Hearing Science: Exploring the Temporal Bone and Its Anatomy
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What does the stapes do?
vibrates the fluid inside the oval window of the inner ear
How many major bones are in the human skull?
22
How much does the adult head weigh?
8-12 pounds
How much does the skull itself weigh?
2.2 pounds
How big is the human skull
8" x 8" x 8"
What is the temporal bone?
forms the side and base of the skull
What are the four major articulations within the temporal bone?
Occipital bone
Parietal bone
Sphenoid bone
Zygomatic bone
Central
related to the brain
Peripheral
related to structure which is distal to the brain
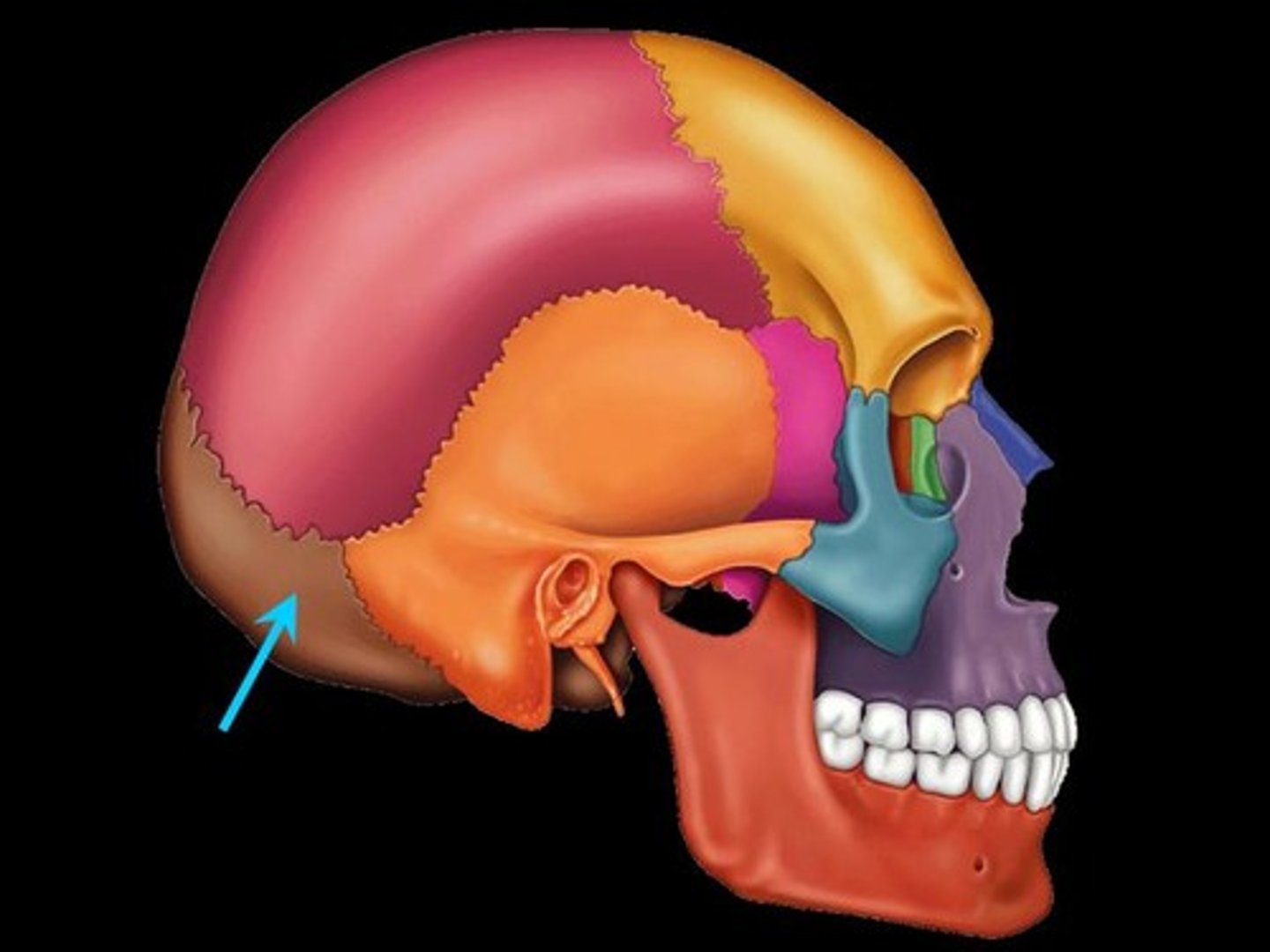
Occipital Bone
posterior to the temporal bone
-skullbase
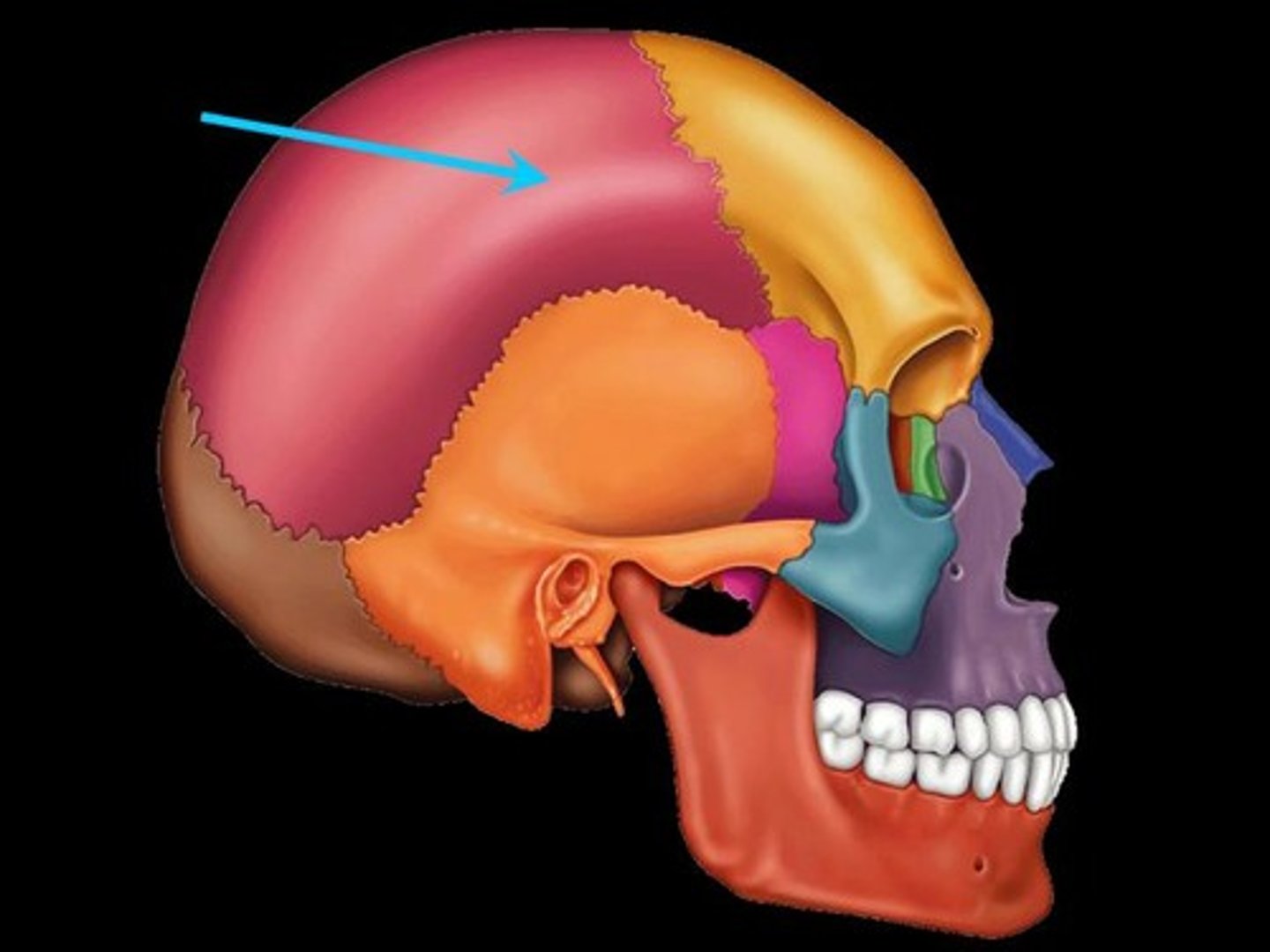
Parietal Bone
superior and posterior to the temporal bone
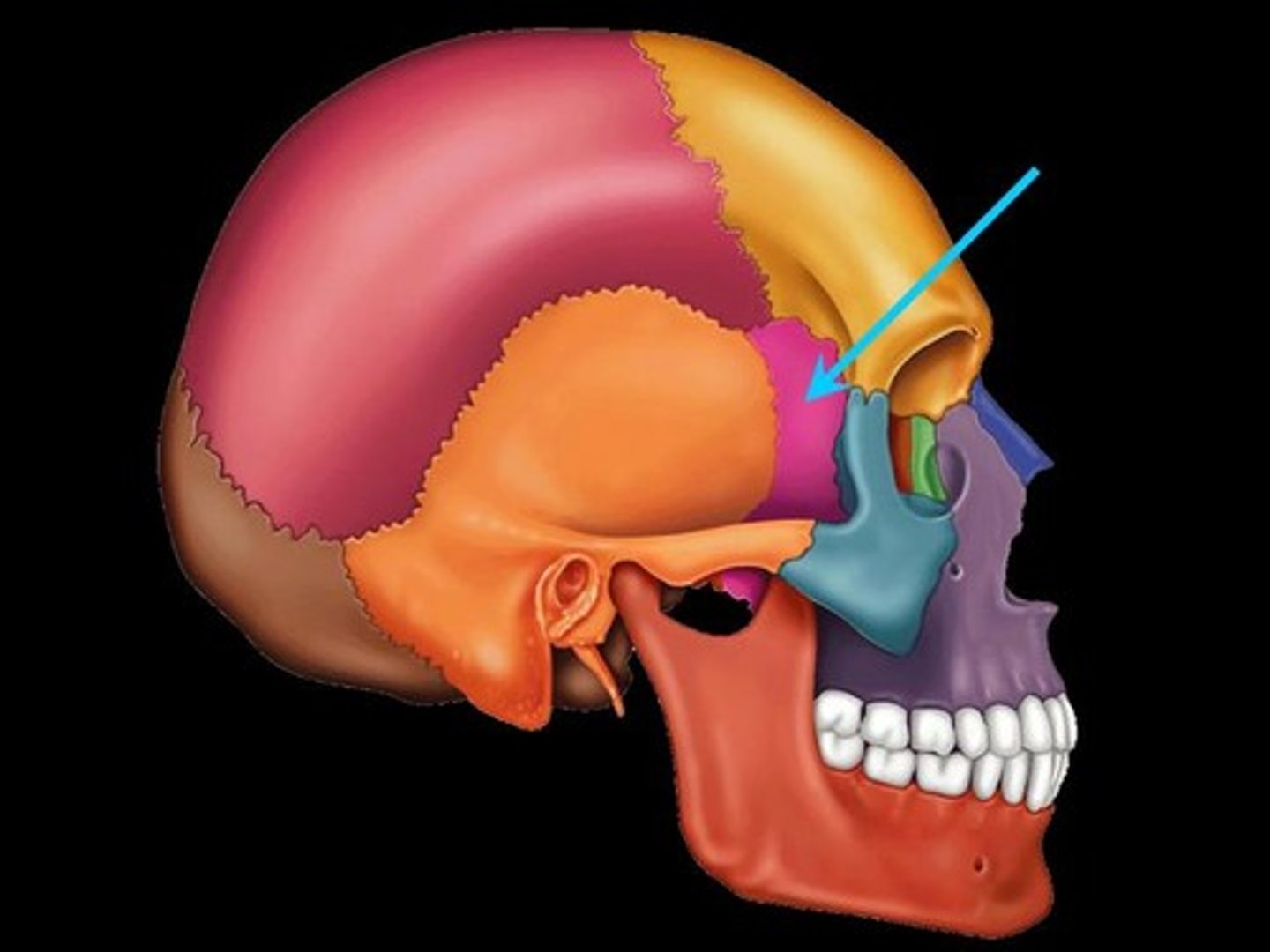
Sphenoid Bone
anterior and medial to the temporal bone
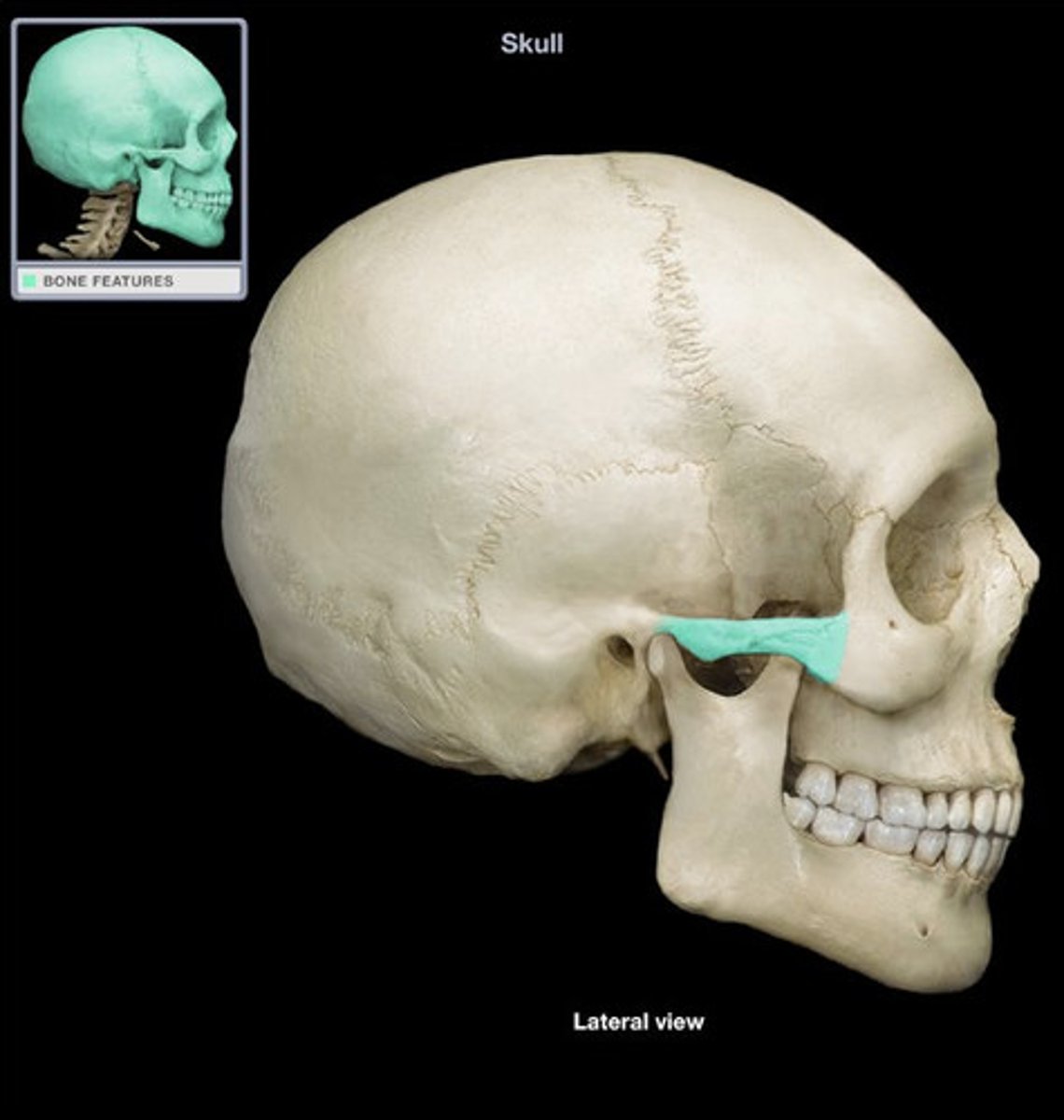
Zygomatic Bone
anterior to the temporal bone
What are the four major divisions of the temporal bone?
Squamas
Mastoid
Tympanic
Petrous
How is the squamos characterized?
cover with or characterized by scales
-consisting of or denoting a layer of epithelium that consists of very thin flattened cells
What does the squamas protect?
it protects the skull contents (in the event of a significant blow to the head, the temporal bone will shatter, absorbing much of the energy before it reaches the middle and inner ears)
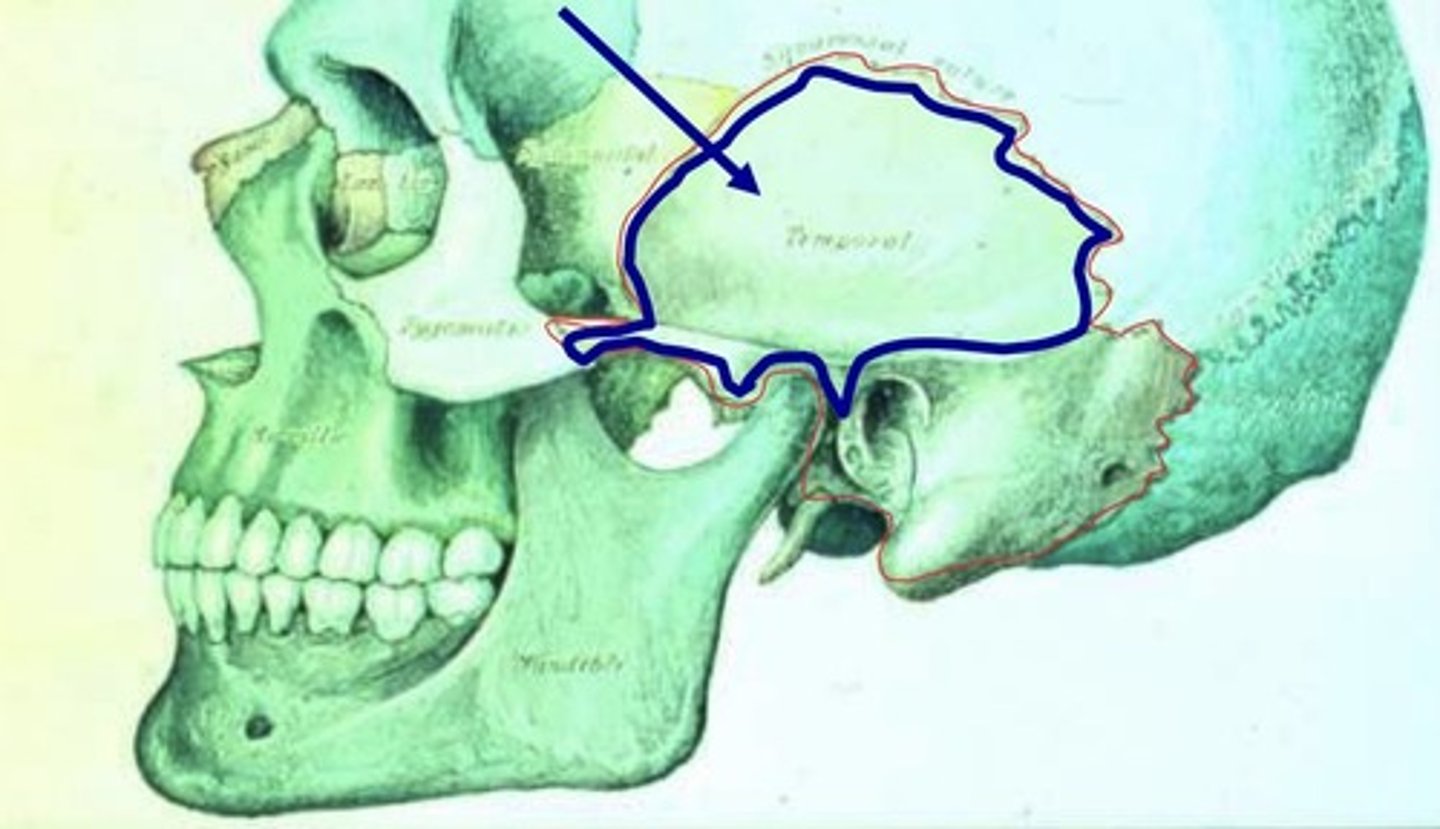
Squamas Portion
-located on the lateral surface of the skull
-thin plate of hard bone
-exterior surface roughened for muscle attachments
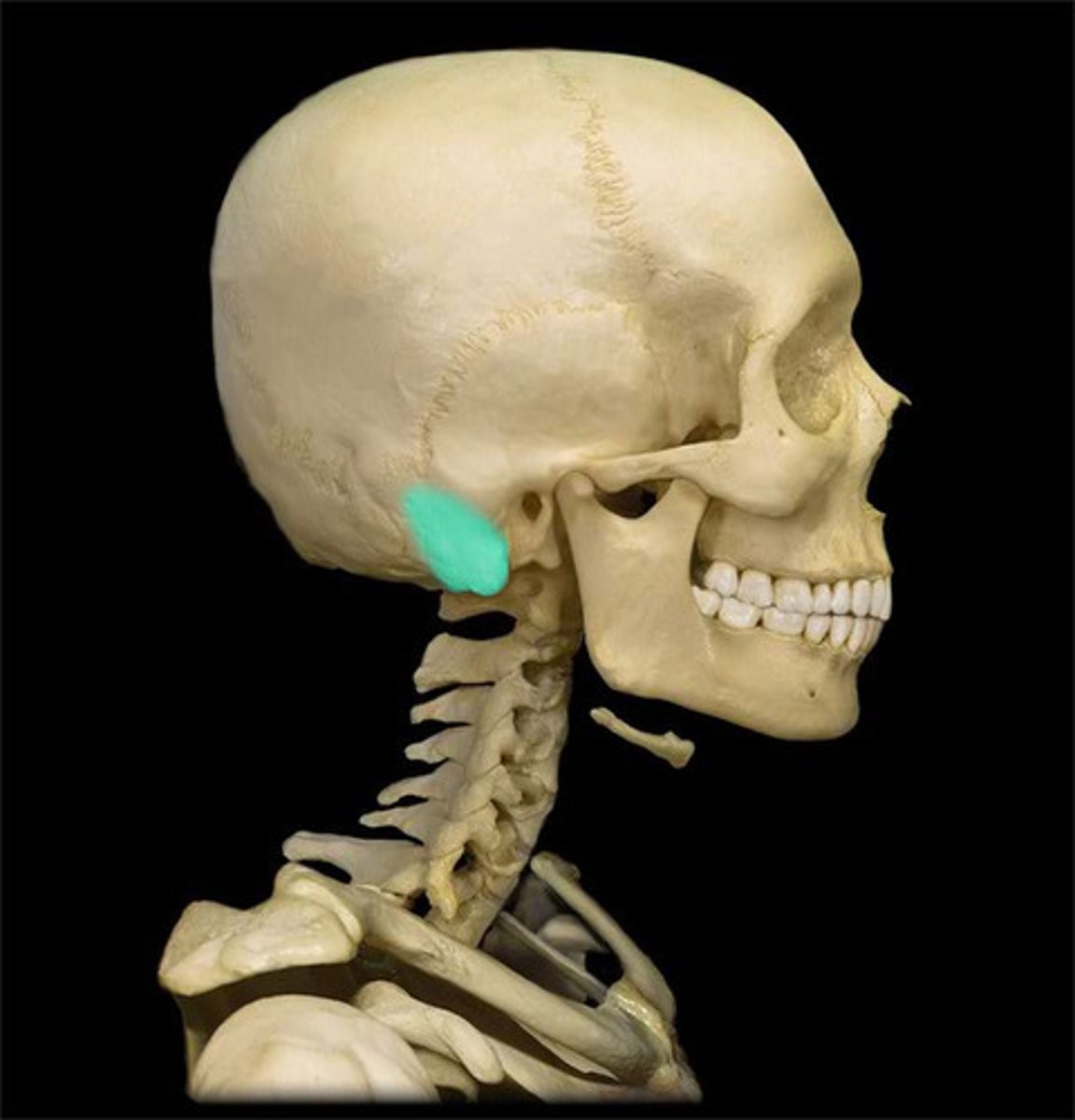
Mastoid Portion
-located posteriorly and inferiorly to the external ear canal
-forms part of the skull base
-contains air cells that are lined with mucus membrane
-exterior surface: muscle attachment
-protective function for skull contents
How is the mastoid shaped?
like a nipple
Which portion of the temporal bone contains air cells?
mastoid portion
-it is the extension of the airway from the nasopharynx, eustachian tube, middle ear
Tympanic Portion
-related to the middle ear or ear drum
-cartilaginous portion of ear canal is the outer 1/3; the bony portion is the inner 2/3
-provides rigid superstructure to canal (keeps canal open)
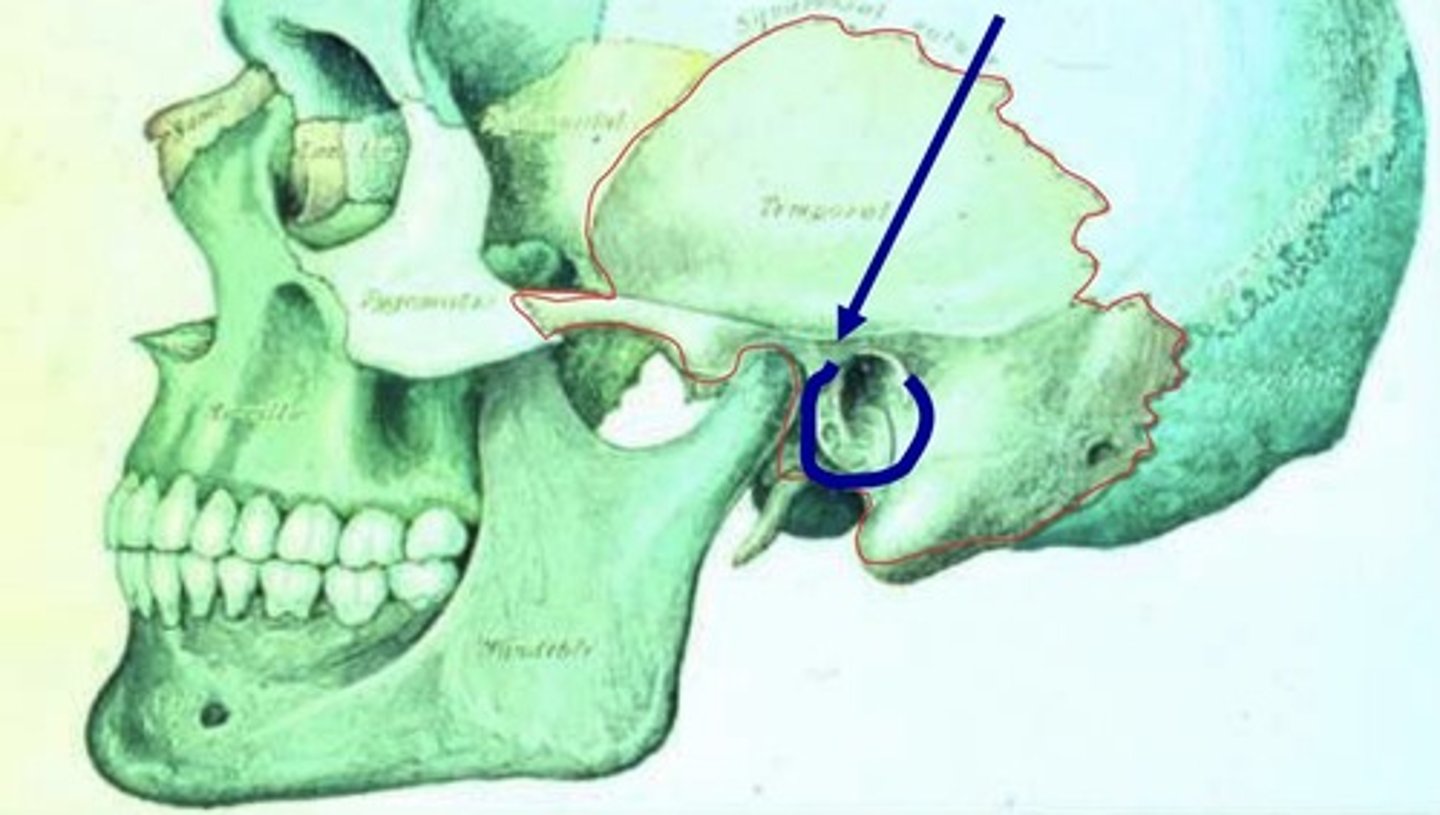
What does the tympanic portion form?
the anterior, inferior, and part of the posterior walls of the external ear canal
Where is the middle ear located?
tympanic cavity
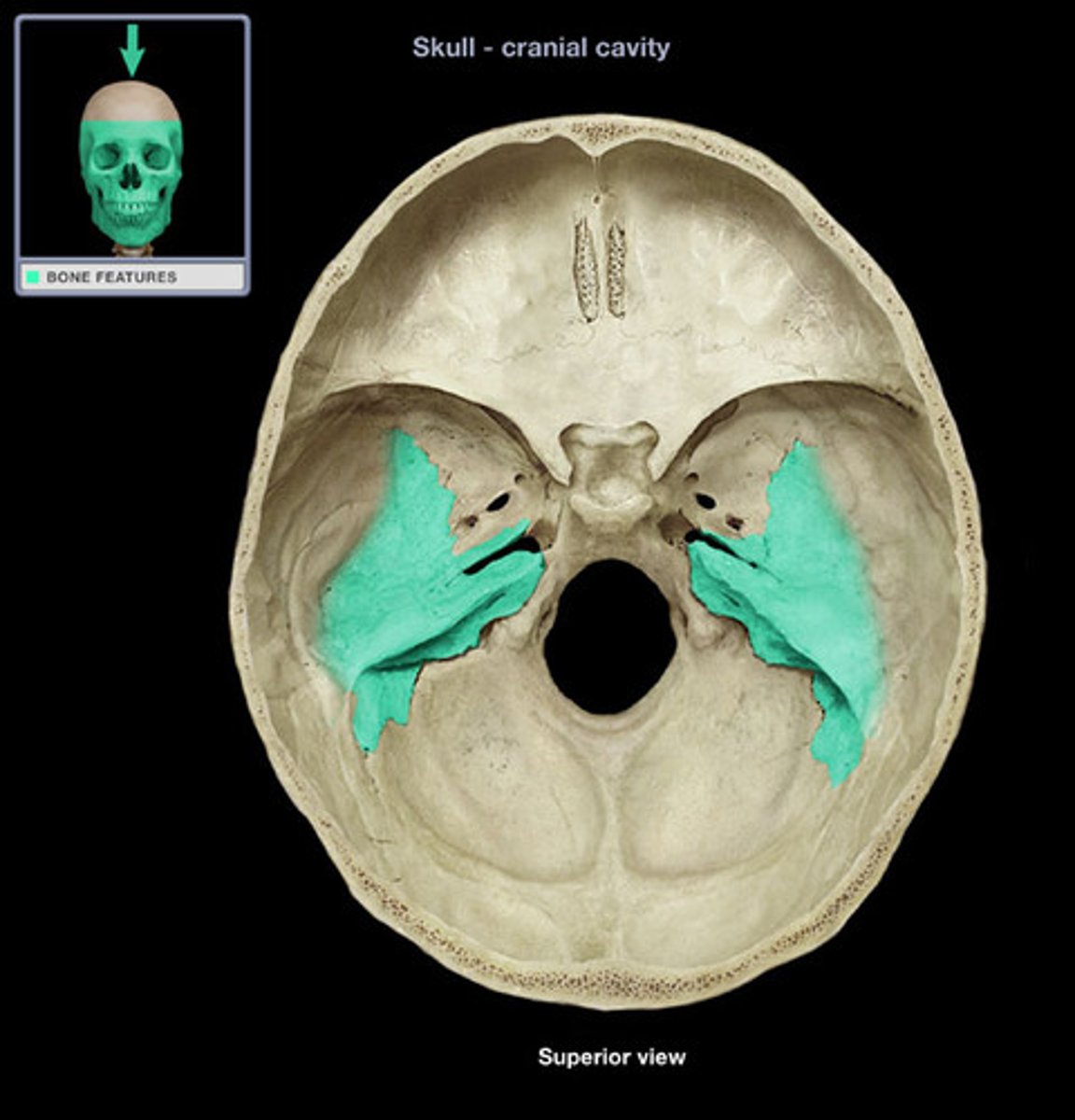
Petrous Portion
relating to or resembling a rock. especially in hardness (stony)
-located between the middle fossa and posterior fossa on the cranium floor
-located in the interior of the cranium floor
-triangular shaped (petrous pyramid); the base is wider than the apex
-contains the inner ear
What does the petrous portion separate?
the posterior fossa and middle fossa
-anterior surface faces the middle fossa
-posterior surface faces the posterior fossa
What does the petrous portion protect?
the cochlea
Fossa
a small cavity or depression
What two structures are within the petrous portion?
Tympanum (tympanic cavity for the middle ear)
Bony labyrinth (chamber for the inner ear)
Where is the tympanic membrane located?
within the tympanic cavity of the middle ear
What is a part of the anterior surface of the petrous bone?
tegman tympani and arcuate eminence
Tegman Tympani
roof of the middle ear (roof of tympanic cavity)
-thin, smooth area
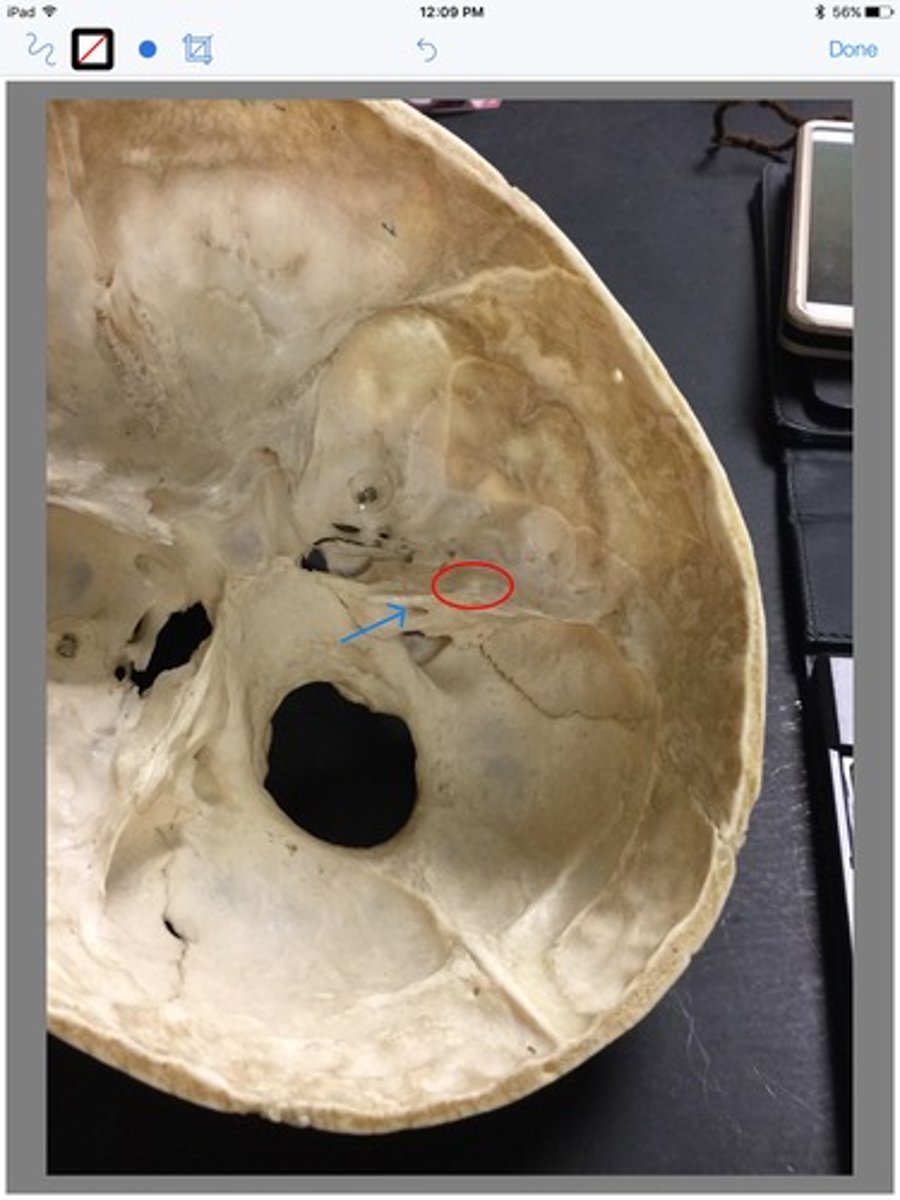
Arcuate Eminence
prominence on the anterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone
-superior semicircular canal is below,
along with rest of inner ear
-slight bulge
What is a feature of the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone?
internal auditory canal
Internal Auditory Canal
contains the internal ear canal and VIIIth nerve (hearing nerve)
What are the four structures within the internal auditory canal?
Cochlear branch of the VIIIth nerve
Vestibular branch of the VIIIth nerve
Facial nerve (VIIth nerve)
Blood supply: artery