Plant Lec: Parasitic Plants
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Parasitic plant
-When a plant attaches to and derives nutrients from another plant
-Form of parasitism
-Some parasitic plants attach to the roots of other plants (the host)
Holoparasitism
-Complete parasites (can’t live on their own)
-Most extreme form of plant parasitism
-Lack chlorophyll, leaves, stomata, and are usually small, just a stalk with flowers
-Highly modified roots
Myco-heterotrophs
-Rather than attach directly to plant roots, often a fungi (mycorrhizae) that bridges the gap between the plants
-Host plant ‘leaks’ organic compounds into the soil
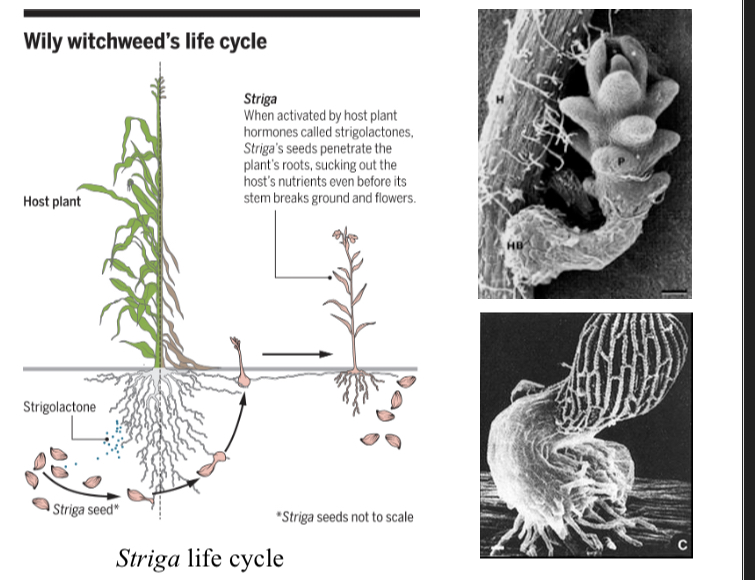
Parasitic plant seeds detect these compounds (called strigolactones) to know when to germinate
The seedlings modified roots, called haustoria, attach to the mycorrhizae on the host roots
-Parasite absorbs sugars, amino acids, and other useful solutes (called photoassimilates) from the plant’s phloem and water from the xylem (via the mycorrhizae)
Dodder
-Holoparasite that attaches to the stem of host plants (not roots)
-No mycorrhizae involved when the parasite attaches above the ground
-Can sense chemical gradients and grow toward its host
-Roots of these parasites are highly modified. Called haustoria
Hemiparasites
-Plants that obtain nutrients from other plants, but have chlorophyll and leaves, so they can photosynthesize
-Also obligate because it cannot live on its own (mistletoe)
Mistletoe
-Obligate Hemiparasites
-Infect the branches of many woody plants, including oaks
-Birds eat berries of mistletoe and poop out seeds
Sticky mucus around seed and causes attachment to stems
Seed germinates and the root penetrates the bark
The root (haustoria) spreads through the phloem and xylem of the host
-High levels of mistletoe concentration can kill trees
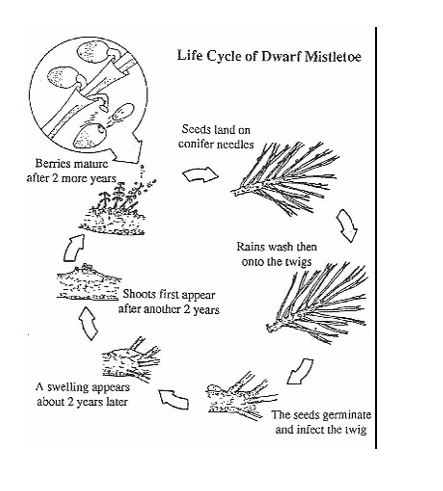
-Dwarf mistletoe infects pines
Ballistically dispersed
Dwarf mistletoe life cycle
Striga
-important pest on the roots of crop plants like corn in Africa
-Reduces crop yields and costs millions of dollars per year
-Life cycle image
Strigolactones
-Plants release these hormones to attract VAM (arbuscular mycorrhizae)
-Parasitic plants also sense the presence of host plants using strigolactones
-If plants successfully inoculate with VAM mycorrhizae, they are less likely to be infected by parasitic plants
-Mycorrhizae helps to protect the plant from its parasites and makes the plant more productive (more fruits and leaves)
Facultative Hemiparasites
-Plant that can photosynthesize (chlorophyll and leaves) and can live on its own
Indian paintbrush will attach to sagebrush if given opportunity
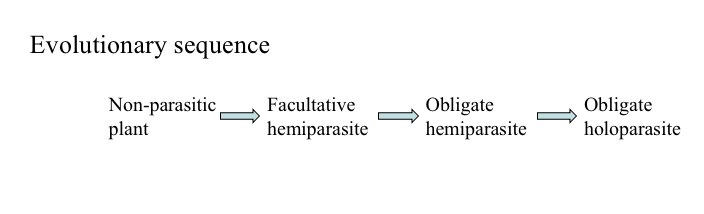
Evolution of an obligate holoparasite must have followed this sequence
Are epiphytes parasites?
-No, they do not extract nutrients from their host
-However, they can become so numerous that they can cause problems for the plant they rest upon
-Needs a substrate, but doesn’t have to be a tree
-Too dry in temperate forests for many
-Can find small epiphytes in subtropical sites
-Tropical forests can have large bromeliads
-Many cacti live on other plants in rain forests
-Loads can weight many tons
Tree fall gaps
-Very important in ecology of rainforests, where canopy is typically closed
-Epiphyte Loads are one of the main causes of tree falls.
-Gaps allow for different types of plants to colonize and fill in the gap
-Allows for greater plant diversity and greater diversity of animals
Strangler fig
-Epiphyte that becomes a parasite
strigolactones
Parasitic plant seeds detect these compounds (called strigolactones) that are leaked from host plant