more medial to the levator anguli oris and attaches to below the orbit, raises top lip into a snarl as well
auricularis anterior, superior, and posterior
muscles surrounding the ear, many people cannot move them voluntarily
occipitalis
attacges to the aponeurosis of skull anteriorly and posteriorly
external carotid artery branches
superficial temporal artery, maxillary artery, facial artery
vertebral compartment of the neck
contains the cervical vertebrae and associated postural muscles
visceral compartment of the neck
contains important glands (thyroid, parathyroid, thymus) and parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts that pass between the head and thorax
vascular compartment of the neck
2 compartments, one on each side, contains major blood vessels and the vagus nerve
layer 1: superficial fascia
contains the platysma
platysma
slightly wrinkles the surface o the skin of the neck, depresses the lower jaw, draws down the lower lip and angle of the mouth and is innervated by CN VII (cervical branch)
layer 2 of the neck
deep investing fascia, contains the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
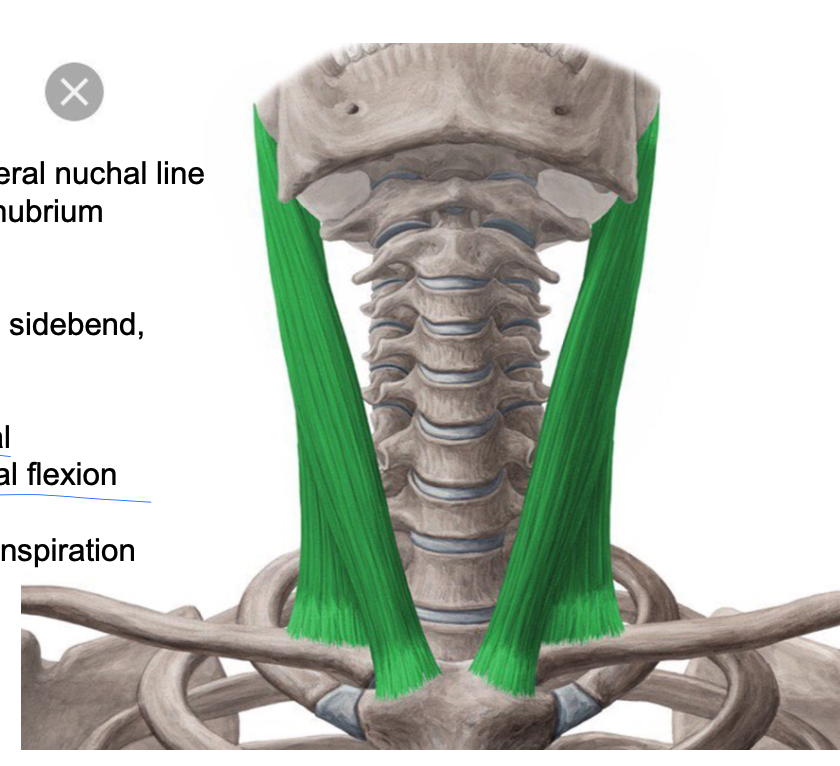
sternocleidomastoid
PA: mastoid process/lateral nuchal line
DA: medial clavicle, manubrium
Inn: CN XI for efferent (motor), C3, C4 for afferent (sensory)
A: unilateral: ipsalateral sidebend and contralateral rotation, bilateral: upper cervical extension and lower cervical flexion
Reverse action: secondary inspiration
forward head
how tight SCM or poor posture might present
torticollis
occurs when there is tightness unilaterally in the SCM, tightness on the R side will tilt the right ear towards the right shoulder and the nose and face will rotate towards the left (happens in babies usually)
layer 3 of the neck
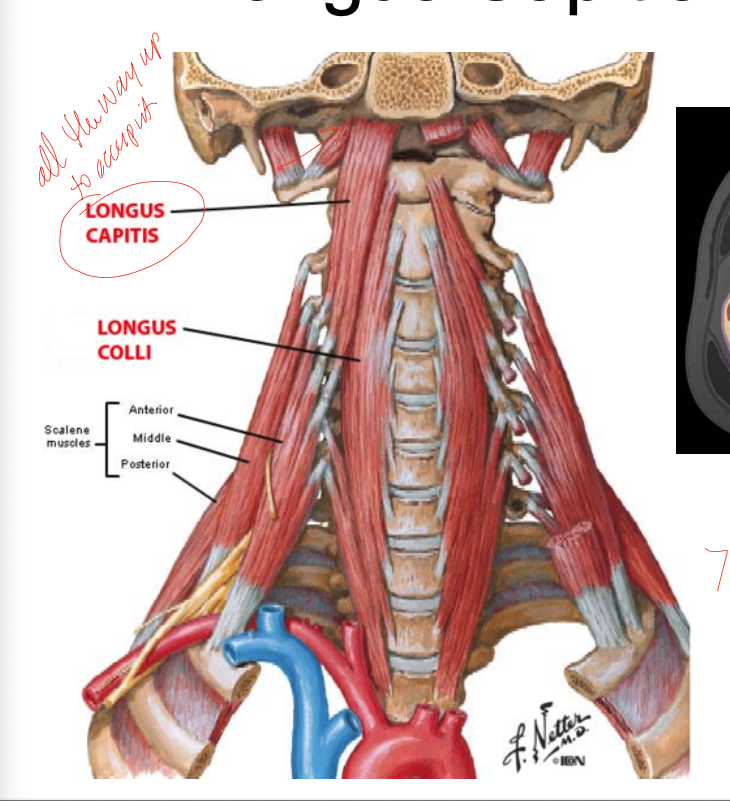
prevertebral, consists of the scalenes, the levator scapulae, longus coli, longus capitis, paraspinals, phrenic nerve, and the branchial plexus
longus capitis
PA: occipital bone
DA: C3-C6 anterior portion of transverse processes
Inn: C3-5 ventral rami
A: neck/head flexion
longus colli
PA: anterior tubercle C1 and bodies of C1-3 and tp of C3-6
DA: bodies C5-T3, tp C3-5
Inn: C2-6 ventral rami
A: bilateral: flexes neck, unilateral: neck/head flexion with ipsilateral rotations
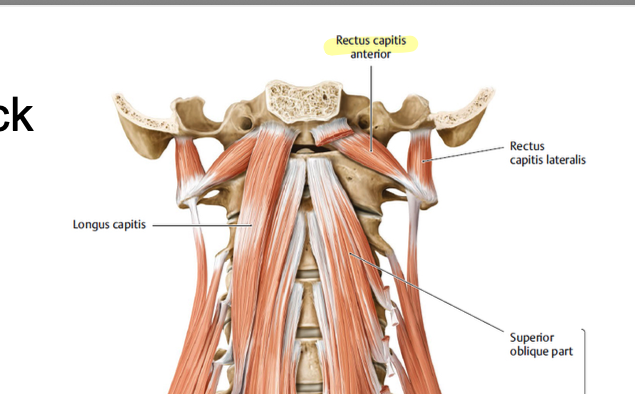
rectus capitis anterior
small muscles on the sides of the neck right beneath skull, aids in flexion of the head and neck
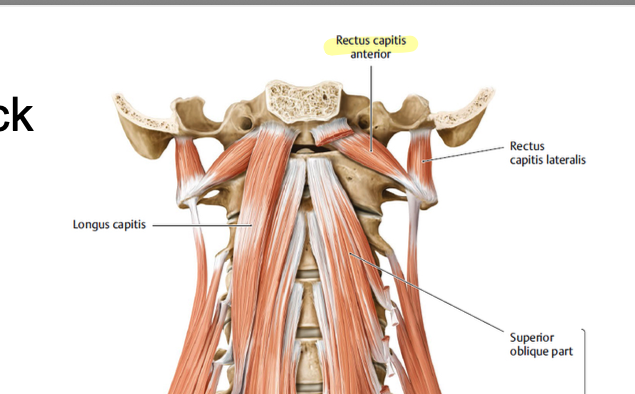
rectus capitis lateralis
stabilizes the head and weakly assists with lateral flexion of the head
ansa cervicalis
part of the cervical plexus, is the primary motor nerves to the strap muscles of the neck
levator scapulae
PA: tp of C1-C4
DA: vertebral border of the scapula between the spine and the superior angle
Inn: dorsal scapular nerve (from ventral ramus C4, C5)
A: elevation of the scapula, downward rotation of the scapula
reverse action: ispilateral side bend and rotation
anterior scalene
PA: tp of mid cervical vertebrae
DA: 1st rib
Inn: ventral rami of C4-6
A: raises 1st rib, ipsilateral beck side bend
middle scalene
PA: most cervical tps
DA: 1st rib
Inn: ventral rami of most cervical nerves
A: raises 1st rib, ispilateral neck side bend
posterior scalene
PA: most cervical tps
DA: 2nd rib
Inn: ventral rami of most cervical nerves
A: raises second rib, ispilateral neck side bend
obliquus capitis inferior
PA: posterior tubercle of C2
DA: transverse process of C1
Inn: suboccipital nerve (C1)
A: head extension and rotation
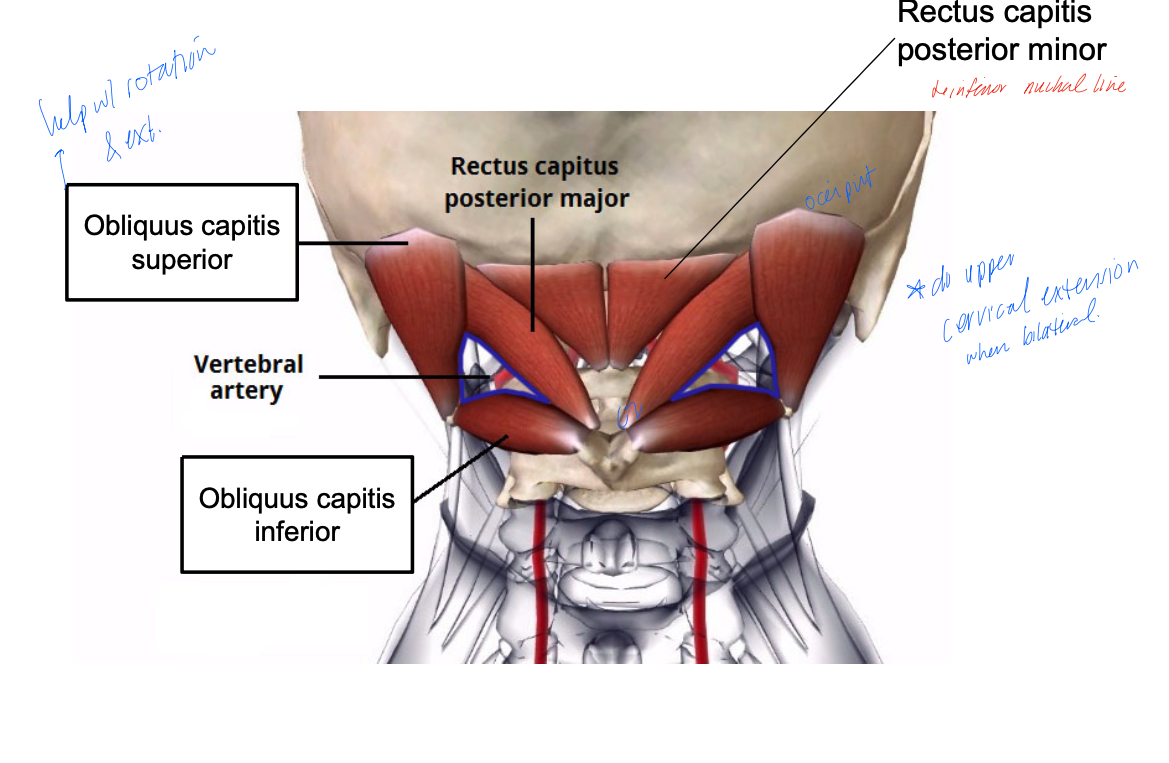
obliquus capitis superior
PA: transverse process of C1
DA: between superior and inferior nuchal line
Inn: suboccipital nerve (C1)
A: head extension and rotation
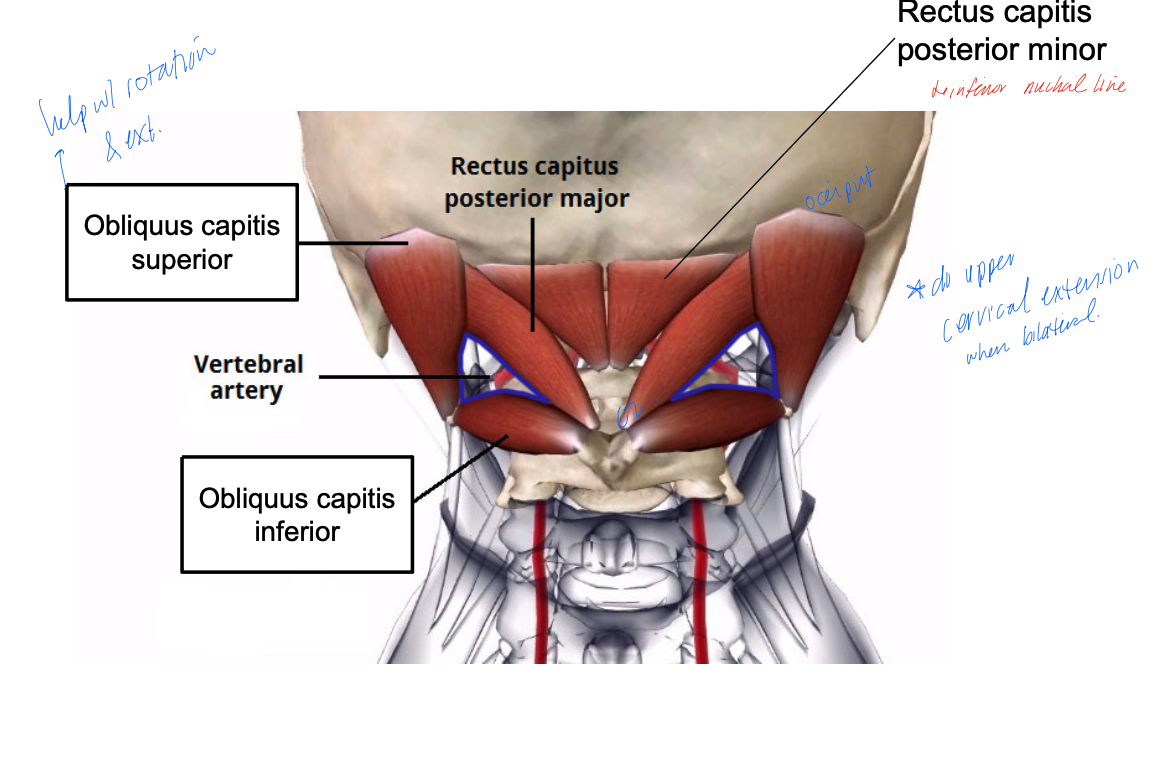
rectus capitis posterior major
PA: inferior nuchal line
DA: C2 spinous processes
Inn: suboccipital nerve (C1)
A: head extension and head rotation
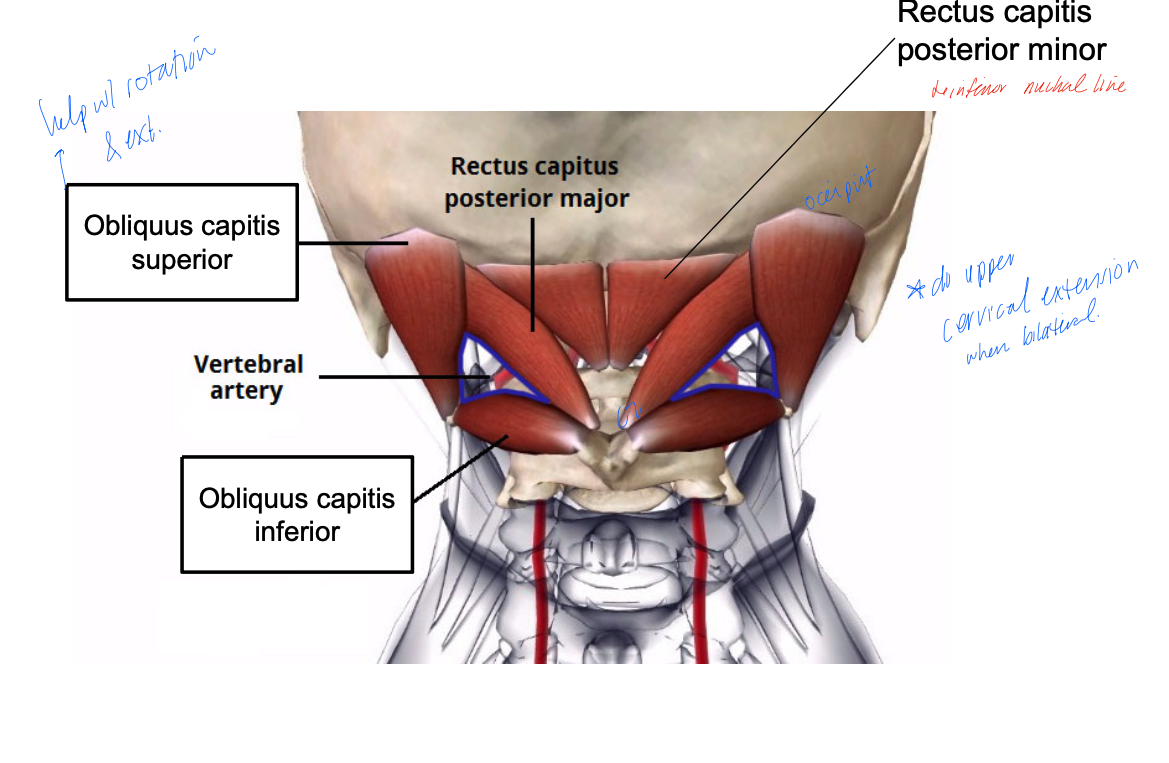
rectus capitis posterior minor
PA: posterior tubercle of C1 (atlas)
DA: inferior nuchal line of occipital bone
Inn: suboccipital nerve (C1)
A: head extension
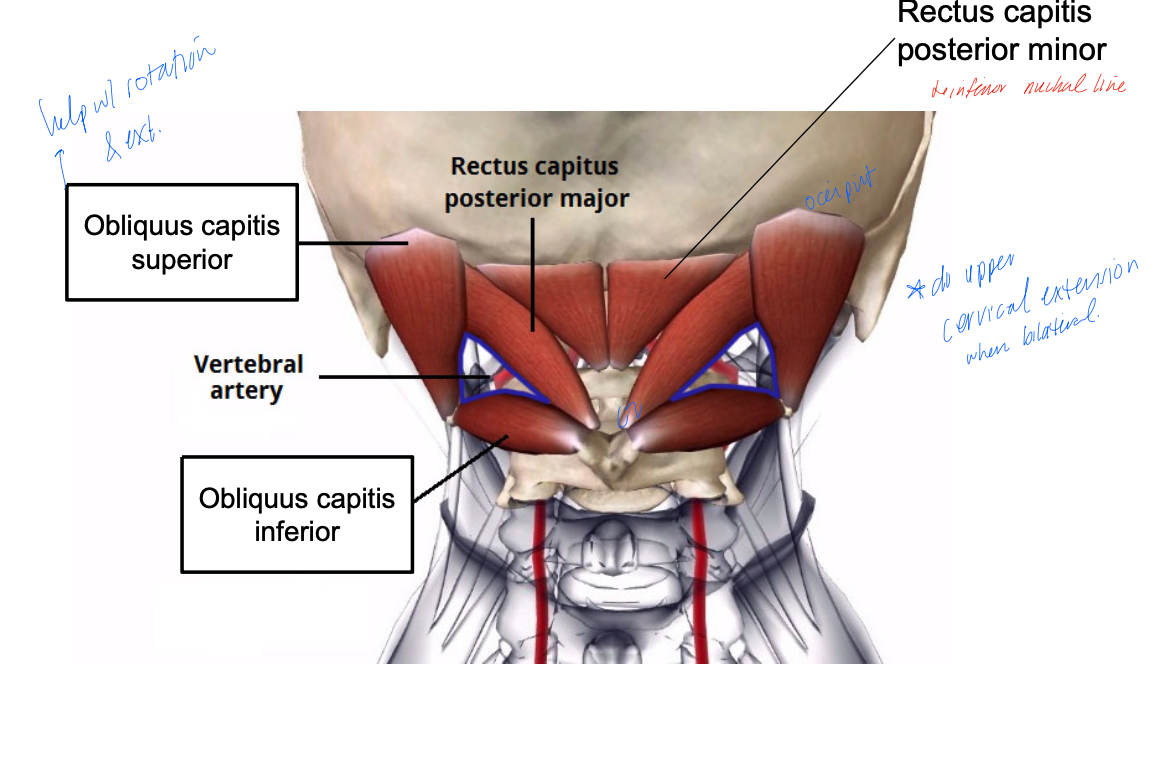
occipital neuralgia
is suboccipital tissue is tight, compression of the suboccipital nerve can occur- results in substantial pain and discomfort- headaches!
compression of C1-2
see headaches in the posterior portion of the neck on the ispilateral side
compression of C2-C3
headaches that radiate towards the front of the skull/forehead
layer 4 of the neck
pretracheal, find the infra and suprahyoid muscles in this layer, as well as neurovasculature of the neck
nerves of the neck
cervical plexus, brachial plexus, phrenic nerve, sympathetic chain
structures of the vascular compartment
carotid artery, jugular vein, vagus nerve
carotid arteries origins
right common carotid originates from teh right brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid is a direct branch from the arch of the aorta,
common carotid
branches into the internal and external carotid
carotid sinus
found at the bifurcation of the common carotid, exists at the bottom of the internal carotid artery- contains receptors that monitor homeostatic changes in partial pressure of oxygen, CO2, pH, and is innervated by a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (X)
vagus nerve
exits the jugular foramen between glossopharyngeal and accessory nerves (X and XI), branches include the pharyngeal branch, superior laryngeal nerve (which has a internal and external branch), and the recurrent laryngeal nerve
visceral compartment structures
pharynx and esophagus, larynx and trachea, thyroid gland
pharynx compartments
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
thyroid cartilage
forms the adam’s apple